1993 FORD MONDEO service interval
[x] Cancel search: service intervalPage 17 of 279

Ford Mondeo maintenance schedule
1•3
1
Maintenance schedule
The manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for these
vehicles is as described below - note that the schedule starts from the
vehicle’s date of registration. These are the minimum maintenance
intervals recommended by the factory for Mondeos driven daily, but
subjected only to “normal” use. If you wish to keep your vehicle in
peak condition at all times, you may wish to perform some of these
procedures even more often. Because frequent maintenance
enhances the efficiency, performance and resale value of your vehicle,
we encourage you to do so. If your usage is not “normal”, shorter
intervals are also recommended - the most important examples of
these are noted in the schedule. These shorter intervals apply
particularly if you drive in dusty areas, tow a caravan or trailer, sit with
the engine idling or drive at low speeds for extended periods (ie, in
heavy traffic), or drive for short distances (less than four miles) in
below-freezing temperatures.
When your vehicle is new, it should be serviced by a Ford dealer
service department to protect the factory warranty. In many cases, the
initial maintenance check is done at no cost to the owner. Note that
this first free service (carried out by the selling dealer 1500 miles or 3
months after delivery), although an important check for a new vehicle,
is not part of the regular maintenance schedule, and is therefore not
mentioned here.
Weekly checks
m mCheck the engine oil level, and top-up if necessary
(Section 3)
m mCheck the brake fluid level, and top-up if necessary
(Section 3). If repeated topping-up is required, check the
system for leaks or damage at the earliest possible
opportunity (Sections 12 and 22)
m mCheck the windscreen/tailgate washer fluid level, and top-
up if necessary (Section 3)
m mCheck the tyre pressures, including the spare (Section 4)
m mVisually check the tyres for excessive tread wear, or
damage (Section 4)
m mCheck the operation of all (exterior and interior) lights and
the horn, wipers and windscreen/tailgate washer system
(Sections 6 and 8). Renew any blown bulbs (Chapter 12),
and clean the lenses of all exterior lights
Monthly checks
m mCheck the coolant level, and top-up if necessary (Sec-
tion 3)
m mCheck the battery electrolyte level, where applicable
(Section 3)
m mCheck the power steering fluid level, and top-up if
necessary (Section 5)
m mVisually check all reservoirs, hoses and pipes for leakage
(Section 12)
m mCheck the operation of the air conditioning system
(Section 14)
m mCheck the operation of the handbrake (Section 23)
m mCheck the aim of the windscreen/tailgate/headlight
washer jets, correcting them if required (Section 6)
m mCheck the condition of the wiper blades, renewing them if
worn or no longer effective - note that the manufacturer
recommends renewing the blades as a safety precaution,
irrespective of their apparent condition, at least once a
year (Section 6)
Every 10 000 miles or 12 months,
whichever occurs first
Note:If the vehicle is used regularly for very short (less than
10 miles), stop/go journeys, the oil and filter should be renewed
between services (ie, every 5000 miles/6 months).
m mCheck the electrical system (Section 8)
m mCheck the battery (Section 9)
m mCheck the seat belts (Section 10)
m mCheck the auxiliary drivebelt (Section 11)
m mCheck for fluid leaks and hose condition (Section 12)
m mCheck the condition of all wiring (Section 13)
m mCheck all air conditioning components (Section 14)
m mChange the engine oil and filter (Section 15)
m mCheck the manual transmission oil level (Section 16)
m mCheck the adjustment of the clutch pedal (Section 17)
m mLubricate the automatic transmission linkage (Section 18)
m mCheck the steering, suspension and wheels (Section 19)
m mCheck the driveshaft gaiters and CV joints (Section 20)
m mCheck the exhaust system (Section 21)
m mCheck the underbody, and all fuel/brake lines (Section 22)
m mCheck the brake system (Section 23)
m mCheck and lubricate the doors and bonnet (Section 24)
m mCheck the security of all roadwheel nuts (Section 25)
m mRoad test (Section 26). Check the level of the automatic
transmission fluid with the engine still hot, after the road
test (Section 7)
Every 20 000 miles or 2 years,
whichever occurs first
Carry out all operations listed above, plus the following:
m mRenew the ventilation system pollen filter (Section 27)
m mRenew the coolant (Sections 2 and 28)
Every 30 000 miles or 3 years,
whichever occurs first
Carry out all operations listed above, plus the following:
m mRenew the air filter element (Section 29). Note that this
task must be carried out at more frequent intervals if the
vehicle is used in dusty or polluted conditions
m mCheck the Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system,
and clean the filter (Section 30)
m mRenew the spark plugs (Section 31)
Every 60 000 miles
Carry out all operations listed above, plus the following:
m
mRenew the timing belt (Section 32)
m mRenew the fuel filter (Section 33)
Every 3 years
(regardless of mileage)
m mRenew the brake fluid (Section 34)
procarmanuals.com
Page 20 of 279

This Chapter is designed to help the home
mechanic maintain the Ford Mondeo models
for peak performance, economy, safety and
long life.
On the following pages are Sections
dealing specifically with each item on the
maintenance schedule. Visual checks,
adjustments, component replacement and
other helpful items are included. Refer to the
accompanying illustrations of the engine
compartment and the underside of the vehicle
for the location of various components.
Servicing your Mondeo in accordance with
the mileage/time maintenance schedule and
the following Sections will provide it with a
planned maintenance programme, which
should result in a long and reliable service life.
This is a comprehensive plan, so maintaining
some items but not others at the specified
service intervals will not produce the same
results.
As you service your Mondeo, you will
discover that many of the procedures can -
and should - be grouped together, because of
the nature of the particular procedure you’re
performing, or because of the close proximity
to one another of two otherwise-unrelated
components.
For example, if the vehicle is raised for anyreason, you should inspect the exhaust,
suspension, steering and fuel systems while
you’re under the vehicle. When you’re
checking the tyres, it makes good sense to
check the brakes and wheel bearings,
especially if the roadwheels have already
been removed.
Finally, let’s suppose you have to borrow or
hire a torque wrench. Even if you only need to
tighten the spark plugs, you might as well
check the torque of as many critical fasteners
as time allows.
