1994 JEEP CHEROKEE air filter
[x] Cancel search: air filterPage 23 of 1784

DRIVETRAIN
INDEX
page page
Automatic Transmission.................... 23
Drive Shafts............................ 27
Front and Rear Axles..................... 26
Hydraulic Clutch......................... 22Manual Transmission...................... 22
Rubber and Plastic Hoses/Tubing............ 28
Transfer Case........................... 25
HYDRAULIC CLUTCH
RECOMMENDED MAINTENANCE
Check fluid level in the hydraulic clutch master
cylinder reservoir (Fig. 1) at the same time engine
oil is changed and oil filter is replaced. Add fluid as
necessary.
FLUID SPECIFICATION
The only fluid recommended for use in a hydraulic
clutch system is MOPAR Brake And Hydraulic
Clutch Fluid., or an equivalent fluid.
CAUTION: Never use reclaimed brake fluid or fluid
from an unsealed container. In addition, do not use
fluid from a container that has been opened and al-
lowed to stand for an extended length of time.
Moisture in the air can be absorbed by the fluid,
which causes dilution with loss of effectiveness.
FLUID LEVEL
Remove the master cylinder fluid reservoir cap
(Fig. 2). The fluid level is determined by its height inrelation to the level indicator ring (Fig. 3) located in-
side the reservoir. If necessary, add fluid until the
height is level with the indicator ring.
MANUAL TRANSMISSION
RECOMMENDED MAINTENANCE
The lube oil level in manual transmissions should
be determined at the same time as the engine oil is
changed and the oil filter is replaced. Add lube oil as
necessary.
Fig. 1 Hydraulic Clutch (YJ)ÐTypical
Fig. 2 Hydraulic Clutch Master Cylinder Fluid
Reservoir
Fig. 3 Hydraulic Clutch Fluid Level
0 - 22 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEJ
Page 33 of 1784
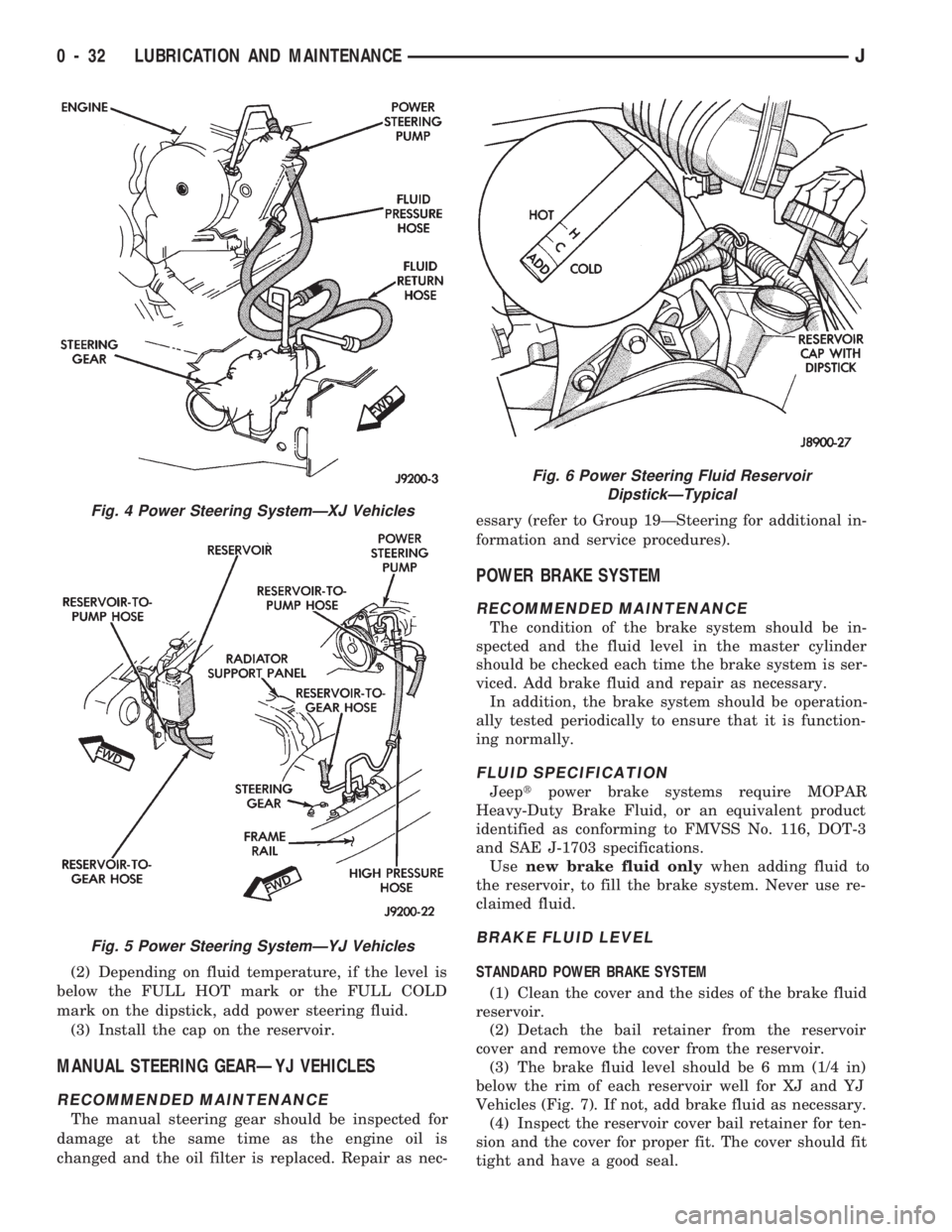
(2) Depending on fluid temperature, if the level is
below the FULL HOT mark or the FULL COLD
mark on the dipstick, add power steering fluid.
(3) Install the cap on the reservoir.
MANUAL STEERING GEARÐYJ VEHICLES
RECOMMENDED MAINTENANCE
