1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 1805 of 1938
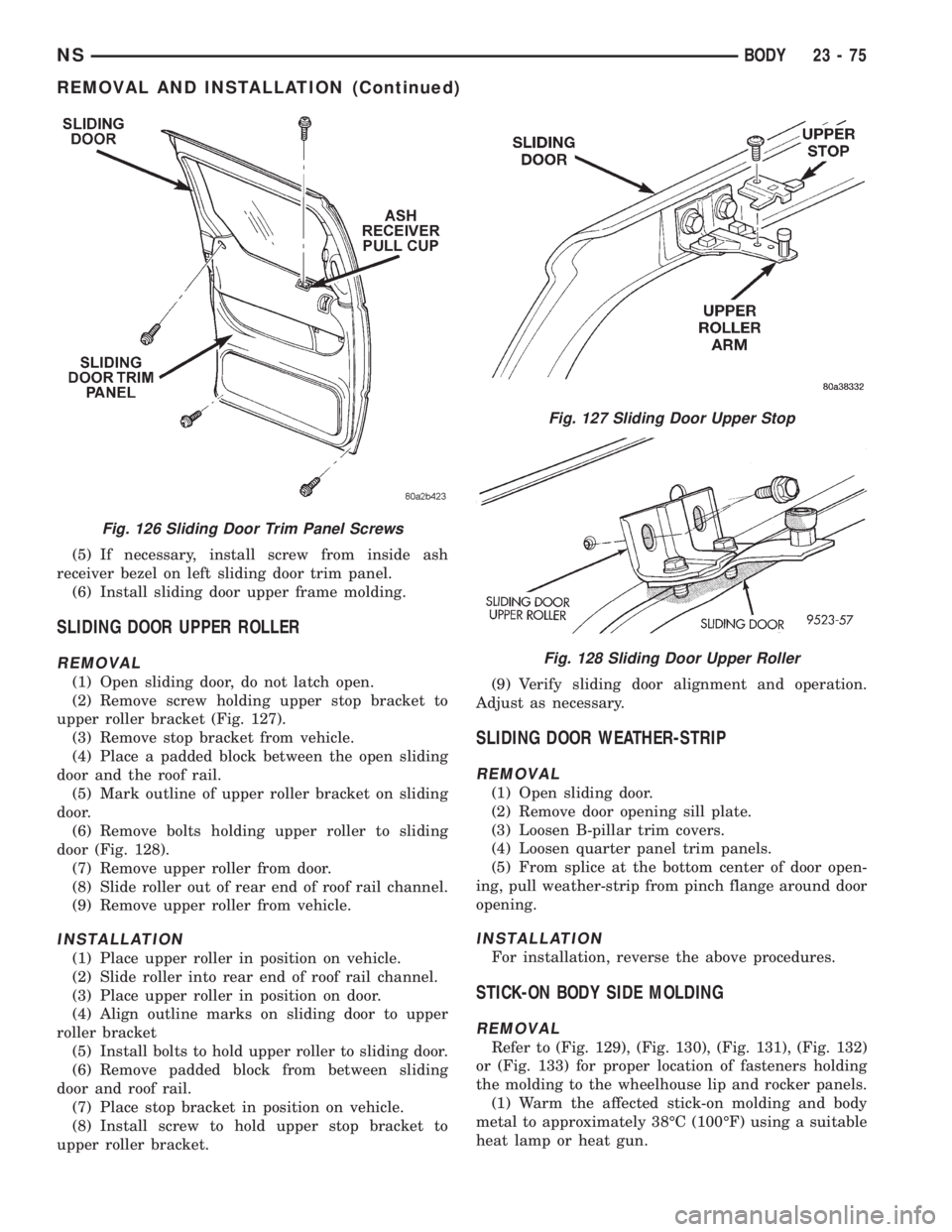
(5) If necessary, install screw from inside ash
receiver bezel on left sliding door trim panel.
(6) Install sliding door upper frame molding.
SLIDING DOOR UPPER ROLLER
REMOVAL
(1) Open sliding door, do not latch open.
