1998 DODGE RAM 1500 relay
[x] Cancel search: relayPage 1982 of 2627
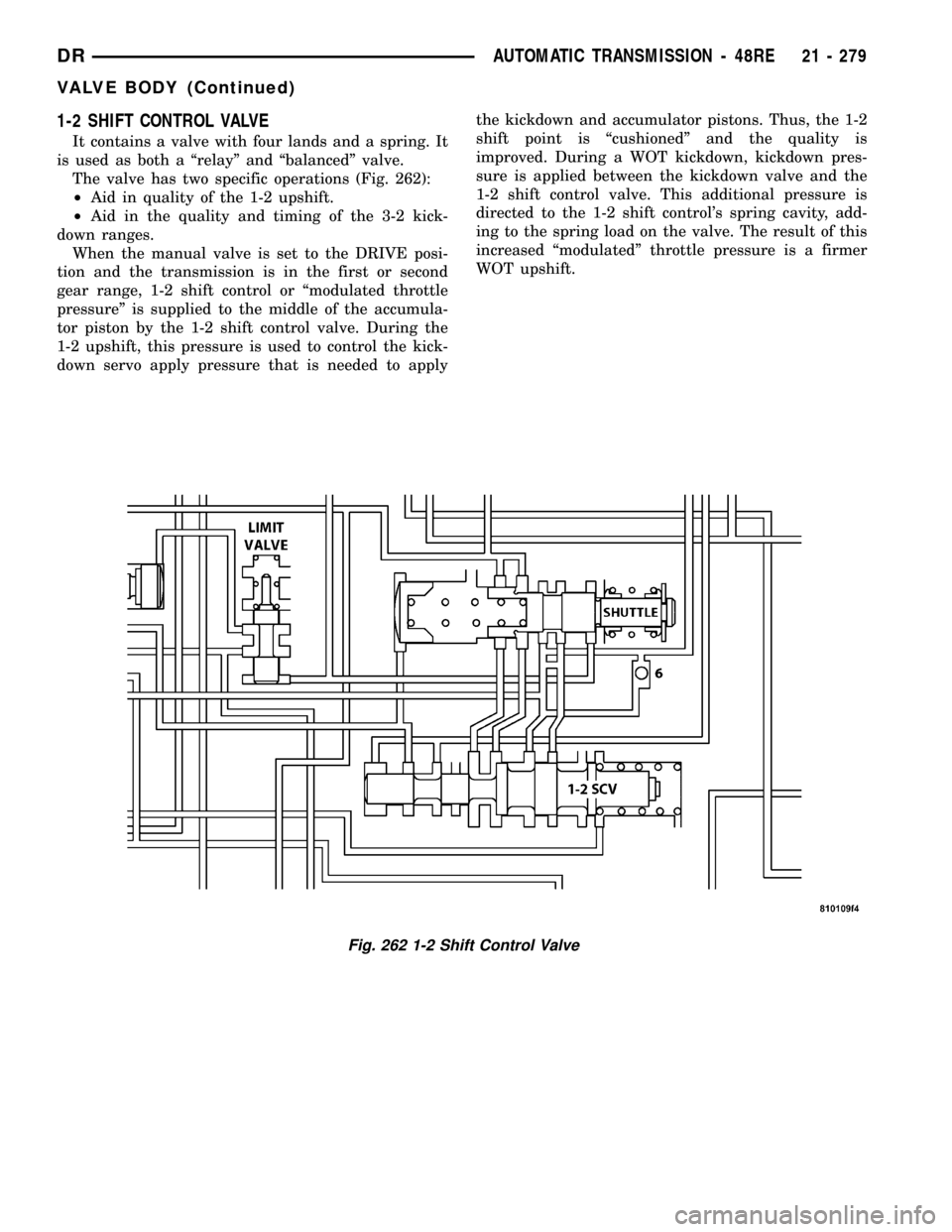
1-2 SHIFT CONTROL VALVE
It contains a valve with four lands and a spring. It
is used as both a ªrelayº and ªbalancedº valve.
The valve has two specific operations (Fig. 262):
²Aid in quality of the 1-2 upshift.
