1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER battery location
[x] Cancel search: battery locationPage 1358 of 1938

REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
THROTTLE BODY
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery cable.
(2) Remove air inlet to throttle body hose clamp.
(3) Remove 2 screws and air inlet resonator (Fig.
104).
(4) Remove throttle and the speed control (if
equipped) cables from lever and bracket (Fig. 105).
(5) Disconnect electrical connectors from the idle
air control motor and throttle position sensor (TPS)
(Fig. 106) or (Fig. 107) or (Fig. 108).(6) Disconnect vacuum hoses from throttle body.
(7) Remove throttle body to intake manifold
attaching nuts.
(8) Remove throttle body and gasket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Reverse procedure for installation. Tighten
throttle body mounting nuts to 25 N´m (225 in. lbs.)
torque.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
The fuel pump relay is located in the PDC. The
inside top of the PDC cover has a label showing relay
and fuse location.
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN (ASD) RELAY
The Automatic Shutdown relay (ASD) relay is
located in the PCD. The inside top of the PDC cover
has a label showing relay and fuse location.
Fig. 104 Air Inlet Resonator
Fig. 105 Throttle Cable Attachment to Throttle Body
Attachment
Fig. 106 Throttle Body Electrical and Vacuum
ConnectionsÐ2.4L
Fig. 107 Throttle Body Electrical and Vacuum
ConnectionsÐ3.0L
14 - 64 FUEL SYSTEMNS
Page 1376 of 1938
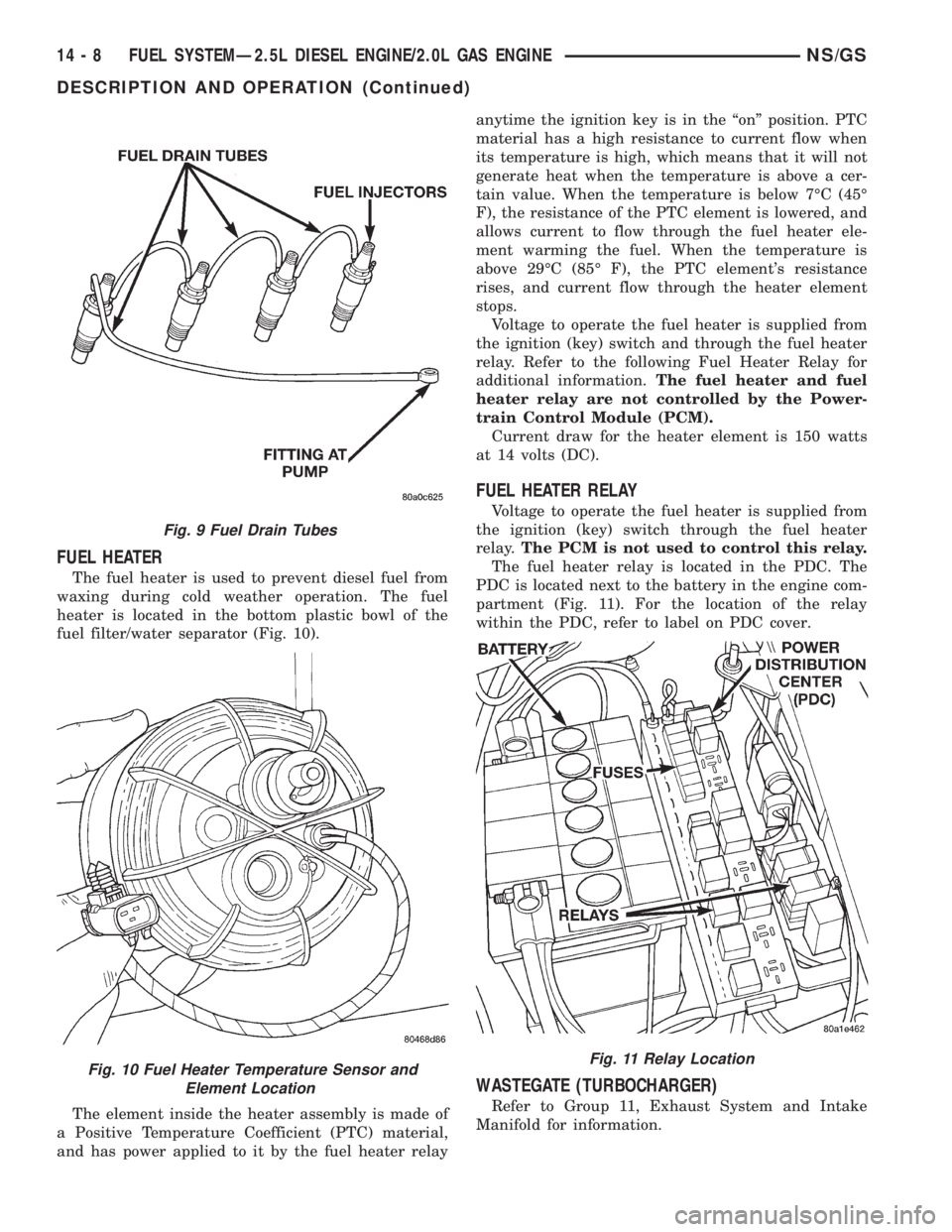
FUEL HEATER
The fuel heater is used to prevent diesel fuel from
waxing during cold weather operation. The fuel
heater is located in the bottom plastic bowl of the
fuel filter/water separator (Fig. 10).
