Page 1095 of 2890

B4M0550A
5) Insert DOJ spline end into bore of side oil seal, and
remove ST.
CAUTION:
Do not allow DOJ splines to damage side oil seal.
ST 28099PA090 SIDE OIL SEAL PROTECTOR
G3M0050
6) Align DOJ and differential splines.
7) Push housing to insert DOJ into differential.
NOTE:
Make sure DOJ is inserted properly.
8) Connect crossmember reinforcement lower to cross-
member (4 door model only).
9) Connect rear housing assembly to trailing link
assembly, and tighten self-locking nut.
Tightening torque:
113±15 N⋅m (11.5±1.5 kg-m, 83±11 ft-lb)
10) Connect rear housing assembly to lateral link
assembly, and tighten self-locking nut.
Tightening torque:
137±20 N⋅m (14±2 kg-m, 101±14 ft-lb)
11) Install stabilizer bracket.
12) While depressing brake pedal, tighten axle nut using
a socket wrench.
Tightening torque:
186±20 N⋅m (19±2 kg-m, 137±14 ft-lb)
CAUTION:
�Use a new axle nut.
�Always tighten axle nut before installing wheel on
vehicle. If wheel is installed and comes in contact with
ground when axle nut is loose, wheel bearings may be
damaged.
�Be sure to tighten axle nut to specified torque. Do
not overtighten it as this may damage wheel bearing.
13) After tightening axle nut, lock it securely.
45
4-2SERVICE PROCEDURE
4. Front and Rear Drive Shafts
Page 1097 of 2890
6. Replacement of Rear DOJ and BJ
Boots
A: REMOVAL
1) Disconnect ground cable from battery.
2) Lift-up vehicle, and remove rear wheel cap and wheels.
NOTE:
Axle nut need not be removed.
3) Remove A.B.S. sensor clamps and parking brake cable
bracket.
4) Disconnect stabilizer link from lateral link.
5) Remove bolts which secure lateral link assembly to rear
housing.
6) Remove bolts which secure trailing link assembly to
rear housing.
7) Remove crossmember reinforcement lower from cross-
member (4 door model only).
G4M0994
8) Remove DOJ from rear differential using ST.
ST 28099PA100 DRIVE SHAFT REMOVER
NOTE:
The side spline shaft circlip comes out together with the
shaft.
G4M0995
CAUTION:
Be careful not to damage side bearing retainer. Always
use bolt as shown in figure, as supporting point for ST
during removal.
ST 28099PA100 DRIVE SHAFT REMOVER
B: INSTALLATION
1) Install DOJ and BJ boots to drive shaft.
47
4-2SERVICE PROCEDURE
6. Replacement of Rear DOJ and BJ Boots
Page 1245 of 2890
G4M0398
9) Remove the following:
�
1Retainer
�
2Washer
�
3Parking lever
�
4Upper shoe return spring
�
5Trailing shoe
�
6Leading shoe
�
7Shoe hold-down spring
�
8Shoe hold-down cup
�
9Adjusting lever
�
10Adjusting spring
�
11Adjuster
�
12Lower shoe return spring
G4M0399
2. BRAKE ASSEMBLY
1) Remove wheel.
2) Remove axle nut.
3) Remove brake drum
4) Unscrew the brake pipe flare nut and disconnect brake
pipe.
5) Remove hub.
G4M0400
6) Remove the bolts installing back plate, and then,
remove brake assembly.
G4M0401
3. WHEEL CYLINDER
1) Remove brake drum and shoes.
2) Unscrew brake pipe flare nut; and disconnect brake
pipe.
3) Remove the bolts installing wheel cylinder on back
plate, and remove it.