The manual steering gear should be inspected for
damage at the same time as the engine oil is
changed and the oil filter is replaced. Repair as nec-essary (refer to Group 19ÐSteering for additional in-
formation and service procedures).
POWER BRAKE SYSTEM
RECOMMENDED MAINTENANCE
The condition of the brake system should be in-
spected and the fluid level in the master cylinder
should be checked each time the brake system is ser-
viced. Add brake fluid and repair as necessary.
In addition, the brake system should be operation-
ally tested periodically to ensure that it is function-
ing normally.
FLUID SPECIFICATION
Jeeptpower brake systems require MOPAR
Heavy-Duty Brake Fluid, or an equivalent product
identified as conforming to FMVSS No. 116, DOT-3
and SAE J-1703 specifications.
Usenew brake fluid onlywhen adding fluid to
the reservoir, to fill the brake system. Never use re-
claimed fluid.
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
STANDARD POWER BRAKE SYSTEM
(1) Clean the cover and the sides of the brake fluid
reservoir.
(2) Detach the bail retainer from the reservoir
cover and remove the cover from the reservoir.
(3) The brake fluid level should be 6 mm (1/4 in)
below the rim of each reservoir well for XJ and YJ
Vehicles (Fig. 7). If not, add brake fluid as necessary.
(4) Inspect the reservoir cover bail retainer for ten-
sion and the cover for proper fit. The cover should fit
tight and have a good seal.
Fig. 4 Power Steering SystemÐXJ Vehicles
Fig. 5 Power Steering SystemÐYJ Vehicles
Fig. 6 Power Steering Fluid Reservoir
DipstickÐTypical
0 - 32 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEJ
Page 35 of 1784

(6) Inspect the disc brake caliper dust boot for cor-
rect installation, damage/tears and indications of
brake fluid leakage. Inspect the bushings and pins
for corrosion, tears and a binding condition.
(7) Pull the rear wheel cylinder dust boot back to
expose the wheel cylinder housing and inspect for
fluid leaks. Inspect the pistons and cylinder bores for
proper appearance.
