1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 1911 of 1938
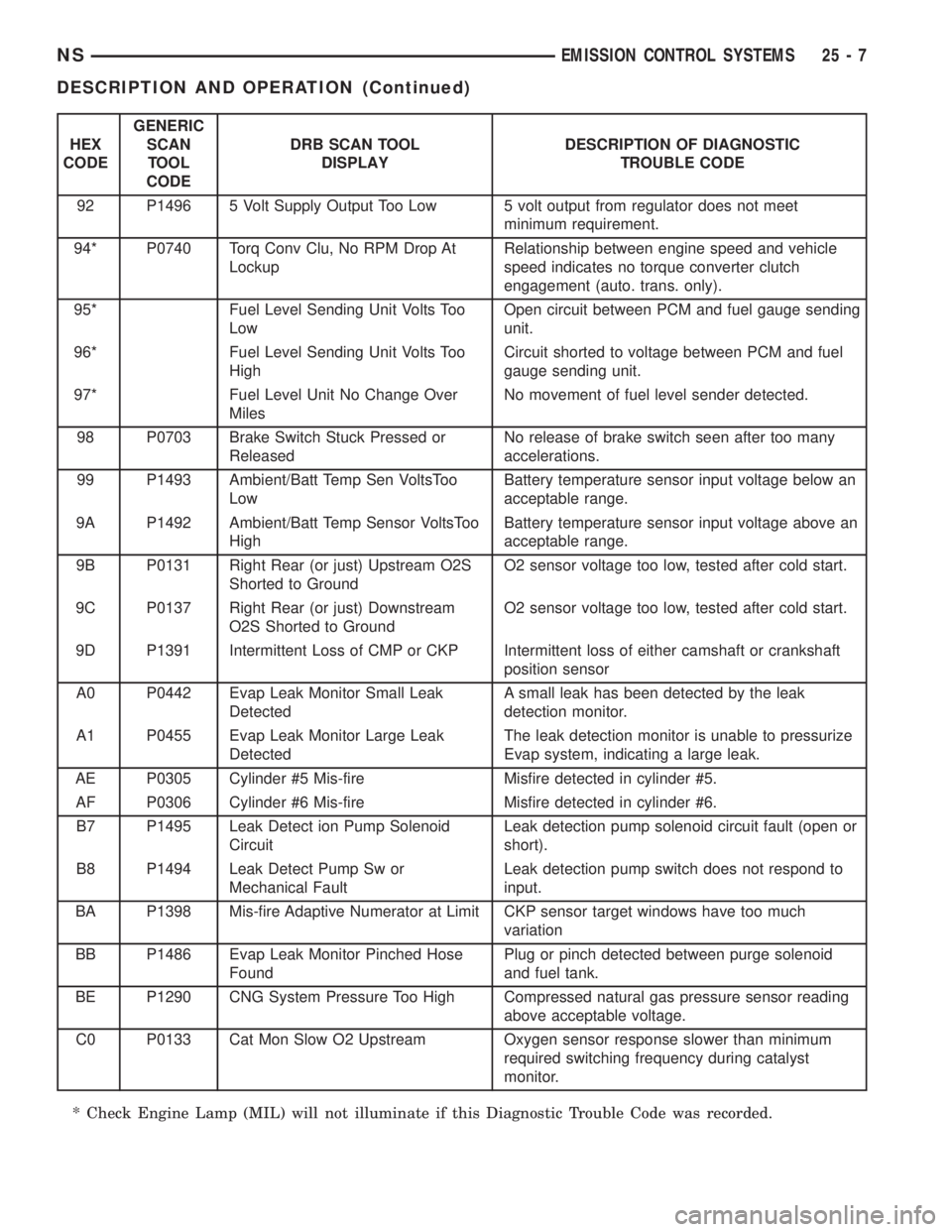
HEX
CODEGENERIC
SCAN
TOOL
CODEDRB SCAN TOOL
DISPLAYDESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC
TROUBLE CODE
92 P1496 5 Volt Supply Output Too Low 5 volt output from regulator does not meet
minimum requirement.
94* P0740 Torq Conv Clu, No RPM Drop At
LockupRelationship between engine speed and vehicle
speed indicates no torque converter clutch
engagement (auto. trans. only).
95* Fuel Level Sending Unit Volts Too
LowOpen circuit between PCM and fuel gauge sending
unit.
96* Fuel Level Sending Unit Volts Too
HighCircuit shorted to voltage between PCM and fuel
gauge sending unit.
