1995 JEEP CHEROKEE transmission
[x] Cancel search: transmissionPage 300 of 2198
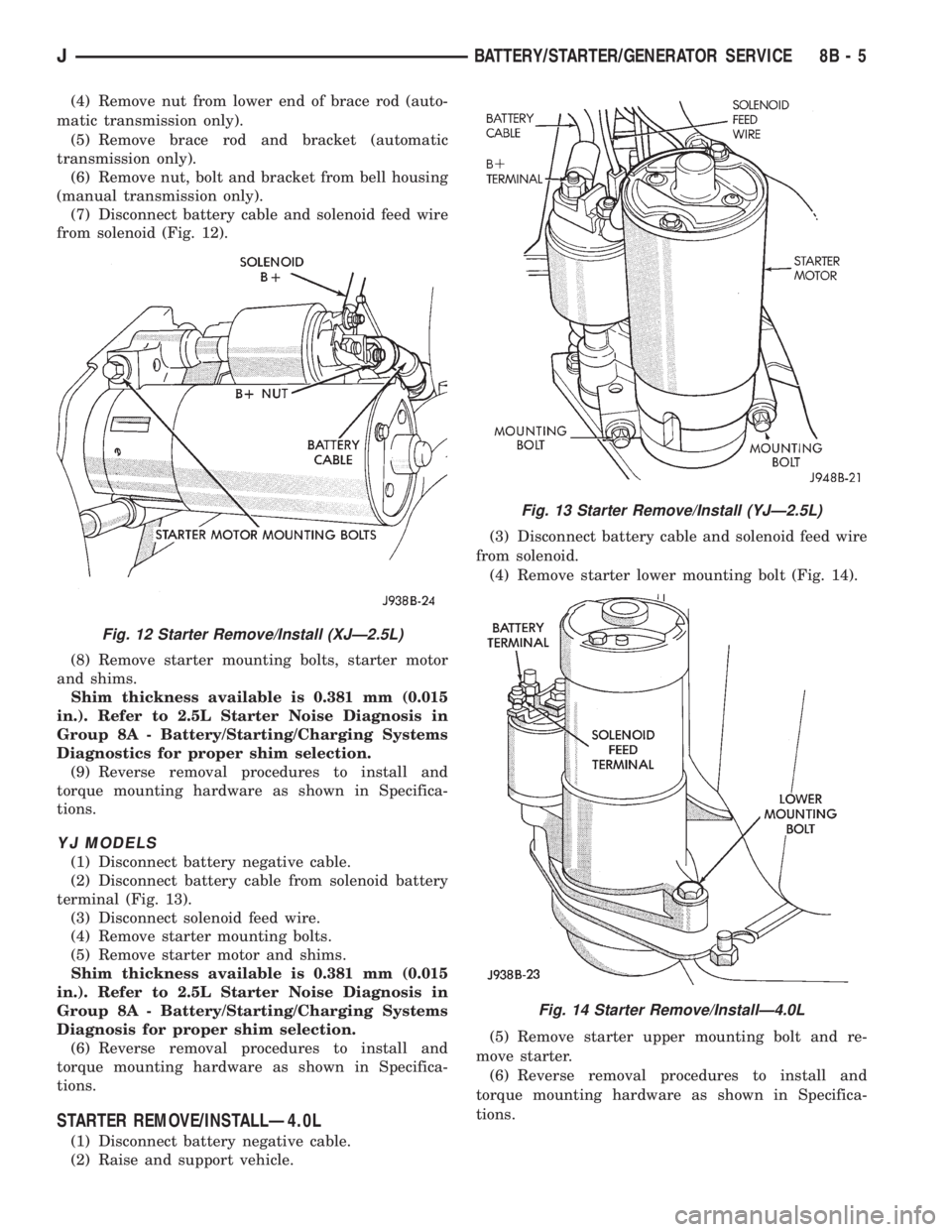
(4) Remove nut from lower end of brace rod (auto-
matic transmission only).
(5) Remove brace rod and bracket (automatic
transmission only).
(6) Remove nut, bolt and bracket from bell housing
(manual transmission only).
(7) Disconnect battery cable and solenoid feed wire
from solenoid (Fig. 12).
(8) Remove starter mounting bolts, starter motor
and shims.
Shim thickness available is 0.381 mm (0.015
in.). Refer to 2.5L Starter Noise Diagnosis in
Group 8A - Battery/Starting/Charging Systems
Diagnostics for proper shim selection.
(9) Reverse removal procedures to install and
torque mounting hardware as shown in Specifica-
tions.
YJ MODELS
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Disconnect battery cable from solenoid battery
terminal (Fig. 13).
(3) Disconnect solenoid feed wire.