(8) Inspect the brake differential warning valve
and housing for indications of leakage, kinked hoses
and loose fittings.
PARK BRAKE
(1) As applicable, engage the park brake lever or
pedal and then release it.
(2) If the park brake is functioning normally, test
it for smooth operation and vehicle-holding capabil-
ity.
(3) Inspect the park brake cables for kinks, fraying
and a binding condition.
(4) With the park brake released, the rear wheels
should rotate without restriction. Adjust the park
brake cable tension at the equalizer (Fig. 10), if nec-
essary.
(5) Repair any park brake malfunctions.
BRAKE OPERATIONAL TEST
(1) Drive the vehicle and test for proper brake ac-
tion.
(2) Note any indication of drum/rotor overheating,
wheel dragging or the vehicle pulling to one side
when the brakes are applied.
(3) Evaluate any performance complaints received
from the owner/operator.
(4) Repair the brake system as necessary (refer to
Group 5ÐBrakes for additional information and ser-
vice procedures).
TIRES
RECOMMENDED MAINTENANCE
The general condition of the tires and the inflation
pressures should be inspected at the same time the
engine oil is changed and the oil filter is replaced.
In addition, the tires/wheels should be rotated pe-
riodically to ensure even tread wear and maximum
tread life. The tires/wheels should be rotated initially
after the first 12 000-km (7,500-miles). Thereafter,
after each 24 000-km (15,000-miles) interval of vehi-
cle operation has elapsed.
INSPECTION
Inspect the tires for excessive wear, damage, etc.
Test the tires for the recommended inflation pres-
sure. Refer to the tire inflation pressure decal located
on the inside of the glove box door, and also to Group
22ÐTires And Wheels.
ROTATION
Refer to Group 22ÐTires And Wheels for the rec-
ommended method of tire/wheel rotation for a Jeept
vehicle.
BODY COMPONENTS
RECOMMENDED MAINTENANCE
Body components should be lubricated (as required)
after each 48 000-km (30,000-miles) interval of vehi-
cle operation has elapsed.
LUBRICANT SPECIFICATIONS
All applicable exterior and interior body compo-
nents should be:
²inspected for excessive wear,
²cleaned, and
²all pivot/sliding contact areas of the components
should be lubricated with the specified lubricant.
Refer to the Body Lubricant Specifications chart
below. When excessive wear is apparent, replace/re-
pair as necessary.
LUBRICATION
All pivoting and sliding contact areas, including:
²seat tracks,
²door hinges/latches/strikers, and
²liftgate/tailgate/hood hinges (Fig. 11),
should be lubricated periodically to ensure quiet,
easy operation and to protect against wear and cor-
rosion.
(1) As required, lubricate the body components
with the specified lubricants.
(2) When lubricating door weatherstrip seals, ap-
ply the lubricant to a cloth and wipe it on the seal.
(3) Prior to the application of lubricant, the compo-
nent should be wiped clean to remove dust, grit and
debris. After lubrication, any excess lubricant should
be removed.
Fig. 10 Park Brake Equalizer (XJ)ÐTypical
0 - 34 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEJ
Page 63 of 1784
(3) Place the socket (driver) against one bearing
cap. Position the yoke with the socket wrench in a
vise.
(4) Compress the vise to force the bearing caps into
the yoke. Force the caps enough to install the retain-
ing clips.
(5) Install the bearing cap retaining clips.
(6) Install the axle shaft, refer to Hub Bearing and
Axle Shaft installation.
