1993 FORD MONDEO oil filter
[x] Cancel search: oil filterPage 41 of 279

Chapter 2 Part A:
In-car engine repair procedures
Auxiliary drivebelt check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Camshaft oil seals - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Camshafts and hydraulic tappets - removal, inspection
and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Compression test - description and interpretation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Crankshaft oil seals - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Crankshaft pulley - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Cylinder head - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Cylinder head and valve components - cleaning and
inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 2B
Cylinder head cover - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Engine oil and filter change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Engine oil level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Engine overhaul - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 2B
Engine/transmission - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . See Chapter 2B
Engine/transmission mountings - inspection and renewal . . . . . . . . 22
Exhaust manifold - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . 7Flywheel/driveplate - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . 21
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Inlet manifold - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Oil cooler - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Oil level sensor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Oil pressure warning light switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . 19
Oil pump - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Repair operations possible with the engine in the vehicle . . . . . . . . 2
Spark plug renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Sump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Timing belt - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Timing belt covers - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Timing belt tensioner and toothed pulleys - removal,
inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Top Dead Centre (TDC) for No 1 piston - locating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Water pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 3
General
Engine type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Four-cylinder, in-line, double overhead camshafts
Engine code:
1.6 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . LIF
1.8 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . RKA
2.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . NGA
Capacity:
1.6 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1597 cc
1.8 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1796 cc
2.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1988 cc
Bore:
1.6 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76.0 mm
1.8 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80.6 mm
2.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84.8 mm
Stroke - all models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88.0 mm
Compression ratio:
1.6 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.3:1
1.8 and 2.0 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.0:1
Compression pressure - at starter motor speed, engine fully warmed-up .Not available
Firing order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3-4-2 (No 1 cylinder at timing belt end)
Direction of crankshaft rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Clockwise (seen from right-hand side of vehicle)
Cylinder head
Hydraulic tappet bore inside diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28.395 to 28.425 mm
Camshafts and hydraulic tappets
Camshaft bearing journal diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25.960 to 25.980 mm
Camshaft bearing journal-to-cylinder head running clearance . . . . . . . . 0.020 to 0.070 mm
Camshaft endfloat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.080 to 0.220 mm
Hydraulic tappet diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28.400 mm
2A•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,suitable
for competent DIY
mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents2A
procarmanuals.com
Page 42 of 279

Lubrication
Engine oil type/specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Engine oil capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Oil pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . No information available at time of writing
Oil pump clearances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . No information available at time of writing
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Cylinder head cover bolts:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 1.5
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 5
Camshaft toothed pulley bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68 50
Camshaft bearing cap bolts:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 14
Cylinder head bolts:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 18
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45 33
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Angle-tighten a further 105°
Timing belt cover fasteners:
Upper-to-middle (outer) cover bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 3
Cover-to-cylinder head or block bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 5
Cover studs-to-cylinder head or block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 to 11 6.5 to 8
Timing belt tensioner bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38 28
Timing belt tensioner backplate locating peg . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 to 11 6 to 8
Timing belt tensioner spring retaining pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Timing belt guide pulley bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35 to 40 26 to 30
Water pump pulley bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Water pump bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 3
Auxiliary drivebelt idler pulley . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48 35
Inlet manifold nuts and bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 13
Alternator mounting bracket-to-cylinder block bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47 35
Cylinder head support plates:
Front plate Torx screws - to power steering pump/air conditioning
compressor mounting bracket and cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47 35
Rear plate/engine lifting eye - to alternator mounting bracket
and cylinder head bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47 35
Front engine lifting eye bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 12
Inlet and exhaust manifold studs-to-cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 maximum 7 maximum
Exhaust manifold heat shield bolts:
Shield-to-cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 5
Shield/dipstick tube . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Shield/coolant pipe-to-manifold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23 17
Exhaust manifold nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 12
Air conditioning refrigerant pipe-to-exhaust manifold bolts . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Crankshaft pulley bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108 to 115 80 to 85
Oil pump-to-cylinder block bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Oil pick-up pipe-to-pump screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Oil baffle/pump pick-up pipe nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 14
Oil filter adaptor-to-pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 to 25 13 to 18
Oil pressure warning light switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 20
Oil level sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 20
Sump bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 to 22 15 to 16
Coolant pipe-to-sump bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Flywheel/driveplate bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110 to 112 81 to 83
Crankshaft left-hand oil seal carrier bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 16
Transmission-to-engine bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40 30
Engine/transmission front mounting:
Mounting bracket-to-transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Not available
Mounting-to-subframe bolts/nuts - stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Mounting-to-subframe bolts/nuts - stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48 35
Mounting centre bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120 89
Engine/manual transmission rear mounting:
Mounting bracket-to-transmission 12 mm fasteners . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78 to 84 58 to 62
Mounting bracket-to-transmission 10 mm fasteners . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48 35
Mounting-to-subframe bolts and nut - stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Mounting-to-subframe bolts and nut - stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48 35
Mounting centre bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120 89
2A•2 In-car engine repair procedures
procarmanuals.com
Page 44 of 279
end of the cylinder block, inboard of the
timing belt, and is driven with the power
steering pump and alternator by a flat
“polyvee”-type auxiliary drivebelt from the
crankshaft pulley.