(2) Remove screw holding upper stop bracket to
upper roller bracket (Fig. 127).
(3) Remove stop bracket from vehicle.
(4) Place a padded block between the open sliding
door and the roof rail.
(5) Mark outline of upper roller bracket on sliding
door.
(6) Remove bolts holding upper roller to sliding
door (Fig. 128).
(7) Remove upper roller from door.
(8) Slide roller out of rear end of roof rail channel.
(9) Remove upper roller from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place upper roller in position on vehicle.
(2) Slide roller into rear end of roof rail channel.
(3) Place upper roller in position on door.
(4) Align outline marks on sliding door to upper
roller bracket
(5) Install bolts to hold upper roller to sliding door.
(6) Remove padded block from between sliding
door and roof rail.
(7) Place stop bracket in position on vehicle.
(8) Install screw to hold upper stop bracket to
upper roller bracket.(9) Verify sliding door alignment and operation.
Adjust as necessary.
SLIDING DOOR WEATHER-STRIP
REMOVAL
(1) Open sliding door.
(2) Remove door opening sill plate.
(3) Loosen B-pillar trim covers.
(4) Loosen quarter panel trim panels.
(5) From splice at the bottom center of door open-
ing, pull weather-strip from pinch flange around door
opening.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
STICK-ON BODY SIDE MOLDING
REMOVAL
Refer to (Fig. 129), (Fig. 130), (Fig. 131), (Fig. 132)
or (Fig. 133) for proper location of fasteners holding
the molding to the wheelhouse lip and rocker panels.
(1) Warm the affected stick-on molding and body
metal to approximately 38ÉC (100ÉF) using a suitable
heat lamp or heat gun.
Fig. 126 Sliding Door Trim Panel Screws
Fig. 127 Sliding Door Upper Stop
Fig. 128 Sliding Door Upper Roller
NSBODY 23 - 75
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1810 of 1938
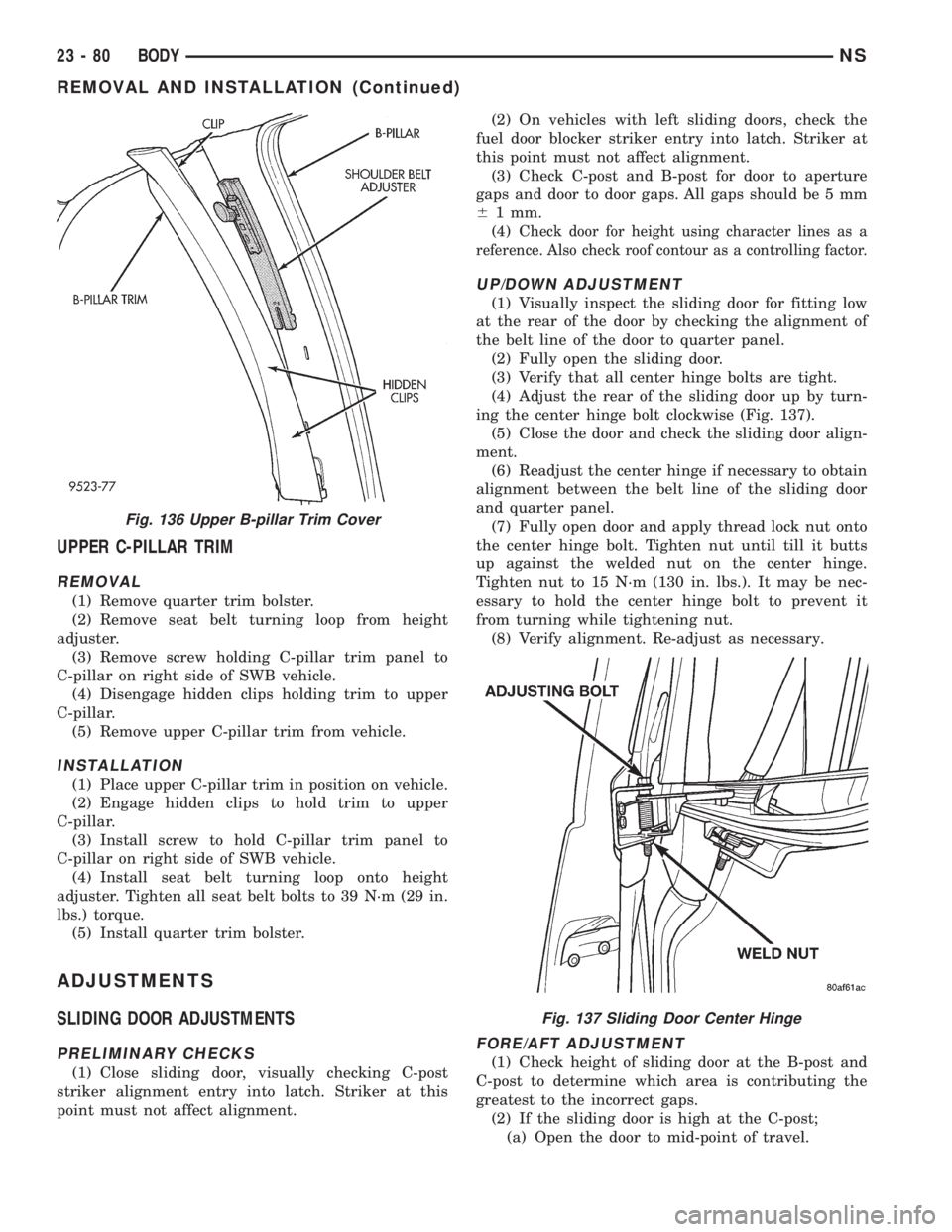
UPPER C-PILLAR TRIM
REMOVAL
(1) Remove quarter trim bolster.
(2) Remove seat belt turning loop from height
adjuster.
(3) Remove screw holding C-pillar trim panel to
C-pillar on right side of SWB vehicle.
(4) Disengage hidden clips holding trim to upper
