1995 JEEP YJ service
[x] Cancel search: servicePage 78 of 2158
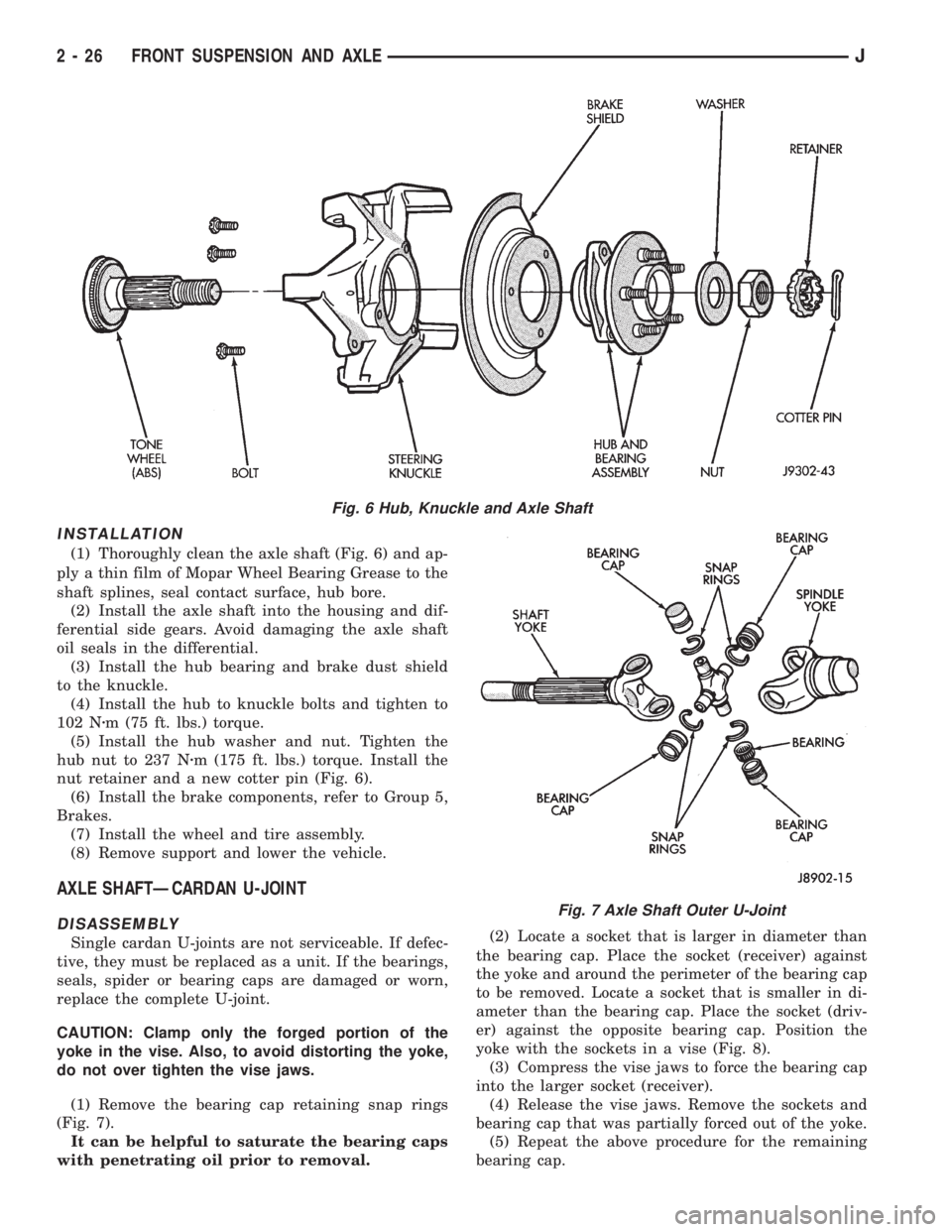
INSTALLATION
(1) Thoroughly clean the axle shaft (Fig. 6) and ap-
ply a thin film of Mopar Wheel Bearing Grease to the
shaft splines, seal contact surface, hub bore.
(2) Install the axle shaft into the housing and dif-
ferential side gears. Avoid damaging the axle shaft
oil seals in the differential.
(3) Install the hub bearing and brake dust shield
to the knuckle.
(4) Install the hub to knuckle bolts and tighten to
102 Nzm (75 ft. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install the hub washer and nut. Tighten the
hub nut to 237 Nzm (175 ft. lbs.) torque. Install the
nut retainer and a new cotter pin (Fig. 6).
(6) Install the brake components, refer to Group 5,
Brakes.