When working on this engine, note that
Torx-type (both male and female heads) and
hexagon socket (Allen head) fasteners are
widely used; a good selection of bits, with the
necessary adaptors, will be required, so that
these can be unscrewed without damage
and, on reassembly, tightened to the torque
wrench settings specified.
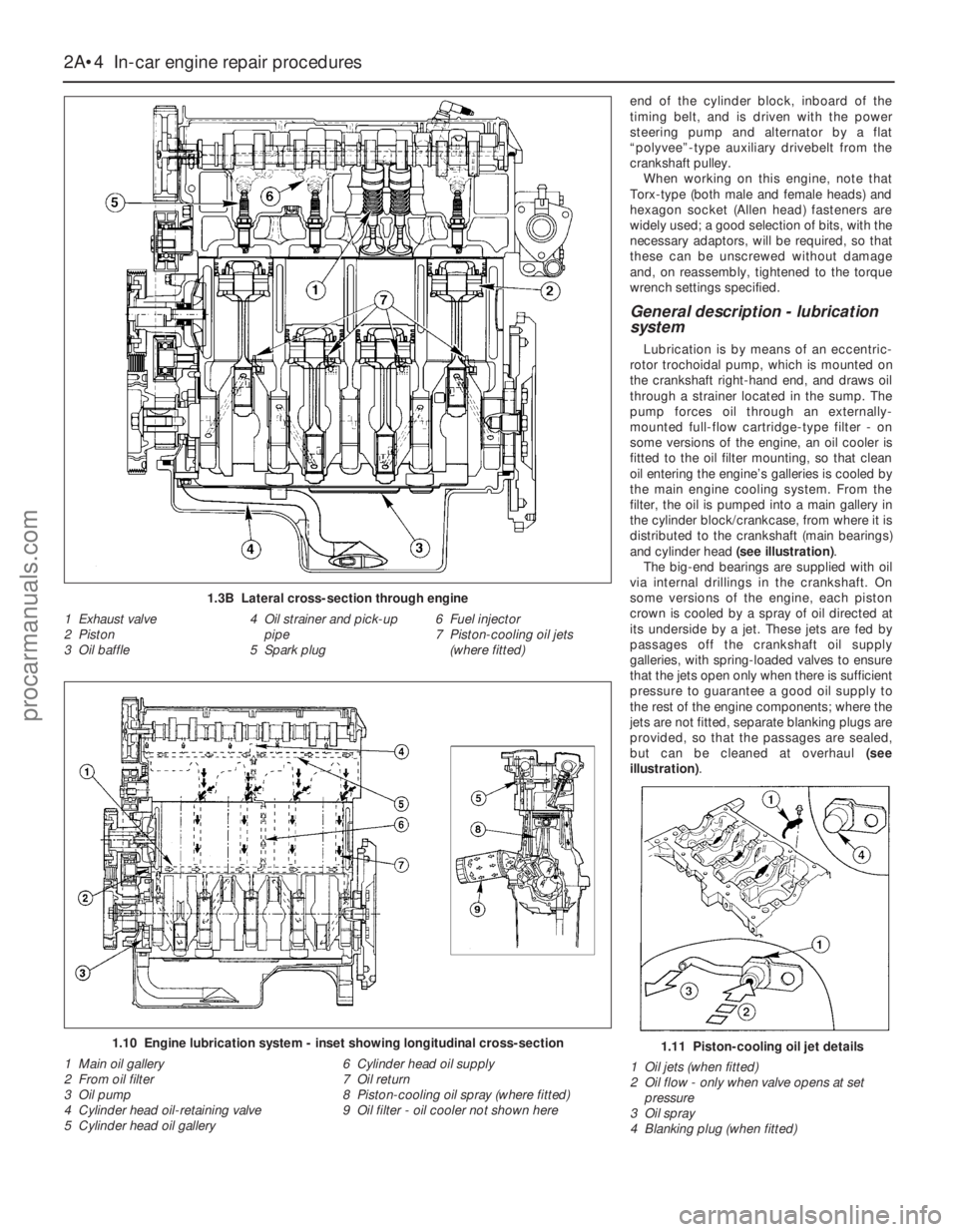
General description - lubrication
system
Lubrication is by means of an eccentric-
rotor trochoidal pump, which is mounted on
the crankshaft right-hand end, and draws oil
through a strainer located in the sump. The
pump forces oil through an externally-
mounted full-flow cartridge-type filter - on
some versions of the engine, an oil cooler is
fitted to the oil filter mounting, so that clean
oil entering the engine’s galleries is cooled by
the main engine cooling system. From the
filter, the oil is pumped into a main gallery in
the cylinder block/crankcase, from where it is
distributed to the crankshaft (main bearings)
and cylinder head (see illustration).
