1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER heater
[x] Cancel search: heaterPage 27 of 1938

LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1
JUMP STARTING, HOISTING AND TOWING . . . 5MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES............... 2
GENERAL INFORMATION
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
ENGINE OIL Ð GASOLINE ENGINES........ 1
ENGINE OILÐDIESEL ENGINES............ 1FLUID CAPACITIES...................... 1
MANUAL TRANSMISSION FLUID
(A-558 and A-598 Models)................ 1
GENERAL INFORMATION
ENGINE OIL Ð GASOLINE ENGINES
Use only oils conforming to API (American Petro-
leum Institute) Quality SJ and Energy Conserving II,
or SH and Energy Conserving II, or ACEA A1±96.
SAE VISCOSITY GRADE
To assure of properly formulated engine oils, it is
recommended that SAE Grade 5W-30 engine oils that
meet Chrysler material standard MS-6395, be used.
SAE Grade 10W-30 oils are also acceptable when the
temperatures do not fall below 0ÉC. In areas where
these grades are not generally available, higher SAE
grades may be used.
Lubricants which have both an SAE grade number
and the proper API service classification shown on
the container should be used.
ENGINE OILÐDIESEL ENGINES
Use only Diesel Engine Oil meeting standardMIL-
2104Cor API ClassificationSG/CDorCCMC PD2.
SAE VISCOSITY GRADE
CAUTION: Low viscosity oils must have the proper
API quality or the CCMC G5 designation.
To assure of properly formulated engine oils, it is recom-
mended that SAE Grade 15W-40 engine oils that meet
Chrysler material standard MS-6395, be used. European
Grade 10W-40 oils are also acceptable.
Oils of the SAE 5W-30 or 10W-30 grade number
are preferred when minimum temperatures consis-
tently fall below -12ÉC.
MANUAL TRANSMISSION FLUID (A-558 and A-598
Models)
Use only SAE 10W-40 engine oils carrying the
European CCMC-G5 classification to fill the A-598
5±speed manual transmission.
FLUID CAPACITIES
Fuel Tank.............................76L
2.0L Gasoline Engine Oil with Filter........4.3L
2.5L VM Diesel Engine Oil With Filter......6.5L
2.0L Gasoline Engine Cooling System*.......6.0L
2.5L VM Diesel Engine Cooling System*....10.0 L
TransmissionÐ5-Speed Manual............2.2L
* Includes heater and coolant recovery tank filled
to Max level. Add 2.76L if equipped with Rear
Heater.
NS/GSLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 1
Page 130 of 1938

drain hose (Fig. 107) from wiper module. Remove the
2 nuts attaching the master cylinder to the vacuum
booster (Fig. 107).
NOTE: It is not necessary to remove the brake
tubes from the master cylinder when removing the
master cylinder from the vacuum booster.
(11) Remove the master cylinder and brake tubes
as an assembly from the vacuum booster. When mas-
ter cylinder is removed, lay it out of the way on top
of the left motor mount
(12) Disconnect vacuum hose from check valve
located on vacuum booster.DO NOT REMOVE
CHECK VALVE FROM POWER BRAKE
BOOSTER.
(13) Locate the vacuum booster input rod to brake
pedal attachment under instrument panel. Position a
small screwdriver between the center tang on the
vacuum booster input rod to brake pedal pin retain-
ing clip (Fig. 108).(14) Rotate screwdriver enough to allow retaining
clip center tang to pass over end of brake pedal pin.
Then pull retaining clip off brake pedal pin.Discard
retaining clip. It is not to be reused. Replace
only with a new retaining clip when assembled.
(15) Remove the 4 nuts attaching the vacuum
booster to the dash panel. Nuts are accessible from
under dash panel in area of the steering column and
pedal bracket assembly.
(16) From outside the vehicle, slide vacuum
booster forward until its mounting studs clear dash
panel. Then tilt the booster up and toward the center
of vehicle to remove.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to disassemble the vac-
uum booster it is to be serviced ONLY as a com-
plete assembly.
INSTALL
CAUTION: When installing the vacuum booster in
the vehicle be sure the heater hoses do not become
trapped between the booster and the dash panel of
the vehicle.
(1) Position vacuum booster onto dash panel using
the reverse procedure for its removal.
(2) Install the 4 mounting nuts for the vacuum
booster. Tighten the 4 mounting nuts to a torque of
29 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(3) Using lubriplate, or an equivalent, coat the sur-
face of the brake pedal pin where it contacts the vac-
uum booster input rod.
