1994 JAGUAR XJ6 check oil
[x] Cancel search: check oilPage 190 of 521

Driveshafts & Final Drive
9.6 OUTPUT SHAFT BEARING, RENEW
@ SRO 51.10.22
9.7
SRO 51.20.04
. Disconnect vehicle battery ground lead.
. Support the vehicle at the rear and remove the rear road wheel (or wheels).
9 'Match mark' the axle shaft flange to the output shaft flange and remove fixings, note camber shim.
. Thoroughly clean the area around the output shaft housing and differential case.
. Release fixings and remove output shaft assembly, discard '0' ring.
. Mark bearing retaining collar axially and drill 3 off holes 4,O mm diameter equally spaced, to a MAXIMUM depth of
. With a suitable chisel (2 Fig. 1) strike the collar across the three drilled holes to relieve tension within the steel.
CAUTION: Do not drill into the output shaft, it is not necessary to break the inside diameter of the collar. There is
no need to to split the collar when chiselling.
Using a suitable press, remove bearing and collar, remove the oil seal and discard it along with bearing.
CAUTION: The original bearing must NOT be cleaned and reused; always renew it.
Inspect the output shaft oil seal surface for damage corrosion or grooving and replace as necessary.
W:
OUTPUT SHAFT OIL SEAL, RENEW
5,O mm (1 Fig. 1).
Do not use abrasive cloth or paper to remove imperfections from the seal surface
. Using special tools JD 550-1 and 18G 134, assemble new oil seal to housing, ensuring that the seal top face is 1,8 mm below the housing top face and NOT down on the counterbore face.
Lubricate the output shaft seal diameter and oil seal lip and position the housing assembly to the shaft.
Using special tool SL 7 and a suitable press, assemble bearing to output shaft.
. Using special tool SL 7 and a suitable press, assemble retaining collar to output shaft.
= Fit the original shims and using hand pressure only to seat the assembly, check that theclearance between the output
. Using a new '0' ring and sealant on the mating faces, assemble the output shaft assembly to the differential case.
. Fitting and reassembly is the reversal of this procedure ensuring that all fixings are tightened to specification and
shaft
housing and differential case is in the range
0,05 to 0,13 mm. Shim to suit if not in this range.
See Sub
-Section 9.3 Output Shaft End Float Check.
new locking nuts are used.
Correct the final drive oil level
if required.
Issue 1 August 1994 X300 VSM
Page 192 of 521

Driveshafts & Final Drive
. Remove upper link assembly from differential and wide mounting bracket / 'A' frame.
. Release fixings, 'A' frame to differential, 'A' frame to wishbone tie and wide mounting bracket to 'A' frame.
. Remove wishbone tie assembly, rear mounting bracket and pendulum assembly.
. Release fixings differential nose to wide mounting bracket.
. Assembly and fitting is the reversal of this procedure, taking note of the following:
Drive shaft must be aligned in accordance with Sub
-Section 9.2.
Renew all self locking nuts.
Renew all bolts that were originally fitted with thread locking adhesive.
Replace all locking wire and split pins (cotter pins).
Tighten all fixings to the specified torque.
Correct the final drive oil level
if required.
Check and adjust rear wheel camber setting as required.
9.9 AXLE SHAFT ASSEMBLY, RENEW
SRO
47.10.01
Disconnect vehicle battery ground lead.
. Slacken appropriate axle shaft hub nut.
. Support the vehicle at the rear and remove rear road
. Remove brake caliper in accordance with 70.55.03. Sec-
wheel.
tion 12, but do not disconnect hydraulics.
Slacken hub carrier fulcrum and remove ABS sensor from
hub carrier.
. Remove axle shaft hub nut and collar.
. Remove fixings axle shaft to differential output shaft
flange, note camber shim.
. With service tools JD 1D/7 (Fig. 1) and JD ID (Fig. 21, push
shaft through hub.
. Remove axle shaft assembly.
CAUTION: Take care not to introduce debris into the hub
bearings, or damage seal.