The big-end bearings are supplied with oil
via internal drillings in the crankshaft. On
some versions of the engine, each piston
crown is cooled by a spray of oil directed at
its underside by a jet. These jets are fed by
passages off the crankshaft oil supply
galleries, with spring-loaded valves to ensure
that the jets open only when there is sufficient
pressure to guarantee a good oil supply to
the rest of the engine components; where the
jets are not fitted, separate blanking plugs are
provided, so that the passages are sealed,
but can be cleaned at overhaul (see
illustration).
2A•4 In-car engine repair procedures
1.3B Lateral cross-section through engine
1 Exhaust valve
2 Piston
3 Oil baffle4 Oil strainer and pick-up
pipe
5 Spark plug6 Fuel injector
7 Piston-cooling oil jets
(where fitted)
1.10 Engine lubrication system - inset showing longitudinal cross-section
1 Main oil gallery
2 From oil filter
3 Oil pump
4 Cylinder head oil-retaining valve
5 Cylinder head oil gallery6 Cylinder head oil supply
7 Oil return
8 Piston-cooling oil spray (where fitted)
9 Oil filter - oil cooler not shown here1.11 Piston-cooling oil jet details
1 Oil jets (when fitted)
2 Oil flow - only when valve opens at set
pressure
3 Oil spray
4 Blanking plug (when fitted)
procarmanuals.com
Page 48 of 279

16Unscrew the bolts and nuts securing the
manifold to the cylinder head and withdraw it
(see illustration). Take care not to damage
vulnerable components such as the EGR pipe
and valve as the manifold assembly is
manoeuvred out of the engine compartment.
Refitting
17Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure, noting the following points:
(a) When using a scraper and solvent to
remove all traces of old gasket material
and sealant from the manifold and
cylinder head, be careful to ensure that
you do not scratch or damage the
material of either; the cylinder head is of
aluminium alloy, while the manifold is a
plastics moulding - any solvents used
must be suitable for this application. If the
gasket was leaking, have the mating
surfaces checked for warpage at an
automotive machine shop. While it may
be possible to have the cylinder head
gasket surface skimmed if necessary, to
remove any distortion, the manifold must
be renewed if it is found to be warped,
cracked - check with special care around
the mounting points for components such
as the idle speed control valve and EGR
pipe - or otherwise faulty.
(b) Provided the relevant mating surfaces are
clean and flat, a new gasket will besufficient to ensure the joint is gas-tight.
Do notuse any kind of silicone-based
sealant on any part of the fuel system or
inlet manifold.
(c) Fit a new gasket, then locate the manifold
on the head and install the nuts and bolts
(see illustration).
(d) Tighten the nuts/bolts in three or four
equal steps to the torque listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications. Work from the
centre outwards, to avoid warping the
manifold.
(e) Refit the remaining parts in the reverse
order of removal - tighten all fasteners to
the torque wrench settings specified.
(f) When reassembling the
engine/transmission right-hand mounting,
renew the self-locking nuts, and do not
allow the mounting to twist as the middle
two of the bracket’s six nuts are
tightened.
(g) Before starting the engine, check the
accelerator cable for correct adjustment
and the throttle linkage for smooth
operation.
(h) When the engine is fully warmed up,
check for signs of fuel, intake and/or
vacuum leaks (see illustration).
(i) Road test the vehicle, and check for
proper operation of all disturbed
components.Warning: The engine must be
completely cool before beginning
this procedure.
Note:In addition to the new gasket and any
other parts, tools or facilities needed to carry
out this operation, a new plastic guide sleeve
will be required on reassembly.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
- see Chapter 5, Section 1.
2Unbolt the resonator support bracket from
the engine compartment front crossmember,
slacken the two clamp screws securing the
resonator to the air mass meter and plenum
chamber hoses, then swing the resonator up
clear of the thermostat housing (see Chapter 4).
3Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
4Disconnect the coolant hose and the
coolant pipe/hose from the thermostat
housing; secure them clear of the working
area.
5Unbolt the exhaust manifold heat shield,
and withdraw both parts of the shield (see
illustration). Apply penetrating oil to the EGR
pipe sleeve nut, and to the exhaust manifold
mounting nuts (also to the pulse-air system
sleeve nuts, if they are to be unscrewed).
6Unscrew the sleeve nut securing the EGR
pipe to the manifold, remove the two screws
securing the pipe to the ignition coil bracket,
then slacken the sleeve nut securing the pipe
to the EGR valve - see Chapter 6 for full
details if required.
7While the manifold can be removed with
the pulse-air system components attached -
unbolt the filter housing and disconnect its
vacuum hose if this is to be done - it is easier
to remove the pulse-air assembly first, as
described in Chapter 6 (see illustration).
8Unplugging the oxygen sensor electrical
connector to avoid straining its wiring,
unscrew the nuts to disconnect the exhaust
system front downpipe from the manifold (see
Chapter 4).