C-pillar.
(5) Remove upper C-pillar trim from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place upper C-pillar trim in position on vehicle.
(2) Engage hidden clips to hold trim to upper
C-pillar.
(3) Install screw to hold C-pillar trim panel to
C-pillar on right side of SWB vehicle.
(4) Install seat belt turning loop onto height
adjuster. Tighten all seat belt bolts to 39 N´m (29 in.
lbs.) torque.
(5) Install quarter trim bolster.
ADJUSTMENTS
SLIDING DOOR ADJUSTMENTS
PRELIMINARY CHECKS
(1) Close sliding door, visually checking C-post
striker alignment entry into latch. Striker at this
point must not affect alignment.(2) On vehicles with left sliding doors, check the
fuel door blocker striker entry into latch. Striker at
this point must not affect alignment.
(3) Check C-post and B-post for door to aperture
gaps and door to door gaps. All gaps should be 5 mm
61 mm.
(4) C
heck door for height using character lines as a
reference. Also check roof contour as a controlling factor.
UP/DOWN ADJUSTMENT
(1) Visually inspect the sliding door for fitting low
at the rear of the door by checking the alignment of
the belt line of the door to quarter panel.
(2) Fully open the sliding door.
(3) Verify that all center hinge bolts are tight.
(4) Adjust the rear of the sliding door up by turn-
ing the center hinge bolt clockwise (Fig. 137).
(5) Close the door and check the sliding door align-
ment.
(6) Readjust the center hinge if necessary to obtain
alignment between the belt line of the sliding door
and quarter panel.
(7) Fully open door and apply thread lock nut onto
the center hinge bolt. Tighten nut until till it butts
up against the welded nut on the center hinge.
Tighten nut to 15 N´m (130 in. lbs.). It may be nec-
essary to hold the center hinge bolt to prevent it
from turning while tightening nut.
(8) Verify alignment. Re-adjust as necessary.
FORE/AFT ADJUSTMENT
(1) Check height of sliding door at the B-post and
C-post to determine which area is contributing the
greatest to the incorrect gaps.
(2) If the sliding door is high at the C-post;
(a) Open the door to mid-point of travel.