The element inside the heater assembly is made of
a Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) material,
and has power applied to it by the fuel heater relayanytime the ignition key is in the ªonº position. PTC
material has a high resistance to current flow when
its temperature is high, which means that it will not
generate heat when the temperature is above a cer-
tain value. When the temperature is below 7ÉC (45É
F), the resistance of the PTC element is lowered, and
allows current to flow through the fuel heater ele-
ment warming the fuel. When the temperature is
above 29ÉC (85É F), the PTC element's resistance
rises, and current flow through the heater element
stops.
Voltage to operate the fuel heater is supplied from
the ignition (key) switch and through the fuel heater
relay. Refer to the following Fuel Heater Relay for
additional information.The fuel heater and fuel
heater relay are not controlled by the Power-
train Control Module (PCM).
Current draw for the heater element is 150 watts
at 14 volts (DC).
FUEL HEATER RELAY
Voltage to operate the fuel heater is supplied from
the ignition (key) switch through the fuel heater
relay.The PCM is not used to control this relay.
The fuel heater relay is located in the PDC. The
PDC is located next to the battery in the engine com-
partment (Fig. 11). For the location of the relay
within the PDC, refer to label on PDC cover.
WASTEGATE (TURBOCHARGER)
Refer to Group 11, Exhaust System and Intake
Manifold for information.
Fig. 9 Fuel Drain Tubes
Fig. 10 Fuel Heater Temperature Sensor and
Element LocationFig. 11 Relay Location
14 - 8 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1377 of 1938

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GENERAL INFORMATION
This section of the group will cover a general diag-
nosis of diesel engine fuel system components.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes:Refer to On-Board
Diagnostics in Group 25, Emission Control System
for a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's) for cer-
tain fuel system components.
The PCM must be tested with the DRBIII scan
tool. The DRBIII should be the first step in any diag-
nosis of engine performance complaints. Refer to the
1997 GS 2.5L Diesel Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures manual for diagnosis and testing of the diesel
engine control system.
VISUAL INSPECTION
A visual inspection for loose, disconnected, or incor-
rectly routed wires and hoses should be made before
attempting to diagnose or service the diesel fuel
injection system. A visual check will help find these
conditions. It also saves unnecessary test and diag-
nostic time. A thorough visual inspection of the fuel
injection system includes the following checks:
(1) Be sure that the battery connections are tight
and not corroded.
(2) Be sure that the 68 way connector is fully
engaged with the PCM (Fig. 12).
(3) Verify that the electrical connections for the
Diesel PCM relay are clean and free of corrosion.
This relay is located in the PDC. For the location ofthe relay within the PDC, refer to label on PDC
cover.
(4) Verify that the electrical connections for the
fuel heater relay are clean and free of corrosion. This
relay is located in the PDC. For the location of the
relay within the PDC, refer to label on PDC cover.
(5) Be sure the electrical connectors at the ends of
the glow plugs (Fig. 13) are tight and free of corro-
sion.
(6) Be sure that the electrical connections at the
glow plug relay are tight and not corroded. The glow
plug relay is located in the engine compartment on
the left±inner fender (Fig. 14).
Fig. 12 PCM LocationÐTypical
Fig. 13 Glow Plug Connector
Fig. 14 Glow Plug Relay Location
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 9
Page 1381 of 1938

A defective fuel injection pump, defective fuel tim-
ing solenoid or misadjusted mechanical pump timing
can cause starting problems or prevent the engine
from revving up. It can also cause:
²Engine surge at idle
²Rough idle (warm engine)
²Low power
²Excessive fuel consumption
²Poor performance
²Low power
²Black smoke from the exhaust
²Blue or white fog like exhaust
²Incorrect idle or maximum speed
The electronically controlled fuel pump has no
mechanical governor like older mechanically con-
trolled fuel pumps. Do not remove the top cover of
the fuel pump, or the screws fastening the wiring
pigtail to the side of the pump.The warranty of
the injection pump and the engine may be void
if those seals have been removed or tampered
with.