The first step of this maintenance
programme is to prepare yourself before the
actual work begins. Read through all the
Sections which are relevant to the procedures
you’re planning to carry out, then make a list
of, and gather together, all the parts and tools
you will need to do the job. If it looks as if you
might run into problems during a particular
segment of some procedure, seek advice
from your local parts man or dealer service
department.
Ford state that, where antifreeze to
specification ESD-M97B-49-A (the type with
which the vehicle’s cooling system would
have been filled on production at the factory)
is used, it will last the lifetime of the vehicle.This is subject to it being used in the
recommended concentration, unmixed with
any other type of antifreeze or additive, and
topped-up when necessary using only that
antifreeze mixed 50/50 with clean water. If any
other type of antifreeze is added, the lifetime
guarantee no longer applies; to restore the
lifetime protection, the system must be
drained and thoroughly reverse-flushed
before fresh coolant mixture is poured in.
If the vehicle’s history (and therefore the
quality of the antifreeze in it) is unknown,
owners who wish to follow Ford’s
recommendations are advised to drain and
thoroughly reverse-flush the system, as
outlined in Section 28, before refilling with
fresh coolant mixture. If the appropriate
quality of antifreeze is used, the coolant can
then be left for the life of the vehicle.
If any antifreeze other than Ford’s is to be
used, the coolant must be renewed at regular
intervals to provide an equivalent degree of
protection; the conventional recommendation
is to renew the coolant every two years.
The above assumes the use of a mixture (in
exactly the specified concentration) of clean,
soft water and of antifreeze to Ford’s
specification or equivalent. It is also assumed
that the cooling system is maintained in a
scrupulously-clean condition, by ensuring that
only clean coolant is added on topping-up,
and by thorough reverse-flushing whenever
the coolant is drained (Section 28).
2 Coolant renewal
1 Introduction
1•6Weekly checks
Weekly checks
General
1Fluids are an essential part of the
lubrication, cooling, braking and other
systems. Because these fluids gradually
become depleted and/or contaminated during
normal operation of the vehicle, they must be
periodically replenished. See “Lubricants and
fluids and capacities”at the beginning of this
Chapter before adding fluid to any of the
following components. Note:The vehicle
must be on level ground before fluid levels can
be checked.
Engine oil
2The engine oil level is checked with a
dipstick located at the front of the engine; it
can be identified by its yellow/black plastic
grip (see illustration). The dipstick extends
through a metal tube, from which it protrudes
down into the sump at the bottom of the
engine.
3The oil level should be checked before the
vehicle is driven, or about 5 minutes after the
engine has been switched off.4Pull the dipstick from the tube, and wipe all
the oil from the end with a clean rag or paper
towel; note the dipstick’s maximum and
minimum levels, indicated by notches (seeillustration). Insert the clean dipstick all the way
back into its metal tube, and pull it out again.
Observe the oil on the end of the dipstick; its
level should be between these two notches.
5Do not allow the level to drop below the
minimum level notch, or oil starvation may
cause engine damage. Conversely, overfilling
the engine (adding oil above the maximum
level notch) may cause oil-fouled spark plugs,
oil leaks or oil seal failures.
6The yellow/black plastic oil filler cap is
screwed into the left-hand front end of the
3 Fluid level checks
3.2 The engine oil dipstick (arrowed) is
located at the front of the engine - note
yellow/black plastic grip
3.4 The oil level should be at or near the
maximum level notch (A) - if not, add
enough oil to correct the level. It takes
approximately 0.5 to 1.0 litre of oil to raise
the level from the minimum level notch (B)
to the maximum
If the level is checked
immediately after driving the
vehicle, some of the oil will
remain in the engine upper
components, producing an inaccurate
dipstick reading.
procarmanuals.com
Page 33 of 279
evidence of leaks, severe corrosion, or
damage. Make sure that all brackets and
rubber mountings are in good condition, and
tight; if any of the mountings are to be
renewed, ensure that the replacements are of
the correct type (see illustration). Leakage at
any of the joints or in other parts of the system
will usually show up as a black sooty stain in
the vicinity of the leak. Note:Exhaust sealants
should not be used on any part of the exhaust
system upstream of the catalytic converter -
even if the sealant does not contain additives
harmful to the converter, pieces of it may
break off and foul the element, causing local
overheating.
3At the same time, inspect the underside of
the body for holes, corrosion, open seams,
etc. which may allow exhaust gases to enter
the passenger compartment. Seal all body
openings with silicone or body putty.
4Rattles and other noises can often be
traced to the exhaust system, especially the
rubber mountings. Try to move the system,
silencer(s) and catalytic converter. If any
components can touch the body or
suspension parts, secure the exhaust system
with new mountings.
5Check the running condition of the engine
by inspecting inside the end of the tailpipe;
the exhaust deposits here are an indication of
the engine’s state of tune. The inside of the
tailpipe should be dry, and should vary in
colour from dark grey to light grey/brown; if it
is black and sooty, or coated with white
deposits, the engine is in need of a thorough
fuel system inspection.
1With the vehicle raised and supported on
axle stands or over an inspection pit,
thoroughly inspect the underbody and wheel
arches for signs of damage and corrosion. In
particular, examine the bottom of the side
sills, and any concealed areas where mud can
collect. Where corrosion and rust is evident,press and tap firmly on the panel with a
screwdriver, and check for any serious
corrosion which would necessitate repairs. If
the panel is not seriously corroded, clean
away the rust, and apply a new coating of
underseal. Refer to Chapter 11 for more
details of body repairs.
2At the same time, inspect the PVC-coated
lower body panels for stone damage and
general condition.
3Inspect all of the fuel and brake lines on the
underbody for damage, rust, corrosion and
leakage. Also make sure that they are
correctly supported in their clips. Where
applicable, check the PVC coating on the
lines for damage.
Note:For detailed photographs of the brake
system, refer to Chapter 9.
1The work described in this Section should
be carried out at the specified intervals, or
whenever a defect is suspected in the braking
system. Any of the following symptoms could
indicate a potential brake system defect:
(a) The vehicle pulls to one side when the
brake pedal is depressed.
