1994 JAGUAR XJ6 relay
[x] Cancel search: relayPage 2 of 521

Introduction
FOREWORD
This Vehicle Service Manual (VSM) is Dart
-
of a
set of service literature which covers -. diagnosis and rectification of problems associated with all areas of the X300 family of vehicles.
It is designed to be read in conjunction with other manuals, namely the various Unit Service Manuals (USM) (as
applicable to the particular vehicle under diagnosis/ repair) and the X300 Electrical Diagnostic Manual (EDM); see list
below.
It should be noted that its scope is limited to those areas that are unique to the family, e.g. Remove & Refit procedures
for Body Components, Engine, Transmission etcetera, Fuel, Emissions & Engine Management systems, and so on.
Fault Diagnosis and repair procedures (together
with Technical Data, Recommended Lubricants, Capacities etcetera) for major assemblies such as engines, automatic and manual transmissions, are covered in the separate Unit Service
Manuals.
The Unit Service Manuals are notvehicle
-specific, but are designed to be read in conjunction with this VSM, and, where so equipped, with other Jaguar Vehicle Service Manuals for new models launched subsequent to the X300 family.
The X300 Electrical Diagnostic Manual is the final part of the 'set' of service documentation. This manual
is
family-specific, and is designed to aid theTechnician to isolate electrical faults and to correct them. It covers all aspects
of electrical fault diagnosis, including:
OBD
II Codes and emission control system related fault diagnosis / rectification.
Circuit Diagrams
Component (Relays, fuse boxes, control modules etcetera) Location
/ Harness Diagrams I Ground Locations
Connector Locations.
Service Manuals Required
The Manuals required to service the X300 family of vehicles are as follows:
X300 Vehicle Service Manual
X300 Electrical Diagnostic Manual
Unit Service Manuals:
AJ16 Engine Service Manual
VI2 Engine Service Manual ZF AutomaticTransmissions Service Manual (ZF supplies transmissions for 3.2 liter and 4.0 liter normally aspirated
versions) Powertrain Automatic Transmissions Service Manual (The Powertrain name succeeds that of Hydra
-Matic.
Powertrain are suppliers of the 4L 80 E transmission as fitted to 4.0 litre supercharged and 6.0 litre versions)
Each
of the X3Okpecific manuals is divided into Sections which adopt the same title and number where relevant, i.e. Section 5.1 of both the VSM and the EDM cover Fuel, Emission Control & Engine Management System (AJ16). An
over
-all contents list showing each section title and number together with its page-edge locator is given in this section
and in the introduction to the EDM.
The VSM (not applicable to the EDM) also contains Appendices which cover specialized areas such as the current
vehicle specification, routine maintenance schedule etc. These are carried at the rear of this Manual, and have their
own contents page within this section.
INDEX
rapid location of information. The entries are set out as per the following example: @ This manual carries a comprehensive index at the rear, which is designed to save the Technician time by permitting
CLIMATE CONTROL SYSTEMS. Section 14.
See also Electrical Diagnostic Manual
Clutch
Description: Sect. 7.7 - 10
Fault diagnosis: Sect 7.1 - 11
In the example the heading in upper case lettering is to a section title, and it refers to the section number, 14, and also to the EDM as electrical diagnostic information will be found in that manual's section 14. The entry for clutch tells us that the relevant description will be found on page 10 of Section 7.1 of this manual, and
that fault diagnosis procedures start on page 11. In this case there is no reference to the EDM as electrical diagnosis does not apply to this area.
GLOSSARY OF TERMS
This Section contains a Glossary of general and emissions-related terminology (commencing on page 5).
X300 VSM 1 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 15 of 521

Fan Control FC
Fascia
farad F
I Federal Motor Vehicle Safetv I FMVSS
Standard (US)
fender
fiber
Figure (illustration) Fig.