CAUTION: When installing the brake pedal pin on
the vacuum booster input rod, do not re-use the old
retaining clip.
(4) Connect the vacuum booster input rod on the
brake pedal pin and install aNEWretaining clip
(Fig. 109).
(5) Connect the vacuum hose on the check valve in
the vacuum booster.
CAUTION: The master cylinder is used to create
the seal for holding vacuum in the vacuum booster.
The vacuum seal on the master cylinder MUST be
replaced with a NEW seal whenever the master cyl-
inder is removed from the vacuum booster.
CAUTION: When removing the vacuum seal from
the master cylinder do not use a sharp tool.
(6) Using a soft tool such as a trim stick, remove
the vacuum seal from the master cylinder mounting
flange.
Fig. 107 Master Cylinder Attachment To Vacuum
Booster
Fig. 108 Input Rod Retaining Pin
5 - 48 BRAKESNS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 133 of 1938
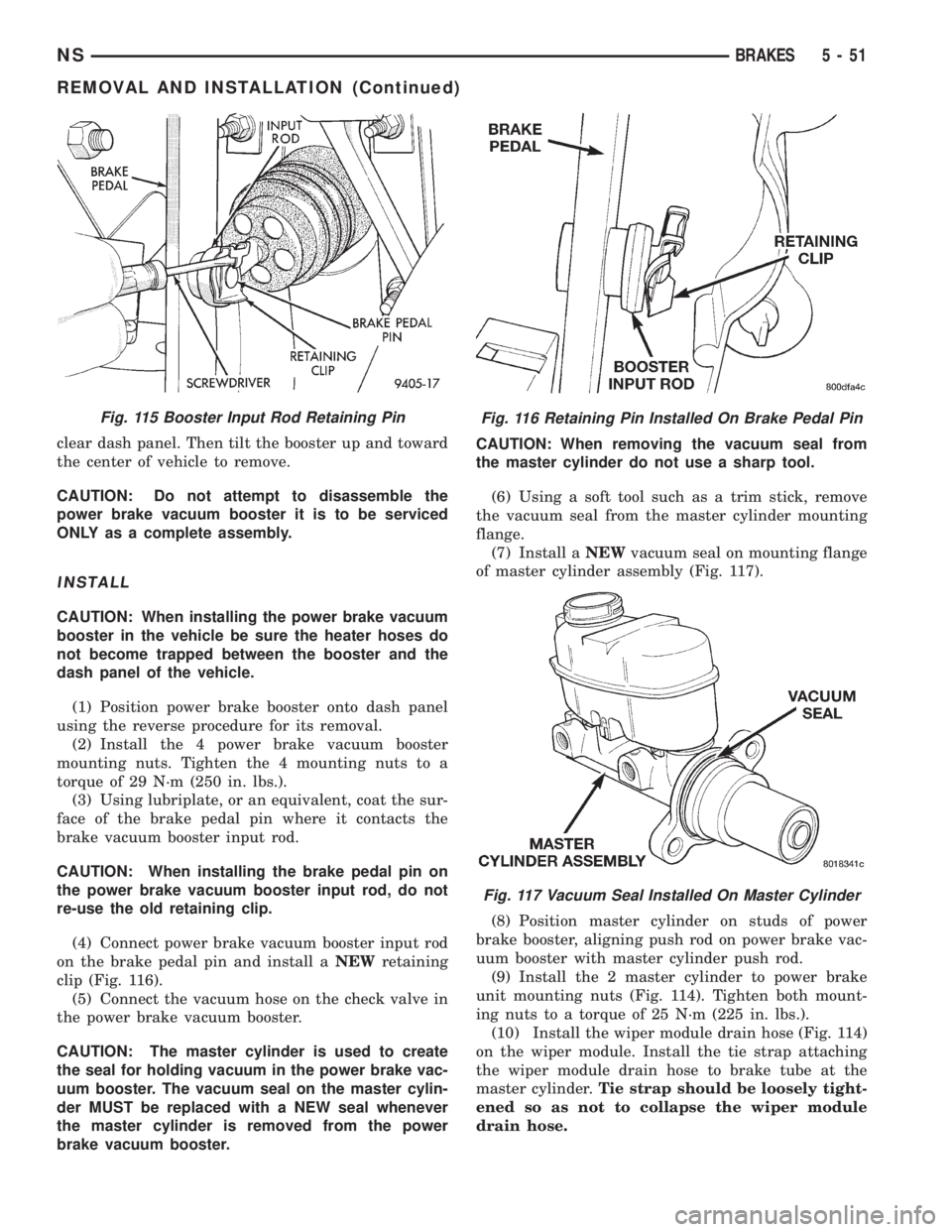
clear dash panel. Then tilt the booster up and toward
the center of vehicle to remove.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to disassemble the
power brake vacuum booster it is to be serviced
ONLY as a complete assembly.
