1994 JAGUAR XJ6 ABS
[x] Cancel search: ABSPage 246 of 521

Brakes
12.7 HYDRAULICCONTROL MODULE- RENEW
SRO 70.60.18
70.60.1
9
Refer to Section 12.4, Brake System Bleeding before carrying out this procedure. Pay particular attention to the warn- ings and cautions relating to brake fluid, cleanliness and cleaning materials.
W: The illustration shows the hydraulic control module of a 6 cyl. vehicle with traction control. Hydraulic control
modules on non-traction control vehicles have only three outlet ports. Apart from this, the removal procedure
is the same for all vehicles.
. Raise the vehicle.
Displace the bleeder screw dust cap of the front LH caliper.
The dust cap will remain captive
on the bleed screw.
. Connect a bleeder tube and bottle to the bleeder screw (1
Fig. 1) and open the bleeder screw.
. Fit a brake pedal hold-down tool (JDS-9013) between the
brake pedal and the steering wheel. Adjust the tool to op
- erate the brake pedal 60mm down. This operation is
necessary to prevent fluid loss from the reservoirthrough
. Re-tighten the front LH caliper bleeder screw. Disconnect
the bleeder tube from the bleeder screw and remove the
tube and bottle. Refit the bleeder screw dust cap.
Undo the securing bolt of the multi-plug connector (1 Fig. 2). The bolt will remain captive. Disconnect the multi-plug
connector and reposition safely.
. Place absorbent material underneath the hydraulic con-
trol module to absorb any spillages.
Undo the tandem master cylinder CTMC) brake pipe gland
nuts (2 Fig.2) and disconnect the brake pipes.
. Fit plugs immediately to the brake pipes and the hydraulic
control module to prevent fluid
loss.
. Undo the rear brake pipe gland nuts (3 Fig. 2) at the pres- sure conscious reducing valves (PCRVs) (4 Fig. 2). Remove
the rear brake pipes.
disconnected brake pipes.
Note: Take necessary steps to prevent rotation of the
PCRVs when removing the rear brake pipes.
Fit plugs immediately to the brake pipes and the PCRVs to
. Undo and remove the PCRVs. Fit plugs immediately to the
Place PCRVs aside to be fitted later to the new hydraulic
. Undo the front brake pipe gland nuts (5 Fig. 2) and remove
. Fit plugs immediately to the brake pipes and the hydraulic
. Undo and remove the three securing nuts (6 Fig. 2) and re-
0 prevent fluid loss.
PCRVs and the hydraulic control module.
control module.
the front brake pipes.
control module to prevent fluid
loss.
move the hydraulic control module. Fia.
1
3 1 J70 296
Fia. 2
Issue 1 August 1994 X300 VSM 23
Page 247 of 521

Remove the absorbent material and clean the mounting bracket and surrounding area.
Fit and align a new hydraulic control module to the mounting bracket. Ensure that the mounting cup tangs fully en-
9 Fit and tighten the securing nuts (6 Fig. 1).
. Place absorbent material underneath the hydraulic con- trol module to absorb any spillages.
. Connect the front hydraulic brake pipes (5 Fig. 1) tothe hy- drauliccontrol module, removing plugs immediately prior
to connection. Tighten the gland nuts.
Fit the PCRVs (4 Fig. 1) to the hydrauliccontrol module, re- moving plugs immediately prior to connection. Tighten
the PCRVs.
Connect the rear hydraulic brake pipes (3 Fig. 1) to the
PCRVs, removing the plugs immediately prior to connec- tion. Tighten the gland nuts.
gage
the bracket slots.
&&a: Take necessary steps to prevent rotation of the
PCRVs when fitting the rear brake pipes.
Connect
theTMC hydraulic brake pipes (2 Fig. 1) to the hy- draulic control module, removing the plugs immediately
prior to connection. Tighten the gland nuts.
. Remove the absorbent material and clean thesurrounding
area.
. Reposition and connect the multi-plug connector. Tighten
the securing bolt (1 Fig. 1).
. Ensure that all fixings are torque tightened to specified tol- erances.
. Release the brake pedal hold-down tool and remove.
. Bleed the brake system (refer to sub-section 12.4.4).
. Examine the hydraulic control module for leaks.