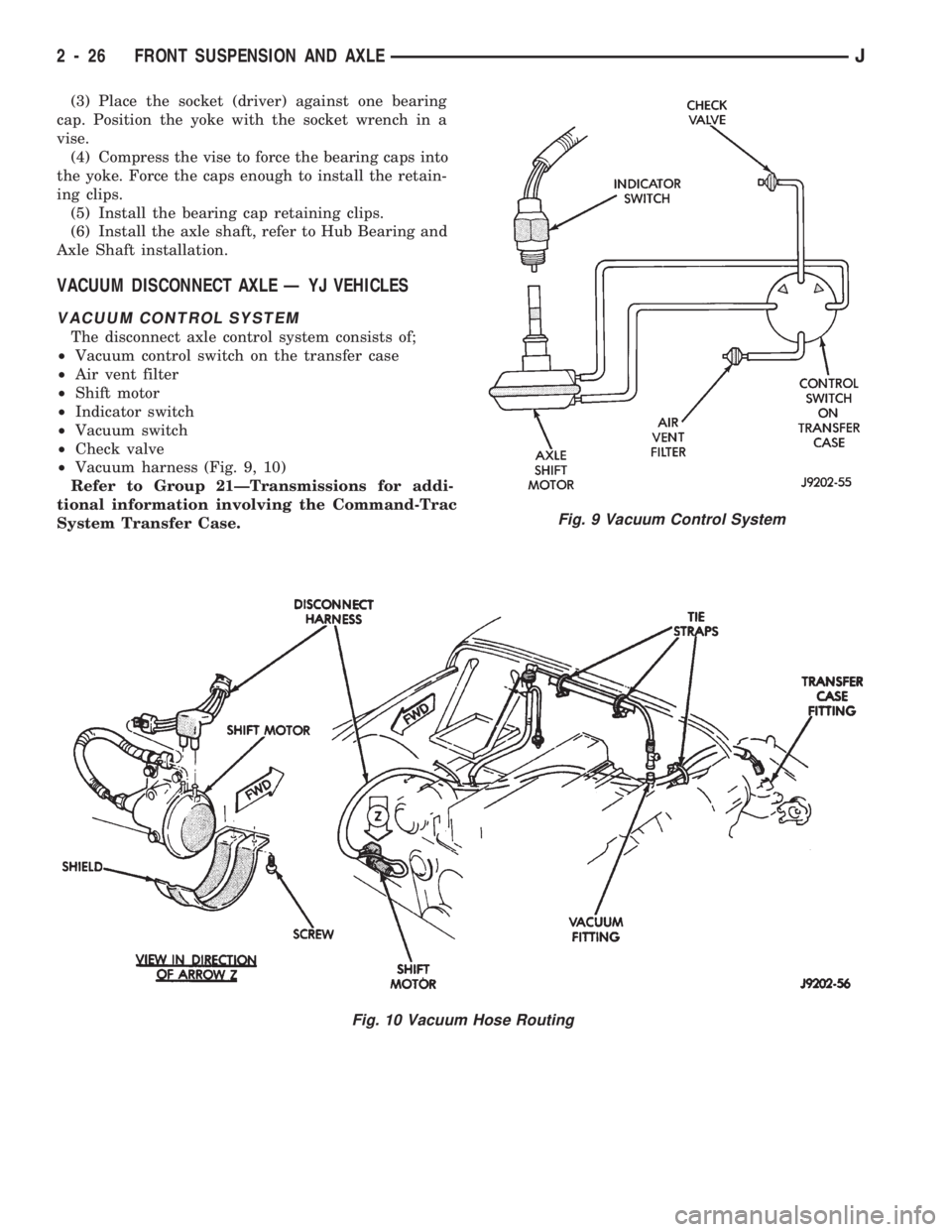
VACUUM DISCONNECT AXLE Ð YJ VEHICLES
VACUUM CONTROL SYSTEM
The disconnect axle control system consists of;
²Vacuum control switch on the transfer case
²Air vent filter
²Shift motor
²Indicator switch
²Vacuum switch
²Check valve
²Vacuum harness (Fig. 9, 10)
Refer to Group 21ÐTransmissions for addi-
tional information involving the Command-Trac
System Transfer Case.
Fig. 9 Vacuum Control System
Fig. 10 Vacuum Hose Routing
2 - 26 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 87 of 1784

line. You may encounter fuels containing 3 percent
or more methanol along with other alcohols called co-
solvents.