40
4-4SERVICE PROCEDURE
3. Rear Drum Brake
Page 2338 of 2890
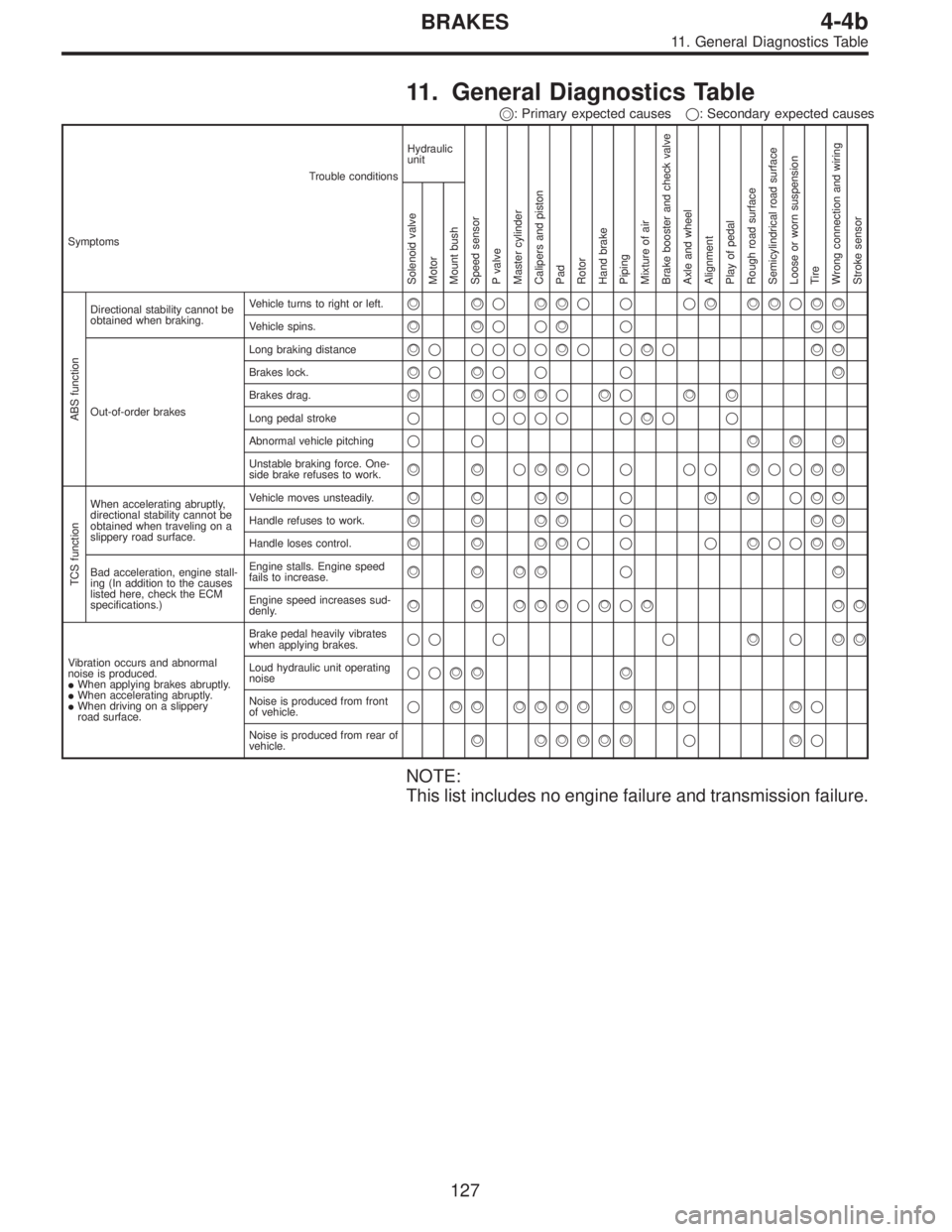
11. General Diagnostics Table
��: Primary expected causes�: Secondary expected causes
Trouble conditions
SymptomsHydraulic
unit
Speed sensor
P valve
Master cylinder
Calipers and piston
Pad
Rotor
Hand brake
Piping
Mixture of air
Brake booster and check valve
Axle and wheel
Alignment
Play of pedal
Rough road surface
Semicylindrical road surface
Loose or worn suspension
Tire
Wrong connection and wiring
Stroke sensor Solenoid valve
Motor
Mount bush ABS function
Directional stability cannot be
obtained when braking.Vehicle turns to right or left.����������� ������������
Vehicle spins.�������������
Out-of-order brakesLong braking distance
��� ���������������
Brakes lock.������� � ��
Brakes drag.�����������������
Long pedal stroke� ���� �����
Abnormal vehicle pitching�� ������
Unstable braking force. One-
side brake refuses to work.����������� ����������
TCS function
When accelerating abruptly,
directional stability cannot be
obtained when traveling on a
slippery road surface.Vehicle moves unsteadily.������������������
Handle refuses to work.�������������
Handle loses control.���������� ���������
Bad acceleration, engine stall-
ing (In addition to the causes
listed here, check the ECM
specifications.)Engine stalls. Engine speed