(b) The brakes make scraping or dragging
noises when applied.
(c) Brake pedal travel is excessive.
(d) The brake fluid requires repeated topping-
up.
2A brake pad wear warning light is fitted, and
it is illuminated when the thickness of the front
(or rear) disc brake pad linings reach the
minimum amount. However, a physical check
should be made to confirm the thickness of
the linings, as follows.
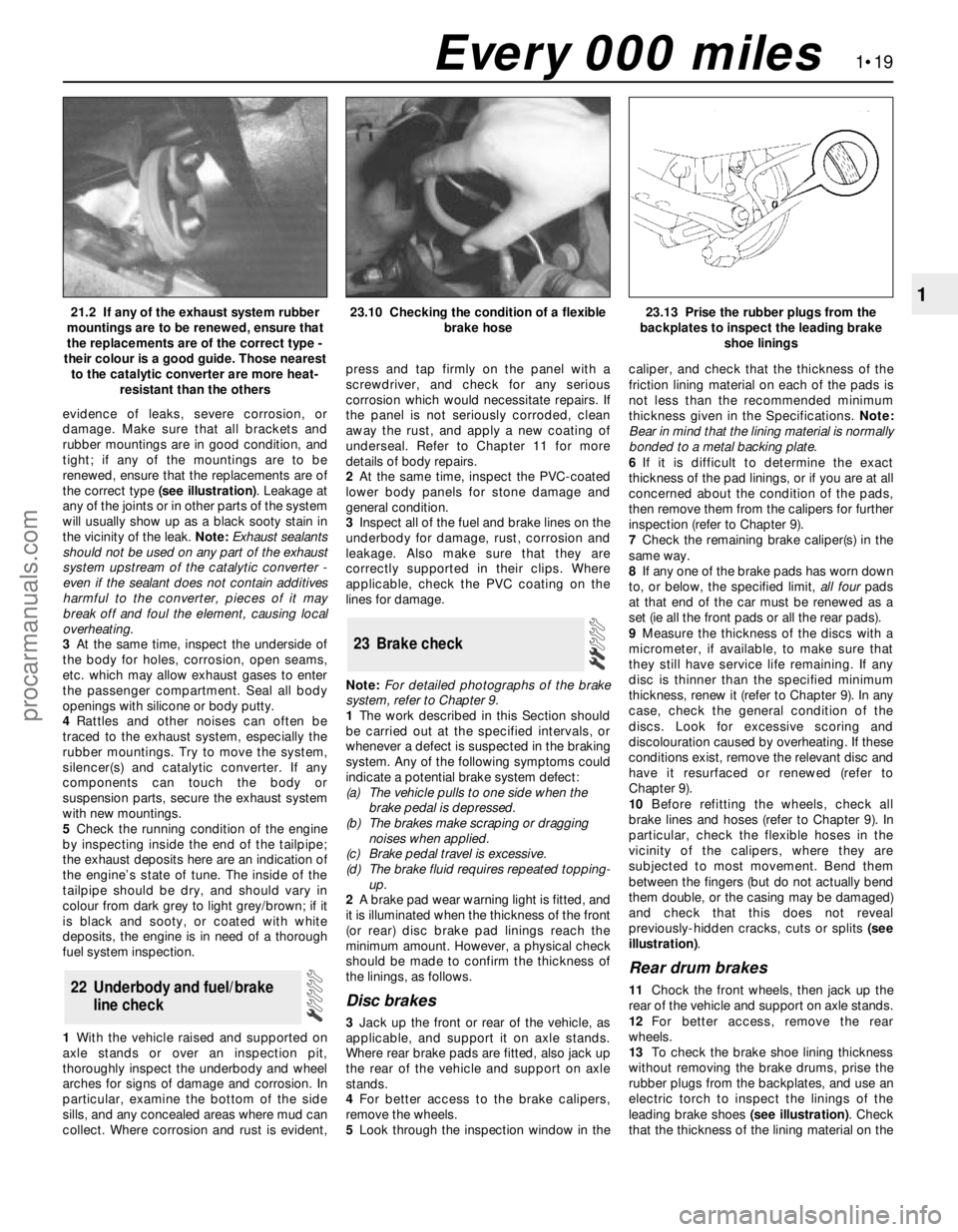
Disc brakes
3Jack up the front or rear of the vehicle, as
applicable, and support it on axle stands.
Where rear brake pads are fitted, also jack up
the rear of the vehicle and support on axle
stands.
4For better access to the brake calipers,
remove the wheels.
5Look through the inspection window in thecaliper, and check that the thickness of the
friction lining material on each of the pads is
not less than the recommended minimum
thickness given in the Specifications. Note:
Bear in mind that the lining material is normally
bonded to a metal backing plate.
6If it is difficult to determine the exact
thickness of the pad linings, or if you are at all
concerned about the condition of the pads,
then remove them from the calipers for further
inspection (refer to Chapter 9).
7Check the remaining brake caliper(s) in the
same way.
8If any one of the brake pads has worn down
to, or below, the specified limit, all fourpads
at that end of the car must be renewed as a
set (ie all the front pads or all the rear pads).
9Measure the thickness of the discs with a
micrometer, if available, to make sure that
they still have service life remaining. If any
disc is thinner than the specified minimum
thickness, renew it (refer to Chapter 9). In any
case, check the general condition of the
discs. Look for excessive scoring and
discolouration caused by overheating. If these
conditions exist, remove the relevant disc and
have it resurfaced or renewed (refer to
Chapter 9).
10Before refitting the wheels, check all
brake lines and hoses (refer to Chapter 9). In
particular, check the flexible hoses in the
vicinity of the calipers, where they are
subjected to most movement. Bend them
between the fingers (but do not actually bend
them double, or the casing may be damaged)
and check that this does not reveal
previously-hidden cracks, cuts or splits (see
illustration).
Rear drum brakes
11Chock the front wheels, then jack up the
rear of the vehicle and support on axle stands.
12For better access, remove the rear
wheels.