7 Exhaust manifold - removal,
inspection and refitting
2A•8 In-car engine repair procedures
6.16 Withdrawing inlet manifold - take
care not to damage delicate components6.17A Always renew inlet manifold gasket
- do not rely on sealants
6.17B Check all disturbed components -
braking system vacuum servo unit hose
(arrowed) shown here - for leaks on
reassembly
7.5 Exhaust manifold heat shield upper
part securing bolts (arrowed)
7.7 Pulse-air system (sleeve nuts arrowed)
need not be removed unless required -
assembly can be withdrawn with exhaust
manifold
procarmanuals.com
Page 55 of 279
wear (scoring, pitting etc) and for ovality, and
renew if necessary.
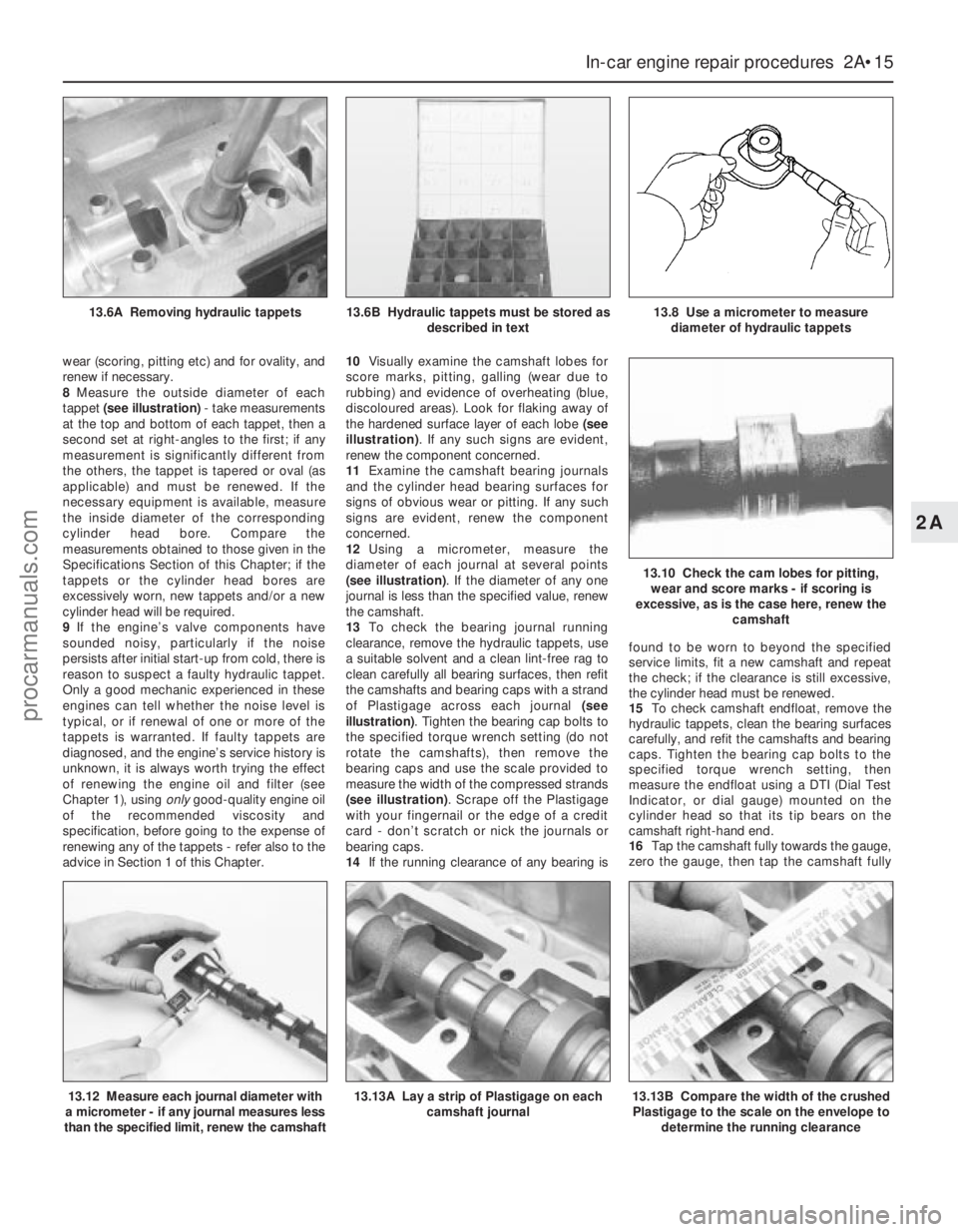
8Measure the outside diameter of each
tappet (see illustration)- take measurements
at the top and bottom of each tappet, then a
second set at right-angles to the first; if any
measurement is significantly different from
the others, the tappet is tapered or oval (as
applicable) and must be renewed. If the
necessary equipment is available, measure
the inside diameter of the corresponding
cylinder head bore. Compare the
measurements obtained to those given in the
Specifications Section of this Chapter; if the
tappets or the cylinder head bores are
excessively worn, new tappets and/or a new
cylinder head will be required.