INSTALL
CAUTION: When installing the power brake vacuum
booster in the vehicle be sure the heater hoses do
not become trapped between the booster and the
dash panel of the vehicle.
(1) Position power brake booster onto dash panel
using the reverse procedure for its removal.
(2) Install the 4 power brake vacuum booster
mounting nuts. Tighten the 4 mounting nuts to a
torque of 29 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(3) Using lubriplate, or an equivalent, coat the sur-
face of the brake pedal pin where it contacts the
brake vacuum booster input rod.
CAUTION: When installing the brake pedal pin on
the power brake vacuum booster input rod, do not
re-use the old retaining clip.
(4) Connect power brake vacuum booster input rod
on the brake pedal pin and install aNEWretaining
clip (Fig. 116).
(5) Connect the vacuum hose on the check valve in
the power brake vacuum booster.
CAUTION: The master cylinder is used to create
the seal for holding vacuum in the power brake vac-
uum booster. The vacuum seal on the master cylin-
der MUST be replaced with a NEW seal whenever
the master cylinder is removed from the power
brake vacuum booster.CAUTION: When removing the vacuum seal from
the master cylinder do not use a sharp tool.
(6) Using a soft tool such as a trim stick, remove
the vacuum seal from the master cylinder mounting
flange.
(7) Install aNEWvacuum seal on mounting flange
of master cylinder assembly (Fig. 117).
(8) Position master cylinder on studs of power
brake booster, aligning push rod on power brake vac-
uum booster with master cylinder push rod.
(9) Install the 2 master cylinder to power brake
unit mounting nuts (Fig. 114). Tighten both mount-
ing nuts to a torque of 25 N´m (225 in. lbs.).
(10) Install the wiper module drain hose (Fig. 114)
on the wiper module. Install the tie strap attaching
the wiper module drain hose to brake tube at the
master cylinder.Tie strap should be loosely tight-
ened so as not to collapse the wiper module
drain hose.
Fig. 115 Booster Input Rod Retaining PinFig. 116 Retaining Pin Installed On Brake Pedal Pin
Fig. 117 Vacuum Seal Installed On Master Cylinder
NSBRAKES 5 - 51
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 136 of 1938

(15) Remove the EGR Valve and the vacuum
transducer (Fig. 125) as an assembly from the intake
manifold.
(16) Disconnect vacuum hose from check valve
located on vacuum booster.DO NOT REMOVE
CHECK VALVE FROM POWER BRAKE
BOOSTER.
(17) Locate the vacuum booster input rod to brake
pedal connection under the instrument panel. Posi-
tion a small screwdriver between the center tang on
the power brake booster input rod to brake pedal pin
retaining clip (Fig. 126).
(18) Rotate screwdriver enough to allow retaining
clip center tang to pass over end of brake pedal pin.
Then pull retaining clip off brake pedal pin.Discard
retaining clip. It is not to be reused. Replace
only with a new retaining clip when assem-
bling.
(19) Remove the 4 nuts attaching the power brake
vacuum booster to the dash panel. Nuts are accessi-ble from under dash panel in area of the steering col-
umn and pedal bracket assembly.
(20) From outside the vehicle, slide power brake
vacuum booster forward until its mounting studs
clear dash panel. Then tilt the booster up and toward
the center of vehicle to remove.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to disassemble the
power brake vacuum booster it is to be serviced
ONLY as a complete assembly.
INSTALL
CAUTION: When installing the power brake vacuum
booster in the vehicle be sure the heater hoses do
not become trapped between the booster and the
dash panel of the vehicle.
(1) Position vacuum booster on dash panel using
the reverse procedure of its removal.
(2) Install the 4 nuts mounting the vacuum
booster to the dash panel. Tighten the 4 mounting
nuts to a torque of 29 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(3) Using lubriplate, or an equivalent, coat the sur-
face of the brake pedal pin where it contacts the vac-
uum booster input rod.
CAUTION: When installing the brake pedal pin on
the power brake vacuum booster input rod, do not
re-use the old retaining clip.
