Page 874 of 2189
Description
(cont'd)
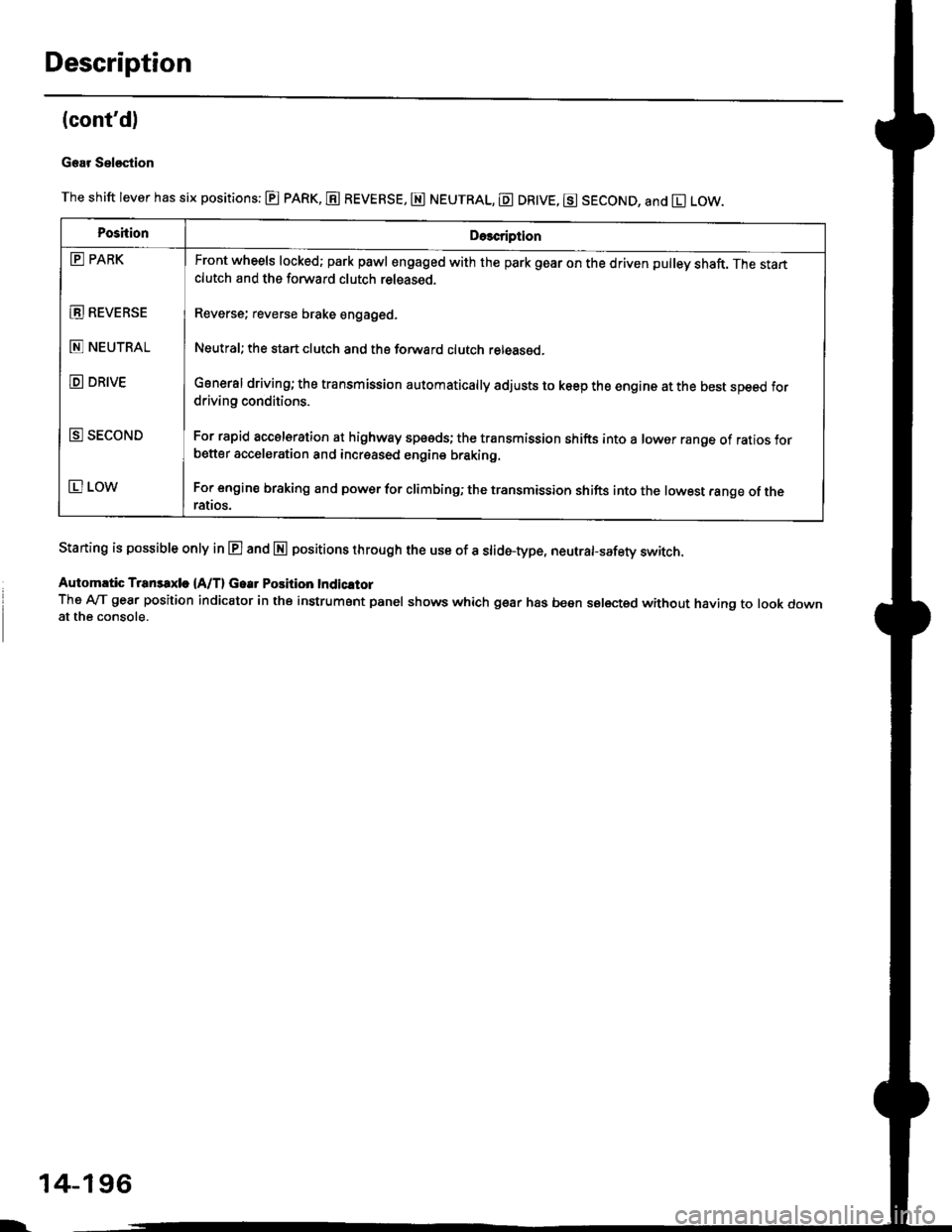
Gear Sel€stion
The shift lever has six positions: @ pARK, E REVERSE, E NEUTRAL, E DR|VE, g SECOND, and El LOW.
Staning is possible only in E and E positions through the use of a slid6-type, neutrafsafety switch.
Automrtic Transaxle {A/T} Gear Position Indicltor
The A-lT gear position indicator in the instrument panel shows which gear has been selected without having to look downat the console.