²Aid in the quality and timing of the 3-2 kick-
down ranges.
When the manual valve is set to the DRIVE posi-
tion and the transmission is in the first or second
gear range, 1-2 shift control or ªmodulated throttle
pressureº is supplied to the middle of the accumula-
tor piston by the 1-2 shift control valve. During the
1-2 upshift, this pressure is used to control the kick-
down servo apply pressure that is needed to applythe kickdown and accumulator pistons. Thus, the 1-2
shift point is ªcushionedº and the quality is
improved. During a WOT kickdown, kickdown pres-
sure is applied between the kickdown valve and the
1-2 shift control valve. This additional pressure is
directed to the 1-2 shift control's spring cavity, add-
ing to the spring load on the valve. The result of this
increased ªmodulatedº throttle pressure is a firmer
WOT upshift.
Fig. 262 1-2 Shift Control Valve
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 279
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1988 of 2627
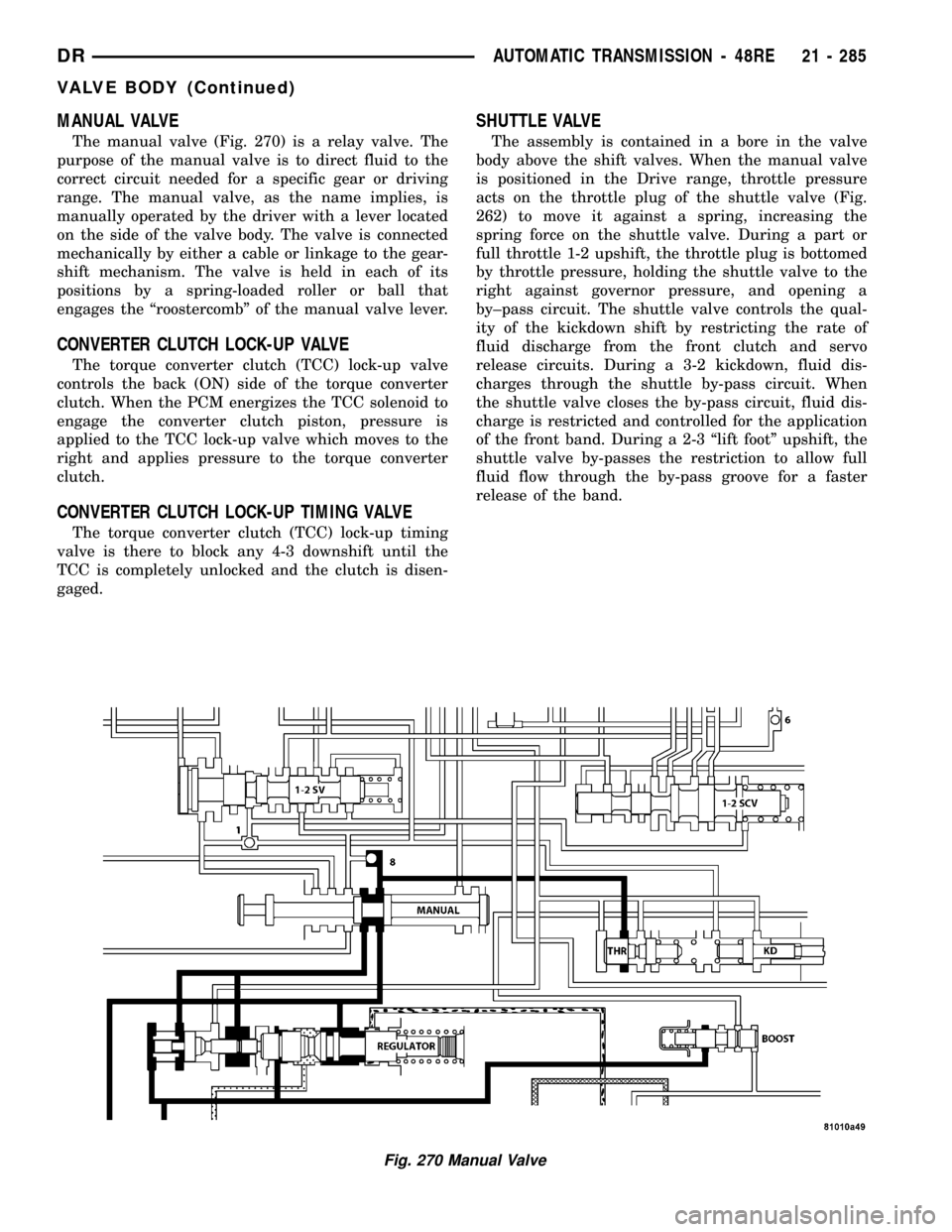
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve (Fig. 270) is a relay valve. The
purpose of the manual valve is to direct fluid to the
correct circuit needed for a specific gear or driving
range. The manual valve, as the name implies, is
manually operated by the driver with a lever located
on the side of the valve body. The valve is connected
mechanically by either a cable or linkage to the gear-
shift mechanism. The valve is held in each of its
positions by a spring-loaded roller or ball that
engages the ªroostercombº of the manual valve lever.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up valve
controls the back (ON) side of the torque converter
clutch. When the PCM energizes the TCC solenoid to
engage the converter clutch piston, pressure is
applied to the TCC lock-up valve which moves to the
right and applies pressure to the torque converter
clutch.