(4) Remove starter mounting bolts.
(5) Remove starter motor and shims.
Shim thickness available is 0.381 mm (0.015
in.). Refer to 2.5L Starter Noise Diagnosis in
Group 8A - Battery/Starting/Charging Systems
Diagnosis for proper shim selection.
(6) Reverse removal procedures to install and
torque mounting hardware as shown in Specifica-
tions.
STARTER REMOVE/INSTALLÐ4.0L
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Raise and support vehicle.(3) Disconnect battery cable and solenoid feed wire
from solenoid.
(4) Remove starter lower mounting bolt (Fig. 14).
(5) Remove starter upper mounting bolt and re-
move starter.
(6) Reverse removal procedures to install and
torque mounting hardware as shown in Specifica-
tions.
Fig. 12 Starter Remove/Install (XJÐ2.5L)
Fig. 13 Starter Remove/Install (YJÐ2.5L)
Fig. 14 Starter Remove/InstallÐ4.0L
JBATTERY/STARTER/GENERATOR SERVICE 8B - 5
Page 314 of 2198
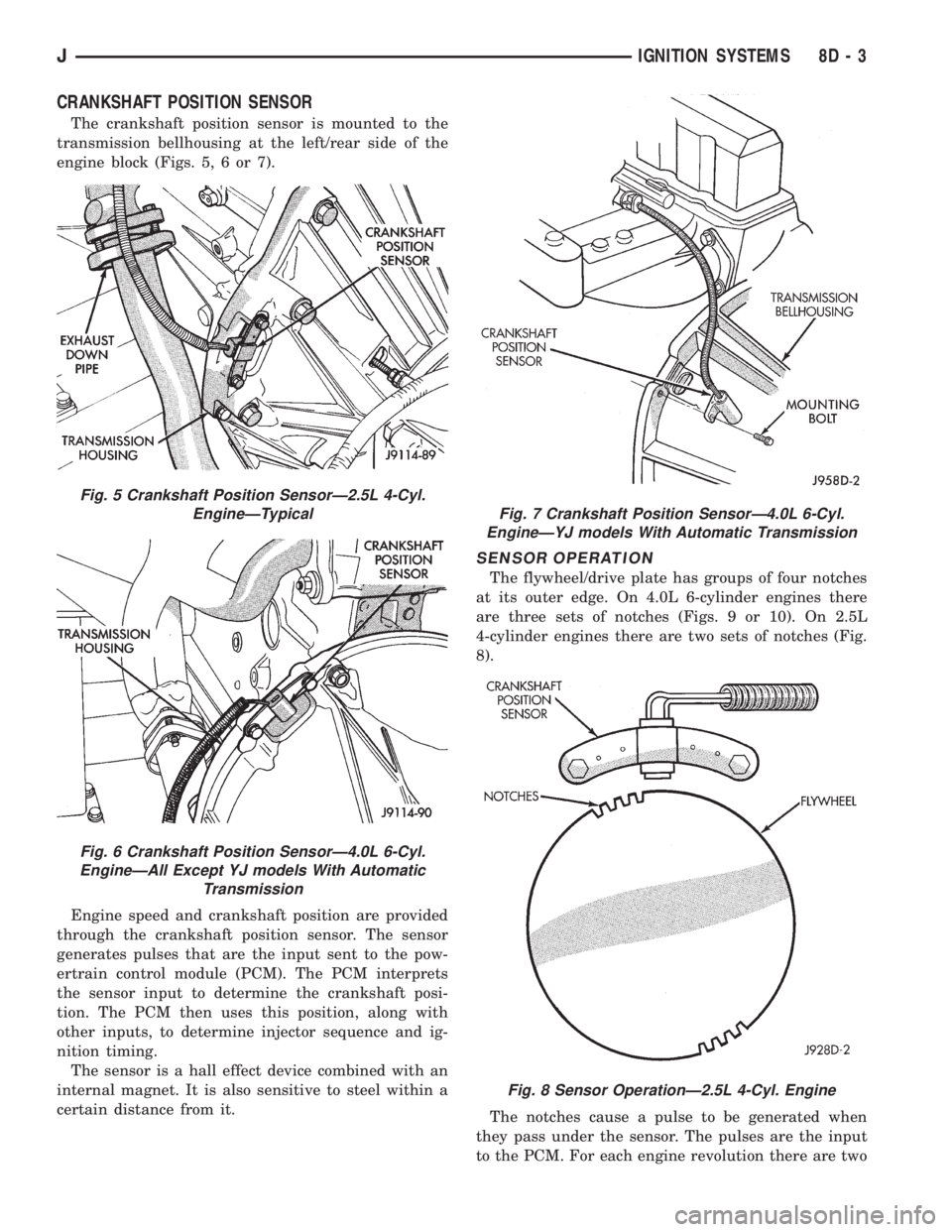
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The crankshaft position sensor is mounted to the
transmission bellhousing at the left/rear side of the
engine block (Figs. 5, 6 or 7).