(7) Install the wheel and tire assembly.
(8) Remove support and lower the vehicle.
AXLE SHAFTÐCARDAN U-JOINT
DISASSEMBLY
Single cardan U-joints are not serviceable. If defec-
tive, they must be replaced as a unit. If the bearings,
seals, spider or bearing caps are damaged or worn,
replace the complete U-joint.
CAUTION: Clamp only the forged portion of the
yoke in the vise. Also, to avoid distorting the yoke,
do not over tighten the vise jaws.
(1) Remove the bearing cap retaining snap rings
(Fig. 7).
It can be helpful to saturate the bearing caps
with penetrating oil prior to removal.(2) Locate a socket that is larger in diameter than
the bearing cap. Place the socket (receiver) against
the yoke and around the perimeter of the bearing cap
to be removed. Locate a socket that is smaller in di-
ameter than the bearing cap. Place the socket (driv-
er) against the opposite bearing cap. Position the
yoke with the sockets in a vise (Fig. 8).
(3) Compress the vise jaws to force the bearing cap
into the larger socket (receiver).
(4) Release the vise jaws. Remove the sockets and
bearing cap that was partially forced out of the yoke.
(5) Repeat the above procedure for the remaining
bearing cap.
Fig. 6 Hub, Knuckle and Axle Shaft
Fig. 7 Axle Shaft Outer U-Joint
2 - 26 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 83 of 2158
SHIFT MOTORÐREMOVAL/DISASSEMBLY
(1) Disconnect the vacuum and wiring connector
from the shift housing.
(2) Remove indicator switch.
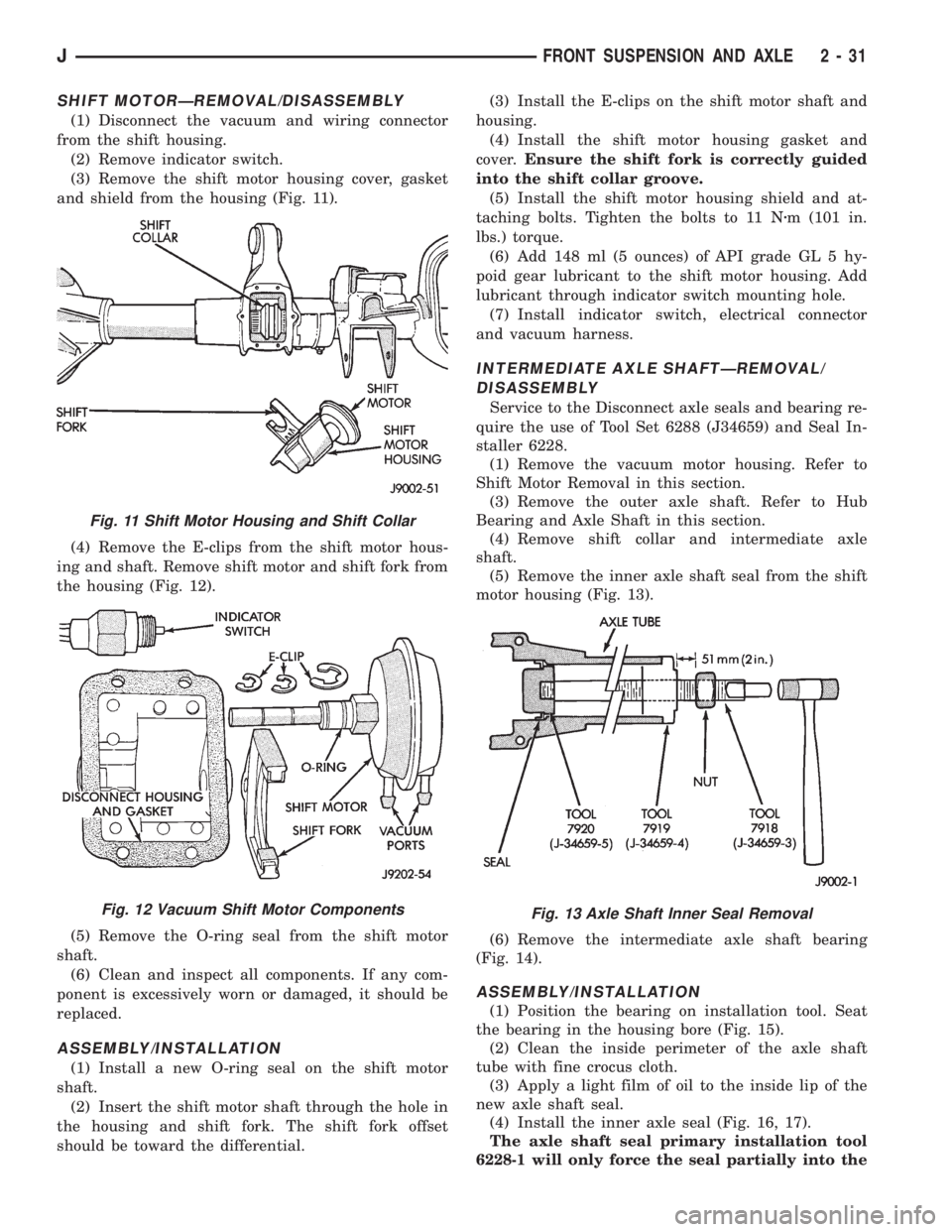
(3) Remove the shift motor housing cover, gasket
and shield from the housing (Fig. 11).