CONVERTER CLUTCH LOCK-UP TIMING VALVE
The torque converter clutch (TCC) lock-up timing
valve is there to block any 4-3 downshift until the
TCC is completely unlocked and the clutch is disen-
gaged.
SHUTTLE VALVE
The assembly is contained in a bore in the valve
body above the shift valves. When the manual valve
is positioned in the Drive range, throttle pressure
acts on the throttle plug of the shuttle valve (Fig.
262) to move it against a spring, increasing the
spring force on the shuttle valve. During a part or
full throttle 1-2 upshift, the throttle plug is bottomed
by throttle pressure, holding the shuttle valve to the
right against governor pressure, and opening a
by±pass circuit. The shuttle valve controls the qual-
ity of the kickdown shift by restricting the rate of
fluid discharge from the front clutch and servo
release circuits. During a 3-2 kickdown, fluid dis-
charges through the shuttle by-pass circuit. When
the shuttle valve closes the by-pass circuit, fluid dis-
charge is restricted and controlled for the application
of the front band. During a 2-3 ªlift footº upshift, the
shuttle valve by-passes the restriction to allow full
fluid flow through the by-pass groove for a faster
release of the band.
Fig. 270 Manual Valve
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 285
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 2015 of 2627

INSTALLATION........................391
OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................391
OPERATION..........................391
REMOVAL............................391
INSTALLATION........................392
TOW/HAUL OVERDRIVE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION........................392
OPERATION..........................392
REMOVAL............................392
INSTALLATION........................393
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION........................393
OPERATION..........................393
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
DESCRIPTION........................395
OPERATION..........................396
DISASSEMBLY........................396
CLEANING...........................396
INSPECTION.........................397
ASSEMBLY...........................397
SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION........................398
OPERATION..........................398
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
DESCRIPTION........................398
OPERATION..........................398
SOLENOIDS
DESCRIPTION........................398OPERATION..........................399
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION........................399
OPERATION..........................403
REMOVAL............................404
INSTALLATION........................404
TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
DESCRIPTION........................405
OPERATION..........................405
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................405
OPERATION..........................405
TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION........................406
OPERATION..........................406
REMOVAL............................407
INSTALLATION........................408
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................408
OPERATION..........................408
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION........................408
OPERATION..........................408
REMOVAL............................410
DISASSEMBLY........................410
CLEANING...........................412
INSPECTION.........................413
ASSEMBLY...........................414
INSTALLATION........................414
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION -
45RFE/545RFE
DESCRIPTION
The 45RFE/545RFE automatic transmissions is a
sophisticated, multi-range, electronically controlled
transmission which combines optimized gear ratios
for responsive performance, state of the art efficiency
features and low NVH. Other features include driver
adaptive shifting and three planetary gear sets to
provide wide ratio capability with precise ratio steps
for optimum driveability. The three planetary gear
sets also make available a unique alternate second
gear ratio. The primary 2nd gear ratio fits between
1st and 3rd gears for normal through-gear accelera-
tions. The alternate second gear ratio (2prime) allows
smoother 4-2 kickdowns at high speeds to provide
2nd gear passing performance over a wider highway
cruising range.