Fig. 136 Upper B-pillar Trim Cover
Fig. 137 Sliding Door Center Hinge
23 - 80 BODYNS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1813 of 1938

BODY
CONTENTS
page page
BODY COMPONENT SERVICE............... 3 SEATS .................................. 1
SEATS
INDEX
page page
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
BENCH SEAT BACK COVER................ 2
HEAD RESTRAINT ESCUTCHEON........... 1HEAD RESTRAINT SLEEVE................. 2
HEAD RESTRAINT........................ 1
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
HEAD RESTRAINT
REMOVAL
(1) Lift head restraint to top of travel.
(2) Depress lock button on side of sleeve at top of
seat back (Fig. 1).
(3) Pull head restraint from top of seat back.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position head restraint to seat.
(2) Depress lock button on side of sleeve at top of
seat back.
(3) Insert head restraint into sleeves at top of seat
back.
HEAD RESTRAINT ESCUTCHEON
REMOVAL
(1) Remove head restraint from seat.
(2) Remove escutcheon from head restraint sleeve
(Fig. 2).
(3) Remove head restraint retainer from sleeve.
(4) Separate escutcheon and retainer from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position escutcheon and retainer to seat.
(2) Install retainer to sleeve.
(3) Install escutcheon to sleeve.
(4) Install head restraint to seat.
Fig. 1 Head RestraintÐBucket Seat
NS/GSBODY 23 - 1
Page 1814 of 1938
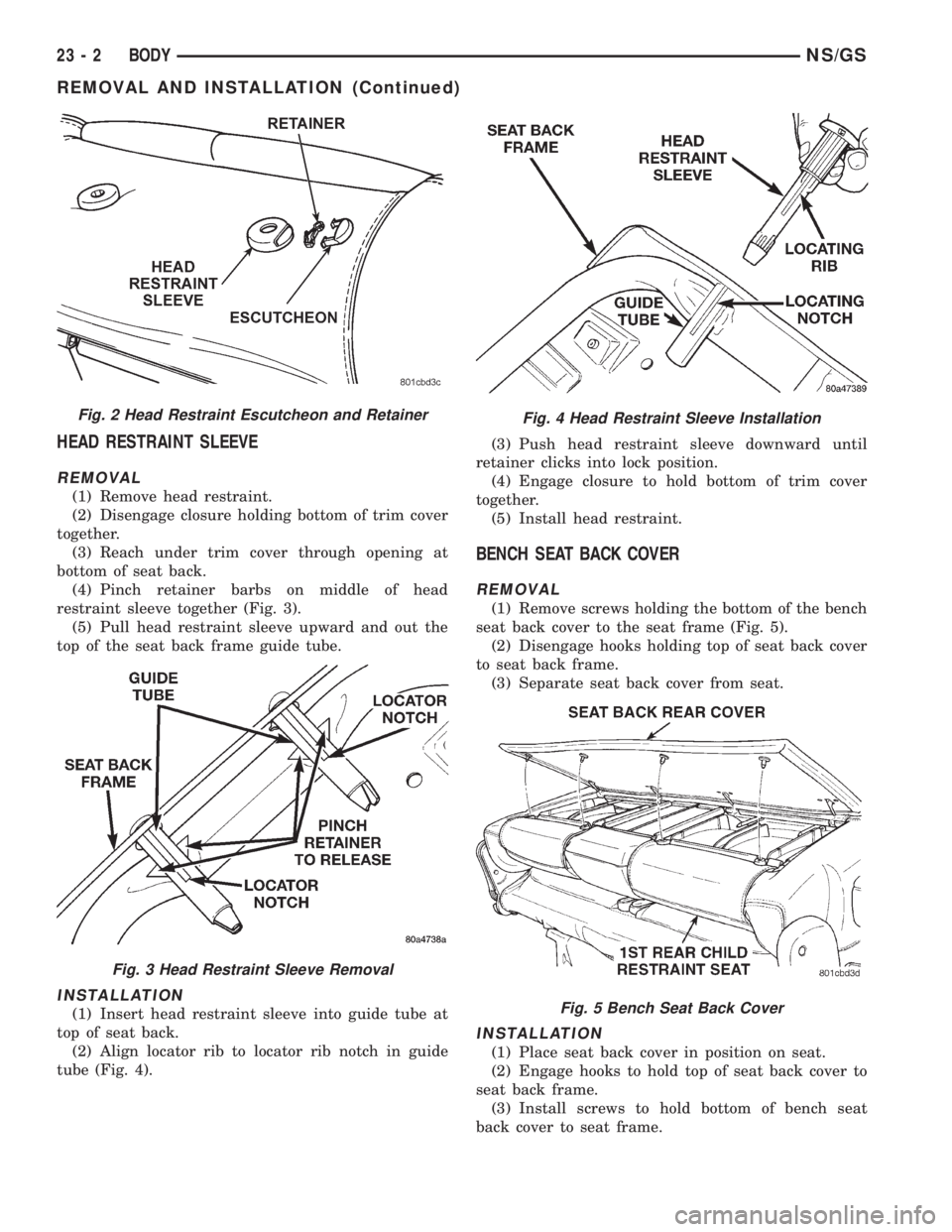
HEAD RESTRAINT SLEEVE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove head restraint.
(2) Disengage closure holding bottom of trim cover
together.
(3) Reach under trim cover through opening at
bottom of seat back.
(4) Pinch retainer barbs on middle of head
restraint sleeve together (Fig. 3).
(5) Pull head restraint sleeve upward and out the
top of the seat back frame guide tube.
INSTALLATION
(1) Insert head restraint sleeve into guide tube at
top of seat back.
(2) Align locator rib to locator rib notch in guide
tube (Fig. 4).(3) Push head restraint sleeve downward until
retainer clicks into lock position.
(4) Engage closure to hold bottom of trim cover
together.
(5) Install head restraint.
BENCH SEAT BACK COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove screws holding the bottom of the bench
seat back cover to the seat frame (Fig. 5).
(2) Disengage hooks holding top of seat back cover
to seat back frame.
(3) Separate seat back cover from seat.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place seat back cover in position on seat.
(2) Engage hooks to hold top of seat back cover to
seat back frame.
(3) Install screws to hold bottom of bench seat
back cover to seat frame.
Fig. 2 Head Restraint Escutcheon and Retainer
Fig. 3 Head Restraint Sleeve Removal
Fig. 4 Head Restraint Sleeve Installation
Fig. 5 Bench Seat Back Cover
23 - 2 BODYNS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1817 of 1938

HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING
CONTENTS
page page
FRONT HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING
SYSTEM............................... 1REAR HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING
SYSTEM.............................. 41
FRONT HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION......................... 2
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS...... 2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER.............. 2
A/C SERVICE PORTS..................... 2
AIR DISTRIBUTION DUCTS................. 2
COMPRESSOR HIGH-PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE................................ 3
CONDENSATE DRAIN..................... 3
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS . . 3
EVAPORATOR PROBE..................... 3
HANDLING TUBING AND FITTINGS........... 3
HVAC CONTROL MODULE................. 4
REAR BLOWER SPEED SWITCH............ 3
SIDE DOOR HEATER A/C OUTLETS.......... 4
SIDE WINDOW DEMISTER................. 4
SYSTEM AIRFLOW....................... 4
SYSTEM OIL LEVEL...................... 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
A/C PERFORMANCE TEST................ 12
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER............. 12
ACTUATOR CALIBRATION/DIAGNOSTICS AND
COOLDOWN TEST...................... 6
BLOWER MOTOR AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY.... 13
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL.............. 13
COMPRESSOR NOISE DIAGNOSIS.......... 13
EXPANSION VALVE...................... 13
HEATER PERFORMANCE TEST............ 15
HVAC CONTROL DIAGNOSTIC CONDITIONS . . . 9
SYSTEM CHARGE LEVEL TEST............ 16SERVICE PROCEDURES
CHARGING REFRIGERANT SYSTEM........ 17
EVACUATING REFRIGERANT SYSTEM....... 18
R-134a REFRIGERANT................... 16
STICKING HVAC CONTROL MODULE PUSH
BUTTONS............................ 19
SYSTEM LEAK CHECKING................ 19
THERMOCOUPLE PROBE................. 19
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER............. 20
A/C SERVICE PORTS.................... 20
BLEND-AIR DOOR ACTUATOR............. 20
BLOWER MOTOR AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY.... 21
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR BLOCK........ 21
BLOWER MOTOR WHEEL................. 22
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL.............. 23
COMPRESSOR......................... 23
CONDENSER ASSEMBLY................. 25
DISCHARGE LINE....................... 26
EVAPORATOR PROBE.................... 27
EXPANSION VALVE...................... 28
FILTER-DRIER ASSEMBLY................. 28
HEATER A/C UNIT HOUSING............... 29
HEATER CORE......................... 30
HEATER HOSES........................ 31
LIQUID LINE........................... 32
MODE DOOR ACTUATOR................. 32
RECIRC DOOR ACTUATOR................ 34
SIDE WINDOW DEMISTER DUCTS.......... 33
SUCTION LINE.......................... 33
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