Engine speed and crankshaft position are provided
through the crankshaft position sensor. The sensor
generates pulses that are the input sent to the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM). The PCM interprets
the sensor input to determine the crankshaft posi-
tion. The PCM then uses this position, along with
other inputs, to determine injector sequence and ig-
nition timing.
The sensor is a hall effect device combined with an
internal magnet. It is also sensitive to steel within a
certain distance from it.
SENSOR OPERATION
The flywheel/drive plate has groups of four notches
at its outer edge. On 4.0L 6-cylinder engines there
are three sets of notches (Figs. 9 or 10). On 2.5L
4-cylinder engines there are two sets of notches (Fig.
8).
The notches cause a pulse to be generated when
they pass under the sensor. The pulses are the input
to the PCM. For each engine revolution there are two
Fig. 5 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ2.5L 4-Cyl.
EngineÐTypical
Fig. 6 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ4.0L 6-Cyl.
EngineÐAll Except YJ models With Automatic
Transmission
Fig. 7 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ4.0L 6-Cyl.
EngineÐYJ models With Automatic Transmission
Fig. 8 Sensor OperationÐ2.5L 4-Cyl. Engine
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 3
Page 315 of 2198

groups of four pulses generated on 2.5L 4-cylinder
engines. There are 3 groups of four pulses generated
on 4.0L 6-cylinder engines.
The trailing edge of the fourth notch, which causes
the pulse, is four degrees before top dead center
(TDC) of the corresponding piston.
The engine will not operate if the PCM does not re-
ceive a crankshaft position sensor input.
For component testing, refer to the Diagnostics/Ser-
vice Procedures section of this group.
For removal and installation of this sensor, refer to
the Component Removal/Installation section of this
group.
DISTRIBUTORS
All engines are equipped with a camshaft driven
mechanical distributor containing a shaft driven dis-
tributor rotor. All distributors are equipped with an
internal camshaft position (fuel sync) sensor. This
sensor provides fuel injection synchronization and
cylinder identification.
The distributors on both the 2.5L 4-cylinder and
the 4.0L-6 cylinder engines do not have built in cen-
trifugal or vacuum assisted advance. Base ignition
timing and all timing advance is controlled by the
powertrain control module (PCM). Because ignition
timing is controlled by the PCM,base ignition tim-
ing is not adjustable on any of these engines.
The distributor is locked in place by a fork with a
slot located on the distributor housing base. The dis-
tributor holddown clamp bolt passes through this slot
when installed. Because the distributor position is
locked when installed, its rotational position can not
be changed.Do not attempt to modify the dis-tributor housing to get distributor rotation.
Distributor position will have no effect on igni-
tion timing. The position of the distributor will
determine fuel synchronization only.
All distributors contain an internal oil seal that
prevents oil from entering the distributor housing.
The seal is not serviceable.
Distributor removal and installation procedures
have changed for the 1995 model year. Refer to Dis-
tributor in the Component Removal/Installation sec-
tion of this group.
IGNITION COIL
Battery voltage is supplied to the ignition coil pos-
itive terminal from the ASD relay.
The powertrain control module (PCM) opens and
closes the ignition coil ground circuit for ignition coil
operation. This is done through pin/cavity number 19
of the PCM 60-way connector.
Base ignition timing is not adjustable.By con-
trolling the coil ground circuit, the PCM is able to set
the base timing and adjust the ignition timing ad-
vance. This is done to meet changing engine operat-
ing conditions.
The ignition coil is not oil filled. The windings are
embedded in an epoxy compound. This provides heat
and vibration resistance that allows the ignition coil
to be mounted on the engine.
On the 2.5L 4-cylinder engine, the ignition coil is
mounted to a bracket on the side of the engine (to
the rear of the distributor).
Fig. 9 Sensor OperationÐ4.0L 6-Cyl. EngineÐAll
Except YJ Models With Automatic Transmission
Fig. 10 Sensor OperationÐ4.0L 6-Cyl. EngineÐYJ
Models With Automatic Transmission
8D - 4 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 318 of 2198

(8) If voltage is not present at supply wire, check
for voltage at pin-7 of powertrain control module
(PCM) 60-way connector. Leave the PCM connector
connected for this test.
(9) If voltage is still not present, perform vehicle
test using the DRB scan tool.
(10) If voltage is present at pin-7, but not at the
supply wire:
(a) Check continuity between the supply wire.