PoshionDe3cription
E PARK
E REVEBSE
E NEUTRAL
D DRIVE
E SECOND
E LOW
Front wheels locked; park pawl engaged with the park gear on the driven pulley shaft. The startclutch and the forward clutch released.
Reverse; reverse brake engaged.
Neutral; the start clutch and the forward clutch released.
General driving; the transmission automatically adjusts to keep the engine at the best speed fordriving conditions.
For rapid accelsration at highway speeds; the transmission shifts into a lower range of ratios forbetter acceleration and increased engine braking.
For engine braking and power for climbinO; the transmission shifts into the lowest range of theralros.
l-
14-196
Page 875 of 2189
STEEL BELT
START CLUTCH
INPUT SHAFT
DRIVE PULLEY
ATF FILTER
14-197
Page 876 of 2189

Description
Clutches/Reverse Brake/Planetary Gear/Pulleys
Clulches/Reverse Brake
The CVT uses the hydraulically-actuated clutches and brake to engage or disengage the transmission gears. When
hydraulic pressure is introduced into the clutch drum and the reverse brake piston cavity, the clutch piston and the reverse
brake piston move. This presses the friction djscs and the steel plates together, locking them so they don't slip. Power is
then transmitted through the engaged clutch pack to its hub-mounted gear. and through engaged ring gear to pinion
gears.
Likewise, when the hydraulic pressure is bled from the clutch pack and the reverse brake piston cavity, the piston releases
the friction discs and the steel plates, and they are free to slide past each. This allows the gear to spin independently on its
shaft, transmitting no power.
Start Clutch
The start clutch, which is located at the end of the driven pulley shaft, engages/disengages the secondary drive gear.
The start clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipes within the driven pulley shaft.
Forward Clutch
The forward clutch, which is located at the end of the drive pulley shaft, engages/disengages the sun gear.
The forward clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipe within the drive pulley shaft.
Reverse Brake
The reverse brake, which is located inside the inte.mediate housing around the ring gear, locks the ring gear in E posi-
tion. The reverse brake discs are mounted to the ring gear and the reverse brake plates are mounted to the intermediate
housing. The reverse brake is supplied hydraulic pressure by a circuit connected to the internal hydraulic circuit.
Planetary Gear
The planetary gear consists of a sun gear, a carrier assembly, and a ring gear. The sun gear is connected to the input shaft
with splines. The pinion gears are mounted to the carrier which is mounted to the fo.ward clutch drum. The sun gear
inputs the engine power via the input shaft to the planetary gear, and the carrier outputs the engine power. The ring gear
is only used for switching the rotation direction of the pullev shafts,
In E. E, and E positions (forward range), the pinion gears don't rotate and revolve with the sun gear, so the carrier
rotates. In E] positjon {reverse range), the reverse brake locks the ring gear and the sun gear drives the pinion gears to
rotate. The pinion gears rotate and revolve in the opposite direction from the rotation direction of the sun gear, and the
carrier rotates with pinion gear revolution.
Pulleys
Each pulley consists of a movable face and a fixed face, and the effective pulley .atio changes with engine speed. The
drive pulley and the driven pulley are linked by the steel belt.
To achieve a low pulley ratio, high hydraulic pressure works on the movable face of the driven pulley and reduces the
effective diameter of the drive pulley. and a lower hydraulic pressure works on the movable face of the drive pulley to
eliminate the steel belt slippage. To achieve a high pulley ratio, high hydraulic pressure works on the movable face of the
drive pulley and reduces the eifective diameter of the driven pulley, and a lower hydraulic pressure works on the movable
face of the driven pulley to eliminate the steel belt slippage.
b
14-198
Page 877 of 2189
ATF PUMPDRIVEN SPROCKET
RING GEAR
FLYWHEEL
DRIVE PLATE
ATF PUMP
DRIVE PULLEYREVERSE BRAKEPISTON
FORWARD CLUTCH
BEVERSE BRAKE
CARRIER
RING GEAR
PLANETARYPINION GEARS
INPUT SHAFT
ATF PUMPDRIVE CHAIN
ATF PUMPDRIVE SPROCKET
START CLUTCH
DRIVEN PULLEY
STEEL BELT
SECONDARY DRIVE GEAR
PARK GEAR
DRIVEN PULLEYSHAFT
FINAL DRIVE GEAR
SECONDARY GEARSHAFT
a--
i___
il
14-199
Page 878 of 2189
Description
Power Flow
E Position
. Start Clutch: released
. Forward Clutch: released
. Reverse Brake: released
Hydraulic pressure is not applied to the start clutch. forward clutch, and the reverse brake. Power is not transmitted to the
secondary drive gear.