HEATER A/C UNIT RECONDITION........... 34
NSHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 1
Page 1819 of 1938

The High Side service port is a two piece port and
is serviceable. The Low Side service port is not ser-
viceable, the suction line would have to be replaced.
REAR BLOWER SPEED SWITCH
The rear blower speed switch controls the rear
blower with the choice of low and high speeds. When
the switch is on it allows the blower speed switch
located on the rear headliner to control rear blower
speed. This switch will override the rear headliner
blower switch. For operation instructions refer to the
Owner's Manual. The rear blower speed switch is
serviced separately from the A/C control module. For
service procedures, refer to Group 8E, Instrument
Panel And Gauges.
COMPRESSOR HIGH-PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
The High Pressure Relief Valve prevents damage
to the air conditioning system if excessive pressure
develops. Excessive pressure can be caused by con-
denser air flow blockage, refrigerant overcharge, or
air and moisture in the system.The high pressure relief valve vents only a small
amount of refrigerant necessary to reduce system
pressure and then reseats itself. The majority of the
refrigerant is conserved in the system. The valve is
calibrated to vent at a pressure of 3450 to 4140 kPa
(500 to 600 psi). If a valve has vented a small
amount of refrigerant, it does not necessarily mean
the valve is defective.
The High Pressure Relief Valve is located on the
compressor manifold at the discharge passage.
NOTE: Special effort must be used to keep all
R-134a system components moisture-free. Moisture
in the oil is very difficult to remove and will cause a
reliability problem with the compressor.
CONDENSATE DRAIN
Condensation from the evaporator housing is
drained through the dash panel and on to the
ground. This drain must be kept open to prevent
water from collecting in the bottom of the housing.
If the drain is blocked condensate cannot drain,
causing water to back up and spill into the passenger
compartment. It is normal to see condensate drain-
age below the vehicle.
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
To maintain ample temperature levels from the
heating-A/C system, the cooling system must be in
proper working order. Refer to Group 0, Lubrication
and Maintenance or Group 7, Cooling System of this
manual.
The use of a bug screen is not recommended. Any
obstructions forward of the condenser can reduce the
effectiveness of the air conditioning system.
EVAPORATOR PROBE
The Evaporator probe is located on the HVAC. The
probe prevents evaporator freeze-up by signaling the
Powertrain Control Module to cycle the compressor
ON and OFF. The probe monitors the temperature of
the refrigerant after expansion.
The evaporator probe is inserted into the evapora-
tor between the coils. The probe is a sealed unit and
cannot be adjusted or repaired. It must be replaced if
found defective.