Problems that are the result of using methanol/gas-
oline blends are not the responsibility of Chrysler
Corporation. They may not be covered by the vehicle
warranty.
MTBE/ETBE
Gasoline and MTBE (Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether)
blends are a mixture of unleaded gasoline and up to
15 percent MTBE. Gasoline and ETBE (Ethyl Ter-
tiary Butyl Ether) are blends of gasoline and up to
17 percent ETBE. Gasoline blended with MTBE or
ETBE may be used in your vehicle.CLEAN AIR GASOLINE
Many gasolines are now being blended that con-
tribute to cleaner air, especially in those areas of the
country where air pollution levels are high. These
new blends provide a cleaner burning fuel and some
are referred to asReformulated Gasoline.
In areas of the country where carbon monoxide lev-
els are high, gasolines are being treated with oxy-
genated materials such as MTBE, ETBE and
ethanol.
Chrysler Corporation supports these efforts toward
cleaner air and recommends that you use these gas-
olines as they become available.
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
INDEX
page page
Fuel Filter............................... 8
Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test............... 7
Fuel Pressure Release Procedure............. 5
Fuel Pump Capacity Test................... 7
Fuel Pump Electrical Control................. 5Fuel Pump Module........................ 2
Fuel System Pressure Test.................. 5
Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps........... 9
Quick-Connect Fittings..................... 9
FUEL PUMP MODULE
The fuel pump module is installed in the top of the
fuel tank. The fuel pump module contains the follow-
ing components:
²Electric fuel pump
²Fuel pump reservoir
²In-tank fuel filter
²Fuel gauge sending unit
²Fuel supply and return tube connections
The fuel pump used on all vehicles is a gear/rotor
type pump. It is driven by a permanent magnet 12
volt electric motor that is immersed in the fuel tank.
The electrical pump is integral with the fuel sender
unit. The pump/sender assembly is installed inside
the fuel tank.
The fuel pump has a check valve at the outlet end
that consists of a ball held against a seat by force ap-
plied from a spring. When the pump is operating,
fuel pressure overcomes spring pressure and forces
the ball off its seat, allowing fuel to flow. When the
pump is not operating, spring pressure forces the ball
back against the seat preventing fuel backflow
through the pump.
Fuel system pressure is maintained at approxi-
mately 214 kPa (31 psi). This is when the pump is
operating and vacuum is supplied to the fuel pres-
sure regulator. If vacuum is not supplied to the pres-
sure regulator, fuel pressure will be approximately
55-69 kPa (8-10 psi) higher. This may be due to a
broken or clogged vacuum line. When the fuel pumpis not operating, system fuel pressure of 131-269 kPa
(19-39 psi) is maintained. This is done by the fuel
pump outlet check valve and the vacuum assisted
fuel pressure regulator.
REMOVALÐXJ MODELS
The fuel pump/gauge sender unit assembly can be
removed from the fuel tank without removing the
tank from the vehicle.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL PUMP MODULE,
THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE RE-
LEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL PRESSURE RE-
LEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS GROUP.
WARNING: EXTINGUISH ALL TOBACCO SMOKING
PRODUCTS BEFORE SERVICING THE FUEL SYS-
TEM. KEEP OPEN FLAME AWAY FROM FUEL SYS-
TEM COMPONENTS.
(1) Remove fuel filler cap. Perform the Fuel Pres-
sure Release Procedure as outlined in this group.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(3) Using an approved portable gasoline siphon/
storage tank, drain fuel tank until fuel level is below
one quarter (1/4) full.
(4) Raise and support vehicle.
14 - 2 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 94 of 1784

(1) Place fuel filter in retaining strap with the
marked ends in the correct position.
(2) Install retaining strap bolt and tighten to 12
Nzm (106 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install inlet and outlet hoses and hose clamps.
For procedures, refer to Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and
Clamps. Also refer to Quick-Connect Fittings. These
can be found in the Fuel Delivery System section of
this group.
(4) On YJ models, install fuel filter shield (Fig. 13).