3 1 J70 296
Fig. 1
Issue 1 August 1994 ~~ X300 VSM
Page 248 of 521

Brakes
12.8
SRO 70.60.21
PRESSURE CONSCIOUS REDUCING VALVES - RENEW
Refer to Section 12.4, Brake System Bleeding before carrying out this procedure. Pay particular attention to the warn- ings and cautions relating to brake fluid, cleanliness and cleaning materials.
Note: The illustration shows the hydraulic control module of a 6 cyl. vehicle with traction control. Hydraulic control
modules on non-traction control vehicles have only three outlet ports. Apart from this, the removal procedure
is the same for all vehicles.
. Raise the vehicle.
Displace the bleeder screw dust cap of the front LH caliper.
The dust cap will remain captive on the bleed screw.
rn Connect a bleeder tube and bottle to the bleeder screw (1 Fig. 1) and open the bleeder screw.
Fit a brake pedal hold-down tool (JDS-9013) between the
brake pedal and the steering wheel. Adjust the tool to op- erate the brake pedal 60mm down. This operation is
necessary to prevent fluid
loss from the reservoir through
disconnected brake pipes.
. Re-tighten the front LH caliper bleeder screw. Disconnect
the bleeder tube from the bleeder screw and remove the
tube and bottle. Refit the bleeder screw dust cap.
rn Place absorbent material underneath the hydraulic con- trol module to absorb any spillages.
. Undo the rear brake pipe gland nuts (1 Fig. 2) at the pres- sure conscious reducing valves (PCRVs) (2 Fig. 2). Remove
the rear brake pipes.
m: Take necessary steps to prevent rotation of the
PCRVs when removing the rear brake pipes.
Fit plugs immediately to the brake pipes and the PCRVs to
Undo and remove the PCRVs. Fit plugs immediately to the
. Clean the surrounding area.
. Fit new PCRVs to the hydraulic control module, removing
plugs immediately priorto connection. Tighten the PCRVs.
. Connect the rear hydraulic brake pipes to the PCRVs, re- moving the plugs immediately prior to connection.
Tighten the gland nuts.
prevent
fluid loss.
PCRVs
and the hydraulic control module.
0
Note: Take necessary steps to prevent rotation of the
PCRVs when fitting the rear brake pipes.
. Removethe absorbent material and clean the surrounding
. Ensure that all fixings are torque tightened to specified tol-
Release the brake pedal hold-down tool and remove.
. Bleed the brake system (refer to sub-section 12.4.4).