. Prior to assembly, remove all traces of adhesive from hub
. Assembly and fitting is the reversal of this procedure
Adhesive should be applied to axle shaft splines over
a radial area of
30 to 50%.
Renew all bolts that were originally fitted with thread
locking adhesive.
Replace all locking wire and split pins (cotter pins).
Tighten all fixings to the specified torque.
Check and adjust rear wheel camber setting.
Verify operation of brakes.
Renew all self locking nuts.
splines.
taking
note of the following:
0
NQ&: The axle shaft nut is a self-locking item with a thread
insert and must NOT be reused.
Fig. 1
Fig.2
- Iss ue 1 August 1994
__~
7 X300 VSM
Page 196 of 521

SECTION CONTENTS 0
Sub-Section Title SRO Page
i to iii ............ Preliminary Pages ................................................................ i To iv
10.1
............. Steering System Description ........................................................... 1
10.1.1 ............ Steering System Description. Steering Column Major Components ........................... 1
10.1 .2 ............ Steering System Description. Steering Column Operating Principle ........................... 1
10.1.3 ............ Steering System Description. Hydraulic System Major Components .......................... 2
10.1.4
............ Steering System Description. Hydraulic System Features .................................... 2
10.1.5
............ Steering System Description. Hydraulic System Operating Principle .......................... 2
10.2 ............. Service Procedures-Safety Related ...................................................... 5
10.2.1
............ Service ProceduresSafety Related. Airbag ............................................... 5
10.3
............. Service Procedures ................................................................... 5
10.3.1
............ Service Procedures Working Practices ................................................... 5
10.3.2
............ Service Procedures Working Practices. Fluid Level Check & Topup .......................... 5
10.3.3
............ Service Procedures Working Practices. System Bleed ...................................... 5
10.3.4
............ Service Procedures Working Practices. Fluid Reservoir ..................................... 5
10.3.5.
........... Service Procedures Working Practices. Hydraulic Connections .............................. 5
10.4
............. Diagnostic Procedure ................................................................. 6
10.4.1 ............ Diagnostic Procedure. introduction ..................................................... 6
10.4.2. ........... Diagnostic Procedure. Preliminary Action ................................................ 6
10.4.3 ............ Diagnostic Chart 1 ................................................................... 6
10.4.4. ........... Diagnostic Chart 2 ................................................................... 7
10.4.5 ............ Diagnostic Chart3 ................................................................... 8
10.5
............. Outer Track Rod Ball Joint. Renew ................................ 57.55.02 ............. 9
10.6 ............. Front Hub Assembly, Renew ..................................... 60.25.01 ............. 9
10.7
............. Front Hub Bearing End Float. Check & Adjust ...................... 60.25.12 ............. 9
10.8
............. Front Hub Bearing. Renew ...................................... 60.25.16 ............. 9
10.9
............. Front Hub Oil Seal. Renew ...................................... 60.25.17 ............. 9
X300 VSM i Issue 1 August 1994
Page 200 of 521

10.1 STEERING SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
10.1.1 Steering Column Major Components
Integrated column assembly incorporating power, or manual, reach /tilt mechanism and lock.
Ignition switch.
Ignition interlock solenoid.
Key transponder coil.
Body attachment points.
Depending upon model, the steering column may be adjusted for
tilt and reach, either by electrical or manual means.
Power variants may be either automatically or manually adjusted and all types have the entry / exit feature.
10.1.2 Steering Column Operating Principle
Power Adjust: Two independent motor / gearbox assemblies provide infinite adjustment for reach and height within
approximate ranges of 35mm and
13O respectively. Adjustments may be automatically made in conjunction with the
seat memory facility or manually when the adjustment switch is used. It should be noted that selection of 'Off will
disable the automatic entry / exit mode.
Manual Adjust: The cable operated reach adjustment is infinite within a range of 35mm, with the desired position being
fixed
by a rack and wedge. Tilt variations are stepped at approximately 3O intervals with 6 positions being available,
the uppermost being unlatched.