firewall
Flash Electrically Erasable Pro- FEEPROM grammable Read-only Memory
Flash Erasable Programmable
FEPROM Read-only Memory
Flywheel Sensor CKFS
fueling Fuel Injectors FI
Fuel Pressure Regulator Control FPRC
Fuel Pump FP
Fuel Pump Monitor FPM
Fuel Pump Relay FPR
fuel
rich/lean
engine cooling fan control
SI unit of electrostatic capacitance; more
usually subdivided to microfarad fascia,
facia
wing,
(also tonneau)
fibre
bulkhead,
dash panel
sensor mounted
so as to be triggered by each flywheel sensor
flywheel ring gear tooth to give an engine
speed signal
fuelling
iniectors
solenoid operated
devices that spray a fuel injectors,
metered auantitv of fuel into the inlet
~0rt.s
Drimarilv to aive extra fuel at cold start-uo used I
controls fuel pressure regulator;
I I
monitors oDeration of fuel DumD I I
qualitative evaluation of airbuel ratio based on a ratio known as stoichiometry, or 14.7:l
(Lambda)
Issue 1 August 1994 14 X300 VSM
0
0
Page 23 of 521
(if applicable) term(s) (or Eng- lish Equivalent)
I R
Radio Data System
Random Access Memory
I rear wheel drive
relay
relay module
reservoir
return
revolutions per minute
right
-hand
right
-hand drive vehicle
I rocker panel
I roof lining
RDS
RAM
ROM RWD
RM
RES
RTN
RPM
RH
RHD
local traffic information service which
automatically breaks
in to whichever station
is being received. Also programmable to
lock onto the strongest available frequency
for a given nationally available radio station,
regardless ofthe geographical location of the
receiver
fast access memory store which is accessible
for entry or extraction of data
fast access memory
in which data is fixed and
mav not be entered or extracted
an (usually) electro
-mechanical device in which connections in one circuit are opened
or closed by changes
in another circuit
a module containing two or more relays
container, usually for oils, coolants or
hydraulic fluids
a dedicated sensor ground circuit
shaft
-speed of a device, usually an engine or
motor
I
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994 22
Page 24 of 521

0
Term(s) Abbreviation Definition
(if applicable)
Introduction i
Previously used term(s) (or Eng-
GLOSSARY OF TERMS
I lish Equivalent) A 3
Scan Tool
Seat Control Module
Secondary Air
Secondary Air Injection
Secondary Air Injection Bypass
..
Secondary Air -Injection Check
Valve
Secondary Air Injection
Diverter
Secondary Air Injection Magnetic
Clutch
Secondary Air Injection Pump
Secondary Air Injection Relay
Secondary Air Injection Switching
Valve
Security
& Locking Control Mod- ule
sedan
Sensor
Service Bulletin
Service Manual
Service Manual Preliminary
In-
formation Bulletin
Service Repair Operation
(number)
ST
SCM
AIR
AlRB
AI RC
AlRD
AIRPC
AlRP
AlRR
AIRS
SLCM
-
S
SE
SM
SMPlB
SRO
device that interfaces with and
communicates information on a data link
module controlling the seat motor systems
(not electric
raisejower-only seats)
air provided
to the exhaust system
system used for a period of time each time
the engine is started, unless certain
temperature criteria are met. Pumps air
directly into the exhaust system which
generates extra heat and reduces the time
taken for the catalytic converters to reach
operating temperature
vents secondary air to atmosphere
valve which prevents back
-flow of exhaust
gas to the AIR system when the system is
inoDerative
diverts secondary air to either the catalyst or
exhaust manifold
clutch mounted on the AlRP drive shaft
mechanically driven rotary vane
pump,
driven through the AIRPC
controls the injection of air into the exhaust
system
vacuum operated valve backing
-up the AlRC
module controlling the vehicle‘s security and
closure
-locking functions
passenger car having two or four doors, and
front and rear
seatsfor driver and passengers
generic name for a device that senses either
the absolute value or a change
in a physical
quantity such as temperature, pressure or
flow rate, and converts that change into an
electrical auantitv sianal
__
form of Service Bulletin specifically designed
to enable the rapid issue of temporary pages
for inclusion in the Service Manual
Number
generated by Jaguar Methods &
Techniques system which relates to the time
allowed to complete a repair operation.