97* Fuel Level Unit No Change Over
MilesNo movement of fuel level sender detected.
98 P0703 Brake Switch Stuck Pressed or
ReleasedNo release of brake switch seen after too many
accelerations.
99 P1493 Ambient/Batt Temp Sen VoltsToo
LowBattery temperature sensor input voltage below an
acceptable range.
9A P1492 Ambient/Batt Temp Sensor VoltsToo
HighBattery temperature sensor input voltage above an
acceptable range.
9B P0131 Right Rear (or just) Upstream O2S
Shorted to GroundO2 sensor voltage too low, tested after cold start.
9C P0137 Right Rear (or just) Downstream
O2S Shorted to GroundO2 sensor voltage too low, tested after cold start.
9D P1391 Intermittent Loss of CMP or CKP Intermittent loss of either camshaft or crankshaft
position sensor
A0 P0442 Evap Leak Monitor Small Leak
DetectedA small leak has been detected by the leak
detection monitor.
A1 P0455 Evap Leak Monitor Large Leak
DetectedThe leak detection monitor is unable to pressurize
Evap system, indicating a large leak.
AE P0305 Cylinder #5 Mis-fire Misfire detected in cylinder #5.
AF P0306 Cylinder #6 Mis-fire Misfire detected in cylinder #6.
B7 P1495 Leak Detect ion Pump Solenoid
CircuitLeak detection pump solenoid circuit fault (open or
short).
B8 P1494 Leak Detect Pump Sw or
Mechanical FaultLeak detection pump switch does not respond to
input.
BA P1398 Mis-fire Adaptive Numerator at Limit CKP sensor target windows have too much
variation
BB P1486 Evap Leak Monitor Pinched Hose
FoundPlug or pinch detected between purge solenoid
and fuel tank.
BE P1290 CNG System Pressure Too High Compressed natural gas pressure sensor reading
above acceptable voltage.
C0 P0133 Cat Mon Slow O2 Upstream Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum
required switching frequency during catalyst
monitor.
* Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will not illuminate if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1914 of 1938

The primary components within the assembly are:
A three port solenoid that activates both of the func-
tions listed above; a pump which contains a switch,
two check valves and a spring/diaphragm, a canister
vent valve (CVV) seal which contains a spring loaded
vent seal valve.
Immediately after a cold start, between predeter-
mined temperature thresholds limits, the three port
solenoid is briefly energized. This initializes the
pump by drawing air into the pump cavity and also
closes the vent seal. During non test conditions the
vent seal is held open by the pump diaphragm
assembly which pushes it open at the full travel posi-
tion. The vent seal will remain closed while the
pump is cycling due to the reed switch triggering of
the three port solenoid that prevents the diaphragm
assembly from reaching full travel. After the brief
initialization period, the solenoid is de-energized
allowing atmospheric pressure to enter the pump
cavity, thus permitting the spring to drive the dia-
phragm which forces air out of the pump cavity and
into the vent system. When the solenoid is energized
and de energized, the cycle is repeated creating flow
in typical diaphragm pump fashion. The pump is con-
trolled in 2 modes:
Pump Mode:The pump is cycled at a fixed rate to
achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten the
overall test length.
Test Mode:The solenoid is energized with a fixed
duration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur when
the diaphragm reaches the Switch closure point.
The spring in the pump is set so that the system
will achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5º H20.
The cycle rate of pump strokes is quite rapid as the
system begins to pump up to this pressure. As the
pressure increases, the cycle rate starts to drop off. If
there is no leak in the system, the pump would even-
tually stop pumping at the equalized pressure. If
there is a leak, it will continue to pump at a rate rep-
resentative of the flow characteristic of the size of the
leak. From this information we can determine if the
leak is larger than the required detection limit (cur-
rently set at .020º orifice by CARB). If a leak is
revealed during the leak test portion of the test, the
test is terminated at the end of the test mode and no
further system checks will be performed.
After passing the leak detection phase of the test,
system pressure is maintained by turning on the
LDP's solenoid until the purge system is activated.
Purge activation in effect creates a leak. The cycle
rate is again interrogated and when it increases due
to the flow through the purge system, the leak check
portion of the diagnostic is complete.