9If the engine’s valve components have
sounded noisy, particularly if the noise
persists after initial start-up from cold, there is
reason to suspect a faulty hydraulic tappet.
Only a good mechanic experienced in these
engines can tell whether the noise level is
typical, or if renewal of one or more of the
tappets is warranted. If faulty tappets are
diagnosed, and the engine’s service history is
unknown, it is always worth trying the effect
of renewing the engine oil and filter (see
Chapter 1), using onlygood-quality engine oil
of the recommended viscosity and
specification, before going to the expense of
renewing any of the tappets - refer also to the
advice in Section 1 of this Chapter.10Visually examine the camshaft lobes for
score marks, pitting, galling (wear due to
rubbing) and evidence of overheating (blue,
discoloured areas). Look for flaking away of
the hardened surface layer of each lobe (see
illustration). If any such signs are evident,
renew the component concerned.
11Examine the camshaft bearing journals
and the cylinder head bearing surfaces for
signs of obvious wear or pitting. If any such
signs are evident, renew the component
concerned.
12Using a micrometer, measure the
diameter of each journal at several points
(see illustration). If the diameter of any one
journal is less than the specified value, renew
the camshaft.
13To check the bearing journal running
clearance, remove the hydraulic tappets, use
a suitable solvent and a clean lint-free rag to
clean carefully all bearing surfaces, then refit
the camshafts and bearing caps with a strand
of Plastigage across each journal (see
illustration). Tighten the bearing cap bolts to
the specified torque wrench setting (do not
rotate the camshafts), then remove the
bearing caps and use the scale provided to
measure the width of the compressed strands
(see illustration). Scrape off the Plastigage
with your fingernail or the edge of a credit
card - don’t scratch or nick the journals or
bearing caps.
14If the running clearance of any bearing isfound to be worn to beyond the specified
service limits, fit a new camshaft and repeat
the check; if the clearance is still excessive,
the cylinder head must be renewed.
15To check camshaft endfloat, remove the
hydraulic tappets, clean the bearing surfaces
carefully, and refit the camshafts and bearing
caps. Tighten the bearing cap bolts to the
specified torque wrench setting, then
measure the endfloat using a DTI (Dial Test
Indicator, or dial gauge) mounted on the
cylinder head so that its tip bears on the
camshaft right-hand end.
16Tap the camshaft fully towards the gauge,
zero the gauge, then tap the camshaft fully
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•15
2A
13.12 Measure each journal diameter with
a micrometer - if any journal measures less
than the specified limit, renew the camshaft13.13A Lay a strip of Plastigage on each
camshaft journal13.13B Compare the width of the crushed
Plastigage to the scale on the envelope to
determine the running clearance
13.6A Removing hydraulic tappets13.6B Hydraulic tappets must be stored as
described in text13.8 Use a micrometer to measure
diameter of hydraulic tappets
13.10 Check the cam lobes for pitting,
wear and score marks - if scoring is
excessive, as is the case here, renew the
camshaft
procarmanuals.com
Page 57 of 279

23If using Ford’s recommended procedure,
fit new oil seals to the camshafts as
described in paragraph 5 of Section 12.
24Using the marks and notes made on
dismantling to ensure that each is refitted to
its original camshaft, refit the toothed pulleys
to the camshafts, tightening the retaining
bolts loosely (see illustration). Slip the timing
belt back onto the pulleys (refer to para-
graph 21 of Section 10) and tighten the bolts
securely - use the forked holding tool
described in paragraph 18 of Section 10.
25The remainder of the reassembly
procedure, including checking the camshaft
alignment (valve timing) and setting the timing
belt tension, is as described in paragraphs 17
to 27 of Section 10.
Removal
Note:The following text assumes that the
cylinder head will be removed with both inlet
and exhaust manifolds attached; this
simplifies the procedure, but makes it a bulky
and heavy assembly to handle - an engine
hoist will be required, to prevent the risk of
injury, and to prevent damage to any delicate
components as the assembly is removed and
refitted. If it is wished first to remove the
manifolds, proceed as described in Sections
6 and 7 of this Chapter; amend the following
procedure accordingly.1Relieve the fuel system pressure (see
Chapter 4).
2With the vehicle parked on firm level
ground, open the bonnet and disconnect the
battery negative (earth) lead - see Chapter 5,
Section 1.
3Whenever you disconnect any vacuum
lines, coolant and emissions hoses, wiring
loom connectors, earth straps and fuel lines
as part of the following procedure, always
label them clearly, so that they can be
correctly reassembled.
4Unplugging the two electrical connectors,
disconnecting the vacuum hose (where fitted)
and disconnecting the crankcase breather
hose from the cylinder head cover, remove
the complete air cleaner assembly with the air
mass meter, the resonator and the plenum
chamber (see Chapter 4).