E Position
. Start Clutch: released
. Forward Clutch: released
a Reverse Brake; released
Hydraulic pressure is not applied to the start clutch, forward clutch, and the reverse brake. Power is not transmitted to the
secondary drive gear. The secondary drive gear is locked by the park pawl interlocking the park gea..
FI-YWHEELFORWARD
INPUT SHAFT
SUN GEAR
START CLUTCHORIVEN PULLEY
FINAL ORIVEGEAR
PARK GEAR
FINAL DRIVEN GEAR
D
14-200
Page 879 of 2189
E, E, and E Positions {Forward Rangel
. Sta rt Clutch: engaged
. Forward Clutch: engaged
o Reverse Brake: released
1, The hydraulic pressure is applied to the forward clutch and the start clutch, and the sun gear drives the torward
clutch.
2. The torward clutch drives the drive pulleV shaft. which drives the driven pulley shaft linked by the steel belt.
3, The driven pulley shaft drives the secondary drive gear, via the start clutch.
4. Power is transmitted to the secondary driven gear, which drives the final driven gear.
NOTE: The working hydraulic pressure on the movable face of each shaft depends on the throttle opening position.
DRIVE PULI.f YFLYWHEELSTEEL AELT
CLUTCH
INPUT SHAFT
START CLUTCH
SECONDARY DRIVENGEAR
(cont'd)
FINAL DRIVEN GEAR
14-201
Page 880 of 2189
Description
Power Flow (cont'd)
E Position
. Sta rt Clutch: engaged
. Forward Clutch: released
. Reverse Brake: engaged
1. The hydraulic pressure is applied to the reverse brake and the start clutch. The sun gear drives the pinion gears, and
the pinion gears revolve around the sun gear. The carrier assembly rotates in the opposite direction from the rotation
direction of the sun gear.
The carrier assembly drives the drive pulley shaft via the forward clutch drum, and the drive pulley shaft drives the
driven pulley shaft linked by the steel belt.
The driven pulley shaft drives the secondary drive gear via the start clutch.
Power is transmitted to the secondary driven gear, which drives the final driven gear.
3.
4.
2.