13To check the brake shoe lining thickness
without removing the brake drums, prise the
rubber plugs from the backplates, and use an
electric torch to inspect the linings of the
leading brake shoes (see illustration). Check
that the thickness of the lining material on the
23 Brake check
22 Underbody and fuel/brake
line check
1•19
121.2 If any of the exhaust system rubber
mountings are to be renewed, ensure that
the replacements are of the correct type -
their colour is a good guide. Those nearest
to the catalytic converter are more heat-
resistant than the others23.10 Checking the condition of a flexible
brake hose23.13 Prise the rubber plugs from the
backplates to inspect the leading brake
shoe linings
Every 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 34 of 279

brake shoes is not less than the
recommendation given in the Specifications.
14If it is difficult to determine the exact
thickness of the brake shoe linings, or if you
are at all concerned about the condition of the
shoes, then remove the rear drums for a more
comprehensive inspection (refer to Chapter 9)
(see illustration).
15With the drum removed, check the shoe
return and hold-down springs for correct
installation, and check the wheel cylinders for
leakage of brake fluid. Check the friction
surface of the brake drums for scoring and
discoloration. If excessive, the drum should
be resurfaced or renewed.
16Before refitting the wheels, check all
brake lines and hoses (refer to Chapter 9). On
completion, apply the handbrake and check
that the rear wheels are locked. The
handbrake is self-adjusting, and no manual
adjustment is possible.
1Check that the doors, bonnet and
tailgate/boot lid close securely. Check that
the bonnet safety catch operates correctly.
Check the operation of the door check straps.
2Lubricate the hinges, door check straps,
the striker plates and the bonnet catch
sparingly with a little oil or grease.1Apply the handbrake.
2Remove the wheel covers, using the flat
end of the wheelbrace supplied in the tool kit
(on models with the RS trim kit, it will be
necessary to unscrew the retaining bolts with
the special key).
3Check that the roadwheel nuts are tightened
to the specified torque wrench setting.
4Refit the wheel covers.
Check the operation and
performance of the braking
system
1Make sure that the vehicle does not pull to
one side when braking, and that the wheels
do not lock prematurely when braking hard.
2Check that there is no vibration through the
steering when braking.
3Check that the handbrake operates
correctly, without excessive movement of the
lever, and that it holds the vehicle stationary
on a slope.
4With the engine switched off, test the
operation of the brake servo unit as follows.
Depress the footbrake four or five times to
exhaust the vacuum, then start the engine. As
the engine starts, there should be a noticeable
“give” in the brake pedal as vacuum builds
up. Allow the engine to run for at least two
minutes, and then switch it off. If the brake
pedal is now depressed again, it should be
possible to detect a hiss from the servo as the
pedal is depressed. After about four or five
applications, no further hissing should be
heard, and the pedal should feel considerably
harder.
Steering and suspension
5Check for any abnormalities in the steering,
suspension, handling or road “feel”.
6Drive the vehicle, and check that there are
no unusual vibrations or noises.
7Check that the steering feels positive, with
no excessive sloppiness or roughness, andcheck for any suspension noises when
cornering and driving over bumps.
Drivetrain
8Check the performance of the engine,
transmission and driveshafts.
9Check that the engine starts correctly, both
when cold and when hot.
10Listen for any unusual noises from the
engine and transmission.
11Make sure that the engine runs smoothly
when idling, and that there is no hesitation
when accelerating.
12On manual transmission models, check
that all gears can be engaged smoothly
without noise, and that the gear lever action is
not abnormally vague or “notchy”.
13On automatic transmission models, make
sure that all gearchanges occur smoothly
without snatching, and without an increase in
engine speed between changes. Check that
all the gear positions can be selected with the
vehicle at rest. If any problems are found, they
should be referred to a Ford dealer.
14Listen for a metallic clicking sound from
the front of the vehicle as the vehicle is driven
slowly in a circle with the steering on full-lock.
Carry out this check in both directions. If a
clicking noise is heard, this indicates wear in a
driveshaft joint, in which case renew the joint
if necessary.
Clutch
15Check that the clutch pedal moves
smoothly and easily through its full travel, and
that the clutch itself functions correctly, with
no trace of slip or drag. If the movement is
uneven or stiff in places, check that the cable
is routed correctly, with no sharp turns.
16Inspect both ends of the clutch inner
cable, both at the gearbox end and inside the
car, for signs of wear and fraying.
17Check the pedal stroke as described in
Chapter 8, Section 3, and adjust if necessary.
Instruments and electrical
equipment
18Check the operation of all instruments
and electrical equipment.
19Make sure that all instruments read
correctly, and switch on all electrical
equipment in turn, to check that it functions
properly.
26 Road test
25 Roadwheel nut tightness
check
24 Door and bonnet check and
lubrication
1•20
23.14 If the lining is bonded to the brake
shoe, measure the lining thickness from
the outer surface to the metal shoe, as
shown here; if the lining is riveted to the
shoe, measure from the lining outer
surface to the rivet head
Every 20 000 miles
Every 20 000 miles or 2 years
1The air entering the vehicle’s ventilation
system is passed through a very fine pleated-
paper air filter element, which removes
particles of pollen, dust and other airborne
foreign matter. To ensure its continued
effectiveness, this filter’s element must be
renewed at regular intervals.2Remove the left-hand side windscreen
wiper arm (Chapter 12).
3Prise off their trim caps, then unscrew the two
screws securing the windscreen edge of the cowl
grille panel; open the bonnet and remove the
remaining three retaining screws (see illustration).
4Peel back the rubber seal and withdraw the
cowl grille panel.
5Releasing the clip at each end, lift out the
pollen filter housing, and withdraw the
element (see illustrations).6Wipe out the ventilation system intake and
the filter housing, removing any leaves, dead
insects etc.
7If carrying out a routine service, the element
must be renewed regardless of its apparent
condition. If you are checking the element for
any other reason, inspect its front surface; if it
is very dirty, renew the element. If it is only
moderately dusty, it can be re-used by
blowing it clean from the rear to the front
surface with compressed air. Because it is a
27 Ventilation system pollen
filter renewal
procarmanuals.com
Page 36 of 279

are correctly secured, and that the radiator
drain plug is securely tightened. Refit the
radiator undershield, noting that it is located
by three clips at its front edge; tighten the
retaining screws securely (see illustration). If
it was raised, lower the vehicle to the ground.