The hydraulic portion of the transmission consists
of the transmission fluid, fluid passages, hydraulic
valves, and various line pressure control components.The primary mechanical components of the trans-
mission consist of the following:
²Three multiple disc input clutches
²Three multiple disc holding clutches
²Five hydraulic accumulators
²Three planetary gear sets
²Dual Stage Hydraulic oil pump
²Valve body
²Solenoid pack
The TCM is the ªheartº or ªbrainº of the electronic
control system and relies on information from vari-
ous direct and indirect inputs (sensors, switches, etc.)
to determine driver demand and vehicle operating
conditions. With this information, the TCM can cal-
culate and perform timely and quality shifts through
various output or control devices (solenoid pack,
transmission control relay, etc.).
21 - 312 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
Page 2108 of 2627

(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The relay is supplied fused B+ voltage, energized
by the TCM, and is used to supply power to the sole-
noid pack when the transmission is in normal oper-
ating mode.
OPERATION
When the relay is ªoffº, no power is supplied to the
solenoid pack and the transmission is in ªlimp-inº
mode. After a controller reset, the TCM energizes the
relay. Prior to this, the TCM verifies that the con-
tacts are open by checking for no voltage at the
switched battery terminals. After this is verified, the
voltage at the solenoid pack pressure switches is
checked. After the relay is energized, the TCM mon-
itors the terminals to verify that the voltage is
greater than 3 volts.
TRANSMISSION RANGE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) is part of
the solenoid module, which is mounted to the top of
the valve body inside the transmission.
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) has five
switch contact pins that:
²Determine shift lever position
²Supply ground to the Starter Relay in Park and
Neutral only.
²
Supply +12 V to the backup lamps in Reverse only.
The TRS also has an integrated temperature sen-
sor (thermistor) that communicates transmission
temperature to the TCM and PCM.
OPERATION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) communi-
cates shift lever position to the TCM as a combina-
tion of open and closed switches. Each shift lever
position has an assigned combination of switch states
(open/closed) that the TCM receives from four sense
circuits. The TCM interprets this information and
determines the appropriate transmission gear posi-
tion and shift schedule.
There are many possible combinations of open and
closed switches (codes). Seven of these possible codes
are related to gear position and five are recognized
as ªbetween gearº codes. This results in many codes
which shouldnever occur. These are called
ªinvalidº codes. An invalid code will result in a DTC,
and the TCM will then determine the shift lever
position based on pressure switch data. This allows
reasonably normal transmission operation with a
TRS failure.
GEAR C5 C4 C3 C2 C1
ParkCL OP OP CL CL
Temp 1CL OP OP CL OP
ReverseOP OP OP CL OP
Temp 2OP OP CL CL OP
Neutral 1OP OP CL CL CL
Neutral 2OP CL CL CL CL
Temp 3OP CL CL CL OP
DriveOP CL CL OP OP
Temp 4OP CL OP OP OP
Manual 2CL CL OP OP OP
Temp 5CL OP OP OP OP
Manual 1CL OP CL OP OP
Fig. 125 Checking Torque Converter Seating-Typical
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 405
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 2109 of 2627

TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/
TRS ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION
The transmission solenoid/TRS assembly is inter-
nal to the transmission and mounted on the valve
body assembly (Fig. 126). The assembly consists of
six solenoids that control hydraulic pressure to the
six friction elements (transmission clutches), and the
torque converter clutch. The pressure control sole-
noid is located on the side of the solenoid/TRS assem-
bly. The solenoid/TRS assembly also contains five
pressure switches that feed information to the TCM.
OPERATION
SOLENOIDS
Solenoids are used to control the L/R, 2C, 4C, OD,
and UD friction elements. The reverse clutch is con-
trolled by line pressure and the position of the man-
ual valve in the valve body. All the solenoids are
contained within the Solenoid and Pressure Switch
Assembly. The solenoid and pressure switch assembly
contains one additional solenoid, Multi-Select (MS),
which serves primarily to provide 2nd and 3rd gear
limp-in operation.