(4) Install vacuum booster input rod on brake
pedal pin and install aNEWretaining clip (Fig. 127).
(5) Connect the vacuum hose on the check valve in
the power brake vacuum booster.
(6) Install EGR Valve and vacuum transducer (Fig.
125) on the intake manifold. Install and tighten the 2
EGR valve mounting bolts to a torque of 22 N´m (200
in. lbs.).
Fig. 125 EGR Valve Attachment To Intake Manifold
Fig. 126 Vacuum Booster Input Rod Retaining Pin
Fig. 127 Retaining Pin Installed On Brake Pedal Pin
5 - 54 BRAKESNS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 215 of 1938

COOLING SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS................ 1
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION OIL COOLERÐ
2.4L................................. 3
COOLANT RECOVERY SYSTEM (CRS)....... 3
COOLANT.............................. 3
COOLING SYSTEM....................... 2
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER.................. 5
ENGINE THERMOSTAT.................... 3
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP................ 4
RADIATOR............................. 3
WATER PUMPS......................... 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
COOLANT PERFORMANCE................. 6
RADIATOR HOSES AND CLAMPS........... 6
WATER PIPESÐ3.0L ENGINE.............. 6
WATER PUMPÐ3.3/3.8L ENGINES.......... 7
WATER PUMPÐ2.4L ENGINE.............. 6
WATER PUMPÐ3.0L ENGINE.............. 6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT.................. 7
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS............. 8
DEAERATION.......................... 16
ELECTRIC FAN MOTOR TEST.............. 14
LOW COOLANT LEVEL AERATION.......... 15
PRESSURE TESTING RADIATOR CAP....... 15
RADIATOR CAP TO FILLER NECK SEAL
PRESSURE RELIEF CHECK.............. 15
RADIATOR COOLANT FLOW TEST.......... 14
RADIATOR FAN CONTROL................ 14
TEMPERATURE GAUGE INDICATION........ 16
TESTING COOLING SYSTEM FOR LEAKS.... 14
SERVICE PROCEDURES
COOLANT LEVEL CHECKÐROUTINE........ 16
COOLANT LEVEL SERVICE................ 16COOLANTÐADDING ADDITIONAL.......... 16
COOLING SYSTEMÐDRAINING............ 16
COOLING SYSTEMÐREFILLING........... 16
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTSÐ2.4L.......... 23
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTSÐ3.0L.......... 24
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTÐ3.3/3.8L........ 24
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER................. 23
FAN MODULE.......................... 22
RADIATOR DRAINCOCK.................. 21
RADIATOR............................ 21
THERMOSTATÐ2.4L ENGINE............. 19
THERMOSTATÐ3.0L ENGINE............. 20
THERMOSTATÐ3.3/3.8L ENGINES......... 20
WATER PUMP INLET TUBEÐ2.4L ENGINE . . . 17
WATER PUMPÐ3.3/3.8L ENGINES......... 19
WATER PUMPÐ2.4L ENGINE............ 17
WATER PUMPÐ3.0L ENGINE............. 18
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT................. 25
CHEMICAL CLEANING................... 25
COOLING SYSTEM CLEANING............. 25
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP............... 25
REVERSE FLUSHING THE ENGINE......... 25
REVERSE FLUSHING THE RADIATOR....... 25
WATER PUMP......................... 24
ADJUSTMENTS
BELT TENSION CHART................... 26
BELT TENSION GAUGE METHOD........... 26
PROPER BELT TENSION................. 25
SPECIFICATIONS
COOLING SYSTEM CAPACITY............. 26
TORQUE CHART........................ 26
SPECIAL TOOLS
COOLING............................. 26
GENERAL INFORMATION
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS
The accessory drive system utilizes two different
style of drive belts. The conventional V-belt and the
Poly-V belt are used to drive the generator, air con-
ditioning compressor, power steering pump and waterpump. Satisfactory performance of these belts
depends on belt condition and proper belt tension.
Belt tensioning should be performed with the aid of a
Burroughs gauge Special Tool C-4162. Because of
space limitations in the engine compartment, the use
of the gauge may be restricted. Raise the vehicle on a
hoist and then remove the splash shield to gain
access to the drive belts.
NSCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 1
Page 216 of 1938

COOLING SYSTEM
The cooling system has a radiator, coolant, electric fan
motor, shroud, pressure cap, thermostat, coolant reserve
system, transmission oil cooler, a water pump to circulate
the coolant, hoses, and clamps to complete the circuit.