12Prepare a sufficient quantity of the
specified coolant mixture (see below); allow
for a surplus, so as to have a reserve supply
for topping-up.
13Slowly fill the system through the
expansion tank; since the tank is the highest
point in the system, all the air in the system
should be displaced into the tank by the rising
liquid. Slow pouring reduces the possibility of
air being trapped and forming air-locks.
14Continue filling until the coolant level
reaches the expansion tank “MAX” level line,
then cover the filler opening to prevent
coolant splashing out.
15Start the engine and run it at idle speed,
until it has warmed-up to normal operating
temperature and the radiator electric cooling
fan has cut in; watch the temperature gauge
to check for signs of overheating. If the level in
the expansion tank drops significantly, top-up
to the “MAX” level line, to minimise the
amount of air circulating in the system.
16Stop the engine, allow it to cool down
completely(overnight, if possible), then
uncover the expansion tank filler opening and
top-up the tank to the “MAX” level line. Refit
the filler cap, tightening it securely, and washoff any spilt coolant from the engine
compartment and bodywork.
17After refilling, always check carefully all
components of the system (but especially any
unions disturbed during draining and flushing)
for signs of coolant leaks. Fresh antifreeze has
a searching action, which will rapidly expose
any weak points in the system.
18 Note:If, after draining and refilling the
system, symptoms of overheating are found
which did not occur previously, then the fault
is almost certainly due to trapped air at some
point in the system, causing an air-lock and
restricting the flow of coolant; usually, the air
is trapped because the system was refilled too
quickly. In some cases, air-locks can be
released by tapping or squeezing the various
hoses. If the problem persists, stop the engine
and allow it to cool down completely, before
unscrewing the expansion tank filler cap or
disconnecting hoses to bleed out the trapped
air.
Antifreeze mixture
19If the antifreeze used is not to Ford’s
specification, it should always be renewed at
the suggested intervals. This is necessary not
only to maintain the antifreeze properties, but
also to prevent the corrosion which would
otherwise occur as the corrosion inhibitors
become progressively less effective. Always
use an ethylene glycol-based antifreeze which
is suitable for use in mixed-metal cooling
systems.
20If the antifreeze used is to Ford’s
specification, the levels of protection it affords
are indicated in the Specifications Section of
this Chapter. To give the recommended
standardmixture ratio for this antifreeze, 40%
(by volume) of antifreeze must be mixed with
60% of clean, soft water; if you are using any
other type of antifreeze, follow its
manufacturer’s instructions to achieve the
correct ratio. It is best to make up slightly
more than the system’s specified capacity, so
that a supply is available for subsequent
topping-up.
21Before adding antifreeze, the cooling
system should be completely drained,
preferably flushed, and all hoses checked forcondition and security. As noted earlier, fresh
antifreeze will rapidly find any weaknesses in
the system.
22After filling with antifreeze, a label should
be attached to the expansion tank, stating the
type and concentration of antifreeze used,
and the date installed. Any subsequent
topping-up should be made with the same
type and concentration of antifreeze. If
topping-up using antifreeze to Ford’s
specification, note that a 50/50 mixture is
permissible, purely for convenience.
23Do not use engine antifreeze in the
windscreen/tailgate washer system, as it will
damage the vehicle’s paintwork. A screen
wash additive should be added to the washer
system in its maker’s recommended
quantities.
General cooling system checks
24The engine should be cold for the cooling
system checks, so perform the following
procedure before driving the vehicle, or after it
has been shut off for at least three hours.
25Remove the expansion tank filler cap (see
Section 3), and clean it thoroughly inside and
out with a rag. Also clean the filler neck on the
expansion tank. The presence of rust or
corrosion in the filler neck indicates that the
coolant should be changed. The coolant
inside the expansion tank should be relatively
clean and transparent. If it is rust- coloured,
drain and flush the system, and refill with a
fresh coolant mixture.
26Carefully check the radiator hoses and
heater hoses along their entire length; renew
any hose which is cracked, swollen or
deteriorated (see Section 12).
27Inspect all other cooling system
components (joint faces, etc.) for leaks. A leak
in the cooling system will usually show up as
white- or rust-coloured deposits on the area
adjoining the leak. Where any problems of this
nature are found on system components,
renew the component or gasket with
reference to Chapter 3.
28Clean the front of the radiator with a soft
brush to remove all insects, leaves, etc,
embedded in the radiator fins. Be careful not
to damage the radiator fins, or cut your fingers
on them.
1•22
28.11 Ensure radiator undershield is
located securely in three clips at front
edge (arrowed) when refitting
Every 30 000 miles
Every 30 000 miles or 3 years
1The air filter element is located in the air
cleaner assembly on the left-hand side of the
engine compartment. Release the clips, and
lift the air cleaner cover (see illustrations). If
the additional working clearance is required,
unclip the cover from the air mass meter, and
withdraw it completely.
2Lift out the element, and wipe out thehousing (see illustration). Check that no
foreign matter is visible, either in the air intake
or in the air mass meter.
3If carrying out a routine service, the element
must be renewed regardless of its apparent
condition; note that the small foam filter in the
rear right-hand corner of the air cleaner
housing must be cleaned whenever the air
filter element is renewed (see Section 30).
4If you are checking the element for any
other reason, inspect its lower surface; if it is
oily or very dirty, renew the element. If it is
only moderately dusty, it can be re-used byblowing it clean from the upper to the lower
surface with compressed air. Because it is a
pleated-paper type filter, it cannot be washed
or re-oiled. If it cannot be cleaned
satisfactorily with compressed air, discard
and renew it.
Warning: Wear eye protection
when using compressed air!
Caution: Never drive the vehicle
with the air cleaner filter element
removed. Excessive engine wear could
result, and backfiring could even cause a
fire under the bonnet.