This is checked between the distributor connector
and pin-7 at the PCM. If continuity is not present,
repair the harness as necessary.
(b) Check for continuity between the camshaft
position sensor output wire and pin-44 at the PCM.
If continuity is not present, repair the harness as
necessary.
(c) Check for continuity between the ground cir-
cuit wire at the distributor connector and ground.
If continuity is not present, repair the harness as
necessary.
(11) While observing the voltmeter, crank the en-
gine with ignition switch. The voltmeter needle
should fluctuate between 0 and 5 volts while the en-
gine is cranking. This verifies that the camshaft po-
sition sensor in the distributor is operating properly
and a sync pulse signal is being generated.
If sync pulse signal is not present, replacement of
the camshaft position sensor is necessary.
For removal or installation of ignition system com-
ponents, refer to the Component Removal/Installa-
tion section of this group.
For system operation and component identification,
refer to the Component Identification/System Opera-
tion section of this group.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR TEST
To perform a complete test of this sensor and its
circuitry, refer to the DRB scan tool. Also refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures man-
ual. To test the sensor only, refer to the following:
The sensor is located on the transmission bellhous-
ing at the left/rear side of the engine block (Figs. 2, 3
or 4).
(1) Near the rear of the intake manifold, discon-
nect sensor pigtail harness connector from main wir-
ing harness.
(2) Place an ohmmeter across terminals B and C
(Fig. 5). Ohmmeter should be set to 1K-to-10K scale
for this test. The meter reading should be open (no
resistance). Replace sensor if a low resistance is indi-
cated.
For removal or installation of ignition system com-
ponents, refer to the Component Removal/Installa-
tion section of this group.DISTRIBUTOR CAP
INSPECTION
Remove the distributor cap and wipe it clean with
a dry lint free cloth. Visually inspect the cap for
cracks, carbon paths, broken towers, or damaged ro-
tor button (Figs. 6 and 7). Also check for white depos-
its on the inside (caused by condensation entering
the cap through cracks). Replace any cap that dis-
plays charred or eroded terminals. The inside flat
surface of a terminal end (faces toward rotor) will in-