²When Engine is cold: thermostat is closed, cool-
ing system has no flow through the radiator. The
coolant bypass flows through the engine only.
²
When Engine is warm: thermostat is open, cooling
system has bypass flow and coolant flow through radia-
tor.
Its primary purpose is to maintain engine temper-
ature in a range that will provide satisfactory engine
performance and emission levels under all expected
driving conditions. It also provides hot water (cool-
ant) for heater performance and cooling for automatic
transmission oil. It does this by transferring heat
from engine metal to coolant, moving this heated
coolant to the radiator, and then transferring this
heat to the ambient air.
Coolant flow circuits for 2.4L and 3.3/3.8L engines
are shown in (Fig. 1), and 3.0L engine coolant rout-
ing is shown in (Fig. 2)
Fig. 1 Cooling System Operation 2.4L and 3.3/3.8L Engines
Fig. 2 Cooling System Operation 3.0L Engine
7 - 2 COOLING SYSTEMNS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 217 of 1938

COOLANT RECOVERY SYSTEM (CRS)
This system works with the radiator pressure cap
to use thermal expansion and contraction of the cool-
ant to keep the coolant free of trapped air. Provides a
convenient and safe method for checking coolant
level and adjusting level at atmospheric pressure
without removing the radiator pressure cap. It also
provides some reserve coolant to cover deaeration
and evaporation or boiling losses. All vehicles are
equipped with this system and take various shapes
and forms. (Fig. 3) shows a typical system in the typ-
ical location.
See Coolant Level Service, and Deaeration, and
Pressure Cap sections for operation and service.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION OIL COOLERÐ2.4L
Oil cooler is internal oil to coolant type, mounted
in the radiator left tank (Fig. 4). Rubber oil lines feed
the oil cooler and the automatic transmission. Use
only approved transmission oil cooler hose. Since
these are molded to fit space available, molded hoses
are recommended.
ENGINE THERMOSTAT
The engine cooling thermostats are a wax pellet
driven, reverse poppet choke type. They are designed
to provide the fastest warm up possible by prevent-
ing leakage through them and to guarantee a mini-
mum engine operating temperature of 88 to 93ÉC
(192 to 199ÉF). They also automatically reach wide
open so they do not restrict flow to the radiator as
temperature of the coolant rises in hot weather to
around 104ÉC (220ÉF). Above this temperature the
coolant temperature is controlled by the fan, the
radiator, and the ambient temperature, not the ther-
mostat.
WATER PUMPS
A quick test to tell whether the pump is working is
to see if the heater warms properly. A defective pump
can not circulate heated coolant through the long
heater hose.The water pump on all models can
be replaced without discharging the air condi-
tioning system.
COOLANT
The cooling system is designed around the coolant.
The coolant must accept heat from engine metal, in
the cylinder head area near the exhaust valves. Cool-
ant then carries this heat to the radiator, where the
tube/fin assemblies of these components can give it
up to the air.
The use of aluminum cylinder heads, intake mani-
folds, and water pumps requires special corrosion
protection. MopartAntifreeze or the equivalent is
recommended for best engine cooling without corro-
sion, when mixed only to a freeze point of -37ÉC
(-35ÉF) to -59ÉC (-50ÉF). If it loses color or becomes
contaminated, drain, flush, and replace with fresh
properly mixed solution.
CAUTION: Do not use well water, or suspect water
supply in cooling system. A 50/50 ethylene glycol
and distilled water mix is recommended.
RADIATOR
The radiators are cross-flow types (horizontal
tubes) with design features that provide greater
strength along with sufficient heat transfer capabili-
Fig. 3 Coolant Recovery System
Fig. 4 Automatic Transmission Oil Cooler
NSCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 3
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 219 of 1938

If the gasket is dirty or damaged, a vacuum
may not be achieved, resulting is loss of coolant
and eventual overheating due to low coolant
level in radiator and engine.
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
The engine block heater is available as an optional
accessory on all models. The heater is operated by
ordinary house current (110 Volt A.C.) through a
power cord located behind the radiator grille. This
provides easier engine starting and faster warm-up
when vehicle is operated in areas having extremely
low temperatures. The heater is mounted in a core
hole (in place of a core hole plug) in the engine block,
with the heating element immersed in coolant.
Fig. 7 Cooling ModuleÐ3.0L (Front A/C Only)
Fig. 8 Cooling ModuleÐ3.0/3.3/3.8L (With Rear A/C)
Fig. 9 Radiator Pressure Cap Filler Neck
NSCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 5
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)