The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pumpdiaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
Evaporative system functionality will be verified by
using the stricter evap purge flow monitor. At an
appropriate warm idle the LDP will be energized to
seal the canister vent. The purge flow will be clocked
up from some small value in an attempt to see a
shift in the 02 control system. If fuel vapor, indicated
by a shift in the 02 control, is present the test is
passed. If not, it is assumed that the purge system is
not functioning in some respect. The LDP is again
turned off and the test is ended.
TRIP DEFINITION
A ªTripº means vehicle operation (following an
engine-off period) of duration and driving mode such
that all components and systems are monitored at
least once by the diagnostic system. The monitors
must successfully pass before the PCM can verify
that a previously malfunctioning component is meet-
ing the normal operating conditions of that compo-
nent. For misfire or fuel system malfunction, the
MIL may be extinguished if the fault does not recur
when monitored during three subsequent sequential
driving cycles in which conditions are similar to
those under which the malfunction was first deter-
mined.
Anytime the MIL is illuminated, a DTC is stored.
The DTC can self erase only when the MIL has been
extinguished. Once the MIL is extinguished, the
PCM must pass the diagnostic test for the most
recent DTC for 40 warm-up cycles (80 warm-up
cycles for the Fuel System Monitor and the Misfire
Monitor). A warm-up cycle can best be described by
the following:
²The engine must be running
²A rise of 40ÉF in engine temperature must occur
from the time when the engine was started
²Engine coolant temperature must reach at least
160ÉF
²A ªdriving cycleº that consists of engine start up
and engine shut off.
Once the above conditions occur, the PCM is con-
sidered to have passed a warm-up cycle. Due to the
conditions required to extinguish the MIL and erase
the DTC, it is most important that after a repair has
been made, all DTC's be erased and the repair veri-
fied.
COMPONENT MONITORS
There are several components that will affect vehi-
cle emissions if they malfunction. If one of these com-
ponents malfunctions the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (Check Engine) will illuminate.
Some of the component monitors are checking for
proper operation of the part. Electrically operated
25 - 10 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1920 of 1938
the inlet. This results in maximum vapor flow
through the valve (Fig. 9).
CRANKCASE VENT FILTER
All engines use filtered air to vent the crankcase.
The filtered air is drawn through the resonator
assembly located between the air cleaner and throttle
body.
VEHICLE EMISSION CONTROL INFORMATION
LABEL
All models have a Vehicle Emission Control Infor-
mation (VECI) Label. Chrysler permanently attaches
the label in the engine compartment. It cannot be
removed without defacing information and destroying
the label.
The label contains the vehicle's emission specifica-
tions and vacuum hose routings. All hoses must be
connected and routed according to the label.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Manual for testing procedures.
PCV VALVE TEST
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR
BLOCK WHEELS BEFORE PERFORMING ANY TEST
OR ADJUSTMENT WITH THE ENGINE OPERATING.
With the engine idling, remove the PCV valve from
its attaching point. If the valve is operating properly,
a hissing noise will be heard and a strong vacuum
felt when placing a finger over the valve inlet (Fig.
10). With the engine off, shake the valve. The valve
should rattle when shaken. Replace the valve if it
does not operate properly.Do not attempt to clean
the PCV valve.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
LEAK DETECTION PUMP REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is located under
the driver's side in the cast cradle under the steering
gear (Fig. 11).
(1) Raise and support vehicle on a hoist.