. Examine the hydraulic control module for leaks.
area.
erances. Fia.
1
Fia. 2
X300 VSM 25 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 249 of 521
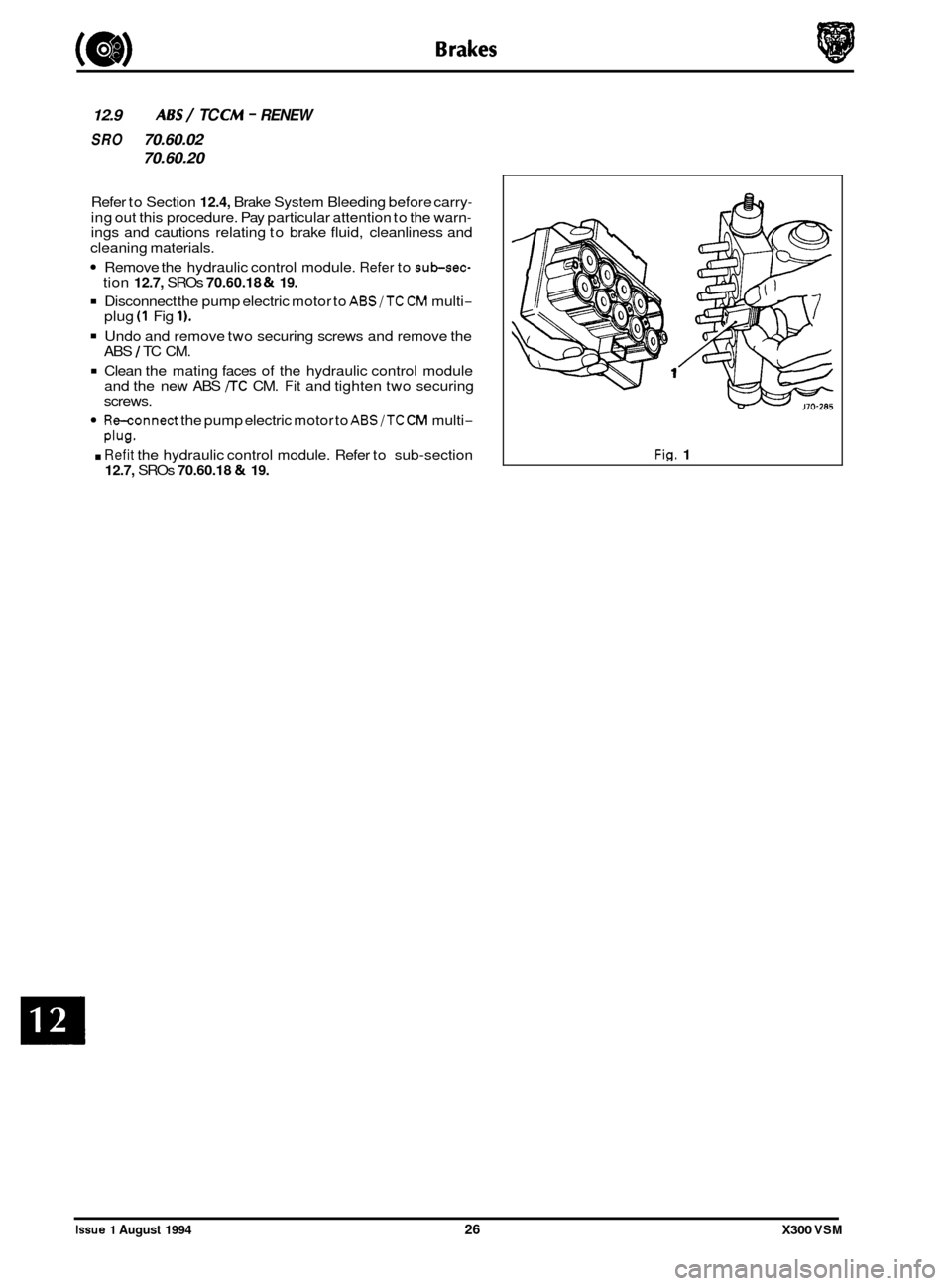
12.9 ABS/ TC CM - RENEW
SRO 70.60.02
70.60.20
Refer to Section 12.4, Brake System Bleeding before carry-
ing out this procedure. Pay particular attention to the warn- ings and cautions relating to brake fluid, cleanliness and
cleaning materials.
Remove the hydraulic control module. Refer to sub-sec- tion 12.7, SROs 70.60.18 & 19.
Disconnect the pump electric motor to ABS/TC CM multi- plug (1 Fig 1).
Undo and remove two securing screws and remove the
ABS 1 TC CM.
Clean the mating faces of the hydraulic control module
and the new ABS /TC CM. Fit and tighten two securing
screws.
Re-connect the pump electric motor to ABS/TC CM multi-
Plug.
. Refit the hydraulic control module. Refer to sub-section 12.7, SROs 70.60.18 & 19.
Fig. 1
Issue 1 August 1994 26 X300 VSM
0
e
Page 257 of 521

Body Components & Trim d-!P
13.2
13.2.1 Doors, Description
Doors are of welded, mild steel frames welded to the door panels; sponge rubber primary and secondary seals are
mounted on the doors. Internal insulation is provided by a foam water shedder attached to the door by press fitting and doublesided adhesive tape.
Front and rear door armrests are attached to supports riveted to each door frame; the attaching screws are fitted
with access covers. Upper and lower trim pads and a door pocket are attached to each of the doors by clips and screws. multi-plug connectors are used to provide a means of connecting the guard lamps, window lift switches and loud- speakers, external mirror and regulator (front doors only), which are housed within the doors.
Central locking is provided subject to market variations: Dead Locking for UK
/ Europe and Driver only unlock for N America. Door locks are eight disc, bayonet fixing, barrels with integral lock / unlock switches. Keys include ‘in-key’
transponders which are programmed to the vehicle via the Jaguar Diagnostic System also operate the engine immobi
- lisation system.
CAUTION: When removing the door panel water shedder, a foam membrane attached to each door panel by a com- bination of pressfitting (upper area) and bydouble-sided tape (bottom area), it is important that the shed- der is refitted correctly to maintain the water seal.