HANDLING TUBING AND FITTINGS
Kinks in the refrigerant tubing or sharp bends in
the refrigerant hose lines will greatly reduce the
capacity of the entire system. High pressures are pro-
duced in the system when it is operating. Extreme
care must be exercised to make sure that all connec-
tions are pressure tight. Dirt and moisture can enter
the system when it is opened for repair or replace-
ment of lines or components. The refrigerant oil will
Fig. 1 A/C Pressure Transducer
Fig. 2 Valve Service Ports
NSHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1829 of 1938

BLOWER MOTOR AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY
VIBRATION AND/OR NOISE DIAGNOSIS
The blower speed switch, in conjunction with the
resistor block, supplies the blower motor with varied
voltage.
CAUTION: Stay clear of the blower motor and resis-
tor block (Hot). Do not operate the blower motor
with the resistor block removed from the heater A/C
housing.
Refer to the Blower Motor Vibration/Noise chart in
this section for diagnosis.
COMPRESSOR NOISE DIAGNOSIS
Excessive noise while the A/C is being used, can be
caused by loose mounts, loose clutch, or high operat-
ing pressure. Verify compressor drive belt condition,
proper refrigerant charge and head pressure before
compressor repair is performed.
If the A/C drive belt slips at initial start-up, it does
not necessarily mean the compressor has failed.
With the close tolerances of a compressor it is pos-
sible to experience a temporary lockup. The longer
the A/C system is inactive, the more likely the condi-
tion to occur.
This condition is the result of normal refrigerant
movement within the A/C system caused by temper-
ature changes. The refrigerant movement may wash
the oil out of the compressor.
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL
The air conditioning compressor clutch electrical
circuit is controlled by the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule. It is located in the engine compartment outboard
of the battery.If the compressor clutch does not engage verify
refrigerant charge.
If the compressor clutch still does not engage check
for battery voltage at the pressure transducer located
on the liquid line. If voltage is not detected, refer to:
²Group 8W, Wiring diagrams.
²Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures manual for
diagnostic information.
If voltage is detected at the pressure transducer,
connect pressure transducer and check for battery
voltage between the compressor clutch connector ter-
minals.
If voltage is detected, perform A/C Clutch Coil
Tests.
TESTS
(1) Verify battery state of charge. (Test indicator in
battery should be green).
(2) Connect an ampmeter (0-10 ampere scale) in
series with the clutch coil terminal. Use a voltmeter
(0-20 volt scale) with clip leads measuring voltage
across the battery and A/C clutch.
(3) With A/C control in A/C mode and blower at
low speed, start the engine and run at normal idle.
(4) The A/C clutch should engage immediately and
the clutch voltage should be within two volts of the
battery voltage. If the A/C clutch does not engage,
test the fuse.
(5) The A/C clutch coil is acceptable if the current
draw is 2.0 to 3.7 amperes at 11.5-12.5 volts at clutch
coil. This is with the work area temperature at 21ÉC
(70ÉF). If voltage is more than 12.5 volts, add electri-
cal loads by turning on electrical accessories until
voltage reads below 12.5 volts.
(6) If coil current reads zero, the coil is open and
should be replaced. If the ammeter reading is 4
amperes or more, the coil is shorted and should be
replaced. If the coil voltage is not within two volts of
the battery voltage, test clutch coil feed circuit for
excessive voltage drop.
EXPANSION VALVE
NOTE: Special effort must be used to keep all
R-134a system components moisture-free. Moisture
in the oil is very difficult to remove and will cause a
reliability problem with the compressor.
TESTS
NOTE: Expansion valve tests should be performed
after compressor tests.
Review Safety Precautions and Warnings in this
group. The work area and vehicle temperature must
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER VOLTAGE
VOLTAGE CONDITION
0 TRANSDUCER FAULTY
OR NO VOLTAGE FROM
PCM
.150 TO .450 TRANSDUCER
GOOD/LOW PRESSURE
CUTOUT CONDITION
.451 TO 4.519 NORMAL OPERATING
CONDITION
4.520 TO 4.850 TRANSDUCER
GOOD/HIGH
PRESSURE CUTOUT
CONDITION
5 TRANSDUCER FAULTY
NSHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 13
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1831 of 1938

be 21ÉC to 27ÉC (70ÉF to 85ÉF). To test the expansion
valve:
NOTE: Liquid CO2 is required to test the expansion
valve. It is available from most welding supply facil-
ities. CO2 is also available from companies which
service and sell fire extinguishers.
