Page 2104 of 2543
(See page IN±30).
(1) Connect SST (check harness ªAº).
(See page EG±510)
SST 09990±01000
(2) Turn ignition switch ON.
Measure voltage between terminal FPU of engine
control module connector and body ground.
Voltage: 9 Ð 14 V
Check voltage between terminal FPU of engine control module
connector and body ground.
Proceed to next circuit inspection shown
on matrix chart (See page Eg±514).
Repair or replace harness or connector.
Check for open and short in harness and connector between engine control
module and VSV, VSV and EFI main relay (See page IN±30).
Check and replace engine control module.
± ENGINE2JZ±GTE ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTINGEG±597
Page 2132 of 2543
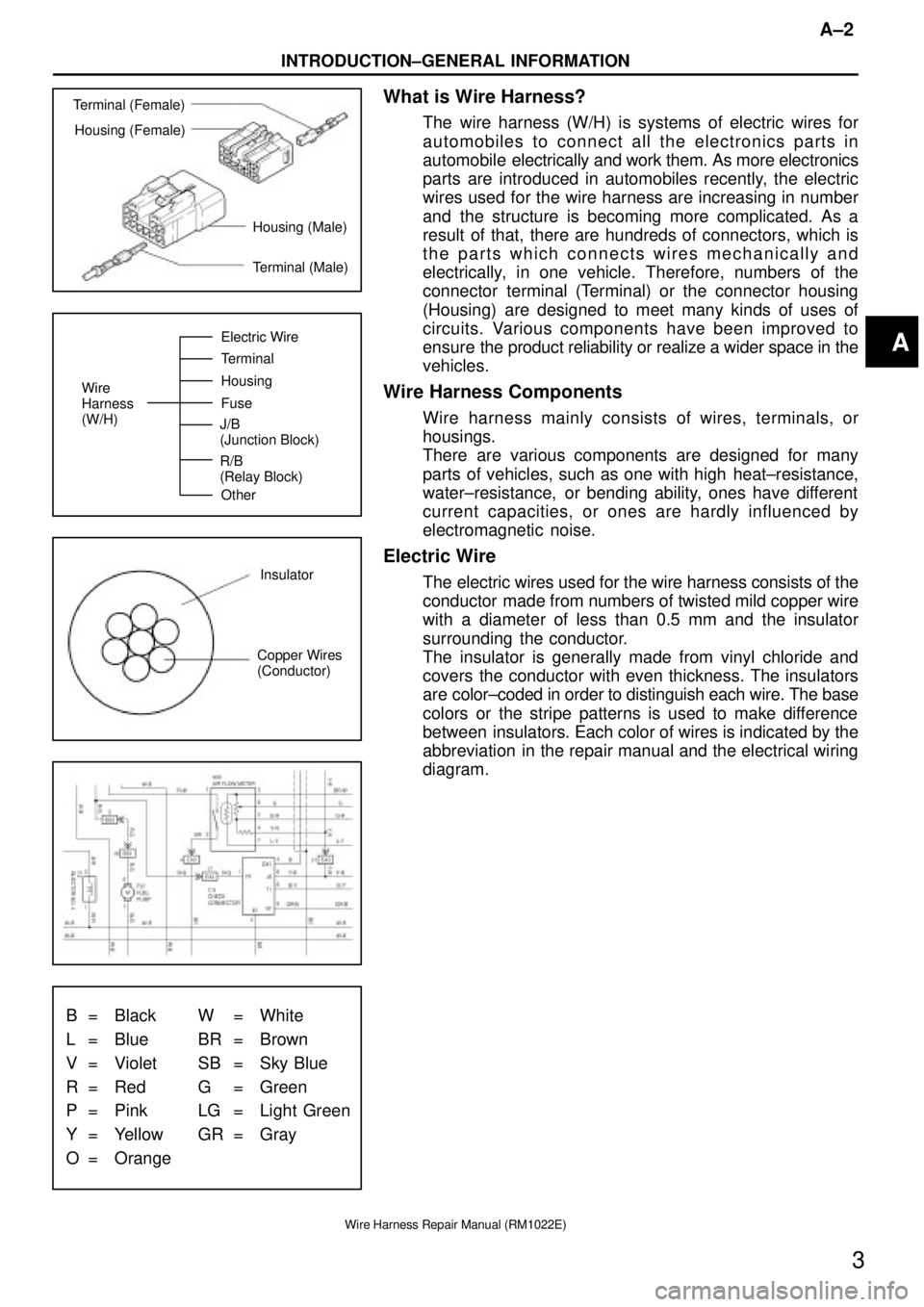
Terminal (Female)
Housing (Female)
Housing (Male)
Terminal (Male)
Wire
Harness
(W/H)Electric Wire
Terminal
Housing
Fuse
Other J/B
(Junction Block)
R/B
(Relay Block)
Insulator
Copper Wires
(Conductor)
B = Black W = White
L = Blue BR = Brown
V = Violet SB = Sky Blue
R = Red G = Green
P = Pink LG = Light Green
Y = Yellow GR = Gray
O = Orange
A±2
INTRODUCTION±GENERAL INFORMATION
3
Wire Harness Repair Manual (RM1022E)
What is Wire Harness?
The wire harness (W/H) is systems of electric wires for
automobiles to connect all the electronics parts in
automobile electrically and work them. As more electronics
parts are introduced in automobiles recently, the electric
wires used for the wire harness are increasing in number
and the structure is becoming more complicated. As a
result of that, there are hundreds of connectors, which is
the parts which connects wires mechanically and
electrically, in one vehicle. Therefore, numbers of the
connector terminal (Terminal) or the connector housing
(Housing) are designed to meet many kinds of uses of
circuits. Various components have been improved to
ensure the product reliability or realize a wider space in the
vehicles.