Further information on the system can be
found
in the separate Jaguar Publications
(for each model range) entitled ‘Repair
Operat ion Times’. AIP,
AI,
Thermac, air injection sys-
tem
NRV, non-return
valve
air
pump clutch
AIP, air
pump
air injection relay
air switching
valve
saloon
Issue 1 August 1994 23 X300 VSM
Page 25 of 521

i Introduction
GLOSSARY OF TERMS
0 [if applicable)
ss
Term(s) term(s) (or Eng-
lish Equivalent)
part of the shift mechanism of a manual selectorfork
transmission, mounted on the shift rail, and
relaying movement in the shift lever to the
sleeve coupling which moves gears in and
out of engagement
rail which carries the shift fork
controls shifting in an automatic
transmission
part engine, usually the cylinder block, short engine
crankshaft
I connecting rod I piston
assemblv. suDDlied as a reconditioned unit selector
rod
shift
fork
an undesirable connection between a
(usually electrical) circuit and any other point
in
-line engine which is mounted in the
vehicle at an angle from the perpendicular, as
AJ6
shift rail
shift
solenoid
inclined engine
short
block
SRCM
SIG RTN
short circuit
sun roof
sun roof control
module
slant engine
buffer block, usually of a rubber compound,
which fits between the axle and the body unit,
and absorbs any excess travel
device consisting of an electrical coil which,
when energized, produces a magnetic field
in
a plunger which is pulled to a central
position. A solenoid may be used as an
actuator
in a valve or switch
SAE
sliding roof
sliding roof control module
ci rcl
ip
bump stop
signal return
sc
snap ring
ing brake
brake lamp
sulphur,
-ic
an intake system which utilizes a
snubber
SCB
SRS
Society of Automotive Engineers
solenoid
supercharger (mechanically driven device
that pressurizes intake air, thereby increasing
density of charge air and the consequent
power output from a given displacement)
airbag restraint system for driver and front
splash
guard
speed
Speed Control Control Module
square centimeters
stabilizer bar
standard
station wagon
stop lamp
sulfur, sulfuric
supercharger
- - __. . . . ... - . Supercharger Bypass
Supplementary Restraint System Abbreviation
I Definition 1 Previously used
I mud flap
I the
magnitude of velocity (regardless of I I direction)
SCCM
I Module controlling Speed Control System I Cruise Control
cm2
std
1 seat passenger
SP I supply port of valve I
0
0
0
Issue 1 August 1994 24 X300 VSM
Page 76 of 521

striker and the-fuel cap stowage magnet.
The fuel bowl, retained around the filler neck by a clip, containing a drain tube filter located over the mating drain tube,
is rubber moulded onto a steel armature and fitted to the BIW decking panel by five M5 nuts.
The fuel lid latching assembly fitted to the metal armature of the fuel bowl by an M5 nut, includes the locking pin and
the operating actuator.
The actuator operates from the central locking system driven by the security and locking control module
(SLCM).
The fuel tank, mounted across thevehicle behind the passenger compartment rear bulkhead, is held in position by two
retaining straps, tightened by two M5 fixing arrangements.
The fuel tank of AJ16 engined vehicles contains one fuel pump, supplying fuel to the normally aspirated engine and
two fuel pumps, supplyingfuel to the supercharged engine. They are regenerative turbine pumps supplied by
Nippon- Denso. Nominal operating pressure is 3 bar (3.7 bar for supercharged engine) above the manifold depression and
pump delivery is 90 litredhour minimum at 13.2 volts, 3 bar outlet pressure. The pump(s) draw a nominal current of 7 amperes at 13 volts, 3 bar outlet pressure, ambient temperatures. Built in to the pump assembly is a over-pressure
relief valve which blows at 4.5 - 8.5 bar.
Fuel is drawn by the pumps from the fuel tank and is then supplied to the fuel rail via a
70 micron filter and the fuel
feed line connected in series by fuel filter.
The amount of fuel being injected into the engine
is controlled by the fuel injectors combined with the engine control module (ECM). - Any excessive fuel flowing through the system, is returned to the fuel tankvia the fuel regulator valve mounted on the
fuel rail, the fuel return line and the check valve also located inside the tank.
The two filters prevent contaminants from entering the fuel rail and possible damage to the fuel injectors, the engine,
the pump and the underfloor filter.
The fuel pumps are switched on and off by relays controlled by the engine control module
(ECM).
The second fuel pump for the supercharged engine operates only in the higher speed range, switching on at 4000rpm and off at 3200rpm.