dicate some evidence of erosion from normal opera-
tion. Examine the terminal ends for evidence of
mechanical interference with the rotor tip.
If replacement of the distributor cap is necessary,
transfer spark plug cables from the original cap to
the new cap. This should be done one cable at a time.
Each cable is installed onto the tower of the new cap
that corresponds to its tower position on the original
Fig. 2 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ2.5L 4-Cyl.
EngineÐTypical
Fig. 3 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ4.0L 6-Cyl.
EngineÐAll Except YJ models With Auto. Trans.
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 7
Page 329 of 2198
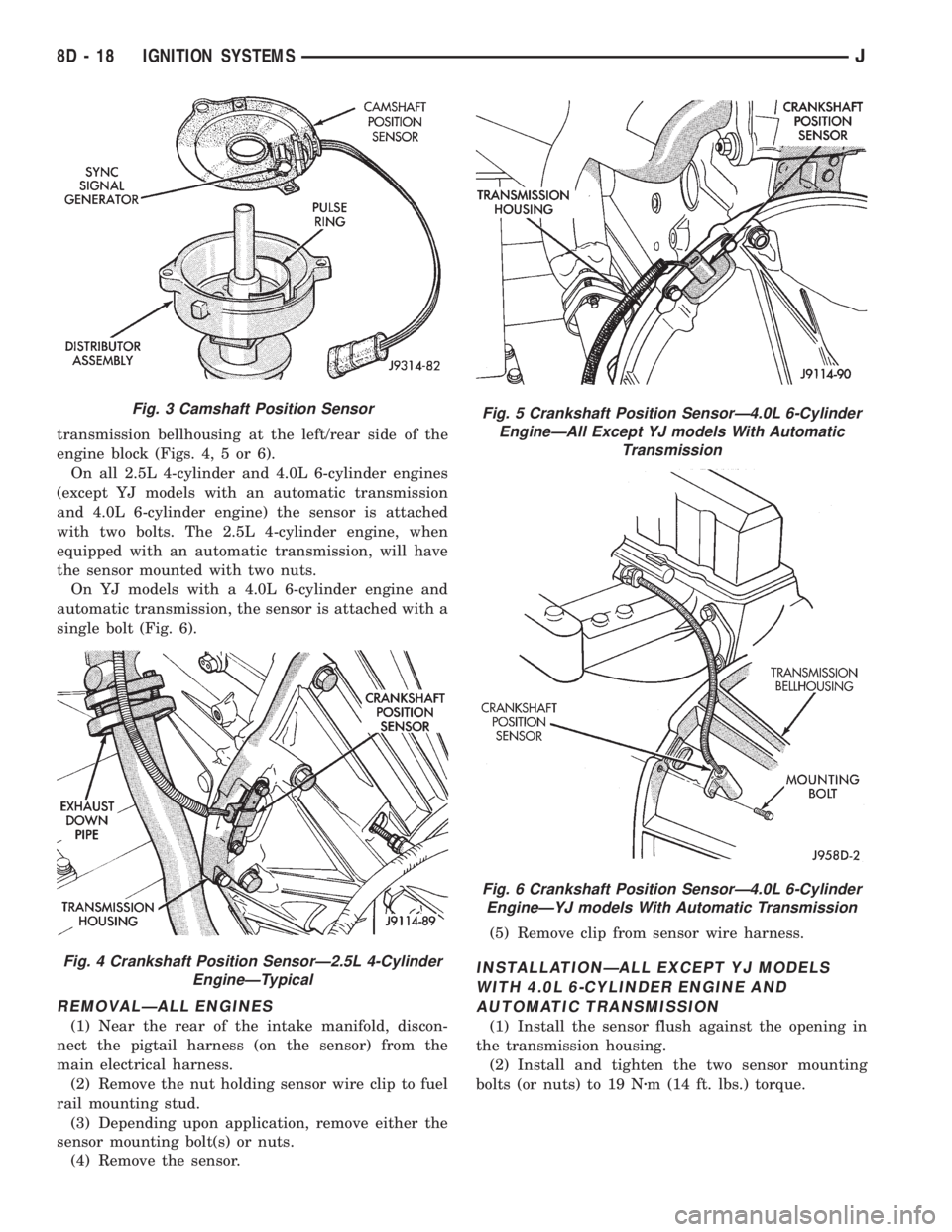
transmission bellhousing at the left/rear side of the
engine block (Figs. 4, 5 or 6).
On all 2.5L 4-cylinder and 4.0L 6-cylinder engines
(except YJ models with an automatic transmission
and 4.0L 6-cylinder engine) the sensor is attached
with two bolts. The 2.5L 4-cylinder engine, when
equipped with an automatic transmission, will have
the sensor mounted with two nuts.
On YJ models with a 4.0L 6-cylinder engine and
automatic transmission, the sensor is attached with a
single bolt (Fig. 6).
REMOVALÐALL ENGINES
(1) Near the rear of the intake manifold, discon-
nect the pigtail harness (on the sensor) from the
main electrical harness.
(2) Remove the nut holding sensor wire clip to fuel
rail mounting stud.
(3) Depending upon application, remove either the
sensor mounting bolt(s) or nuts.
(4) Remove the sensor.(5) Remove clip from sensor wire harness.
INSTALLATIONÐALL EXCEPT YJ MODELS
WITH 4.0L 6-CYLINDER ENGINE AND
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
(1) Install the sensor flush against the opening in
the transmission housing.
(2) Install and tighten the two sensor mounting
bolts (or nuts) to 19 Nzm (14 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 3 Camshaft Position Sensor
Fig. 4 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ2.5L 4-Cylinder
EngineÐTypical
Fig. 5 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ4.0L 6-Cylinder
EngineÐAll Except YJ models With Automatic
Transmission
Fig. 6 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ4.0L 6-Cylinder
EngineÐYJ models With Automatic Transmission
8D - 18 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 330 of 2198
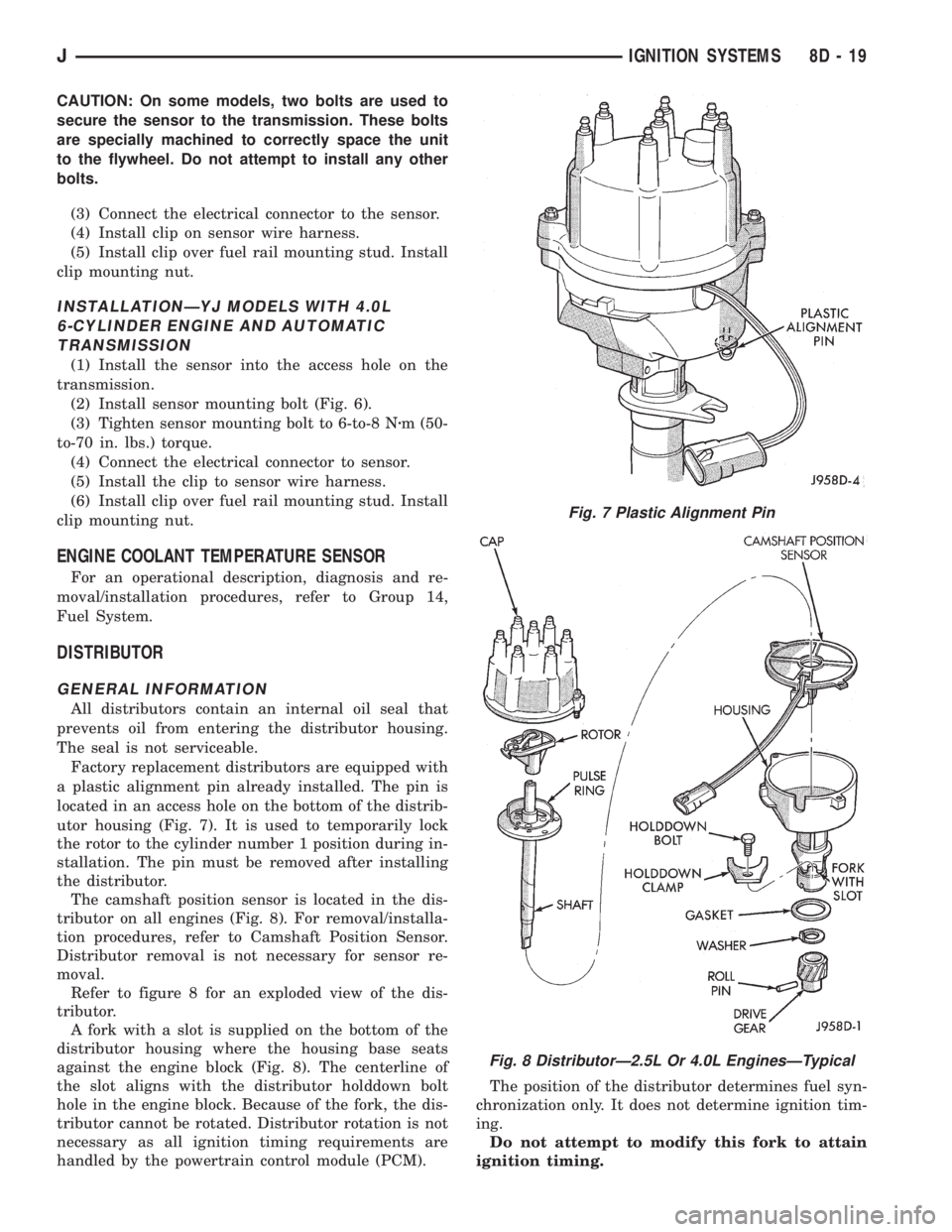