(4) Remove the E-clips from the shift motor hous-
ing and shaft. Remove shift motor and shift fork from
the housing (Fig. 12).
(5) Remove the O-ring seal from the shift motor
shaft.
(6) Clean and inspect all components. If any com-
ponent is excessively worn or damaged, it should be
replaced.
ASSEMBLY/INSTALLATION
(1) Install a new O-ring seal on the shift motor
shaft.
(2) Insert the shift motor shaft through the hole in
the housing and shift fork. The shift fork offset
should be toward the differential.(3) Install the E-clips on the shift motor shaft and
housing.
(4) Install the shift motor housing gasket and
cover.Ensure the shift fork is correctly guided
into the shift collar groove.
(5) Install the shift motor housing shield and at-
taching bolts. Tighten the bolts to 11 Nzm (101 in.
lbs.) torque.
(6) Add 148 ml (5 ounces) of API grade GL 5 hy-
poid gear lubricant to the shift motor housing. Add
lubricant through indicator switch mounting hole.
(7) Install indicator switch, electrical connector
and vacuum harness.
INTERMEDIATE AXLE SHAFTÐREMOVAL/
DISASSEMBLY
Service to the Disconnect axle seals and bearing re-
quire the use of Tool Set 6288 (J34659) and Seal In-
staller 6228.
(1) Remove the vacuum motor housing. Refer to
Shift Motor Removal in this section.
(3) Remove the outer axle shaft. Refer to Hub
Bearing and Axle Shaft in this section.
(4) Remove shift collar and intermediate axle
shaft.
(5) Remove the inner axle shaft seal from the shift
motor housing (Fig. 13).
(6) Remove the intermediate axle shaft bearing
(Fig. 14).
ASSEMBLY/INSTALLATION
(1) Position the bearing on installation tool. Seat
the bearing in the housing bore (Fig. 15).
(2) Clean the inside perimeter of the axle shaft
tube with fine crocus cloth.
(3) Apply a light film of oil to the inside lip of the
new axle shaft seal.
(4) Install the inner axle seal (Fig. 16, 17).
The axle shaft seal primary installation tool
6228-1 will only force the seal partially into the
Fig. 11 Shift Motor Housing and Shift Collar
Fig. 12 Vacuum Shift Motor ComponentsFig. 13 Axle Shaft Inner Seal Removal
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 31
Page 84 of 2158
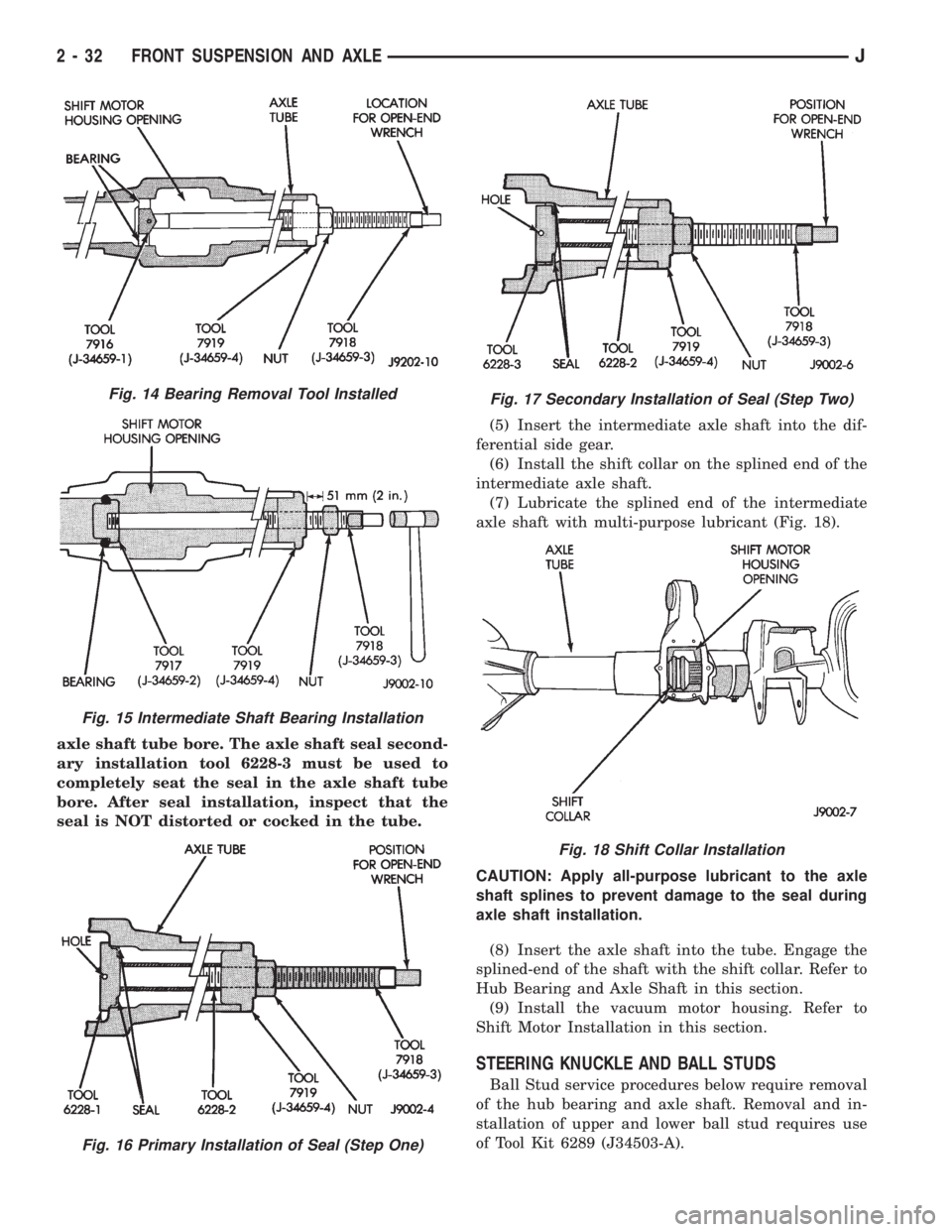