The solenoids receive electrical power from the
Transmission Control Relay through a single wire.
The TCM energizes or operates the solenoids individ-
ually by grounding the return wire of the solenoid as
necessary. When a solenoid is energized, the solenoid
valve shifts, and a fluid passage is opened or closed
(vented or applied), depending on its default operat-
ing state. The result is an apply or release of a fric-
tional element.
The MS and UD solenoids are normally applied to
allow transmission limp-in in the event of an electri-
cal failure.The continuity of the solenoids and circuits are
periodically tested. Each solenoid is turned on or off
depending on its current state. An inductive spike
should be detected by the TCM during this test. If no
spike is detected, the circuit is tested again to verify
the failure. In addition to the periodic testing, the
solenoid circuits are tested if a speed ratio or pres-
sure switch error occurs.
Fig. 126 Transmission Solenoid/TRS Assembly
1 - PRESSURE CONTROL SOLENOID
2 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SELECTOR PLATE
3 - 23-WAY CONNECTOR
4 - SOLENOID PACK
5 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
6 - VALVE BODY
21 - 406 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
Page 2111 of 2627

INSTALLATION
(1) Place TRS selector plate in the PARK position.
(2) Position the transmission solenoid/TRS assem-
bly onto the valve body. Be sure that both alignment
dowels are fully seated in the valve body and that
the TRS switch contacts are properly positioned in
the selector plate
(3) Install the screws to hold the transmission
solenoid/TRS assembly onto the valve body.
(4) Tighten the solenoid assembly screws adjacent
to the arrows cast into the bottom of the valve body
first. Tighten the screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in.lbs.).
(5) Tighten the remainder of the solenoid assembly
screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in.lbs.).
(6) Install the valve body into the transmission.
TRANSMISSION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The transmission temperature sensor is a ther-
mistor that is integral to the Transmission Range
Sensor (TRS).
OPERATION
The transmission temperature sensor is used by
the TCM to sense the temperature of the fluid in the
sump. Since fluid temperature can affect transmis-
sion shift quality and convertor lock up, the TCM
requires this information to determine which shift
schedule to operate in.
Calculated Temperature
A failure in the temperature sensor or circuit will
result in calculated temperature being substituted for
actual temperature. Calculated temperature is a pre-
dicted fluid temperature which is calculated from a
combination of inputs:
²Battery (ambient) temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²In-gear run time since start-up
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The valve body consists of a cast aluminum valve
body, a separator plate, and a transfer plate. The
valve body contains valves and check balls that con-
trol fluid delivery to the torque converter clutch,
bands, and frictional clutches. The valve body con-
tains the following components (Fig. 129) and (Fig.
130):
²Solenoid switch valve
²Manual valve
²Low/reverse switch valve
²5 Accumulators
²7 check balls
OPERATION
NOTE: Refer to the Hydraulic Schematics for a
visual aid in determining valve location, operation
and design.
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
The Solenoid Switch Valve (SSV) controls the direc-
tion of the transmission fluid when the L/R-TCC sole-
noid is energized.
When shifting into 1st gear, a special hydraulic
sequence is performed to ensure SSV movement into
the downshifted position. The L/R pressure switch is
monitored to confirm SSV movement. If the move-
ment is not confirmed (the L/R pressure switch does
not close), 2nd gear is substituted for 1st. A DTC will
be set after three unsuccessful attempts are made to
get into 1st gear in one given key start.
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve is a relay valve. The purpose of
the manual valve is to direct fluid to the correct cir-
cuit needed for a specific gear or driving range. The
manual valve, as the name implies, is manually oper-
ated by the driver with a lever located on the top of
the valve body. The valve is connected mechanically
by a cable to the gearshift mechanism. The valve is
held in each of its positions by a roller detent spring
(Fig. 131) that engages the ªroostercombº of the TRS
selector plate.