The fuel lines are made up of an assembly, combining steel under floor pipes and flexible conductive anti-permeation
tubing. In orderto perform speedy remove and refit operations, the underfloor steel lines are linked through the engine
bay bulkhead to the flexible tubing, leading to the fuel rail and the fuel regulator by using positive sealing, quick-fit
type connectors. The same type connectors, are used to connect the fuel feed and return line to the fuel tank.
Connectors used inside the engine bay are of different sizes tocorrespond with the difference in pipe diameter, whereas
the connectors for the feed and return lines at the fuel tank are the same size.
Except for the return line connector at the fuel tank, two release tools, one for each size of connector are required to
release all remaining connectors.
-~
Fuel, Emission Control & Engine Management (AJ16)
5.1.2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
m: WORKING ON THE FUEL SYSTEM MAY RESULT IN FUEL AND FUEL VAPOUR BEING PRESENT IN THE
ATMOSPHERE. FUEL VAPOUR IS EXTREMELY FLAMMABLE, HENCE GREAT CARE MUST BE TAKEN WHllST WORKING ON THE FUEL SYSTEM. ADHERE STRICTLY TO THE FOLLOWING PRECAUTIONS:
DO NOT
SMOEIN THE WORK AREA.
DISPLAY 'NO SMOKING
' SIGNS AROUND THE AREA.
ENSURE THAT A
CO2 FIRE EXTINGUISHER IS CLOSE AT HAND.
ENSURE THAT DRY SAND
IS AVAILABLE TO SOAK UP ANY FUEL SPILLAGE.
EMPTY FUEL USING SUITABLE FIRE
PROOF EQUIPMENT INTO AN AUTHORIZED EXPLOSIOWROOF
CONTAINER.
DO NOT EMPTY FUEL
INTO A PIT.
ENSURE THAT WORKING AREA
IS WELL VENTILATED.
ENSURE THAT ANY WORK ON THE FUEL SYSTEM
IS ONLY CARRIED OUT BY EXPERIENCED AND WELL
QUALIFIED MAINTENANCE PERSONNEL.
The fuel filler assembly, supplied complete with serviceable lid, hinge and hinge spring, is fixed to the Body-in-White
(BIW) decking panel by two M5 nuts. Additional parts of the assembly comprise a adjustable rubber buffer, a snap-in
X300 VSM 3 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 97 of 521
Fuel, Emission Control & Engine Management (V12)
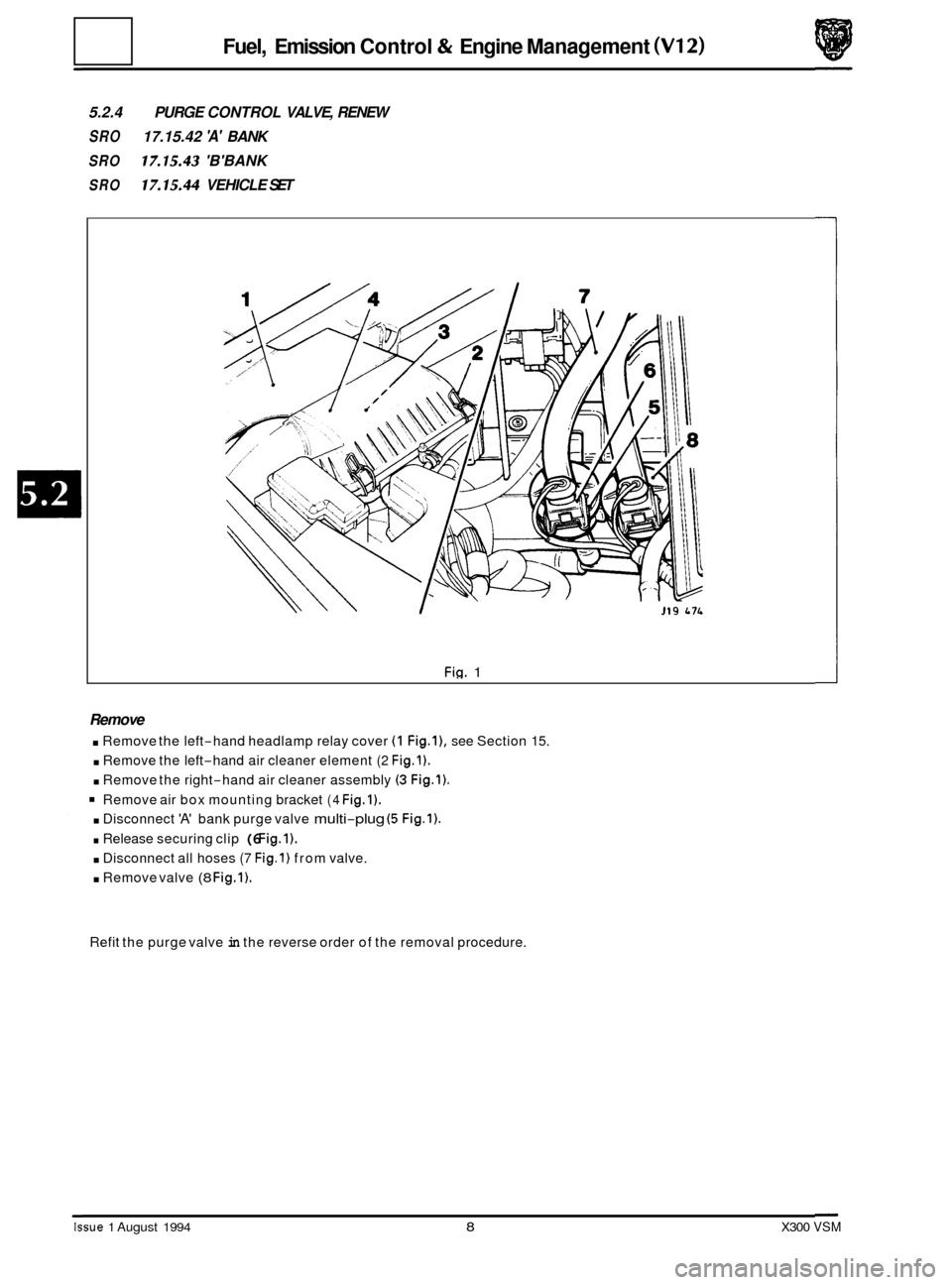
5.2.4 PURGE CONTROL VALVE, RENEW