axle shaft tube bore. The axle shaft seal second-
ary installation tool 6228-3 must be used to
completely seat the seal in the axle shaft tube
bore. After seal installation, inspect that the
seal is NOT distorted or cocked in the tube.(5) Insert the intermediate axle shaft into the dif-
ferential side gear.
(6) Install the shift collar on the splined end of the
intermediate axle shaft.
(7) Lubricate the splined end of the intermediate
axle shaft with multi-purpose lubricant (Fig. 18).
CAUTION: Apply all-purpose lubricant to the axle
shaft splines to prevent damage to the seal during
axle shaft installation.
(8) Insert the axle shaft into the tube. Engage the
splined-end of the shaft with the shift collar. Refer to
Hub Bearing and Axle Shaft in this section.
(9) Install the vacuum motor housing. Refer to
Shift Motor Installation in this section.
STEERING KNUCKLE AND BALL STUDS
Ball Stud service procedures below require removal
of the hub bearing and axle shaft. Removal and in-
stallation of upper and lower ball stud requires use
of Tool Kit 6289 (J34503-A).
Fig. 14 Bearing Removal Tool Installed
Fig. 15 Intermediate Shaft Bearing Installation
Fig. 16 Primary Installation of Seal (Step One)
Fig. 17 Secondary Installation of Seal (Step Two)
Fig. 18 Shift Collar Installation
2 - 32 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 86 of 2158

(4) Install the Hub Bearing and Axle Shaft accord-
ing to the installation procedure.
(5) Reconnect the tie-rod or drag link end onto the
steering knuckle arm. Install the ABS sensor wire
and bracket to the knuckle, refer to Group 5 Brakes.
AXLE BUSHING REPLACEMENT
Refer to Axle Bushing Replacement in the Front
Suspension section.
DIFFERENTIAL REMOVAL
To service the differential the axle assembly and
axle shafts must be removed. Refer to the removal
procedures in this Group.
(1) Note the installation reference letters stamped
on the bearing caps and housing machined sealing
surface (Fig. 22).
(2) Remove the differential bearing caps.
(3) Position Spreader W-129-B with the tool dowel
pins seated in the locating holes (Fig. 23). Install the
holddown clamps and tighten the tool turnbuckle fin-
ger-tight.