21 - 408 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFEDR
TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 2491 of 2627
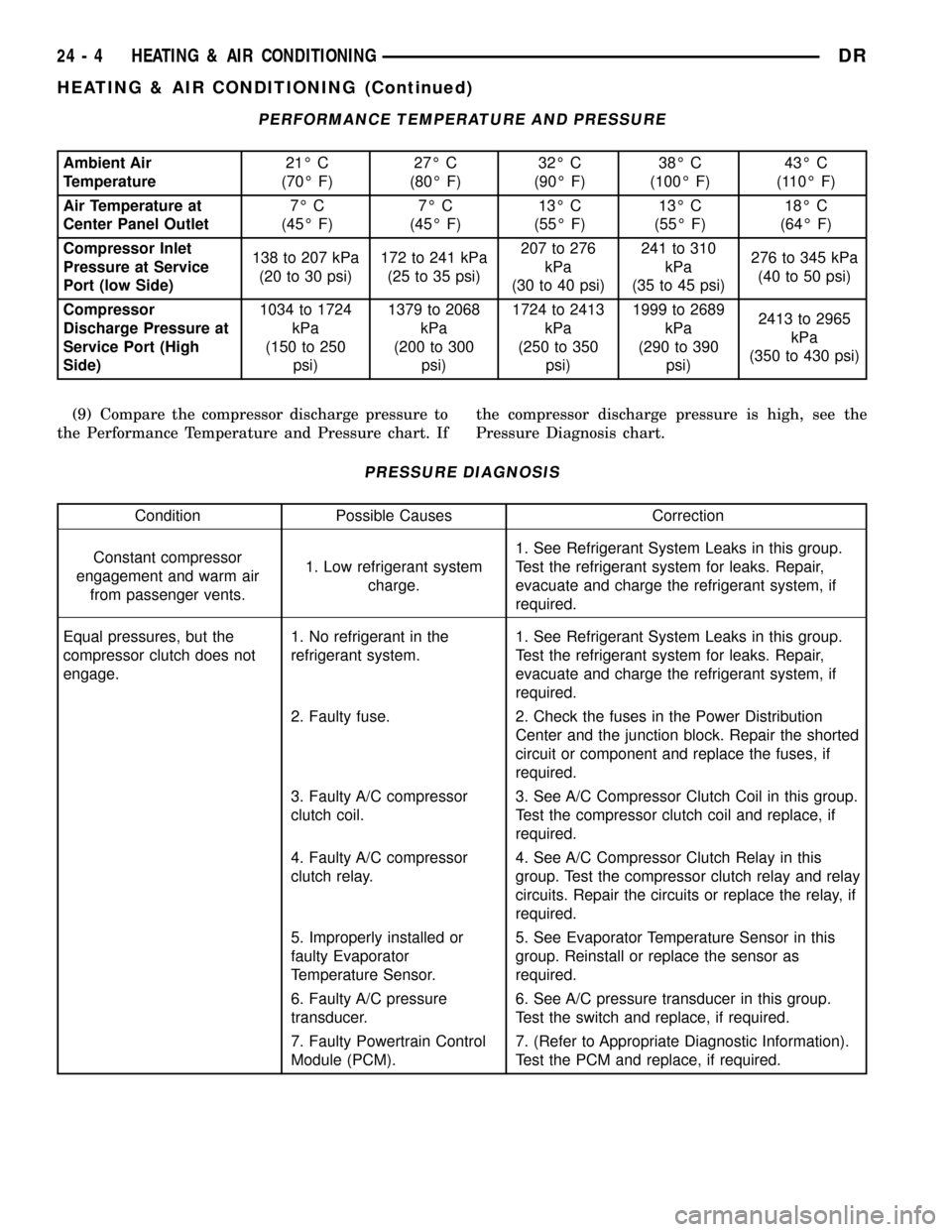
PERFORMANCE TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE
Ambient Air
Temperature21É C
(70É F)27É C
(80É F)32É C
(90É F)38É C
(100É F)43É C
(110É F)
Air Temperature at
Center Panel Outlet7É C
(45É F)7É C
(45É F)13É C
(55É F)13É C
(55É F)18É C
(64É F)
Compressor Inlet
Pressure at Service
Port (low Side)138 to 207 kPa
(20 to 30 psi)172 to 241 kPa
(25 to 35 psi)207 to 276
kPa
(30 to 40 psi)241 to 310
kPa
(35 to 45 psi)276 to 345 kPa
(40 to 50 psi)
Compressor
Discharge Pressure at
Service Port (High
Side)1034 to 1724
kPa
(150 to 250
psi)1379 to 2068
kPa
(200 to 300
psi)1724 to 2413
kPa
(250 to 350
psi)1999 to 2689
kPa
(290 to 390
psi)2413 to 2965
kPa
(350 to 430 psi)
(9) Compare the compressor discharge pressure to
the Performance Temperature and Pressure chart. Ifthe compressor discharge pressure is high, see the
Pressure Diagnosis chart.