DRIVE PULLEYSTEEL EELT
DRIVEPULLEYREVERSE BRAKE
CARRIER ASSEMBLY
INPUT SHAFT
SUN GEAR
PINION GEAB
RING GEAB
STABT CLUTCHDRIVEN PULLEY
SECONDARY DRIVEGEAR
FINALGEAB
SECONDARY ORIVENGEAR
FINAL ORIVEN GEAR
14-202
Page 886 of 2189
Description
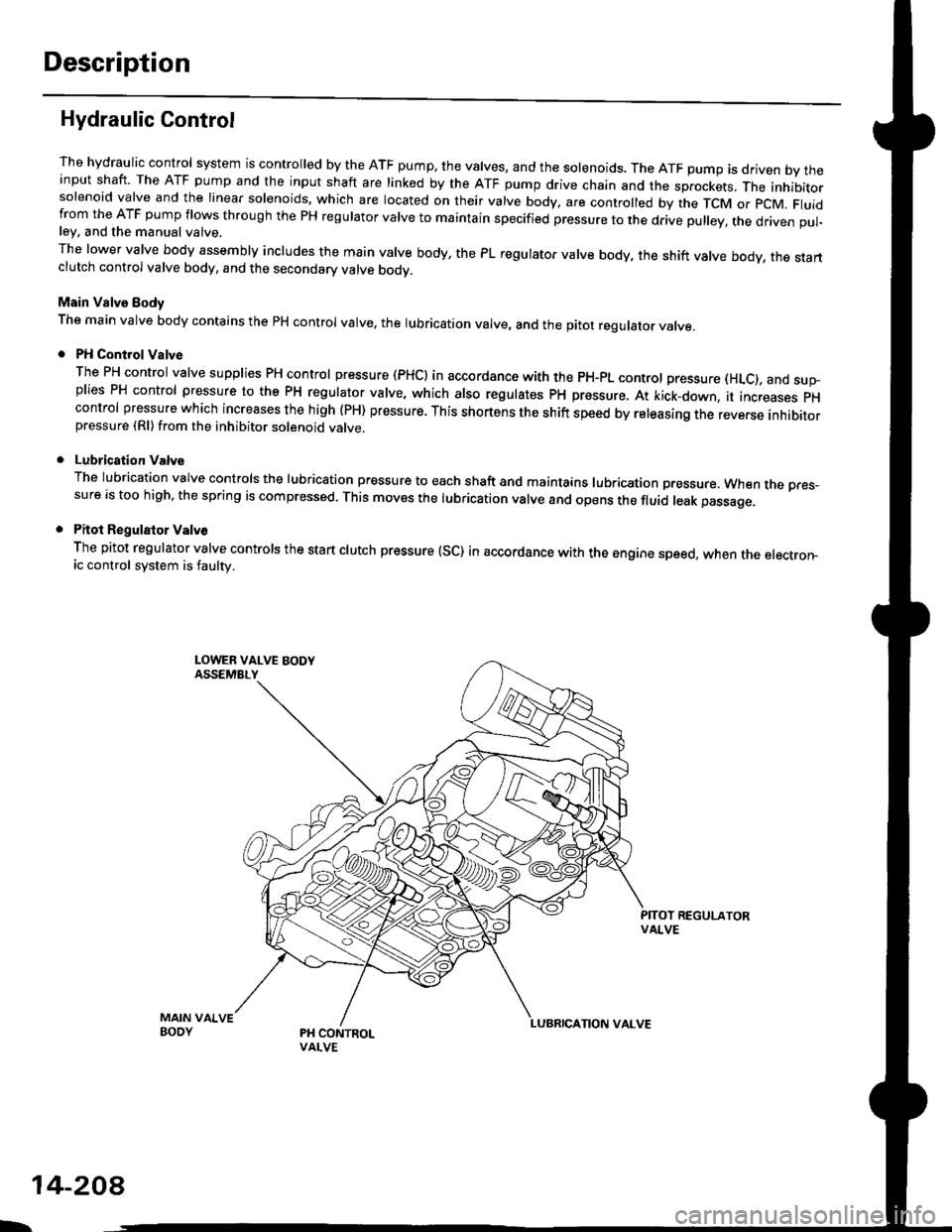
Hydraulic Control
The hydraulic control system is controlled by the ATF pump. the valves, and the solenoids. The ATF pump is driven by theinput shaft. The ATF pump and the input shaft are linked by the ATF pump drive chain and the sprockets, The inhibitorsolenoid valve and the linear solenoids. which are located on their valve body, are controlled by the TCM or pcM. Fluidfrom the ATF pump flows through the PH regulator valve to maintain specified pressure to the drive pulley, the driven pul-ley, and the manual valve,
The lower valve body assembly includes the main valve body, the PL regulator valve body, the shift valve body, the startclutch control valve body, and the secondary valve bodv.
Main Valve Eody
The main valve body contains the pH control valve, the rubrication valve, and the pitot regulator valve.
PH Control Valve
The PH control valve supplies PH control pressure (PHCI in accordance with the pH-pL control pressure (HLc), and sup-plies PH control pressure to the PH regulator valve, which also regulatss PH pressure. At kick-down, it increases pHcontrol pressure which increases the high (PH) pressure. This shortens the shift speed by releasing the reverse inhibitorpressure (Rl)from the inhibitor solenoid valve.
Lubrication Valve
The lubrication valve controls the lubrication pressure to each shaft and maintains lubrication pressure. When rne pres-sure is too high, the spring is compressed. This moves the lubrication valve and opens the fluid leak passage.
Pitot Regulalor Valv6
The pitot regulator valve controls the start clutch pressure (SC) in accordance with the engine speed, when the electron-ic control system is faulw.
MAIN VAIVEBODY
L.
14-208