Fig. 9 Moderate Intake Manifold VacuumÐMaximum
Vapor Flow
Fig. 10 PCV Test ÐTypical
Fig. 11 Leak Detection Pump
25 - 16 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1921 of 1938
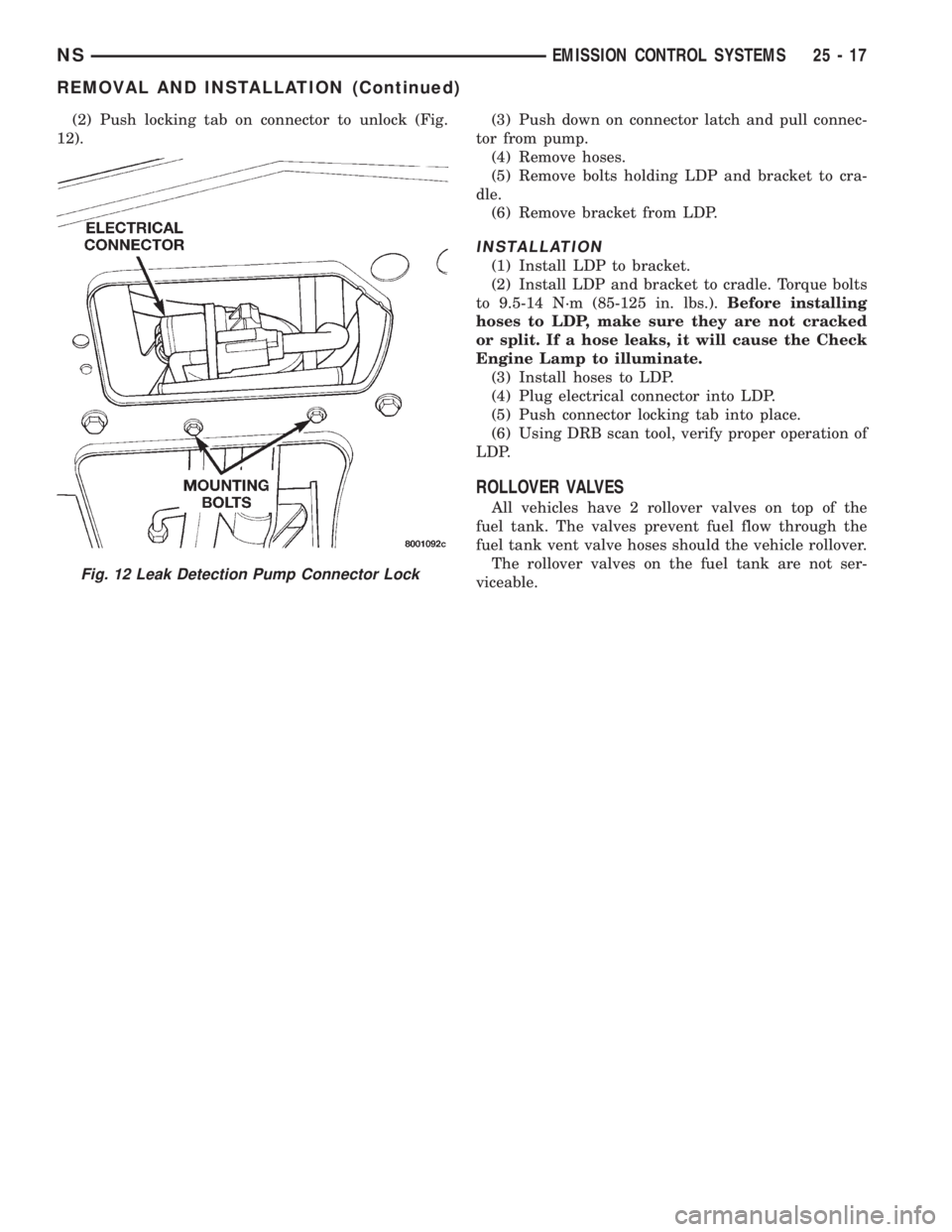
(2) Push locking tab on connector to unlock (Fig.
12).(3) Push down on connector latch and pull connec-
tor from pump.
(4) Remove hoses.
(5) Remove bolts holding LDP and bracket to cra-
dle.
(6) Remove bracket from LDP.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install LDP to bracket.
(2) Install LDP and bracket to cradle. Torque bolts
to 9.5-14 N´m (85-125 in. lbs.).Before installing
hoses to LDP, make sure they are not cracked
or split. If a hose leaks, it will cause the Check
Engine Lamp to illuminate.
(3) Install hoses to LDP.
(4) Plug electrical connector into LDP.
(5) Push connector locking tab into place.
(6) Using DRB scan tool, verify proper operation of
LDP.
ROLLOVER VALVES
All vehicles have 2 rollover valves on top of the
fuel tank. The valves prevent fuel flow through the
fuel tank vent valve hoses should the vehicle rollover.
The rollover valves on the fuel tank are not ser-
viceable.
Fig. 12 Leak Detection Pump Connector Lock
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 17
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1923 of 1938

the amount of EGR supplied to the engine. This pro-
vides the correct amount of exhaust gas recirculation
for different operating conditions.
This system does not allow EGR at idle. The EGR
systems can operate at all coolant temperatures
above 60ÉF as long as the battery ambient tempera-
ture is above 7ÉF.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
EGR SYSTEM ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
The PCM performs an on-board diagnostic check of
the EGR system. The diagnostic system uses the
electronic EGR transducer for the system tests.