PRESSURE DIAGNOSIS
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Constant compressor
engagement and warm air
from passenger vents.1. Low refrigerant system
charge.1. See Refrigerant System Leaks in this group.
Test the refrigerant system for leaks. Repair,
evacuate and charge the refrigerant system, if
required.
Equal pressures, but the
compressor clutch does not
engage.1. No refrigerant in the
refrigerant system.1. See Refrigerant System Leaks in this group.
Test the refrigerant system for leaks. Repair,
evacuate and charge the refrigerant system, if
required.
2. Faulty fuse. 2. Check the fuses in the Power Distribution
Center and the junction block. Repair the shorted
circuit or component and replace the fuses, if
required.
3. Faulty A/C compressor
clutch coil.3. See A/C Compressor Clutch Coil in this group.
Test the compressor clutch coil and replace, if
required.
4. Faulty A/C compressor
clutch relay.4. See A/C Compressor Clutch Relay in this
group. Test the compressor clutch relay and relay
circuits. Repair the circuits or replace the relay, if
required.
5. Improperly installed or
faulty Evaporator
Temperature Sensor.5. See Evaporator Temperature Sensor in this
group. Reinstall or replace the sensor as
required.
6. Faulty A/C pressure
transducer.6. See A/C pressure transducer in this group.
Test the switch and replace, if required.
7. Faulty Powertrain Control
Module (PCM).7. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic Information).
Test the PCM and replace, if required.
24 - 4 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGDR
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2496 of 2627

CONTROLS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION............................9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH COIL...........10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH BREAK-IN.......10
REMOVAL.............................10
INSPECTION..........................11
INSTALLATION.........................12
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................13
REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................14
A/C HEATER CONTROL
DESCRIPTION.........................14
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................15
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................16
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C PRESSURE
TRANSDUCER.......................16
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................17
OPERATION...........................17
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................18
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR BLOCK
DESCRIPTION.........................18OPERATION...........................18
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BLOWER
MOTOR RESISTOR BLOCK..............19
REMOVAL.............................19
INSTALLATION.........................19
BLOWER MOTOR SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................20
OPERATION...........................20
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BLOWER
MOTOR SWITCH......................20
DEFROST DOOR ACTUATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................20
OPERATION...........................21
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................21
EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................22
OPERATION...........................22
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................22
MODE DOOR ACTUATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................23
OPERATION...........................23
REMOVAL.............................23
INSTALLATION.........................23
RECIRCULATION DOOR ACTUATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................24
OPERATION...........................24
REMOVAL.............................24
INSTALLATION.........................25
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/
COIL
DESCRIPTION
The compressor clutch assembly consists of a sta-
tionary electromagnetic coil, a pulley bearing and
pulley assembly, and a clutch plate (Fig. 1). The elec-
tromagnetic coil and the pulley bearing and pulley
assembly are each retained on the nose of the com-
pressor front housing with snap rings. The clutch
plate is keyed to the compressor shaft and secured
with a nut. These components provide the means toengage and disengage the compressor from the
engine serpentine accessory drive belt.
OPERATION
The A/C compressor clutch provides the means to
engage and disengage the A/C compressor from the
engine serpentine accessory drive belt. When the
clutch coil is energized, it magnetically draws the
clutch into contact with the pulley and drives the
compressor shaft. When the coil is not energized, the
pulley freewheels on the pulley bearing, which is
part of the pulley assembly. The compressor clutch
DRCONTROLS 24 - 9