FUEL SUPPLY RESTRICTIONS
LOW±PRESSURE LINES
Restricted or Plugged supply lines or fuel filter can
cause a timing fault that will cause the PCM to oper-
ate the engine in a ªLimp Homeº mode. See the
introduction of the Fuel Injection System in this
group for more information on the Limp Home mode.
Fuel supply line restrictions can cause starting prob-
lems and prevent the engine from revving up. The
starting problems include; low power and blue or
white fog like exhaust. Test all fuel supply lines for
restrictions or blockage. Flush or replace as neces-
sary. Bleed the fuel system of air once a fuel supply
line has been replaced. Refer to the Air Bleed Proce-
dure section of this group for procedures.
HIGH±PRESSURE LINES
Restricted (kinked or bent) high±pressure lines can
cause starting problems, poor engine performance
and black smoke from exhaust.
Examine all high±pressure lines for any damage.
Each radius on each high±pressure line must be
smooth and free of any bends or kinks.
Replace damaged, restricted or leaking high±pres-
sure fuel lines with the correct replacement line.
CAUTION: The high±pressure fuel lines must be
clamped securely in place in the holders. The lines
cannot contact each other or other components. Do
not attempt to weld high±pressure fuel lines or to
repair lines that are damaged. Only use the recom-
mended lines when replacement of high±pressure
fuel line is necessary.
FUEL SHUTDOWN SOLENOID TEST
Since diesel fuel injection does not use spark plugs
to start combustion, the only way to stop the engine
is to cut off the fuel supply. This is done with the
Fuel Shutdown Solenoid. If the engine cranks, but
refuses to start, it may be caused by a defective fuel
shutdown solenoid.
The fuel shutdown solenoid is not controlled
or operated by the PCM.Voltage to operate the
solenoid is supplied from the ignition (key) switch.
NOTE: Although the fuel shutdown solenoid is not
operated by the PCM, if the Fuel Shutdown Solenoid
has been disconnected, and the key turned on, the
PCM will sense that the solenoid is not in the circuit,
and will switch to a ªLimp Homeº mode. After recon-
necting the solenoid, the PCM will have to be reset
by clearing the codes with the DRBIII scan tool, or
disconnecting the vehicle's battery for several min-
utes. The DRBIII scan tool is the preferred method
for resetting the PCM. Refer to the 1998 GS 2.5L Die-
sel Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for procedure.
The fuel shutdown (shut±off) solenoid is used to
electrically shut off the diesel fuel supply to the high-
±pressure fuel injection pump. The solenoid is
mounted to the rear of the injection pump (Fig. 23).
The solenoid controls starting and stopping of the
engine regardless of the position of the accelerator
pedal. When the ignition (key) switch is OFF, the sole-
noid is shut off and fuel flow is not allowed to the fuel
injection pump. When the key is placed in the ON or
Fig. 23 Fuel Shutdown Solenoid Location
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 13
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1390 of 1938

(14) Gauge reading should be at 0.60 mm. If not,
the pump must be rotated for adjustment:
(a) Loosen the three injection pump mounting
nuts at the mounting flanges. These flanges are
equipped with slotted holes. The slotted holes are
used to rotate and position the injection pump for
fuel timing. Loosen the three nuts just enough to
rotate the pump.
(b) Rotate the pumpclockwise(as viewed from
front) until .60 mm is indicated on the dial indica-
tor gauge.
(c) Tighten the three pump mounting nuts to 30
N´m (22 ft. lbs.) torque.
(d) Recheck the dial indicator after tightening
the pump mounting nuts. Gauge should still be
reading 0.60 mm. Loosen pump mounting nuts and
readjust if necessary.
(15) Remove dial indicator and adapter tools.
(16) Install access plug and washer to rear of
injection pump.
(17) Install plug at timing gear cover.
(18) Remove dial indicator from valve stem.
(19) Install valve spring and keepers.
(20) Install rocker arm assembly and tighten nuts.
(21) Install and connect the four high±pressure
fuel lines to the fuel injection pump. Also connect
fuel lines at the fuel injectors. For procedures, refer
to High±Pressure Fuel Lines in this group.