From the uppermost position the column may be pulled down to engage the first detent without using the
tilt lever.
WARNING: MANUAL ADJUST ONLY: TO AVOID PERSONAL INJURY, COLUMN UPWARD TRAVEL SHOULD BE MAN- UALLY RESTRAINED TO CHECK UPWARD SPRING ASSISTANCE. THIS IS ESPECIALLY IMPORTANT IF
THE STEERING WHEEL HAS BEEN REMOVED FOR MAINTENANCE REASONS.
WARNING: ALL TYPES; DO NOT REMOVE THE STEERING COLUMN FROM THE VEHICLE WITH THE STEERING
WHEEL ATTACHED UNLESS THE STEERING
IS CENTERED AND THE COLUMN LOCK IS ENGAGED. IFTHE
SERVE THIS MAY RESULT IN AN INOPERATIVE AIRBAG SYSTEM. SEE LABEL ON STEERING WHEEL
HUB. LOCK IS TO BE RENEWED, 'LOCK-WIRE THE ASSEMBLY TO PREVENT ROTATION. FAILURE TO OB-
0
X300 VSM 1 Issue 1 August 1994
J57-27L
3 Ignition switch 1 1 Tilt motor 2 Tilt motor flexible coupling 4 Reach motor
Fig.
1 Major components Power operated steering column
Page 206 of 521

10.4.3 Diagnostic chart 2
0 Trouble
'lay at steering wheel
ieavy when stationary
Excessively heavy when
hiving, stationary effort
3K
Too easy when driving,
itationary effort OK
fffort not equal side to
;ide from center
dariation from heavy to
?asy when driving
:yclic load variation at steering wheel - 2 per
.evolution
:losely spaced cyclic
oad variation at steering
Nheel
Cause
Rack damper loose
Pinion bearing loose
Worn intermediate shaft joint
Worn suspension joint
Loose lower column 'pinch' bolt
Transducer not closed
Transducer not closed
- ground short
Transducer not closed
- no feed voltage
Transducer not closed
- defective cable
SCM defective
Delivery pressure or flow too low
Internal rack leakage
tire pressures low
Transducer open too early
Transducer open too early, incorrect SCM
h/Pe
Transducer open too early, incorrect
speedometer signal
Rack 'reaction limitation valve' CLOSED
or setting incorrect
Transducer not open (no oil flow)
Transducer not open, SCM faulty
Transducer not open, incorrect speedom
-
eter signal
Rack 'reaction limiting valve' OPEN or
setting incorrect
Low pressure pipe 'flattened' or re
-
stricted
Blocked reservoir filter
tire pressure high
Rack check valve leak
Rotary valve blockage Incorrect lower column assembly, see
'Cyclic load variations'
Incorrect speedometer signal
Transducer cable
/ connection faulty or
grounded
Lower column universal joint fitting error
Rack damper too tight
Remedy
Renew rack
Renew rack
Renew joint
Renew joint
Tighten to specification
Inspect and check for debris
Renew transducer*
Investigate and repair
Renew cable
Renew module*
Renew pump
Renew rack
Set to specification
Renew transducer*
Renew
SCM*
Renew speedometer transmitter*
Renew rack
Inspect and check for debris
Renew
SCM*
Renew speedometer transmitter*
Renew rack
Renew pipe
Renew filter
Set to specification
Renew rack
Renew rack
Rectify as required
Renew speedometer transmitter*
Investigate and repair
Verify that the lower column assembly is
correct for that drive.
RH and LH assem- blies MUST NOT be interchanged due to
joint phase differences
Renew rack
W: Items marked * should be validated using EDM test procedures.