29 Air filter element renewal
procarmanuals.com
Page 52 of 279

contamination with oil or coolant. Renew the
belt if there is the slightest doubt about its
condition. As a safety measure, the belt must
be renewed as a matter of course at the
intervals given in Chapter 1; if its history is
unknown, the belt should be renewed
irrespective of its apparent condition
whenever the engine is overhauled. Similarly,
check the tensioner spring (where fitted),
renewing it if there is any doubt about its
condition. Check also the toothed pulleys for
signs of wear or damage, and ensure that the
tensioner and guide pulleys rotate smoothly
on their bearings; renew any worn or
damaged components. If signs of oil or
coolant contamination are found, trace the
source of the leak and rectify it, then wash
down the engine timing belt area and related
components, to remove all traces of oil or
coolant.
17On reassembly, temporarily refit the
crankshaft pulley, to check that the pulley
notches and sump rib are aligned as
described in paragraph 8 above, then ensure
that both camshafts are aligned at TDC by
the special tool (paragraph 10). If the engine
is being reassembled after major dismantling,
both camshaft toothed pulleys should be free
to rotate on their respective camshafts; if the
timing belt alone is being renewed, both
pulleys should still be securely fastened.
18A holding tool will be required to prevent
the camshaft toothed pulleys from rotating
while their bolts are slackened and
retightened; either obtain Ford service tool15-030A, or fabricate a substitute as follows.
Find two lengths of steel strip, one
approximately 600 mm long and the other
about 200 mm, and three bolts with nuts and
washers; one nut and bolt forming the pivot of
a forked tool, with the remaining nuts and
bolts at the tips of the “forks”, to engage with
the pulley spokes as shown in the
accompanying illustrations. Note:Do not use
the camshaft aligning tool (whether genuine
Ford or not) to prevent rotation while the
camshaft toothed pulley bolts are slackened
or tightened; the risk of damage to the
camshaft concerned and to the cylinder head
is far too great. Use only a forked holding tool
applied directly to the pulleys, as described.
19If it is being fitted for the first time, screw
the timing belt tensioner spring retaining pin
into the cylinder head, tightening it to the
specified torque wrench setting. Unbolt the
tensioner, hook the spring on to the pin and
the tensioner backplate, then refit the
tensioner, engaging its backplate on the
locating peg (see illustrations).
20In all cases, slacken the tensioner bolt (if
necessary), and use an Allen key inserted into
its centre to rotate the tensioner clockwise as
far as possible against spring tension, then
retighten the bolt to secure the tensioner (see
illustration).
21Fit the timing belt; if the original is being
refitted, ensure that the marks and notes
made on removal are followed, so that the
belt is refitted the same way round, and to run
in the same direction. Starting at thecrankshaft toothed pulley, work anti-
clockwise around the camshaft toothed
pulleys and tensioner, finishing off at the rear
guide pulley. The front run, between the
crankshaft and the exhaust camshaft toothed
pulleys, mustbe kept taut, without altering
the position either of the crankshaft or of the
camshaft(s) - if necessary, the position of the
camshaft toothed pulleys can be altered by
rotating each on its camshaft (which remains
fixed by the aligning tool). Where the pulley is
still fastened, use the holding tool described
in paragraph 18 above to prevent the pulley
from rotating while its retaining bolt is
slackened - the pulley can then be rotated on
the camshaft until the belt will slip into place;
retighten the pulley bolt.
22When the belt is in place, slacken the
tensioner bolt gently until the spring pulls the
tensioner against the belt; the tensioner
should be retained correctly against the
timing belt inner shield and cylinder head, but
must be just free to respond to changes in
belt tension (see illustration).
23Tighten both camshaft toothed pulley
bolts (or check that they are tight, as
applicable) and remove the camshaft aligning
tool. Temporarily refit the crankshaft pulley,
and rotate the crankshaft through two full
turns clockwise to settle and tension the
timing belt, returning the crankshaft (pulley
notches) to the position described in
paragraph 8 above. Refit the camshaft
aligning tool; it should slip into place as
described in paragraph 10. If all is well,
proceed to paragraph 26 below.
24If one camshaft is only just out of line, fit
the forked holding tool to its toothed pulley,
adjust its position as required, and check that
any slack created has been taken up by the
tensioner; rotate the crankshaft through two
further turns clockwise, and refit the camshaft
aligning tool to check that it now fits as it
should. If all is well, proceed to paragraph 26
below.
25If either camshaft is significantly out of
line, use the holding tool described in
paragraph 18 above to prevent its pulley from
rotating while its retaining bolt is slackened -
the camshaft can then be rotated (gently and
carefully, using an open-ended spanner) until
2A•12 In-car engine repair procedures
10.19A Fitting tensioner spring retaining
pin10.19B Hook spring onto tensioner and
refit as shown - engage tensioner
backplate on locating peg (arrowed) . . .10.20 . . . then use Allen key to position
tensioner so that timing belt can be refitted
10.22 Slacken tensioner bolt to give initial
belt tension10.25 Using forked holding tool while
camshaft toothed pulley bolt is tightened
procarmanuals.com
Page 138 of 279

constantly monitors the oxygen content of the
exhaust gas. If the percentage of oxygen in
the exhaust gas is incorrect, an electrical
signal is sent to the ECU. The ECU processes
this information, and then sends a command
to the fuel injection system, telling it to change
the air/fuel mixture; the end result is an air/fuel
mixture ratio which is constantly maintained
at a predetermined ratio, regardless of driving
conditions. This happens in a fraction of a
second, and goes on almost all the time while
the engine is running - the exceptions are that
the ECU cuts out the system and runs the
engine on values pre-programmed
(“mapped”) into its memory both while the
oxygen sensor is reaching its normal
operating temperature after the engine has
been started from cold, and when the throttle
is fully open for full acceleration.
In the event of a sensor malfunction, a
back-up circuit will take over, to provide
driveability until the problem is identified and
fixed.
Precautions
(a) Always disconnect the power by
uncoupling the battery terminals - see
Section 1 of Chapter 5 - before removing
any of the electronic control system’s
electrical connectors.
(b) When installing a battery, be particularly
careful to avoid reversing the positive and
negative battery leads.
(c) Do not subject any components of the
system (especially the ECU) to severe
impact during removal or installation.
(d) Do not be careless during fault diagnosis.
Even slight terminal contact can invalidate
a testing procedure, and damage one of
the numerous transistor circuits.