It is advisable not to disturb the bottom (taped) portion of the water shedder unless absolutely necessary
- it is possible to unclip the top of the shedder and bend it over to gain access to the inner panel.
If
it is necessary to disturb the bottom attachment, eg to remove the water shedder from the door panel,
the existing water shedder must be discarded and a new one fitted to ensure that the seal is maintained.
On refitting, the new water shedder should be pressed onto the door panel at the top and then the adhes- ive tape backing strip peeled off to enable the shedder to be pressed home at the bottom.
DOORS AND FUEL FILLER FLAP
13.2.2 front and Rear Door Trim Pad Veneer Panel,
Renew
SRO 76.47.11
76.47.12
. Reposition the inner door handle. See Fig. 1.
Remove the inner handle escutcheon plate blanking plate.
Undo and remove the inner handle escutcheon plate se-
. Remove the plate and gasket.
. Carefully Undo and remove the veneer panel.
Undo and remove the retaining clip securing screws.
. Remove the retaining clip assemblies.
9 Place the veneer panel aside.
Place the new veneer panel to the front.
Fit the retaining clip assemblies.
. Fit and tighten the retaining clip securing screws.
. Fit and fully seat the veneer panel to the door.
. Reposition the inner door handle.
. Fit the gasket and plate over the inner door handle.
. Fit and tighten the escutcheon plate securing screw.
. Refit the blanking plate.
curing
screw.
Fig.
1
0
0
0
0
Issue 1 August 1994 2 X300 VSM
Page 301 of 521

Body Components & Trim a
13.7.4
Localized stains caused by accidental spillage may be one of three types:
0 Water based stainscaused byfoodstuffs,starches, sugars, soft drinks,fruit stains, washable inketc. These stains
adhere readily to the pile and do not respond to vacuum cleaning. They are best removed immediately using
the procedure detailed below.
0 Oil /grease based stains caused by spillage or other contamination by butter, grease, hand cream, ball point pen
ink, crayon, lipstick etc.
0 A combination of both these types.
Spot Cleaning - Localized Stains
To remove water based stains:
. Blot up liquids and /or scrape off semi-solids using a spatula.
. Sponge the affected area with clean luke-warm water. Use a clean, damp, undyed, cotton cloth to absorb as much
. If the stain persists, apply a suitable carpet shampoo solution made up to the manufacturers instructions, again work-
= Rinse with clean, warm water, taking care not to over-wet the carpet.
Absorb excess moisture by laying dry, undyed cloths or white paper towels over the moist carpet under light pres-
. When the carpet is thoroughly dry, vacuum clean the area to lift the carpet pile.
CAUTION: When liquids are applied to the pile, use only a clean cloth or sponge. Do not apply liquids directly to the
carpet - when attempting to remove stains, blot the pile as heavy rubbing can destroy the yarn structure of the carpet.
of the moisture as possible, working from the edge to the centre of the stain.
ing from the edge to the centre of the stain.
sure; replace when necessary.
To remove oil /grease based stains:
. Using a suitable aerosol containing solvent loaded with absorbent powder, spray the affected areas of the carpet.
= Allow the solvent to evaporate and remove the powder containing the grease by using a vacuum cleaner or brush.
m:
CAUTION: Solvents must only be used in well-ventilated areas where naked lights and smoking are prohibited.
The solvent loosens the grease from the fibre and the powder then absorbs the grease-carrying solvent.
Neat solvent, eg dry cleaning
fluid, may be used, but should be used sparingly from a clean white cloth.
To remove stains which are a combination of oil and water based contamination (usually resulting from food or drink):
. Treat combination stains as for water based stains.
. Allow to dry out.
. Treat as for grease based stains.
Issue 1 August 1994 46 X300 VSM
Page 303 of 521

Body Components & Trim a
13.8 SEATING AND SEAT BELTS
13.8.1 Seating, Description
The front seats are available in a range of materials consisting of sculptured fabric / leather, leather, sports cloth / leather, embossed leather / leather and autolux. Both seats are available as 'manual', ie manually adjustable with elec- tric rise and fall, manual height adjustment headrests, 'power', ie 12-way electric adjustment, 'power with memory', ie memory controlled, 12-way electric adjustment of seat, steering column and exterior rear view mirrors and 'heated',
ie with integral heating.