5Equalise the pressure in the fuel tank by
removing the filler cap, then undo the fuel
feed and return lines connecting the engine to
the chassis (see Chapter 4). Plug or cap all
open fittings.
6Disconnect the accelerator cable from the
throttle linkage as described in Chapter 4 -where fitted, disconnect also the cruise control
actuator cable (see Chapter 12). Secure the
cable(s) clear of the engine/transmission.
7Unbolt the power steering high-pressure
pipe from the cylinder head rear support
plate/engine lifting eye, and from the front
support plate/pump bracket. Releasing its
wire clip, unplug the power steering pressure
switch electrical connector, then unbolt the
earth lead from the cylinder head rear support
plate/engine lifting eye.
8Remove the three screws securing the
wiring “rail” to the rear of the manifold.
Releasing its wire clip, unplug the large
electrical connector (next to the fuel pressure
regulator) to disconnect the engine wiring from
the main loom (see illustration). Unplug the
electrical connectors on each side of the
ignition coil, and the single connector from
beneath the front of the thermostat housing, to
disconnect the coil and coolant temperature
gauge sender wiring (see illustration).
9Marking or labelling them as they are
unplugged, disconnect the vacuum hoses as
follows:
(a) One from the rear of the throttle housing
(only the one hose - there is no need to
disconnect the second hose running to
the fuel pressure regulator).
(b) One from the union on the inlet manifold’s
left-hand end (see illustration).
(c) The braking system vacuum servo unit
hose (see Chapter 9 for details).
(d) Disconnect all vacuum hoses from the
Exhaust Gas Recirculation system
components - one from the EGR valve
and two from the EGR pipe. (Note that
these last two are of different sizes, as are
their pipe stubs, so that they can only be
connected the correct way round.)
10Unbolt both parts of the exhaust manifold
heat shield; unclip the coolant hose to allow the
upper part to be withdrawn. Either remove the
dipstick and tube, or swing them out of the way.
11Unscrew the single bolt securing the
pulse-air filter housing to the engine/
transmission front mounting bracket, then
disconnect its vacuum hose.
12Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
13Disconnect all coolant hoses from the
thermostat housing (see illustration).
14 Cylinder head -
removal and refitting
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•17
2A
14.9 Disconnect vacuum hoses (arrowed)
as described in text14.13 Disconnect all coolant hoses
(arrowed) from thermostat housing
13.24 . . . while camshaft toothed pulleys
are refitted14.8A Release wire clip to unplug engine
wiring loom connector from inlet manifold14.8B Unplug connectors (arrowed) to
disconnect ignition coil wiring
Masking tape and/or a touch-
up paint applicator work
well for marking items.
Take instant photos, or
sketch the locations of components
and brackets.
procarmanuals.com
Page 59 of 279

then an ordinary socket extension bar and an
angle gauge, to tighten the cylinder head
bolts in the stages given in the Specifications
Section of this Chapter (see illustrations).
Note:Once tightened correctly, following this
procedure, the cylinder head bolts do not
require check-tightening, and must notbe re-
torqued.
33Refit the hydraulic tappets (if removed),
the camshafts, their oil seals and pulleys (see
Sections 10, 11, 12 and 13, as appropriate).
Temporarily refit the crankshaft pulley, and
rotate the crankshaft clockwise to return the
pulley notches to the position described in
paragraph 8 of Section 10.
34Refit the timing belt and covers, checking
the camshaft alignment (valve timing) and
setting the timing belt tension, as described in
Section 10.
35The remainder of reassembly is the
reverse of the removal procedure, noting the
following points:
(a) Tighten all fasteners to the torque wrench
settings specified.
(b) When reassembling the
engine/transmission right-hand mounting,
renew the self-locking nuts, and do not
allow the mounting to twist as the middle
two of the bracket’s six nuts are
tightened.
(c) Refill the cooling system, and top-up the
engine oil.
(d) Check all disturbed joints for signs of oil
or coolant leakage, once the engine has
been restarted and warmed-up to normal
operating temperature.
Removal
Note:To carry out this task with the
engine/transmission installed in the vehicle
requires the assistance of at least one person,
plus the equipment necessary to raise and
support the front of the vehicle (high enough
that the sump can be withdrawn from
underneath), and to lift and support the
complete engine/transmission unit 2 to 3 inches from its mountings while the vehicle
is raised. Precise details of the procedure will
depend on the equipment available - the
following is typical.
The full procedure outlined below must be
followed, so that the mating surfaces can be
cleaned and prepared to achieve an oil-tight
joint on reassembly, and so that the sump
can be aligned correctly; depending on your
skill and experience, and the tools and
facilities available, it may be that this task can
be carried out only with the engine removed
from the vehicle.
Note that the sump gasket must be
renewed whenever it is disturbed.
1With the vehicle parked on firm level
ground, open the bonnet and disconnect the
battery negative (earth) lead - see Chapter 5,
Section 1.