(e) Never attempt to work on the ECU, to test
it (with any kind of test equipment), or to
open its cover.
(f) If you are inspecting electronic control
system components during rainy weather,
make sure that water does not enter any
part. When washing the engine
compartment, do not spray these parts or
their electrical connectors with water.
General
The various components of the fuel, ignition
and emissions control systems (not forgetting
the same ECU’s control of sub-systems such
as the radiator cooling fan, air conditioning
and automatic transmission, where
appropriate) are so closely interlinked that
diagnosis of a fault in any one component is
virtually impossible using traditional methods.
Working on simpler systems in the past, the
experienced mechanic may well have been
able to use personal skill and knowledge
immediately to pinpoint the cause of a fault, or
quickly to isolate the fault, by elimination;however, with an engine management system
integrated to this degree, this is not likely to
be possible in most instances, because of the
number of symptoms that could arise from
even a minor fault.
So that the causes of faults can be quickly
and accurately traced and rectified, the ECU
is provided with a built-in self-diagnosis
facility, which detects malfunctions in the
system’s components. When a fault occurs,
three things happen: the ECU identifies the
fault, stores a corresponding code in its
memory, and (in most cases) runs the system
using back-up values pre-programmed
(“mapped”) into its memory; some form of
driveability is thus maintained, to enable the
vehicle to be driven to a garage for attention.
Any faults that may have occurred are
indicated in the form of three-digit codes
when the system is connected (via the built-in
diagnosis or self-test connectors, as
appropriate) to special diagnostic equipment -
this points the user in the direction of the
faulty circuit, so that further tests can pinpoint
the exact location of the fault.
Given below is the procedure that would be
followed by a Ford technician to trace a fault
from scratch. Should your vehicle’s engine
management system develop a fault, read
through the procedure and decide how much
you can attempt, depending on your skill and
experience and the equipment available to
you, or whether it would be simpler to have
the vehicle attended to by your local Ford
dealer. If you are concerned about the
apparent complexity of the system, however,
remember the comments made in the fourth
paragraph of Section 1 of this Chapter; the
preliminary checks require nothing but care,
patience and a few minor items of equipment,
and may well eliminate the majority of faults.
(a) Preliminary checks
(b) Fault code read-out *
(c) Check ignition timing and base idle
speed. Recheck fault codes to establish
whether fault has been cured or not *
(d) Carry out basic check of ignition system
components. Recheck fault codes to
establish whether fault has been cured or
not *
(e) Carry out basic check of fuel system
components. Recheck fault codes to
establish whether fault has been cured or
not *
(f) If fault is still not located, carry out system
test *
Note:Operations marked with an asterisk
require special test equipment.
Preliminary checks
Note:When carrying out these checks to
trace a fault, remember that if the fault has
appeared only a short time after any part of
the vehicle has been serviced or overhauled,
the first place to check is where that work was
carried out, however unrelated it may appear,
to ensure that no carelessly-refitted
components are causing the problem.If you are tracing the cause of a “partial”
engine fault, such as lack of performance, in
addition to the checks outlined below, check
the compression pressures (see Part A of
Chapter 2) and bear in mind the possibility
that one of the hydraulic tappets might be
faulty, producing an incorrect valve clearance.
Check also that the fuel filter has been
renewed at the recommended intervals.
If the system appears completely dead,
remember the possibility that the
alarm/inhibitor system may be responsible.
1The first check for anyone without special
test equipment is to switch on the ignition,
and to listen for the fuel pump (the sound of
an electric motor running, audible from
beneath the rear seats); assuming there is
sufficient fuel in the tank, the pump should
start and run for approximately one or two
seconds, then stop, each time the ignition is
switched on. If the pump runs continuously all
the time the ignition is switched on, the
electronic control system is running in the
back-up (or “limp-home”) mode referred to by
Ford as “Limited Operation Strategy” (LOS).
This almost certainly indicates a fault in the
ECU itself, and the vehicle should therefore be
taken to a Ford dealer for a full test of the
complete system using the correct diagnostic
equipment; do not waste time trying to test
the system without such facilities.
2If the fuel pump is working correctly (or not
at all), a considerable amount of fault
diagnosis is still possible without special test
equipment. Start the checking procedure as
follows.
3Open the bonnet and check the condition
of the battery connections - remake the
connections or renew the leads if a fault is
found (Chapter 5). Use the same techniques
to ensure that all earth points in the engine
compartment provide good electrical contact
through clean, metal-to-metal joints, and that
all are securely fastened. (In addition to the
earth connection at the engine lifting eye and
that from the transmission to the
body/battery, there is one earth connection
behind each headlight assembly, and one
below the power steering fluid reservoir.)
4Referring to the information given in
Chapter 12 and in the wiring diagrams at the
back of this manual, check that all fuses
protecting the circuits related to the engine
management system are in good condition.
Fit new fuses if required; while you are there,
check that all relays are securely plugged into
their sockets.
5Next work methodically around the engine
compartment, checking all visible wiring, and
the connections between sections of the
wiring loom. What you are looking for at this
stage is wiring that is obviously damaged by
chafing against sharp edges, or against
moving suspension/transmission components
and/or the auxiliary drivebelt, by being
trapped or crushed between carelessly-
refitted components, or melted by being
forced into contact with hot engine castings,
3 Diagnosis system -
general information
6•4 Emissions control systems
procarmanuals.com
Page 141 of 279

24Ford specify the use of their STAR (Self-
Test Automatic Readout) tester; most Ford
dealers should have such equipment, and the
staff trained to use it effectively. The only
alternatives are as follows:
(a) To obtain one of those proprietary readers
which can interpret EEC-IV three-digit
codes - at present, such readers are too
expensive for the DIY enthusiast, but are
becoming more popular with smaller
specialist garages.
(b) To use an analogue voltmeter, whereby
the stored codes are displayed as sweeps
of the voltmeter needle. This option limits
the operator to a read-out of any codes
stored - ie, there is no control of sensors
and/or actuators - but can still be useful in
pinpointing the faulty part of the engine
management system. The display is
interpreted as follows. Each code
(whether fault code or
command/separator) is marked by a
three-to-four second pause - code “538”
would therefore be shown as long (3 to
4 seconds) pause, five fast sweeps of the
needle, slight (1 second) pause, three fast
sweeps, slight pause, eight fast sweeps,
long pause.