CAUTION: On some models, two bolts are used to
secure the sensor to the transmission. These bolts
are specially machined to correctly space the unit
to the flywheel. Do not attempt to install any other
bolts.
(3) Connect the electrical connector to the sensor.
(4) Install clip on sensor wire harness.
(5) Install clip over fuel rail mounting stud. Install
clip mounting nut.
INSTALLATIONÐYJ MODELS WITH 4.0L
6-CYLINDER ENGINE AND AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
(1) Install the sensor into the access hole on the
transmission.
(2) Install sensor mounting bolt (Fig. 6).
(3) Tighten sensor mounting bolt to 6-to-8 Nzm (50-
to-70 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect the electrical connector to sensor.
(5) Install the clip to sensor wire harness.
(6) Install clip over fuel rail mounting stud. Install
clip mounting nut.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
For an operational description, diagnosis and re-
moval/installation procedures, refer to Group 14,
Fuel System.
DISTRIBUTOR
GENERAL INFORMATION
All distributors contain an internal oil seal that
prevents oil from entering the distributor housing.
The seal is not serviceable.
Factory replacement distributors are equipped with
a plastic alignment pin already installed. The pin is
located in an access hole on the bottom of the distrib-
utor housing (Fig. 7). It is used to temporarily lock
the rotor to the cylinder number 1 position during in-
stallation. The pin must be removed after installing
the distributor.
The camshaft position sensor is located in the dis-
tributor on all engines (Fig. 8). For removal/installa-
tion procedures, refer to Camshaft Position Sensor.
Distributor removal is not necessary for sensor re-
moval.
Refer to figure 8 for an exploded view of the dis-
tributor.
A fork with a slot is supplied on the bottom of the
distributor housing where the housing base seats
against the engine block (Fig. 8). The centerline of
the slot aligns with the distributor holddown bolt
hole in the engine block. Because of the fork, the dis-
tributor cannot be rotated. Distributor rotation is not
necessary as all ignition timing requirements are
handled by the powertrain control module (PCM).The position of the distributor determines fuel syn-
chronization only. It does not determine ignition tim-
ing.
Do not attempt to modify this fork to attain
ignition timing.