X300 VSM 7 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 208 of 521
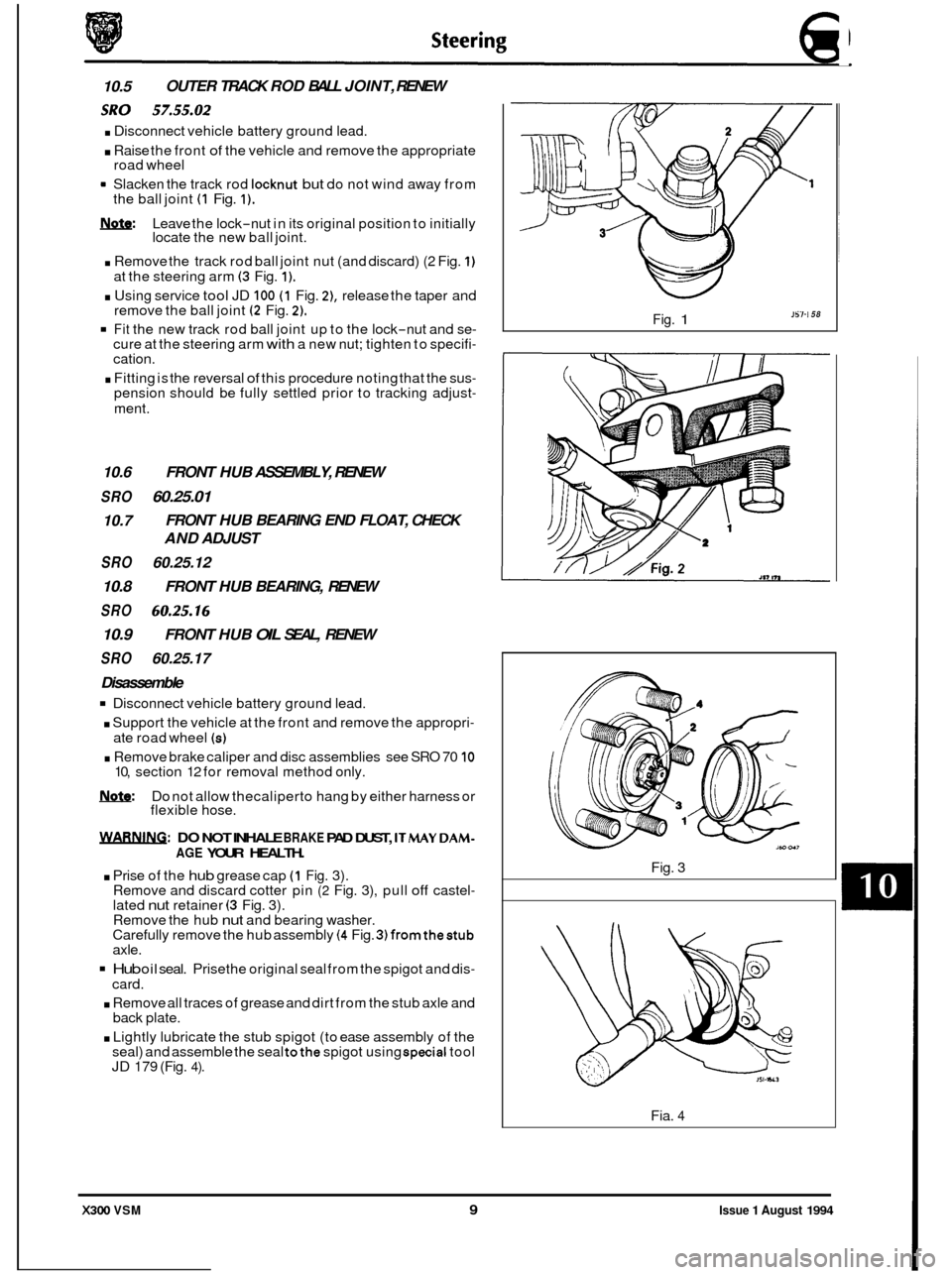
10.5 OUTER
TRACK ROD BALL JOINT, RENEW
sRo . Disconnect 57.55.02 vehicle battery ground lead.
. Raise the front of the vehicle and remove the appropriate
road wheel
Slacken the track rod
locknut but do not wind away from
the ball joint (1 Fig. 1).
m: Leave the lock-nut in its original position to initially
locate the new ball joint.
. Remove the track rod ball joint nut (and discard) (2 Fig. 1)
at the steering arm (3 Fig. 1).
. Using service tool JD 100 (1 Fig. 2), release the taper and
remove the ball joint (2 Fig. 2).
Fit the new track rod ball joint up to the lock-nut and se- cure at the steering arm with a new nut; tighten to specifi- cation.
. Fitting is the reversal of this procedure noting that the sus- pension should be fully settled prior to tracking adjust-
ment.
0 10.6 FRONT HUB ASSEMBLY, RENEW
SRO 60.25.01
10.7
SRO 60.25.12
10.8 FRONT HUB BEARING, RENEW
SRO 60.25.16
10.9
SRO 60.25.17
Disassemble
Disconnect vehicle battery ground lead.
. Support the vehicle at the front and remove the appropri-
. Remove brake caliper and disc assemblies see SRO 70 10
IWQ: Do not allow thecaliperto hang by either harness or
flexible hose.
FRONT HUB BEARING END FLOAT, CHECK
AND ADJUST
FRONT HUB
OIL SEAL, RENEW
ate road wheel (s)
10, section 12 for removal method only.
WARNIM: DO NOT INHALE BRAKE PAD DUST, ITMAY DAM-
0
AGE YOUR HEALTH.
. Prise of the hub grease cap (1 Fig. 3).
Remove and discard cotter pin (2 Fig. 3), pull off castel- lated nut retainer (3 Fig. 3).
Remove the hub nut and bearing washer.
Carefully remove the hub assembly (4 Fig. 3)fromthestub axle.
Hub oil seal. Prise the original seal from the spigot and dis-
card.
. Remove all traces of grease and dirt from the stub axle and
back plate.
. Lightly lubricate the stub spigot (to ease assembly of the
seal) and assemble the seal tothe spigot using special tool JD 179 (Fig. 4).
JS7-i 58 Fig. 1
Fig. 3
Fia.
4
X300 VSM 9 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 217 of 521

Suspension Systems
11.4.3 Front End Inspection
Do not check and adjust front wheel alignment without carrying out the following inspection for front end damage and
wear:
. Check for specified air pressure in all four tires.
Raise front of vehicle off the floor; grasping upper and lower surface of the tire, shake each front wheel to check for
. Check front suspension lower arm ball joint and mounts for looseness, wear and damage.
Check steering gear mountings and all steering linkages for looseness.
. Renew parts if necessary.
. Grasp upper and lower surface of tire and shake each wheel to check wheel bearing end play.
. Check the action of the front dampers and the condition of their attachments, as sticking or binding front dampers
worn
bearings.
Check brake caliper mountings.
may not allow the vehicle to settle in to a normal level position, possibly affecting the front-wheel alignment.
m: Front wheel bearings are adjustable (0.001 to 0.003 in. endfloat).
11.4.4
. Check the wheel bearings.
. Inspect the front suspension upper joint and renew front suspension lower wishbone if needed.
Raise vehicle and position floor jacks beneath the front suspension lower wishbone.
Grasp the lower edge of the tire and move the wheel in and out.
While moving the wheel, observe the upper and lower wishbone.
. Movement between the vertical links and the wishbones indicates abnormal ball joint wear.
. Renew ball joints.
. Check the front wheel bearings.
. Check for excessive play and wear.
Upper / Lower Ball Joint Inspection
11.4.5 Damper Inspection
m: The gas-pressurized hydraulic front dampers are not serviceable, adjustable or refillable.
Verify that all attachments of the suspension components and the front dampers are tight. Renew any front damper
. Check front dampers for external damage.
. Check for oil leakage and vehicle sag.
that
has a damaged integral lower mounting bushing.
0 Oil Leak
Leakage is the condition in which the entire damper body is covered with oil and from where
it will drip on to
the pavement. Due to correct damper lubrication a light film of oil (weepage) can usually be seen on the upper
portion of the damper.
Should there be any leakage, ensure that the fluid does not originate from sources other than the front damper.
Renew worn or damaged dampers.
0 Vehicle Sag
Renewing front dampers will not correct the problem of vehicle sag, as basically this is controlled by the spring
units.
issue 1 August 1994 4 X300 VSM
Page 310 of 521

Climate Control Systems
SECTION CONTENTS
Subsection Title SRO Page
i to iii ............ Preliminary Pages ................................................................ i to iii
14.1
............. Working Practices .................................................................... 1
Working Practices. General ............................................................ 1 14.1.1 ............
14.1.2. ........... Working Practices. Handling Refrigerant ................................................. 1
14.1.3 ............ Working Practices. Handling Lubricating Oil ............................................. 2
14.1.4
............ Working Practices. System Maintenance ................................................. 2
14.2
............. Climate ControlSystem ............................................................... 3
14.2.1
............ Climate Control System. Description .................................................... 3
14.2.2.
........... Climate Control System. Features ....................................................... 3
14.3
............. ClimateControl Panel ................................................................ 4
14.4
.............
14.4.1 ............ Temperature Control. Coolant Circuit .................................................... 6
14.5 ............. Air Conditioning Control Module ....................................................... 7
14.5.1 ............ Air Conditioning Control Module. Description 7
14.5.2. ........... Air Conditioning Control Module. Interfaces .............................................. 8
14.6
............. Control Module Fault & Condition Self-Analysis .......................................... 9
14.6.1
............ Control Module Fault & Condition Self-Analysis. System Health ............................. 9
14.6.2.
........... Control Module Fault & Condition Self-Analysis. System Protection .......................... 9
14.7
............. Air Distribution ..................................................................... 10
14.8
............. Refrigeration Cycle .................................................................. 12
14.9
............. General System Procedures ........................................................... 13
14.9.1
............ General System Procedures. Leak Test .................................................. 13
14.9.2
............ General System Procedures. Charge Recovery (System Depressurization) .................... 13
14.9.3.
........... General System Procedures. Evacuating the System ....................................... 13
14.9.4.
........... General System Procedures. Adding Lubricating Oil (Compressor Related) ................... 13
14.9.5.
........... General System Procedures. Adding Lubricating Oil (Component Related) ................... 14
14.9.6.
........... General System Procedures. Adding Refrigerant .......................................... 14
14.10
............ Fault Diagnosis ..................................................................... 15
14.10.1
.......... Fault Diagnosis. Introduction .......................................................... 15
14.10.2
.......... FaultDiagnosis. FunctionalCheck ..................................................... 15
14.10.3
14.11
............ Systemself- Test .................................................................... 17
14.1 1.1 ........... System Self- Test. Interrogation Procedure via the Control Panel ............................ 17
14.1 1.2 ........... System Self- Test. Control Panel Fault Code Key ......................................... 17
14.1 1.4 ........... System Self- Test. Panel Communication Check .......................................... 18
14.13
............ System Checking With Manifold Gauge Set ............................................. 20
14.7 3.1 .......... System Checking With Manifold Gauge Set. Evacuating the Gauge Set ...................... 20
14.13.2 .......... System Checking With Manifold Gauge Set. Connecting the Manifold Gauge Set .............. 20
14.13.3
.......... System Checking With Manifold Gauge Set. Stabilizing the System ......................... 20
14.14
............ Pressure / Temperature Graph (High Side / Ambient Temperature) ........................... 21
14.15
............ Pressure / Temperature Graph (Low Side / Evaporator Temperature) ......................... 22
14.16
............ System Pressure Fault Classification ................................................... 23
Temperature
Control
.................................................................. 6
............................................ a
.......... Fault Diagnosis. System Symptoms ..................................................... 15 a
14.1 1.3 ........... System Self- Test. Associated Faults .................................................... 18
14.12
............ Manifold Gauge Set ................................................................. 19
X300 VSM ~ i Issue 1 August 1994