The diagnostic check activates only during selected
engine/driving conditions. When the conditions are
met, the PCM energizes the transducer solenoid to
disable the EGR. The PCM checks for a change in
the heated oxygen sensor signal. If the air-fuel mix-
ture goes lean, the PCM will attempt to enrichen the
mixture. The PCM registers a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) if the EGR system is not operating cor-
rectly. After registering a DTC, the PCM turns on the
malfunction indicator (Check Engine) lamp after 2
consecutive trips. There are 2 types of failures sensed
by the PCM. The first is a short or open in the elec-
trical solenoid circuit. The second is a mechanical
failure or loss of vacuum. The Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) indicates the need for service.
If a problem is indicated by the MIL and a DTC for
the EGR system is set, check for proper operation of
the EGR system. Use the System Test, EGR Gas
Flow Test. If the EGR system tests properly, check
the system using the DRB scan tool. Refer to
On-Board Diagnosis sections in this Group. Also,
refer to the DRB scan tool and the appropriate Pow-
ertrain Diagnostics Procedure manual.
EGR SYSTEM TEST
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR
BLOCK WHEELS BEFORE TESTING THE EGR SYS-
TEM.
(1) Check the condition of all EGR system hoses
and tubes for leaks, cracks, kinks and hardening of
rubber hoses. Repair and correct these conditions
before performing any tests.
(2) Be sure the hoses at both the EGR valve and
EGR valve control are connected to the proper fit-
tings (Fig. 4).
(3) Be sure the electrical connector is firmly con-
nected at the valve control.
(4) To check EGR system operation, connect the
DRB scan tool to the 16±way data link connector.
The data link connector is located on the lower edge
of the instrument panel near the steering column.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Pro-
cedures service manual for operation of the DRB
scan tool when diagnosing the EGR system.
(5) After checking the system with the DRB scan
tool, proceed to the following EGR Valve Leakage and
EGR Valve Control Tests and repair as necessary.
Fig. 3 Electric EGR Transducer Assembly
Fig. 4 EGR Value and EGR Value ÐTypical
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 19
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1934 of 1938

²An EGR Solenoid. The EGR solenoid is located
in the engine compartment next to the PDC (Fig. 3).
The EGR solenoid opens and closes the vaccum sup-
ply that opens and closes the EGR valve. The
amount of time the EGR solenoid is held open is con-
trolled by the PCM. This is referred to as the ªon
timeº of the EGR valve.
²An EGR tube (Fig. 2) connecting a passage in
the EGR valve to the rear of the exhaust manifold.
²The vacuum pump, which supplies vacuum for
the EGR Solenoid valve. This pump also supplies
vacuum for operation of the power brake booster. The
pump is located internally in the front of the engine
block (Fig. 4) and is driven by the crankshaft gear.
²Vacuum lines and hoses to connect the various
components.
When the PCM supplies a ªonº or ªoffº signal to the
EGR Solenoid by grounding the circuit, EGR system
operation starts to occur. The PCM will monitor var-
ious engine conditions and determine when to supply
and remove this ground signal. Some of the engine
conditions that are monitored are the engine coolant
temperature, throttle position and engine speed sen-
sors.
When the ground signal is supplied to the EGR
Solenoid, vacuum from the vacuum pump will be
allowed to pass to the EGR valve via a connecting
hose.
Exhaust gas recirculation will begin in this order
when:
²The PCM determines that EGR system opera-
tion is necessary.²The engine is running to operate the vacuum
pump.
²A ground signal is supplied to the EVM.
²Vacuum passes to the EGR valve.
²The inlet seat (poppet valve) at the bottom of
the EGR valve opens to dilute and recirculate
exhaust gas back into the intake manifold.
The EGR system will be shut down by the PCM
after 60 seconds of continuous engine idling to
improve idle quality.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
EGR GAS FLOW TEST
Use the following test procedure to determine if
exhaust gas is flowing through the EGR valve. It can
also be used to determine if the EGR tube is plugged,
or the system passages in the intake or exhaust man-
ifolds are plugged.
This is not to be used as a complete test of the
EGR system.
The engine must be started, running and warmed
to operating temperature for this test.
(1) All EGR valves are equipped with a vacuum
supply fitting located on the EGR valve vacuum
motor (Fig. 2).
(2) Disconnect the rubber hose from the vacuum
supply fitting (Fig. 2).
(3) Connect a hand±held vacuum pump to this fit-
ting.
(4) Start the engine.
Fig. 3 EGR Solenoid
Fig. 4 Internal Vacuum Pump
25 - 6 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMNS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)