Front seats are based on a non
-handed, one-piece frame which includes cushion and squab frames and seat adjuster
mechanisms. The seat switchpacks (powerseats) are fitted to the outboard side of driver and passenger seats; on 'man- ual'seats, the seat height adjustment switch is similarly located. Seat control modules SCMs are contained within the
seat assemblies. The seats are secured through four mounting points to the vehicle floor.
Rear seats are of the bench type with
full width removable cushion and individual seat squabs.
Electrical components installed on the heel board below the rear passenger seat are protected
by two covers secured
by two locating brackets on the floor and by two latches on the cover. The latches are released by pushing down on
the two recesses in the top edge of the cover.
13.8.2 Front Manual Seat, Renew
. Disconnect vehicle battery ground lead.
. Disconnect electrical connections as required.
. Remove the seat forward fixings.
Move the seat fully forward.
. Remove the rear fixing / slide covers.
. Remove the seat rear fixings.
. Reposition seat for access and remove seat from vehicle.
. To refit seat, carry out reversal of above procedure.
13.8.3
. Disconnect vehicle battery ground lead.
. Move the seat fully forward to gain access to squab back
Remove squab side fixings, disconnect lamp harness and
. To refit, carry out reversal of the above procedure.
Front Seat (Power Operated) Squab Back
Cover, Renew
cover outer fixings.
remove squab back cover.
13.8.4
. Position seat as required for access.
. Disconnect vehicle battery ground lead.
. Release sound insulation retainers and displace insula-
. Remove SCM cover, move SCM aside and remove seat
. Remove the seat forward fixings and move the seat fully
. Remove the seat rearward fixing covers and remove the
. Disconnect multi-plugs, seat switch and motor harness to
. Release harness tie strap and remove seat assembly from
Front Seat (Power Operated), Renew
tion.
switch
multi-plug from its mounting bracket.
forward. seat rearward fixings.
SCM.
vehicle.
. To refit, carry out reversal of the above procedure, ensur- ing that fixings are tightened to the correct torque.
Issue 1 August 1994 48 X300 VSM
0
0
0
Page 312 of 521

Climate Control Systems
Description U-
HFC 134A - ICI Klea or
equivalent
Polyalkyleneglycol (PAG) Compressor lubricant
Refrigerant
111.
Notes
Recyclable. NOT
compatible
with CFC 12
Absorbs water readily. NOT
compatible with mineral based
oils
SERVICE MATERIALS
Standard for Recovery I Recycle 1 Recharge Equipment.
Recovery rate
Cleaning capability
Oil separator
.Moisture indicator
Vacuum pump
Filter Replaceable with moisture indicator
Charge Hoses
Feature Requirement
0,014 - 0,062 m3 / min. (1,36 kg in 20 minutes)
15 parts per million (ppm) moisture; 4000 ppm oil; 330 ppm non condensable gases
in air
With hermetic compressor and automatic oil return
Sight glass type, sensitive to 15 ppm minimum
2 stage 0,07 - 0,127 m3 I min.
Selectable charge weight and automatic delivery
Dedicated HFC 134A port connections.
Iv. SERVICE DATA
Application
Charae weight
Lubricant capacity
Compressor pressure relief valve
Drive belt 12 cylinder
Drive belt tension
All figures apply to a cold belt
Special note
Drive belt tension measuring point
Drive belt 6 cyclinder
Drive belt tension
All figures apply to a cold belt
Drive belt tension measuring point
Specification
160 - 200 ml
Opening point 34 Bar. Closing point 27,6 Bar.
Maximum leakage rate of 113 liters 1 minute @ 41 Bar
7 rib Poly
-vee; 1450 mm long
Burroughs method
- New belt 790 N; If tension falls
below 270 N reset at 630 N
Clavis method
- New belt 114 to 120 Hz; If tension falls
below 70 Hz reset at 87 to 93 Hz
For new belt; rotate engine 3 revolutions minimum and
retension
Mid-way between crankshaft and compressor pulley ~
4
rib Poly-vee X 1010 mm long
Burroughs method
- New belt 556 to 578 N; If tension
falls below 245 N reset at 378 to 400
N
Clavis method - New belt 167 to 173 Hz; If tension falls
below 85 Hz reset at 127 to 133 Hz
Mid
-way between crankshaft and compressor pulley on
the upper run
1 Charge pressure I Heating element to increase pressure
Issue 1 August 1994 X300 VSM iii