(22) Install electrical connector at engine coolant
temperature sensor.
(23) Connect electrical connector at fuel shutdown
solenoid.(24) Connect the main engine wiring harness to
the glow plugs.
(25) Connect the fuel timing solenoid pigtail har-
ness to the engine wiring harness.
(26) Connect the overflow valve/banjo fitting (fuel
return line assembly). Replace copper gaskets before
installing.
(27) Connect the rubber fuel return and supply
hoses to metal lines at pump. Tighten hose clamps to
2 N´m (20 in. lbs.) torque.
(28) Install generator assembly.
(29) Install engine accessory drive belt. Refer to
Group 7, Cooling System for procedures.
(30) Install negative battery cable to battery.
(31) Start the engine and bring to normal operat-
ing temperature.
(32) Check for fuel leaks.
FUEL INJECTORS
Four fuel injectors are used on each engine. Of these
four, two different types are used. The fuel injector used
on cylinder number one is equipped with a fuel injector
sensor (Fig. 47). The other three fuel injectors are iden-
tical.
Do not place the fuel injector equipped with
the fuel injector sensor into any other location
except the cylinder number one position.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Thoroughly clean the area around the injector
with compressed air.
(3) Remove the fuel drain hoses (tubes) at each
injector (Fig. 48) being serviced. Each of these hoses
is slip±fit to the fitting on injector.
(4) Remove the high±pressure fuel line at injector
being removed. Refer to High±Pressure Fuel Lines in
this group for procedures.
(5) Remove the injector using special socket tool
number VM.1012A. When removing cylinder number
Fig. 46 Installing Dial Indicator and Special Adapter
Tools
Fig. 47 Fuel Injector SensorÐNumber±1 Cylinder
14 - 22 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1391 of 1938

one injector, thread the wiring harness through the
access hole on the special socket (Fig. 49).
(6) Remove and discard the copper washer (seal) at
bottom of injector (Fig. 47).
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean the injector threads in cylinder head.
(2) Install new copper washer (seal) to injector.
(3) Install injector to engine. Tighten to 70 N´m
(52 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install high±pressure fuel lines. Refer to High-
±Pressure Fuel Lines in this group for procedures.
(5) Install fuel drain hoses (tubes) to each injector.
Do not use clamps at fuel drain hoses.
(6) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(7) Bleed the air from the high±pressure lines.
Refer to the Air Bleed Procedure section of this
group.
FUEL SHUTDOWN SOLENOID
The solenoid is mounted to the rear of the injection
pump (Fig. 50).
REMOVAL
(1) Thoroughly clean the area around the solenoid
with compressed air.
(2) Disconnect the fuel return line and banjo fit-
ting above the solenoid by removing (un±threading)
the overflow valve (Fig. 50). Place a towel below the
valve before removal. Discard old sealing washers
after removal.
(3) Disconnect the electrical connector nut (Fig.
50).
(4) Remove wiring at solenoid.
(5) Remove solenoid from injection pump.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install solenoid into injection pump.
(2) Install wiring and nut at solenoid.
(3) Install new sealing washers to banjo fitting.
(4) Install overflow valve, banjo fitting and fuel
return line to pump.
(5) Bleed air from system. Refer to Air Bleed Pro-
cedures in this section of the group.
FUEL TANK
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Insert fuel siphon hose into fuel filler neck and
push it into the tank.
(3) Drain fuel tank dry into holding tank or a
properly labeleddieselsafety container.
Fig. 48 Fuel InjectorÐTypical
Fig. 49 Wiring Harness Through Socket
Fig. 50 Fuel Shutdown Solenoid Location
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 23
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1404 of 1938

IGNITION COILÐPCM OUTPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Ignition Coil for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L
engines under Description and Operation in the Fuel
Injection System section of group 14 for more infor-
mation.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR (CHECK ENGINE)
LAMPÐPCM OUTPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Malfunction Indicator Lamp for 2.4/
3.0/3.3/3.8L engines under Description and Operation
in the Fuel Injection System section of group 14 for
more information.
RADIATOR FAN CONTROL MODULEÐPCM
OUTPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Radiator Fan Control Module for 2.4/
3.0/3.3/3.8L engines under Description and Operation
in the Fuel Injection System section of group 14 for
more information.
SPEED CONTROL SOLENOIDSÐPCM OUTPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Speed Control Solenoids for 2.4/3.0/3.3/
3.8L engines under Description and Operation in the
Fuel Injection System section of group 14 for more
information.