2Drain the engine oil, then clean and refit the
engine oil drain plug, tightening it to the
specified torque wrench setting. Although not
strictly necessary as part of the dismantling
procedure, owners are advised to remove
and discard the oil filter, so that it can be
renewed with the oil (see Chapter 1).
3Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
4Disconnect the radiator bottom hose from
the radiator union and from the (heater)
coolant pipe. Unbolt the coolant pipe from
the sump; if they will prevent sump removal,
disconnect or release the coolant hoses from
the oil cooler unions (where fitted).
5Unscrew the two bolts securing the powersteering system pipes to the right-hand side
of the subframe.
6Unplug the electrical connector(s) to
disconnect the oxygen sensor and, where
fitted, the oil level sensor wiring - unclip the
connectors to release the wiring where
necessary.
7Where the vehicle is fitted with automatic
transmission, trace the fluid cooler lines from
the transmission to the radiator, and release
them from any clips etc, so that they have as
much movement as possible.
8Remove the auxiliary drivebelt cover (see
Chapter 1).
9Unscrew the nuts to disconnect the
exhaust system front downpipe from the
manifold, then either unhook all the system’s
rubber mountings and withdraw the complete
exhaust system from under the vehicle, or
remove only the downpipe/catalytic converter
(see Chapter 4 for details).
10Unscrew the sump-to-transmission bolts,
also any securing the engine/transmission
lower adaptor plate.
11Unplugging the two electrical connectors,
disconnecting the vacuum hose (where fitted)
and disconnecting the crankcase breather
hose from the cylinder head cover, remove
the complete air cleaner assembly with the air
mass meter, the resonator and the plenum
chamber (see Chapter 4).
12Take the weight of the engine/
transmission unit using the lifting eyes
provided on the cylinder head; bolt on
15 Sump - removal and refitting
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•19
2A
14.32B . . . and to third stage using angle
gauge14.32C Cylinder head bolt tightening
sequence
Note:View from rear of vehicle15.12 Equipment must be available to raise
and support engine/transmission unit while
vehicle is raised, to allow sump removal
14.30 Refitting cylinder head - note
fabricated guide studs (arrowed)14.32A Tightening cylinder head bolts (to
first and second stages) using torque
wrench . . .
procarmanuals.com
Page 61 of 279
and right-hand mountings. Do not yet
release the hoist; the weight of the
engine/transmission unit must not be
taken by the mountings until all are
correctly aligned.
(d) Fitting the Ford service tool in place of the
front mounting, tighten the
engine/transmission mounting fasteners
to their specified torque wrench settings,
and in the sequence described in Part B
of this Chapter, Section 4, paragraphs 49
and 50.
(e) Refill the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
(f) Refill the engine with oil, remembering
that you are advised to fit a new filter (see
Chapter 1).
(g) Check for signs of oil or coolant leaks
once the engine has been restarted and
warmed-up to normal operating
temperature.
Removal
Note:While this task is theoretically possible
when the engine is in place in the vehicle, in
practice, it requires so much preliminary
dismantling, and is so difficult to carry out due
to the restricted access, that owners are
advised to remove the engine from the vehicle
first. Note, however, that the oil pumppressure relief valve can be removed with the
engine in situ - see paragraph 8.
In addition to the new pump gasket and
other replacement parts required, read
through Section 15, and ensure that the
necessary tools and facilities are available.
1Remove the timing belt (see Section 10).
2Withdraw the crankshaft toothed pulley
and the thrustwasher behind it, noting which
way round the thrustwasher is fitted (see
Section 11).
3Remove the sump (see Section 15).
4Undo the screws securing the oil pump
pick-up/strainer pipe to the pump, then
unscrew the nut and withdraw the oil pump
pick-up/strainer pipe. Discard the gasket.