(4) Install a pilot stud at the left side of the differ-
ential housing. Attach Dial Indicator to housing pilot
stud. Load the indicator plunger against the opposite
side of the housing (Fig. 23) and zero the indicator.CAUTION:Do not spread over 0.38 mm (0.015 in). If
the housing is over-separated, it could be distorted
or damaged.
(5) Separate the housing enough to remove the
case from the housing. Measure the distance with the
dial indicator (Fig. 23).
(6) Remove the dial indicator.
(7) Pry the differential case loose from the housing.
To prevent damage, pivot on housing with the end of
the pry bar against spreader (Fig. 24).
Fig. 21 Lower Ball Stud Remove/Install
Fig. 22 Bearing Cap Identification
2 - 34 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 91 of 2158
(5) Lubricate all differential components with hy-
poid gear lubricant.
PINION GEAR DEPTH INFORMATION
Ring and pinion gears are supplied as matched sets
only. The identifying numbers for the ring and pinion
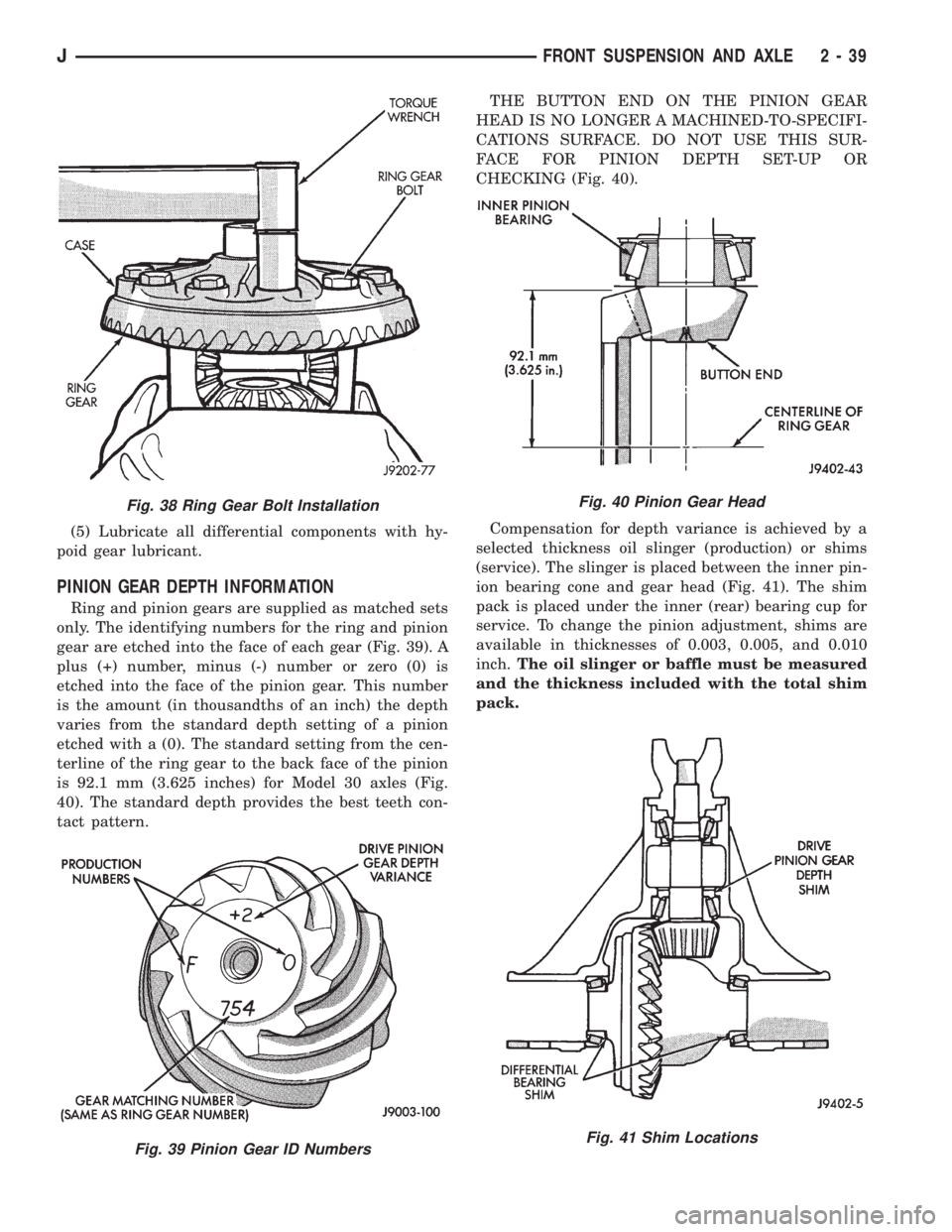
gear are etched into the face of each gear (Fig. 39). A
plus (+) number, minus (-) number or zero (0) is
etched into the face of the pinion gear. This number
is the amount (in thousandths of an inch) the depth
varies from the standard depth setting of a pinion
etched with a (0). The standard setting from the cen-
terline of the ring gear to the back face of the pinion
is 92.1 mm (3.625 inches) for Model 30 axles (Fig.