Fig. 7 Plastic Alignment Pin
Fig. 8 DistributorÐ2.5L Or 4.0L EnginesÐTypical
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 19
Page 338 of 2198
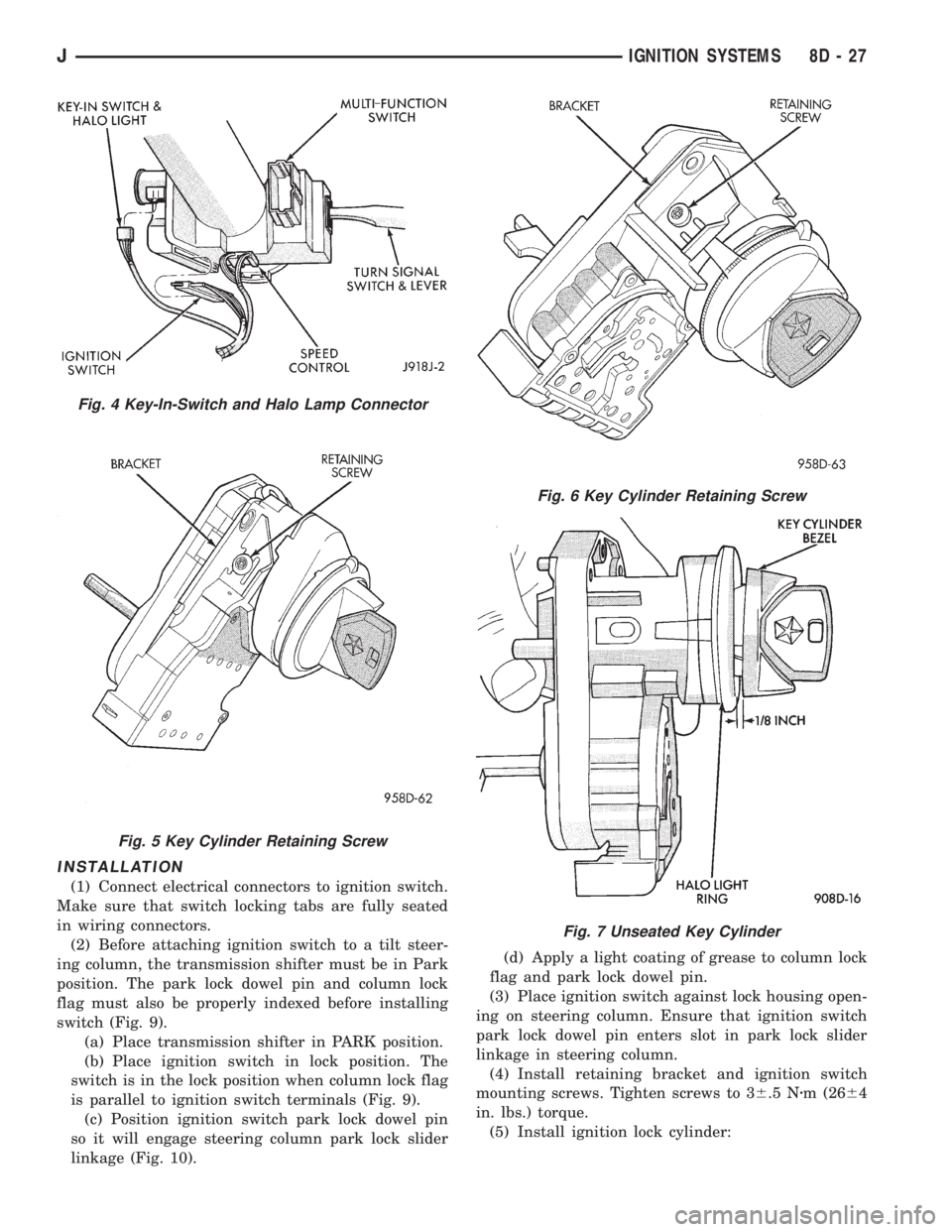
INSTALLATION
(1) Connect electrical connectors to ignition switch.
Make sure that switch locking tabs are fully seated
in wiring connectors.
(2) Before attaching ignition switch to a tilt steer-
ing column, the transmission shifter must be in Park
position. The park lock dowel pin and column lock
flag must also be properly indexed before installing
switch (Fig. 9).
(a) Place transmission shifter in PARK position.
(b) Place ignition switch in lock position. The
switch is in the lock position when column lock flag
is parallel to ignition switch terminals (Fig. 9).
(c) Position ignition switch park lock dowel pin
so it will engage steering column park lock slider
linkage (Fig. 10).(d) Apply a light coating of grease to column lock
flag and park lock dowel pin.
(3) Place ignition switch against lock housing open-
ing on steering column. Ensure that ignition switch
park lock dowel pin enters slot in park lock slider
linkage in steering column.