(1) Connect a charging station or manifold gauge
set to the refrigerant system service ports. Verify the
refrigerant charge level.
(2) Close all doors, windows and vents to the pas-
senger compartment.
(3) Set heater A/C control to A/C, full heat,
FLOOR, and high blower.
(4) Start the engine and allow to idle (1000 rpm).
After the engine has reached running temperature,
allow the passenger compartment to heat up. This
will create the need for maximum refrigerant flow
into the evaporator.
(5) If the refrigerant charge is sufficient, discharge
(high pressure) gauge should read 965 to 1655 kPa
(140 to 240 psi). Suction (low pressure) gauge should
read 140 kPa to 207 kPa (20 psi to 30 psig). If system
cannot achieve proper pressure readings, replace the
expansion valve. If pressure is correct, proceed with
test.
WARNING: PROTECT SKIN AND EYES FROM CON-
TACTING CO2 PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
(6) If suction side low pressure is within specified
range, freeze the expansion valve control head for 30
seconds. Use a super cold substance (liquid CO2).Do
not spray R-134a or R-12 Refrigerant on the
expansion valve for this test.Suction side low
pressure should drop by 10 psi. If not, replace expan-
sion valve.
(7) Allow expansion valve to thaw. The low pres-
sure gauge reading should stabilize at 140 kPa to
240 kPa (20 psi to 30 psig). If not, replace expansion
valve.
(8) When expansion valve test is complete, test
A/C overall performance. Remove all test equipment
before returning vehicle to use.
HEATER PERFORMANCE TEST
PRE-DIAGNOSTIC PREPARATIONS
Review Safety Precautions and Warnings in this
group before performing the following procedures.
Check the coolant level, drive belt tension, vacuum
line connections, radiator air flow and fan operation.
Start engine and allow to warm up to normal tem-
perature.WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE RADIATOR CAP
WHEN ENGINE IS HOT, PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
If vehicle has been run recently, wait 15 minutes
before removing cap. Place a rag over the cap and
turn it to the first safety stop. Allow pressure to
escape through the overflow tube. When the system
stabilizes, remove the cap completely.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT: TEST AND
ACTION
Engine coolant is provided to the heater system by
two 16 mm (5/8 inch inside diameter) heater hoses.
With engine idling at normal running temperature,
set the control to maximum heat, floor, and high
blower setting. Using a test thermometer, check the
air temperature coming from the floor outlets, refer
to Temperature Reference Table.
If the floor outlet air temperature is insufficient,
refer to Group 7, Cooling Systems for specifications.
Both heater hoses should be HOT to the touch (cool-
ant return hose should be slightly cooler than the
supply hose). If coolant return hose is much cooler
than the supply hose, locate and repair engine cool-
ant flow obstruction in heater system.
POSSIBLE LOCATIONS OR CAUSE OF
OBSTRUCTED COOLANT FLOW
(1) Pinched or kinked heater hoses.
(2) Improper heater hose routing.
(3) Plugged heater hoses or supply and return
ports at cooling system connections, refer to Group 7,
Cooling System.
(4) Plugged heater core.
(5) Air locked heater core.
(6) If coolant flow is verified and outlet tempera-
ture is insufficient, a mechanical problem may exist.
POSSIBLE LOCATION OR CAUSE OF
INSUFFICIENT HEAT
(1) Obstructed cowl air intake.
(2) Obstructed heater system outlets.
(3) Blend-air door not functioning properly.
TEMPERATURE REFERENCE TABLE
AMBIENT
TEMPERATUREMINIMUM FLOOR
OUTLET TEMPERATURE
CELSIUS FAHRENHEIT CELSIUS FAHRENHEIT
15.5É 60É 62.2É 144É
21.1É 70É 63.8É 147É
26.6É 80É 65.5É 150É
32.2É 90É 67.2É 153É
NSHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)