40). The standard depth provides the best teeth con-
tact pattern.THE BUTTON END ON THE PINION GEAR
HEAD IS NO LONGER A MACHINED-TO-SPECIFI-
CATIONS SURFACE. DO NOT USE THIS SUR-
FACE FOR PINION DEPTH SET-UP OR
CHECKING (Fig. 40).
Compensation for depth variance is achieved by a
selected thickness oil slinger (production) or shims
(service). The slinger is placed between the inner pin-
ion bearing cone and gear head (Fig. 41). The shim
pack is placed under the inner (rear) bearing cup for
service. To change the pinion adjustment, shims are
available in thicknesses of 0.003, 0.005, and 0.010
inch.The oil slinger or baffle must be measured
and the thickness included with the total shim
pack.
Fig. 38 Ring Gear Bolt Installation
Fig. 39 Pinion Gear ID Numbers
Fig. 40 Pinion Gear Head
Fig. 41 Shim Locations
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 39
Page 93 of 2158
²Axle housing or differential case is replaced
²Pinion select shim pack is unknown
²Ring and pinion gears are replaced
Measurements are done with pinion cups and pin-
ion bearings installed in housing. Take measure-
ments with Pinion Gauge Set 6774, Pinion Block
6733 and Dial Indicator C-3339 (Fig. 44).
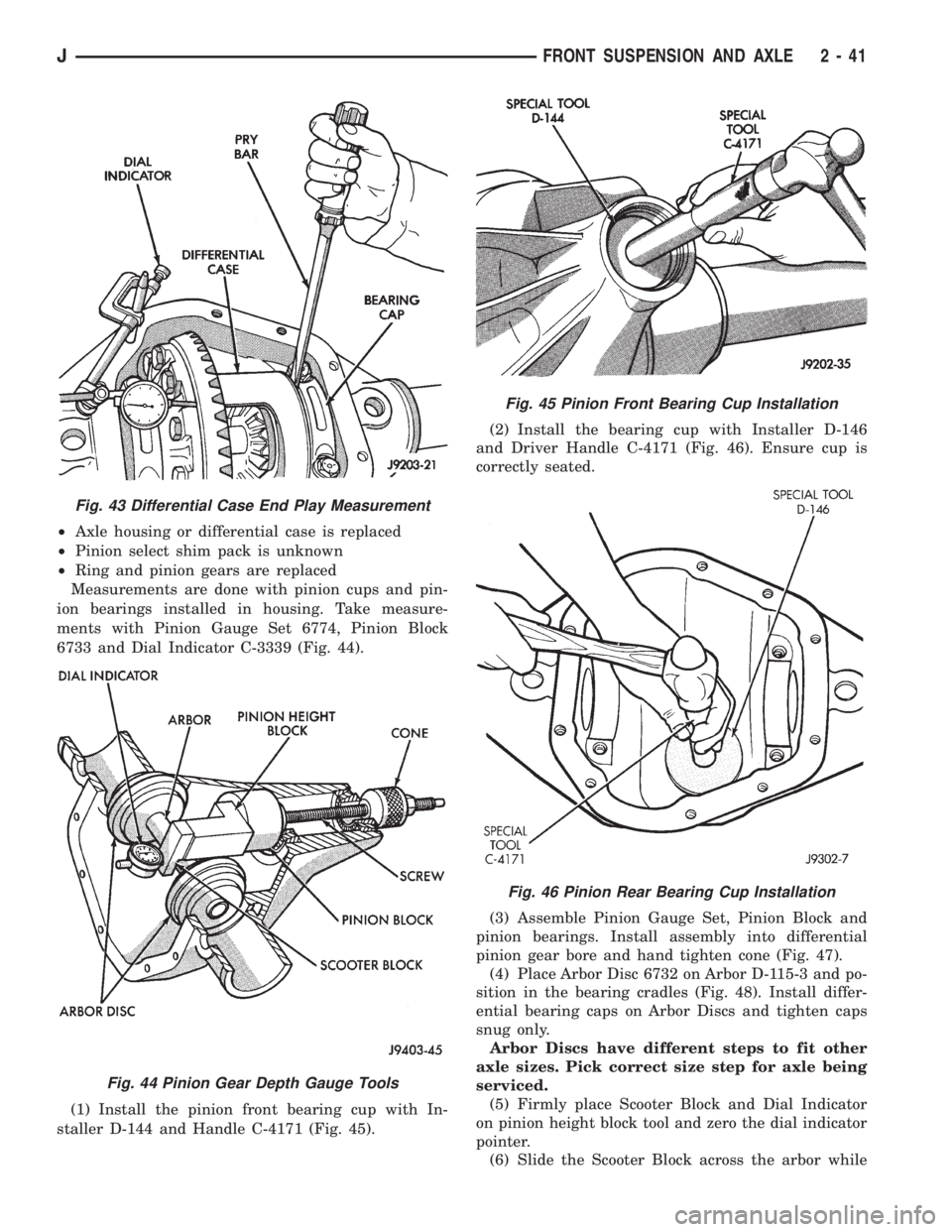
(1) Install the pinion front bearing cup with In-
staller D-144 and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 45).(2) Install the bearing cup with Installer D-146
and Driver Handle C-4171 (Fig. 46). Ensure cup is
correctly seated.