SRO 17.15.42 'A' BANK
SRO 17.15.43 'B'BANK
SRO 17.15.44 VEHICLE SET
Fig. 1
Remove
. Remove the left-hand headlamp relay cover (1 Fig.l), see Section 15.
. Remove the left-hand air cleaner element (2 Fig.1).
. Remove the right-hand air cleaner assembly (3 Fig.1).
Remove air box mounting bracket (4 Fig.1).
. Disconnect 'A' bank purge valve multi-plug (5 Fig.1).
. Release securing clip (6 Fig.1).
. Disconnect all hoses (7 Fig.1) from valve.
. Remove valve (8 Fig.1).
Refit the purge valve in the reverse order of the removal procedure.
Issue 1 August 1994 8 X300 VSM
Page 232 of 521

Brakes (e#
12.1.7. Parking Brake
J70 293
W
1. Parking brake lever 2. Front cable 3. Relay lever 4. Driveshaft securing bracket 5. Intermediate cable 6. Cable equalizer
7. In-line cable connector 8. Rear cable RH 9. Rear cable LH
10. Parking brake switch and harness 11. Parking brake warning lamp
Fig.
1 Parking Brake Layout
All vehicles are fitted with identical parking brake systems.
When the parking brake lever
is operated, the cable system applies equal force to both RH and LH brakeshoe expander
assemblies. The brake shoes expand and press against the hub assembly, locking the rear wheels.
The handbrake lever, ratchet assembly and warning
light switch (item 1) are mounted on the transmission tunnel by means of threeflanged screws a blanking plate and gasket. The front cable (item 2) is connected to the relay lever (item 3) which is mounted on the driveshaft securing bracket (item 4). The relay lever operates the intermediate cable (item 5) which incorporates an adjusting screw to allow cable tension to be adjusted. The intermediate cable operates the
equalizer which ensures that equal force is applied to RH and LH parking brakesvia rearcable RH (item 8) and rear cable
LH (item 9). The rear cables are adjustable to allow cable tension to be adjusted.
The park brake switch (item 10) latches when the lever
is operated and lights the parking brake warning light (item 11 mounted in the instrument panel.
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994