(c) Owners without access to such
equipment must take the vehicle to a Ford
dealer, or to an expert who has similar
equipment and the skill to use it.
25Because of the variations in the design of
fault code readers, it is not possible to give
exact details of the sequence of tests; the
manufacturer’s instructions must be followed,
in conjunction with the codes given below.
The following ten paragraphs outline the
procedure to be followed using a version of
the Ford STAR tester, to illustrate the general
principles, as well as notes to guide the owner
using only a voltmeter.
26The vehicle must be prepared by applying
the handbrake, switching off the air
conditioning (where fitted) and any other
electrical loads (lights, heated rear window,
etc), then selecting neutral (manual
transmission) or the “P” position (automatic
transmission). Where the engine is required to
be running, it must be fully warmed-up to
normal operating temperature before the test
is started. Using any adaptors required,
connect the fault code reader to the system
via the (triangular, three-pin) self-test
connector on the right-hand end of the engine
compartment bulkhead (see illustration). If a
voltmeter is being used, connect its positive
lead to the battery positive terminal, and its
negative lead to the self-test connector’s
output terminal, pin 17. Have a pen and paper
ready to write down the codes displayed.
27Set the tester in operation. For the Ford
STAR tester, a display check will be carried
out and the test mode requirements must be
entered. If a voltmeter is being used, connect
a spare length of wire to earth the self-test
connector’s input terminal, pin 48. Be very
careful to ensure that you earth the correctterminal - the one with the white/green wire.
The first part of the test starts, with the
ignition switched on, but with the engine off.
On pressing the “Mem/test” button, the tester
displays “TEST” and the ready code “000”,
followed by a command code “010” - the
accelerator pedal must be fully depressed
within 10 seconds of the command code
appearing, or fault codes “576” or “577” will
appear when they are called up later. If a
voltmeter is being used, code “000” will not
appear (except perhaps as a flicker of the
needle) and “010” will appear as a single
sweep - to ensure correct interpretation of the
display, watch carefully for the interval
between the end of one code and the
beginning of the next, otherwise you will
become confused and misinterpret the read-
out.
28The tester will then display the codes for
any faults in the system at the time of the test.
Each code is repeated once; if no faults are
present, code “111” will be displayed. If a
voltmeter is being used, the pause between
repetitions will vary according to the
equipment in use and the number of faults in
the system, but was found to be
approximately 3 to 4 seconds - it may be
necessary to start again, and to repeat the
read-out until you are familiar with what you
are seeing.
29Next the tester will display code “010”
(now acting as a separator), followed by the
codes for any faults stored in the ECU’s
memory; if no faults were stored, code “111”
will be displayed.
30When prompted by the tester, the
operator must next depress the accelerator
pedal fully; the tester then checks several
actuators. Further test modes include a
“wiggle test” facility, whereby the operator
can check the various connectors as
described in paragraph 19 above (in this case,
any fault will be logged and the appropriate
code will be displayed), a facility for recalling
codes displayed, and a means for clearing the
ECU’s memory at the end of the test
procedure when any faults have been
rectified.
31The next step when using the Ford STAR
tester is to conduct a test with the engine
running. With the tester set in operation (see
paragraph 26 above) the engine is started and
allowed to idle. On pressing the “Mem/test”
button, the tester displays “TEST”, followed
by one of two codes, as follows.
32If warning code “998” appears, followed
by the appropriate fault code, switch off and
check as indicated the coolant temperature
sensor, the intake air temperature sensor, the
air mass meter, the throttle potentiometer
and/or their related circuits, then restart the
test procedure.
33If command code “020” appears, carry
out the following procedure within ten
seconds:
(a) Depress the brake pedal fully.
(b) Turn the steering to full-lock (either way)and centre it again, to produce a signal
from the power steering pressure switch -
if no signal is sent, fault code “521” will
be displayed.
(c) If automatic transmission is fitted, switch
the overdrive cancel button on and off,
then do the same for the
“Economy/Sport” mode switch.
(d) Wait for separator code “010” to be
displayed, then within 10 seconds,
depress the accelerator pedal fully,
increasing engine speed rapidly above
3000 rpm - release the pedal.
34Any faults found in the system will be
logged and displayed. Each code is repeated
once; if no faults are present, code “111” will
be displayed.
35When the codes have been displayed for
all faults logged, the ECU enters its “Service
Adjustment Programme”, as follows:
(a) The programme lasts for 2 minutes.
(b) The idle speed control valve is
deactivated, and the idle speed is set to
its pre-programmed (unregulated) value. If
the appropriate equipment is connected,
the base idle speed can be checked
(note, however, that it is not adjustable).
(c) The ignition timing can be checked if a
timing light is connected (note, however,
that it is not adjustable).
(d) Pressing the accelerator pedal fully at any
time during this period will execute a
cylinder balance test. Each injector in turn
is switched off, and the corresponding
decrease in engine speed is logged -
code “090” will be displayed if the test is
successful.
(e) At the end of the 2 minutes, the
completion of the programme is shown
by the engine speed briefly rising, then
returning to normal idling speed as
the idle speed control valve is
reactivated.
36As with the engine-off test, further test
modes include a “wiggle test” facility,
whereby the operator can check the various
connectors as described in paragraph 19
above (in this case, any fault will be logged
and the appropriate code will be displayed), a
facility for recalling codes displayed, and a
means for clearing the ECU’s memory at the
end of the test procedure when any faults
have been rectified. If equipment other than
the Ford STAR tester is used, the ECU’s
memory can be cleared by disconnecting the
battery - if this is not done, the code will
reappear with any other codes in the event of
subsequent trouble, but remember that other
systems with memory (such as the clock and
audio equipment) will also be affected. Should
it become necessary to disconnect the
battery during work on any other part of the
vehicle, first check to see if any fault codes
have been logged.
37Given overleaf are the possible codes,
their meanings, and where relevant, the action
to be taken as a result of a code being
displayed.
Emissions control systems 6•7
6
procarmanuals.com