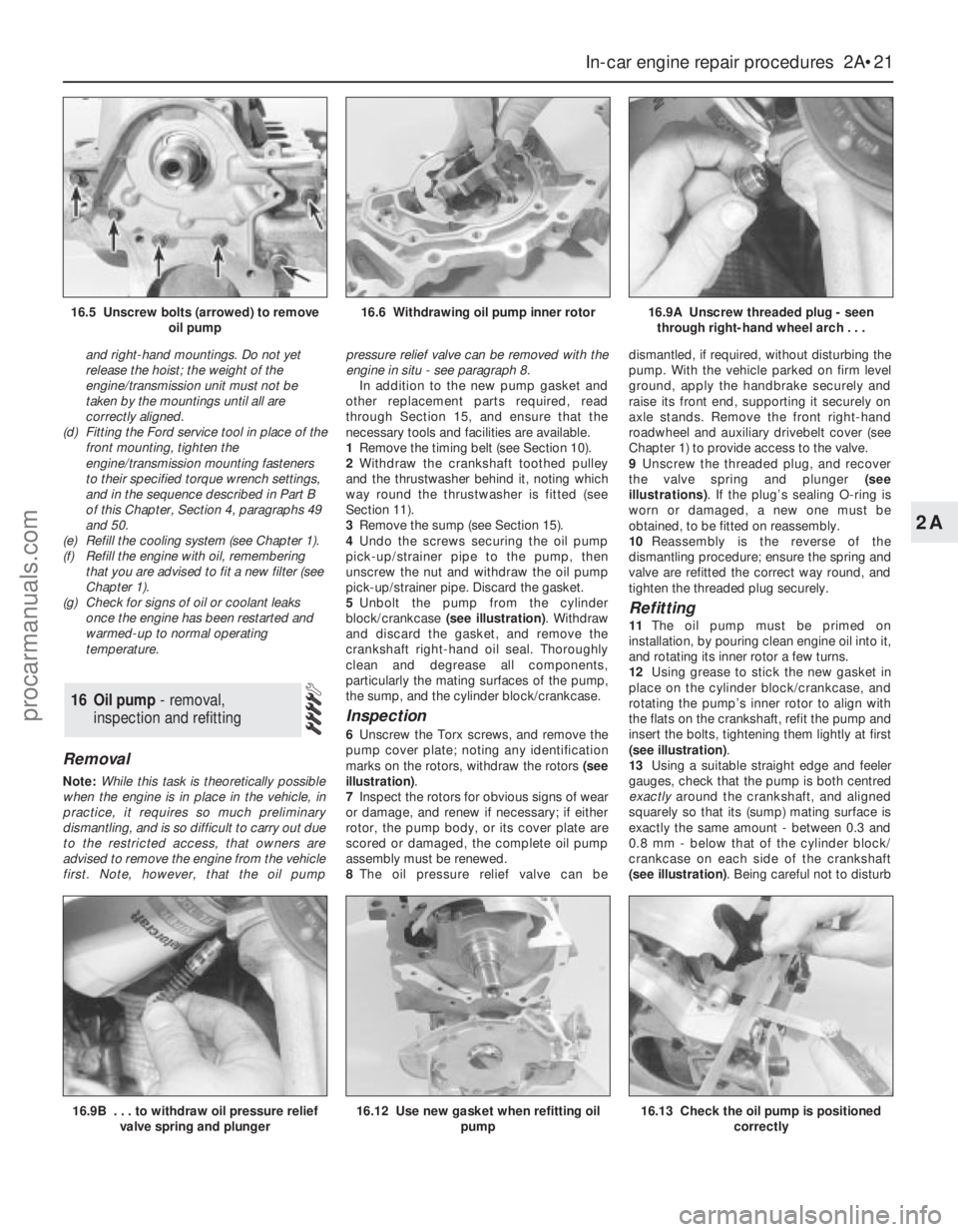
5Unbolt the pump from the cylinder
block/crankcase (see illustration). Withdraw
and discard the gasket, and remove the
crankshaft right-hand oil seal. Thoroughly
clean and degrease all components,
particularly the mating surfaces of the pump,
the sump, and the cylinder block/crankcase.
Inspection
6Unscrew the Torx screws, and remove the
pump cover plate; noting any identification
marks on the rotors, withdraw the rotors (see
illustration).
7Inspect the rotors for obvious signs of wear
or damage, and renew if necessary; if either
rotor, the pump body, or its cover plate are
scored or damaged, the complete oil pump
assembly must be renewed.
8The oil pressure relief valve can bedismantled, if required, without disturbing the
pump. With the vehicle parked on firm level
ground, apply the handbrake securely and
raise its front end, supporting it securely on
axle stands. Remove the front right-hand
roadwheel and auxiliary drivebelt cover (see
Chapter 1) to provide access to the valve.
9Unscrew the threaded plug, and recover
the valve spring and plunger (see
illustrations). If the plug’s sealing O-ring is
worn or damaged, a new one must be
obtained, to be fitted on reassembly.
10Reassembly is the reverse of the
dismantling procedure; ensure the spring and
valve are refitted the correct way round, and
tighten the threaded plug securely.
Refitting
11The oil pump must be primed on
installation, by pouring clean engine oil into it,
and rotating its inner rotor a few turns.
12Using grease to stick the new gasket in
place on the cylinder block/crankcase, and
rotating the pump’s inner rotor to align with
the flats on the crankshaft, refit the pump and
insert the bolts, tightening them lightly at first
(see illustration).
13Using a suitable straight edge and feeler
gauges, check that the pump is both centred
exactlyaround the crankshaft, and aligned
squarely so that its (sump) mating surface is
exactly the same amount - between 0.3 and
0.8 mm - below that of the cylinder block/
crankcase on each side of the crankshaft
(see illustration). Being careful not to disturb
16 Oil pump - removal,
inspection and refitting
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•21
2A
16.9B . . . to withdraw oil pressure relief
valve spring and plunger16.12 Use new gasket when refitting oil
pump16.13 Check the oil pump is positioned
correctly
16.5 Unscrew bolts (arrowed) to remove
oil pump16.6 Withdrawing oil pump inner rotor16.9A Unscrew threaded plug - seen
through right-hand wheel arch . . .
procarmanuals.com