(3) Assemble Pinion Gauge Set, Pinion Block and
pinion bearings. Install assembly into differential
pinion gear bore and hand tighten cone (Fig. 47).
(4) Place Arbor Disc 6732 on Arbor D-115-3 and po-
sition in the bearing cradles (Fig. 48). Install differ-
ential bearing caps on Arbor Discs and tighten caps
snug only.
Arbor Discs have different steps to fit other
axle sizes. Pick correct size step for axle being
serviced.
(5) Firmly place Scooter Block and Dial Indicator
on pinion height block tool and zero the dial indicator
pointer.
(6) Slide the Scooter Block across the arbor while
Fig. 43 Differential Case End Play Measurement
Fig. 44 Pinion Gear Depth Gauge Tools
Fig. 45 Pinion Front Bearing Cup Installation
Fig. 46 Pinion Rear Bearing Cup Installation
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 41
Page 102 of 2158

REAR SUSPENSION AND AXLES
CONTENTS
page page
8 1/4 AXLE............................ 30
AXLE NOISE/VIBRATION DIAGNOSIS......... 9
AXLE SPECIFICATIONS................... 51
GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1
MODEL 35 AXLE........................ 13TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS................ 51
TRAC-LOK DIFFERENTIAL................. 45
XJ SUSPENSION......................... 3
YJ SUSPENSION......................... 6
GENERAL INFORMATION
SUSPENSION COMPONENTS
The Jeep rear suspension is comprised of;
²Drive axle
²Leaf springs
²Dual-action shock absorbers
²Track bar (YJ vehicles)
²Stabilizer bar (XJ vehicles)
²Jounce bumpers
The rear suspension design uses semi-elliptic
multi-leaf springs and a solid drive axle. The forward
end of the springs are mounted to the frame rail
hangers through rubber bushings. The bushings iso-
late road noise as the springs move. The rearward
end of the springs are attached to the frame by the
use of shackles. Again the spring and shackles use
rubber bushings to isolate road noise. The shackles
allow the springs to change their length as the vehi-
cle moves over various road conditions. The spring
and axle travel is limited through the use of bumpers
mounted on frame.
All suspension components that use bushings
should be tightened with the vehicle at normal ride
height. If the springs are not at normal ride position,
vehicle ride comfort could be affected. Rubber bush-
ings must never be lubricated.
The springs are attached to the axle pads with U-
bolts and plates. The springs use a center bolt that
holds the spring leafs in position. The bolt is also
used to locate the spring assembly to the axle pad.
Ride control is accomplished through the use of du-
al-action shock absorbers. The shocks dampen the
jounce and rebound as the vehicle travels over vari-
ous road conditions. The top of shock absorbers are
bolted to the frame bracket. The bottom of the shocks
are bolted to the axle bracket.
The stabilizer bar on the XJ is used to minimize
vehicle rear sway during turns. The bar helps the ve-
hicle maintain a flat attitude to the road surface. The
bar extends across the underside of the chassis and
connects to the frame rails. The links are connectedto the axle brackets. All mounting points of the sta-
bilizer bar are isolated by bushings.
The track bar on the YJ is used to minimize rear
axle side-to-side movement. The track bar is attached
to the frame rail bracket and axle bracket and is iso-
lated with bushings.
The jounce bumpers are used to limit the jounce
and rebound travel of the suspension.