(4) Install retaining bracket and ignition switch
mounting screws. Tighten screws to 36.5 Nzm (2664
in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install ignition lock cylinder:
Fig. 4 Key-In-Switch and Halo Lamp Connector
Fig. 5 Key Cylinder Retaining Screw
Fig. 6 Key Cylinder Retaining Screw
Fig. 7 Unseated Key Cylinder
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 27
Page 345 of 2198

The high-line cluster includes the following gauges:
²coolant temperature gauge
²fuel gauge
²oil pressure gauge
²speedometer/odometer
²tachometer
²trip odometer
²voltmeter.
The high-line cluster includes provisions for the fol-
lowing indicator lamps:
²anti-lock brake system lamp
²brake warning lamp
²four-wheel drive indicator lamps
²headlamp high beam indicator lamp
²low fuel warning lamp
²low washer fluid warning lamp
²malfunction indicator (Check Engine) lamp
²seat belt reminder lamp
²turn signal indicator lamps
²upshift indicator lamp.
GAUGES
With the ignition switch in the ON or START posi-
tion, voltage is supplied to all gauges through the in-
strument cluster gauge area printed circuit. With the
ignition switch in the OFF position, voltage is not
supplied to the gauges. A gauge pointer may remain
within the gauge scale after the ignition switch is
OFF. However, the gauges do not accurately indicate
any vehicle condition unless the ignition switch is
ON.
All gauges except the odometer are air core mag-
netic units. Two fixed electromagnetic coils are lo-
cated within the gauge. These coils are wrapped at
right angles to each other around a movable perma-
nent magnet. The movable magnet is suspended
within the coils on one end of a shaft. The gauge nee-
dle is attached to the other end of the shaft.
One of the coils has a fixed current flowing through
it to maintain a constant magnetic field strength.
Current flow through the second coil changes, which
causes changes in its magnetic field strength. The
current flowing through the second coil can be
changed by:
²a variable resistor-type sending unit (fuel level,
coolant temperature, or oil pressure)
²changes in electrical system voltage (voltmeter)
²electronic control circuitry (speedometer/odometer,
tachometer).
The gauge needle moves as the movable permanent
magnet aligns itself to the changing magnetic fields
created around it by the electromagnets.
COOLANT TEMPERATURE GAUGE
The coolant temperature gauge gives an indication
of engine coolant temperature. The coolant tempera-
ture sending unit is a thermistor that changes elec-
trical resistance with changes in engine coolanttemperature. High sending unit resistance causes
low coolant temperature readings. Low resistance
causes high coolant temperature readings.
The gauge will read at the high end of the scale
when the ignition switch is turned to the START po-
sition. This is caused by the bulb test circuit wiring
provision. The same wiring is used for the high-line
cluster with a coolant temperature gauge and the
low-line cluster with a coolant temperature warning
lamp. Sending unit resistance values are shown in a
chart in Specifications.
FUEL GAUGE
The fuel gauge gives an indication of the level of
fuel in the fuel tank. The fuel gauge sending unit has
a float attached to a swing-arm in the fuel tank. The
float moves up or down within the fuel tank as fuel
level changes. As the float moves, an electrical con-
tact on the swing-arm wipes across a resistor coil,
which changes sending unit resistance. High sending
unit resistance causes low fuel level readings. Low
resistance causes high fuel level readings. Sending
unit resistance values are shown in a chart in Spec-
ifications.
OIL PRESSURE GAUGE
The oil pressure gauge gives an indication of en-
gine oil pressure. The combination oil pressure send-
ing unit contains a flexible diaphragm. The
diaphragm moves in response to changes in engine
oil pressure. As the diaphragm moves, sending unit
resistance increases or decreases. High resistance on
the gauge side of the sending unit causes high oil
pressure readings. Low resistance causes low oil
pressure readings. Sending unit resistance values are
shown in a chart in Specifications.
SPEEDOMETER/ODOMETER
The speedometer/odometer gives an indication of
vehicle speed and travel distance. The speedometer
receives a vehicle speed pulse signal from the Vehicle
Speed Sensor (VSS). An electronic integrated circuit
contained within the speedometer reads and analyzes
the pulse signal. It then adjusts the ground path re-
sistance of one electromagnet in the gauge to control
needle movement. It also sends signals to an electric
stepper motor to control movement of the odometer
number rolls. Frequency values for the pulse signal
are shown in a chart in Specifications.
The VSS is mounted to an adapter near the trans-
mission (two-wheel drive) or transfer case (four-wheel
drive) output shaft. The sensor is driven through the
adapter by a speedometer pinion gear. The adapter
and pinion vary with transmission, transfer case,
axle ratio and tire size. Refer to Group 21 - Trans-
mission and Transfer Case for more information.
8E - 2 INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐXJJ