1993 VOLKSWAGEN CORRADO engine coolant
[x] Cancel search: engine coolantPage 510 of 920

E - THEORY/OPERATION
Article Text (p. 5)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PM
NOTE: Corrado SLC models are equipped with a Distributorless
Ignition System (DIS).
ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM
The electronic ignition system consists of ECM, power output
stage, ignition coil, distributor, mass airflow sensor, throttle valve
potentiometer, engine coolant temperature sensor, and Hall Effect
sensor.
Ignition system uses engine speed, engine load, and throttle
valve potentiometer signals to calculate ignition timing. Engine
coolant temperature signal is used to correct ignition timing when
engine is cold and to activate knock sensor circuit. See KNOCK
SENSOR(S) under IGNITION TIMING CONTROL in this article.
Hall Effect Sensor
On Corrado SLC, this sensor is mounted on end of camshaft
(near ignition coil). Sensor consists of a magnetic enclosure and
integrated semi-conductor circuit. A voltage signal is generated when
trigger wheel, turning at camshaft speed, interrupts magnetic field
created by the semi-conductor. Hall Effect sensor and engine
speed/reference signals are used to identify TDC position of cylinder
No. 1 for sequential fuel injection and spark knock regulation.
DISTRIBUTORLESS IGNITION SYSTEM (DIS)
Hall Effect Sensor
See HALL EFFECT SENSOR under ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM in
this article.
Ignition Coil & Output Stage
The distributorless (direct) ignition system consists of ECM,
power output stage, 3 double-ended ignition coils and secondary
ignition wires. The ECM operates each ignition coil through the power
output stage. The power output stage and heat sink are located behind
ignition coils. The ignition coils are located on left side of
cylinder head. When the power output stage fires an ignition coil, a
spark is supplied to 2 spark plugs at one time. One spark plug fires
during the compression stroke, and the other spark plug fires during
the exhaust stroke (waste spark).
IGNITION TIMING CONTROL
Knock Sensor(s)
The knock sensor(s) work(s) like a microphone to "listen" for
spark knock (detonation). When detonation occurs, ignition timing is
retarded until the knock is eliminated.
On Corrado SLC, 2 knock sensors are mounted on side of engine
block. Knock sensor I monitors cylinders No. 1, 3 and 5. Knock sensor
II monitors cylinders No. 2, 4 and 6.
Page 511 of 920

E - THEORY/OPERATION
Article Text (p. 6)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PM
EMISSION SYSTEMS
AIR INJECTION SYSTEM
The air injection system consists of electrically operated
air pump, inlet valve, shut-off valve (mounted between intake ports
for cylinders No. 2 and 4), and air pump control relay.
The Electronic Control Module (ECM) control operation of air
injection system air pump by completing the ground circuit of the air
pump control relay (located above brake master cylinder). In addition,
the relay operates the secondary air injection inlet valve.
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
The EGR system consist of EGR valve, EGR frequency valve, and
EGR temperature sensor. All Corrado SLC models are equipped with the
EGR system. The EGR system is switched on when engine coolant
temperature reaches 122øF (50øC). The system recirculates a small
portion of exhaust gas into the intake air/fuel mixture to reduce
nitrous oxide emissions (NOx).
EGR Frequency Valve
The EGR frequency valve is mounted on back of intake
manifold. The frequency valve controls the amount of vacuum supplied
to the EGR valve. The ECM, depending on engine speed and load,
controls the frequency valve's ground circuit. In doing so, the ECM
controls the amount of recirculated exhaust gas entering the engine.
EGR Temperature Sensor
Sensor is located in EGR valve exhaust gas recirculation
channel. The EGR temperature sensor measures exhaust gas temperature.
The electrical resistance of the sensor decreases as the temperature
of the exhaust gas increases. The signal generated by the EGR
temperature sensor is ONLY used for diagnosis of the EGR system.
FUEL EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS SYSTEM
Fuel Evaporative (Frequency) Valve
The ECM determines the duty cycle of the frequency valve to
regulate the flow of fuel vapors from fuel evaporative (carbon)
canister into engine. When no current is supplied to valve, it remains
in the open position. The valve is closed (100% duty cycle) when the
engine is started cold. A spring operated check valve inside the
frequency valve closes when the engine is off. This prevents fuel
vapors from entering intake manifold and causing a rich mixture during
engine restart.
Fuel Tank Venting
The engine speed, engine load, engine coolant temperature,
and throttle valve potentiometer input signals are used by the ECM to
control fuel tank venting. Fuel vapors from fuel tank are vented to
fuel evaporative (carbon) canister. When engine is warm and above idle
Page 512 of 920

E - THEORY/OPERATION
Article Text (p. 7)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PM
speed, the vapors will be drawn into intake manifold. Depending on
engine load and oxygen sensor signal, the fuel evaporative (frequency)
valve will regulate the amount of vapors entering the intake manifold.
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
The Electronic Control Module (ECM) recognizes faults (open
circuits, short circuits, missing signals, or a continuously applied
signal voltage) in the following circuits/components.
* EGR Frequency Valve
* EGR Temperature Sensor
* Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
* Engine Speed (RPM)/Reference Sensor
* Fuel Evaporative (Frequency) Valve
* Hall Effect Sensor
* Idle Air Control/Stabilizer Valve
* Intake Air Temperature Sensor
* Knock Sensor(s)
* Throttle Valve Potentiometer
* Oxygen Sensor
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR (CHECK ENGINE) LIGHT
All California models are equipped with a malfunction
indicator (CHECK ENGINE) light. If CHECK ENGINE light comes on and
remains on during vehicle operation, cause of malfunction must be
determined. See the G - TESTS W/CODES article.
END OF ARTICLE
Page 523 of 920
EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
Article Text (p. 9)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
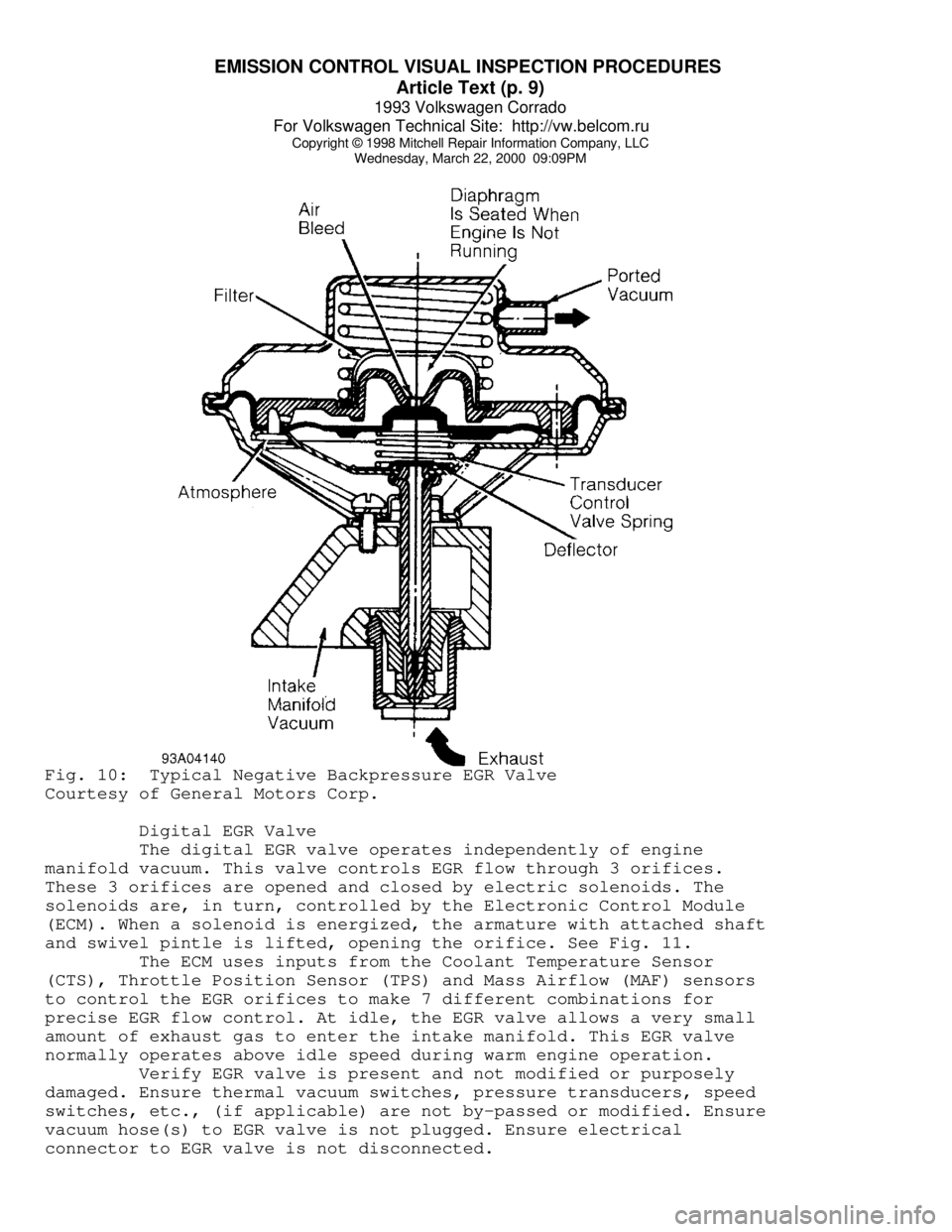
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:09PMFig. 10: Typical Negative Backpressure EGR Valve
Courtesy of General Motors Corp.
Digital EGR Valve
The digital EGR valve operates independently of engine
manifold vacuum. This valve controls EGR flow through 3 orifices.
These 3 orifices are opened and closed by electric solenoids. The
solenoids are, in turn, controlled by the Electronic Control Module
(ECM). When a solenoid is energized, the armature with attached shaft
and swivel pintle is lifted, opening the orifice. See Fig. 11.
The ECM uses inputs from the Coolant Temperature Sensor
(CTS), Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) and Mass Airflow (MAF) sensors
to control the EGR orifices to make 7 different combinations for
precise EGR flow control. At idle, the EGR valve allows a very small
amount of exhaust gas to enter the intake manifold. This EGR valve
normally operates above idle speed during warm engine operation.
Verify EGR valve is present and not modified or purposely
damaged. Ensure thermal vacuum switches, pressure transducers, speed
switches, etc., (if applicable) are not by-passed or modified. Ensure
vacuum hose(s) to EGR valve is not plugged. Ensure electrical
connector to EGR valve is not disconnected.
Page 565 of 920

ENGINE OVERHAUL PROCEDURES - GENERAL INFORMATION
Article Text (p. 36)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:10PM
to ensure correct amount of oil has filled crankcase. Check oil level
while pre-oiling.
If pressure oiler is not available, disconnect ignition
system. Remove oil pressure sending unit and replace with oil pressure
test gauge. Using starter motor, rotate engine starter until gauge
shows normal oil pressure for several seconds. DO NOT crank engine
for more than 30 seconds to avoid starter motor damage.
Ensure oil pressure has reached the most distant point from
the oil pump. Reinstall oil pressure sending unit. Reconnect ignition
system.
INITIAL START-UP
Start the engine and operate engine at low speed while
checking for coolant, fuel and oil leaks. Stop engine. Recheck coolant
and oil level. Adjust if necessary.
CAMSHAFT
Break-in procedure is required when a new or reground
camshaft has been installed. Operate and maintain engine speed between
1500-2500 RPM for approximately 30 minutes. Procedure may vary due to
manufacturers recommendations.
PISTON RINGS
Piston rings require a break-in procedure to ensure seating
of rings to cylinder walls. Serious damage may occur to rings if
correct procedures are not followed.
Extremely high piston ring temperatures are produced obtained
during break-in process. If rings are exposed to excessively high RPM
or high cylinder pressures, ring damage can occur. Follow piston ring
manufacturer's recommended break-in procedure.
FINAL ADJUSTMENTS
Check or adjust ignition timing and dwell (if applicable).
Adjust valves (if necessary). Adjust carburetion or injection idle
speed and mixture. Retighten cylinder heads (if required). If
cylinder head or block is aluminum, retighten bolts when engine is
cold. Follow the engine manufacturer's recommended break-in procedure
and maintenance schedule for new engines.
NOTE: Some manufacturer's require that head bolts be retightened
after specified amount of operation. This must be done to
prevent head gasket failure.
END OF ARTICLE
Page 575 of 920

F - BASIC TESTING
Article Text (p. 10)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:10PM
to specification. If necessary, see the appropriate D - ADJUSTMENTS
article in this section. Refer to the following menu:
NOTE: For the appropriate D - ADJUSTMENTS article, go to:
* For Cabriolet, see: D - ADJUSTMENTS
* For Corrado SLC, see: D - ADJUSTMENTS
* For EuroVan, see: D - ADJUSTMENTS
* For Fox, see: D - ADJUSTMENTS
* For Golf, GTI, Jetta, see: D - ADJUSTMENTS
* For Passat GL 2.0L 4-Cylinder, see: D - ADJUSTMENTS - 4-CYL
* For Passat GLX 2.8L VR6, see: D - ADJUSTMENTS - VR6
IDLE SPEED & CO LEVELÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄApplication Idle RPM CO Level %
Cabriolet (1)
Digifant I ............. 750-850 ......... 0.3-1.2
Digifant II ............ 750-850 ......... 0.3-1.1
Corrado SLC (2) ......... 650-750 ......... 0.3-1.5
Fox ................... (3) 875-925 ....... 0.3-1.2
Golf, Jetta & GTI (2)
800-880
0.3-1.2
Passat GL ............ (4) 800-1000 ....... 0.2-1.2
Passat GLX (2) .......... 650-750 ......... 0.3-1.5
(1) - With engine running, after reconnecting Blue coolant
temperature sensor. See the D - ADJUSTMENTS article
in this section for more information. See menu above.
(2) - Idle speed and fuel mixture (CO level) are not
adjustable.
(3) - If A/C equipped, disconnect idle speed boost valve
harness connector when checking idle speed. Clamp
crankcase breather hose near emission control valve
when checking CO level.
(4) - Idle speed is not adjustable.
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄIGNITION TIMING (Degrees BTDC @ RPM)
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄApplication Checking Adjusting
Cabriolet (1) ....... 4-8 @ 2000-2500 .. 5-7 @ 2000-2500
Corrado SLC ............... (2) .................... (2)
Fox (1) ............. 4-8 @ 2000-2500 .. 5-7 @ 2000-2500
Golf, GTI & Jetta ... (3) 12 @ 800-880 ............ .....
Passat GL ........... 4-8 @ 800-1000 .... 5-7 @ 800-1000
Passat GLX ................ (2) .................... (2)
(1) - On Digifant I systems, ensure engine oil temperature
Page 576 of 920

F - BASIC TESTING
Article Text (p. 11)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:10PM
is 176øF (80øC) and Blue engine coolant temperature
sensor is disconnected.
(2) - Ignition timing is computer controlled. Information
is not available from manufacturer.
(3) - Using Scan Tester (VAG 1551) in START BASIC SETTING
mode. Ignition timing is not adjustable.
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄIGNITION TIMING ADVANCE (Degrees BTDC @ RPM)
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄApplication Specification
Cabriolet
Digifant I (California) .......... (1) 27-33 @ 4500
Digifant II (Other 49 States) .... (1) 20-30 @ 2300
Fox
Digifant I (California) .......... (1) 27-33 @ 4500
Digifant II (Other 49 States) .... (1) 20-30 @ 2300
All Other Models ................................ (2)
(1) - With Blue engine coolant temperature sensor
connected. Specification is in addition to the
initial setting.
(2) - Ignition timing advance is computer controlled.
Information is not available from manufacturer.
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ SUMMARY
If no faults were found while performing the tests in this
article, see H - TESTS W/O CODES article in this section for diagnosis
by symptom (i.e., ROUGH IDLE, NO START, etc.) or intermittent
diagnostic procedures.
END OF ARTICLE
Page 585 of 920

G - TESTS W/CODES
Article Text (p. 3)
1993 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Wednesday, March 22, 2000 09:11PMÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ TROUBLE CODE IDENTIFICATION
TROUBLE CODE IDENTIFICATION (CORRADO SLC) (1)
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄDTC (2) System/ Possible
(Blink) Code Affected Circuit Cause/Repair
00281 (1231 ......... Vehicle Speed Sensor .... Open Ckt (No Signal
From Speedometer)
00513 (2111) ....... Engine Speed Sensor ....... Open Ckt Or Loose
Or Faulty Sensor
00515 (2113) ........ Hall Effect Sensor ....... Open/Short Ckt To
Ground Or Battery
Voltage
00518 (2212) ... Throttle Valve Potentiometer .. Open/Short Ckt To
Ground Or Battery
Voltage
00522 (2312) ....... Coolant Temp. Sensor ...... Open/Short Ckt To
Ground Or Battery
Voltage
00524 (2142) ......... Knock Sensor I ...... Open Ckt Or Short Ckt
To Battery Voltage
00525 (2342) ....... Oxygen (O2) Sensor ........ Open/Short Ckt To
Ground Or Battery
Voltage
00527 (2412) .... Intake Air Temp. Sensor ...... Open/Short Ckt To
Ground Or Battery
Voltage
00532 (2234) ........ Supply Voltage ........ Battery Voltage Less
Than 10.0 Volts Or
More Than 16.0 Volts
00533 (2231) .. Idle (IAC Valve) Regulation .. Intake System Leaks
Or IAC Valve Stuck
Or Dirty
00535 (2141) ..... Knock Sensor (Primary) ........ Defective Knock
Sensor In ECM
(Replace ECM)
00537 (2341) .. Oxygen (O2) Sensor Regulation ... (3) Control Limit
Exceeded Or Not
Reached
00540 (2144) ....... Knock Sensor II .......... Open/Short Ckt (No
Signal to ECM
00543 (2214) .... Maximum RPM Exceeded .. RPM Signal Interference;
Engine RPM Exceeded
Cut-Off Point
00545 (2314) ... Engine/Transmission Signal .. Short Ckt To Ground
00553 (2324) ..... Mass Airflow Sensor ....... Short Ckt To Ground
Or Battery Voltage
00561 (2313) ... Fuel Mixture Adaptation .... ... (4) Control Limit
Not Reached Or