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Connect negative battery cable.
(7) Start engine and check for leaks.
FUEL TUBES/LINES/HOSES AND CLAMPS
Also refer to the proceeding section on Quick-Con-
nect Fittings.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS
GROUP.
Inspect all hose connections such as clamps, cou-
plings and fittings to make sure they are secure and
leaks are not present. The component should be re-
placed immediately if there is any evidence of degra-
dation that could result in failure.
Never attempt to repair a plastic fuel line/tube. Re-
place as necessary.
Avoid contact of any fuel tubes/hoses with other ve-
hicle components that could cause abrasions or scuff-
ing. Be sure that the plastic fuel lines/tubes are
properly routed to prevent pinching and to avoid heat
sources.
The lines/tubes/hoses used on fuel injected vehicles
are of a special construction. This is due to the
higher fuel pressures and the possibility of contami-
nated fuel in this system. If it is necessary to replace
these lines/tubes/hoses, only those marked EFM/EFI
may be used.
The hose clamps used to secure rubber hoses on
fuel injected vehicles are of a special rolled edge con-
struction. This construction is used to prevent the
edge of the clamp from cutting into the hose. Only
these rolled edge type clamps may be used in this
system. All other types of clamps may cut into the
hoses and cause high pressure fuel leaks.
Use new original equipment type hose clamps.
Tighten hose clamps to 1 Nzm (15 in. lbs.) torque.
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS
Also refer to the previous Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses
and Clamps section.Different types of quick-connect fittings are used to
attach various fuel system components. These are: a
single-tab type, a two-tab type or a plastic retainer
ring type.
SINGLE-TAB TYPE
This type of fitting is equipped with a single pull
tab (Fig. 15). The tab is removable. After the tab is
removed, the quick-connect fitting can be separated
from the fuel system component.
CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers) of this type of quick-connect fitting are not ser-
viced separately, but new pull tabs are available. Do
not attempt to repair damaged fittings or fuel lines/
tubes. If repair is necessary, replace the complete
fuel tube/quick-connect fitting assembly.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS
GROUP.
DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
(2) Perform the fuel pressure release procedure.
Refer to the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this
section.
(3) Clean the fitting of any foreign material before
disassembly.
(4) Press the release tab on the side of fitting to re-
lease pull tab (Fig. 15).
Fig. 15 Single-Tab Type Fitting
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 9
Page 114 of 1784

switch will supply a ground circuit to the powertrain
control module (PCM).The switch is available
only with 4.0L engine when supplied with the
optional police package.
CRUISE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature, this
is a Closed Loop mode. At cruising speed, the power-
train control module (PCM) receives inputs from:
²Air conditioning select signal (if equipped)
²Air conditioning request signal (if equipped)
²Battery voltage
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Camshaft position sensor signal (in the distributor)
²Park/Neutral switch (gear indicator signalÐauto.
trans. only)
²Oxygen (O2S) sensor
Based on these inputs, the following occurs:
²Voltage is applied to the fuel injectors with the
PCM. The PCM will then adjust the injector pulse
width by turning the ground circuit to each individ-
ual injector on and off.
²The PCM monitors the O2S sensor input and ad-
justs air-fuel ratio. It also adjusts engine idle speed
through the idle air control (IAC) motor.
²The PCM adjusts ignition timing by turning the
ground path to the coil on and off.
²The PCM operates the A/C compressor clutch
through the clutch relay. This happens if A/C has
been selected by the vehicle operator and requested
by the A/C thermostat.
ACCELERATION MODE
This is an Open Loop mode. The powertrain control
module (PCM) recognizes an abrupt increase in
throttle position or MAP pressure as a demand for
increased engine output and vehicle acceleration.
The PCM increases injector pulse width in response
to increased throttle opening.
DECELERATION MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature, this
is an Open Loop mode. During hard deceleration, the
powertrain control module (PCM) receives the follow-
ing inputs.