fails to increase.�����������
Engine speed increases sud-
denly.��������������������
Vibration occurs and abnormal
noise is produced.
�When applying brakes abruptly.
�When accelerating abruptly.
�When driving on a slippery
road surface.Brake pedal heavily vibrates
when applying brakes.
�� � � �������
Loud hydraulic unit operating
noise��������
Noise is produced from front
of vehicle.���������������������
Noise is produced from rear of
vehicle.����������������
NOTE:
This list includes no engine failure and transmission failure.
127
4-4bBRAKES
11. General Diagnostics Table
Page 2612 of 2890
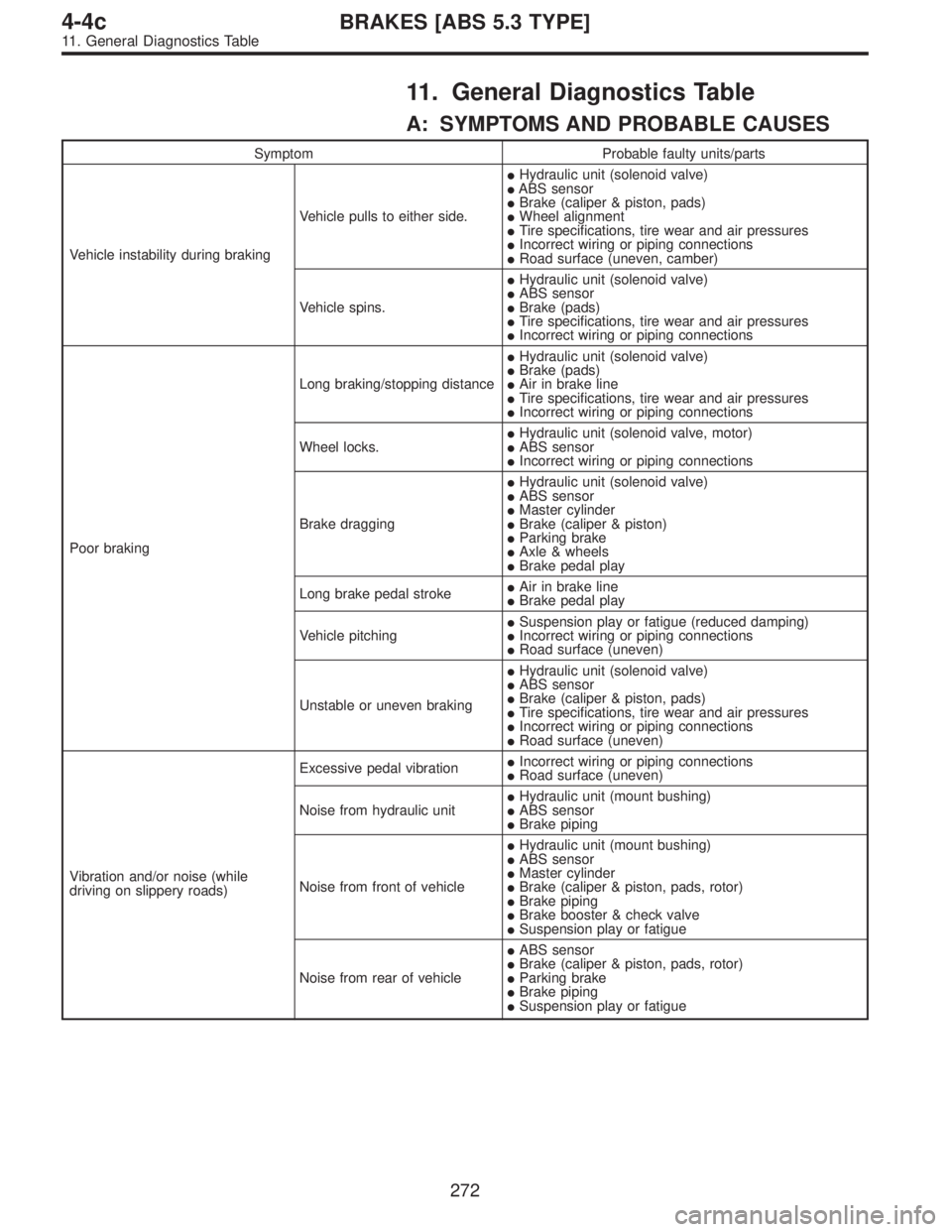
11. General Diagnostics Table
A: SYMPTOMS AND PROBABLE CAUSES
Symptom Probable faulty units/parts
Vehicle instability during brakingVehicle pulls to either side.�Hydraulic unit (solenoid valve)
�ABS sensor
�Brake (caliper & piston, pads)
�Wheel alignment
�Tire specifications, tire wear and air pressures
�Incorrect wiring or piping connections
�Road surface (uneven, camber)
Vehicle spins.�Hydraulic unit (solenoid valve)
�ABS sensor
�Brake (pads)
�Tire specifications, tire wear and air pressures
�Incorrect wiring or piping connections
Poor brakingLong braking/stopping distance�Hydraulic unit (solenoid valve)
�Brake (pads)
�Air in brake line
�Tire specifications, tire wear and air pressures
�Incorrect wiring or piping connections
Wheel locks.�Hydraulic unit (solenoid valve, motor)
�ABS sensor
�Incorrect wiring or piping connections
Brake dragging�Hydraulic unit (solenoid valve)
�ABS sensor
�Master cylinder
�Brake (caliper & piston)
�Parking brake
�Axle & wheels
�Brake pedal play
Long brake pedal stroke�Air in brake line
�Brake pedal play
Vehicle pitching�Suspension play or fatigue (reduced damping)
�Incorrect wiring or piping connections
�Road surface (uneven)
Unstable or uneven braking�Hydraulic unit (solenoid valve)
�ABS sensor
�Brake (caliper & piston, pads)
�Tire specifications, tire wear and air pressures
�Incorrect wiring or piping connections
�Road surface (uneven)
Vibration and/or noise (while
driving on slippery roads)Excessive pedal vibration�Incorrect wiring or piping connections
�Road surface (uneven)
Noise from hydraulic unit�Hydraulic unit (mount bushing)
�ABS sensor
�Brake piping
Noise from front of vehicle�Hydraulic unit (mount bushing)
�ABS sensor
�Master cylinder
�Brake (caliper & piston, pads, rotor)
�Brake piping
�Brake booster & check valve
�Suspension play or fatigue
Noise from rear of vehicle�ABS sensor
�Brake (caliper & piston, pads, rotor)
�Parking brake
�Brake piping
�Suspension play or fatigue
272
4-4cBRAKES [ABS 5.3 TYPE]
11. General Diagnostics Table