AXLES
The Model 35 axle is standard for XJ and YJ vehi-
cles. The 8 1/4 axle is available in XJ vehicles with-
out ABS brakes.
The Model 35 and 8 1/4 axle housings has a cast
iron center section. Two steel axle shaft tubes are
pressed into the differential housing and welded.
It is not necessary to remove the axle from the ve-
hicle for service. A removable differential cover is
provided for routine vehicle service. If the differential
housing is damaged, the complete axle assembly can
be removed.
For complete drive axle assembly removal and in-
stallation refer to Drive Axle Assembly Replacement
in this Group.
IDENTIFICATION
Model 35 axle has the assembly part number and
gear ratio listed on a tag. The tag is attached to the left
side of the housing cover (Fig. 1). Build date identifica-
tion codes on axles are stamped on the axle shaft tube
cover side. The Model 35 axle has a flat housing cover
gasket flange at the outer edge (Fig. 1).
The 8 1/4 axle has the build date code and gear ra-
tio tags attached to the housing cover (Fig. 2). The
housing cover gasket has a rolled gasket flange at
the outer edge (Fig. 2).
²The Model 35 axle has shaft tubes that are 2.625
inch (66.67 mm) in diameter.
²The 8 1/4 axle has axle shaft tubes that are 3.0-
inch (76.2 mm) in diameter.
JREAR SUSPENSION AND AXLES 3 - 1
Page 110 of 2158

AXLE NOISE/VIBRATION DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
Driveline Snap........................... 10
Gear and Bearing Noise..................... 9
General Information........................ 9
Limited Slip Differential..................... 10Low Speed Knock......................... 10
Rear Axle Alignment....................... 10
Vibration................................ 10
GENERAL INFORMATION
Axle bearing problem conditions are usually caused
by:
²Insufficient or incorrect lubricant
²Foreign matter/water contamination
²Incorrect bearing preload torque adjustment
²Incorrect backlash (to tight)
When serviced, the bearings must be cleaned thor-
oughly. They should be dried with lint-free shop tow-
els.Never dry bearings with compressed air.
This will overheat them and brinell the bearing
surfaces. This will result in noisy operation af-
ter repair.
Axle gear problem conditions are usually the result of:
²Insufficient lubrication
²Incorrect or contaminated lubricant
²Overloading (excessive engine torque) or exceeding
vehicle weight capacity
²Incorrect clearance or backlash adjustment
Insufficient lubrication is usually the result of a
housing cover leak. It can also be from worn axle
shaft or pinion gear seals. Check for cracks or porous
areas in the housing or tubes.
Using the wrong lubricant will cause overheating
and gear failure. Gear tooth cracking and bearing
spalling are indicators of this.
Axle component breakage is most often the result of:
²Severe overloading
²Insufficient lubricant
²Incorrect lubricant
²Improperly tightened components
Overloading occurs when towing heavier than rec-
ommended loads. Component breakage can occur
when the wheels are spun excessively. Incorrect lu-
bricant quantity contributes to breakage. Loose dif-
ferential components can also cause breakage.
Incorrect bearing preload or gear backlash will not
result in component breakage. Mis-adjustment will
produce enough noise to cause service repair before a
failure occurs. If a mis-adjustment condition is not
corrected, component failure can result.
Excessive bearing preload may not be noisy. This
condition will cause high temperature which can re-
sult in bearing failure.
GEAR AND BEARING NOISE
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant. Incorrect backlash, tooth contact, or worn/dam-
aged gears can cause noise.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The range is 30 to 40 mph, or above 50 mph.
The noise can also occur during a specific type of
driving condition. These conditions are acceleration,
deceleration, coast, or constant load.
When road testing, accelerate the vehicle to the
speed range where the noise is the greatest. Shift
out-of-gear and coast through the peak-noise range.
If the noise stops or changes greatly, check for insuf-
ficient lubricant. Incorrect ring gear backlash, or
gear damage can cause noise changes.
Differential side and pinion gears can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise in straight-ahead driving. These gears are
loaded during vehicle turns. If noise does occur dur-
ing vehicle turns, the side or pinion gears could be
worn or damaged. A worn pinion gear mate shaft can
also cause a snapping or a knocking noise.
BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion gear bear-
ings can all produce noise when worn or damaged.
Bearing noise can be either a whining, or a growling
sound.
Pinion gear bearings have a constant-pitch noise.
This noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion
bearing noise will be higher because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs the pinion rear bearing is
the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is heard
during a coast, front bearing is the source.
Worn, damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing. The pitch of differential
bearing noise is also constant and varies only with
vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
JREAR SUSPENSION AND AXLES 3 - 9