²Air conditioning select signal (if equipped)
²Air conditioning request signal (if equipped)
²Battery voltage
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Camshaft position sensor signal (in the distributor)²Park/Neutral switch (gear indicator signalÐauto.
trans. only)
If the vehicle is under hard deceleration with the
proper rpm and closed throttle conditions, the PCM
will ignore the oxygen sensor input signal. The PCM
will enter a fuel cut-off strategy in which it will not
supply battery voltage to the injectors. If a hard de-
celeration does not exist, the PCM will determine the
proper injector pulse width and continue injection.
Based on the above inputs, the PCM will adjust en-
gine idle speed through the idle air control (IAC) mo-
tor.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing by turning the
ground path to the coil on and off.
The PCM opens the ground circuit to the A/C
clutch relay to disengage the A/C compressor clutch.
This is done until the vehicle is no longer under de-
celeration (if the A/C system is operating).
WIDE OPEN THROTTLE MODE
This is an Open Loop mode. During wide open
throttle operation, the powertrain control module
(PCM) receives the following inputs.
²Battery voltage
²Crankshaft position sensor
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Intake manifold air temperature sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Camshaft position sensor signal (in the distributor)
During wide open throttle conditions, the following
occurs:
²Voltage is applied to the fuel injectors with the
powertrain control module (PCM). The PCM will
then control the injection sequence and injector pulse
width by turning the ground circuit to each individ-
ual injector on and off. The PCM ignores the oxygen
sensor input signal and provides a predetermined
amount of additional fuel. This is done by adjusting
injector pulse width.
²The PCM adjusts ignition timing by turning the
ground path to the coil on and off.
²The PCM opens the ground circuit to the A/C
clutch relay to disengage the A/C compressor clutch.
This will be done for approximately 15 seconds (if the
air conditioning system is operating).
If the vehicle has a manual transmission, the up-
shift light is operated by the PCM.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE
When ignition switch is turned to OFF position,
the PCM stops operating the injectors, ignition coil,
ASD relay and fuel pump relay.
THROTTLE BODY
Filtered air from the air cleaner enters the intake
manifold through the throttle body (Fig. 25). Fuel
does not enter the intake manifold through the throt-
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 29
Page 120 of 1784

(10) Inspect fuel tube quick-connect fitting-to-fuel
rail connections (Fig. 15).
(11) Verify that hose connections to all ports of
vacuum fittings on intake manifold are tight and not
leaking.
(12) Inspect accelerator cable, transmission throt-
tle cable (if equipped) and cruise control cable con-
nections (if equipped). Check their connections to the
throttle arm of throttle body for any binding or re-
strictions (Fig. 16).
(13) If equipped with vacuum brake booster, verify
that vacuum booster hose is firmly connected to fit-
ting on intake manifold. Also check connection to
brake vacuum booster (Fig. 17).
(14) On XJ models equipped with 4.0L engine and
A/C, verify that auxiliary cooling fan wire connector
is firmly connected to harness (Fig. 18).
(15) Inspect the air cleaner inlet and air filter ele-
ment for restrictions.
(16) Inspect radiator grille area, radiator fins and
air conditioning condenser for restrictions.(17) Verify that intake manifold air temperature
sensor wire connector is firmly connected to harness
connector (Figs. 19 or 20).
(18) Inspect engine ground strap connections at
dash panel and rear cylinder head bolt (Fig. 21).
(19) Verify that MAP sensor electrical connector is
firmly connected to MAP sensor (Fig. 22). Verify that
vacuum hose is firmly connected to MAP sensor and
to the intake manifold.
(20) Verify that fuel injector wire harness connec-
tors are firmly connected to the fuel injectors in the
correct order. Each harness connector is tagged with
the number of its corresponding fuel injector (Fig.
23).
Fig. 15 Fuel Supply TubeÐTypical
Fig. 16 Throttle Body CablesÐTypical
Fig. 17 Brake Vacuum Booster HoseÐTypical
Fig. 18 Auxiliary Cooling Fan ConnectorÐXJ with
4.0L Engine
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 35