TACHOMETERÐPCM OUTPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Tachometer for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L engines
under Description and Operation in the Fuel Injec-
tion System section of group 14 for more information.
THROTTLE BODYÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Throttle Body for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L
engines under Description and Operation in the Fuel
Injection System section of group 14 for more infor-
mation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
VISUAL INSPECTIONÐSOHC
Before diagnosing or servicing the fuel injection
system, perform a visual inspection for loose, discon-
nected, or misrouted wires and hoses. A thorough
visual inspection that includes the following checks
saves unnecessary test and diagnostic time.
(1) Inspect the battery connections. Clean corroded
terminals.
(2) Check the 2 PCM 40-way connector for
stretched wires on pushed out terminals
(3) Open the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
Check for blown fuses. Ensure the relays and fuses
are fully seated in the PDC. A label on the underside
of the PDC cover shows the locations of each relay
and fuse.
(4) Verify the throttle cable operates freely.
(5) Check the electrical connections at the idle air
control motor and throttle position sensor.
(6) Check hose connections between the PCV
valve, vacuum port - intake manifold and the oil sep-
arator (Fig. 13).
(7) Inspect the electrical connections at the MAP
sensor/intake air temperature sensor and the (Fig.
14).
(8) Inspect the fuel injector electrical connections
(Fig. 15).
(9) Inspect the ignition coil electrical connector.
Ensure the spark plug insulators are firmly seated
over the spark plugs (Fig. 16).
(10) Check the electrical connection to the radiator
fan.
(11) Inspect for corrosion on the electrical connec-
tions at the starter motor solenoid. Check the ground
cable connection below the starter motor (Fig. 17).
(12) Inspect the air cleaner filter element. Replace
as necessary. Check the air induction system for
restrictions.
Fig. 10 Ignition CoilÐ2.0L engine
Fig. 11 Throttle BodyÐ2.0L engine
14 - 36 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1412 of 1938

illuminated constantly, it usually indicates a problem
has been detected somewhere within the fuel system.
The DRBIII scan tool is the best method for commu-
nicating with the PCM to diagnose faults within the
system.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is mounted
in the center consule to a bracket located in front of
the Air Bag Module (Fig. 1).
The PCM is a pre±programmed, dual micro±proces-
sor digital computer. It will either directly operate or
partially regulate the:
²Speed Control
²Speed Control LED lamp
²Fuel Timing Solenoid
²Glow Plug Relay
²Glow Plugs
²EGR Solenoid
²Glow Plug Lamp
²Diesel PCM Relay
²Air Conditioning Operation
²Tachometer
²Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Solenoid
The PCM can adapt its programming to meet
changing operating conditions.
The PCM receives input signals from various
switches and sensors. Based on these inputs, the
PCM regulates various engine and vehicle operationsthrough different system components. These compo-
nents are referred to asPCM Outputs.The sensors
and switches that provide inputs to the PCM are con-
sideredPCM Inputs.
PCM Inputs are:
²Air Conditioning Selection
²Theft Alarm
²Clutch Switch
²Diesel PCM Relay
²ISO-Protocol
²Control Sleeve
²Fuel Temperature
²Boost Pressure Sensor
²Accelerator Pedal Sensor
²EGR
²A/C Pressure
²Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
²Low Idle Position Switch
²5 Volt Supply
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Sensor Return
²Glow Plug
²Engine Speed Sensor (rpm)
²Fuel Injector #1 Sensor
²Starter Signal
²Brake Switch
²Speed Control Switch Position
²Power Ground
²Signal Ground
²Ignition (key) Switch Sense
²Battery Voltage
²SCI Receive (DRB scan tool connection)
PCM Outputs:
After inputs are received by the PCM, certain sen-
sors, switches and components are controlled or reg-
ulated by the PCM. These are consideredPCM
Outputs.These outputs are for:
²A/C Clutch Relay (for A/C clutch operation)
²Speed Control LED
²Data Link Connectors (for DRB scan tool)
²Diesel PCM Relay
²Diesel PCM Sense
²Accelarator Pedal
²5 Volts Supply
²Glow Plug Relay
²Fan Relay
²Fuel Quantity
²Fuel Timing Solenoid
²Fuel Shut-Off Solenoid
²Engine Speed Sensor
²Glow Plug Lamp (malfunction indicator lamp)
²Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Solenoid
²Glow Plug Relay
²Tachometer
²SCI transmit (DRB scan tool connection)
Fig. 1 PCM Location
14 - 44 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)