Wire Harness Components
Wire harness mainly consists of wires, terminals, or
housings.
There are various components are designed for many
parts of vehicles, such as one with high heat±resistance,
water±resistance, or bending ability, ones have different
current capacities, or ones are hardly influenced by
electromagnetic noise.
Electric Wire
The electric wires used for the wire harness consists of the
conductor made from numbers of twisted mild copper wire
with a diameter of less than 0.5 mm and the insulator
surrounding the conductor.
The insulator is generally made from vinyl chloride and
covers the conductor with even thickness. The insulators
are color±coded in order to distinguish each wire. The base
colors or the stripe patterns is used to make difference
between insulators. Each color of wires is indicated by the
abbreviation in the repair manual and the electrical wiring
diagram.
A
Page 2135 of 2543
![TOYOTA SUPRA 1995 Service Repair Manual To Ignition SW
IG Terminal
Fuse
Relay
SW2 SolenoidVoltmeter [A]
[B]
[C] SW1
Ohmmeter
SW
INTRODUCTION±HOW TO PERFORM FOR SYSTEM INSPECTION
A±5
6
Wire Harness Repair Manual (RM1022E)
HOW TO PERFORM FO TOYOTA SUPRA 1995 Service Repair Manual To Ignition SW
IG Terminal
Fuse
Relay
SW2 SolenoidVoltmeter [A]
[B]
[C] SW1
Ohmmeter
SW
INTRODUCTION±HOW TO PERFORM FOR SYSTEM INSPECTION
A±5
6
Wire Harness Repair Manual (RM1022E)
HOW TO PERFORM FO](/manual-img/14/57468/w960_57468-2134.png)
To Ignition SW
IG Terminal
Fuse
Relay
SW2 SolenoidVoltmeter [A]
[B]
[C] SW1
Ohmmeter
SW
INTRODUCTION±HOW TO PERFORM FOR SYSTEM INSPECTION
A±5
6
Wire Harness Repair Manual (RM1022E)
HOW TO PERFORM FOR SYSTEM INSPECTION
This inspection procedure is a simple troubleshooting which should be carried out on the vehicle during
system operation and is based on the assumption of system component trouble
Always inspect the trouble taking the following items into consideration:
�Ground point fault
�Open or short circuit of the wire harness
�Connector or terminal connection fault
�Fuse or fusible link fault
NOTICE:
�This is an on±vehicle inspection during system operation.
Therefore, inspect the trouble with due regard for safety.
�If connecting the battery directly, be careful not to cause a short circuit, and select the applicable
voltage.
1. Voltage Check
(a)Establish conditions in which voltage is present at the
check point.
Example:
[A] ± Ignition SW on
[B] ± Ignition SW and SW 1 on
[C] ± Ignition SW, SW 1 and Relay on (SW 2 off)
(b)Using a voltmeter, connect the negative (±) lead to a
good ground point or negative (±) battery terminal
and the positive (+) lead to the connector or
component terminal. This check can be done with a
test bulb instead of a voltmeter.
2. Continuity and Resistance Check
(a)Disconnect the battery terminal or wire so there is no
voltage between the check points.
(b)Contact the two leads of an ohmmeter to each of the
check points.
A
Page 2137 of 2543
![TOYOTA SUPRA 1995 Service Repair Manual Fuse Case Test Bulb
Short [A]
SW1
Short [B]
Relay
Light
Short [C]
SW2 SolenoidDisconnect
Disconnect DisconnectTo Ignition SW
IG Terminal
INTRODUCTION±HOW TO PERFORM FOR SYSTEM INSPECTION
A±7
8
Wire TOYOTA SUPRA 1995 Service Repair Manual Fuse Case Test Bulb
Short [A]
SW1
Short [B]
Relay
Light
Short [C]
SW2 SolenoidDisconnect
Disconnect DisconnectTo Ignition SW
IG Terminal
INTRODUCTION±HOW TO PERFORM FOR SYSTEM INSPECTION
A±7
8
Wire](/manual-img/14/57468/w960_57468-2136.png)
Fuse Case Test Bulb
Short [A]
SW1
Short [B]
Relay
Light
Short [C]
SW2 SolenoidDisconnect
Disconnect DisconnectTo Ignition SW
IG Terminal
INTRODUCTION±HOW TO PERFORM FOR SYSTEM INSPECTION
A±7
8
Wire Harness Repair Manual (RM1022E)
4. Finding a Short Circuit
(a)Remove the blown fuse and eliminate all loads from
the fuse.
(b)Connect a test bulb in place of the fuse.
(c)Establish conditions in which the test bulb comes on.
Example:
[A] ± Ignition SW on
[B] ± Ignition SW and SW 1 on
[C] ± Ignition SW, SW 1 and Relay on (Connect the Relay)
and SW 2 off (or disconnect SW 2)
(d)Disconnect and reconnect the connectors while
watching the test bulb. The short lies between the
connector where the test bulb stays lit and the
connector where the bulb goes out.
(e)Find the exact location of the short by lightly shaking
the problem wire along the body.
CAUTION:
(a)Do not open the cover or the case of the ECU
unless absolutely necessary. (If the IC terminals
are touched, the IC may be destroyed by static
electricity.)
(b)When replacing the internal mechanism (ECU
part) of the digital meter, be careful that no part of
your body or clothing comes in contact with the
terminals of leads from the IC, etc. of the
replacement part (spare part).
A