1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM ignition
[x] Cancel search: ignitionPage 270 of 2438
DIAGNOSTIC CONNECTOR
On the AA, AG, AJ and AP bodies, the Bendix An-
ti-Lock System diagnostic connector is located under
the fuse panel access cover. The access cover is lo-
cated on the lower section of the instrument panel on
the left side of the steering column. The diagnostics
connector is a blue 6 way connector see (Fig. 8).
ANTI-LOCK SYSTEM RELAYS AND WARNING
LAMPS
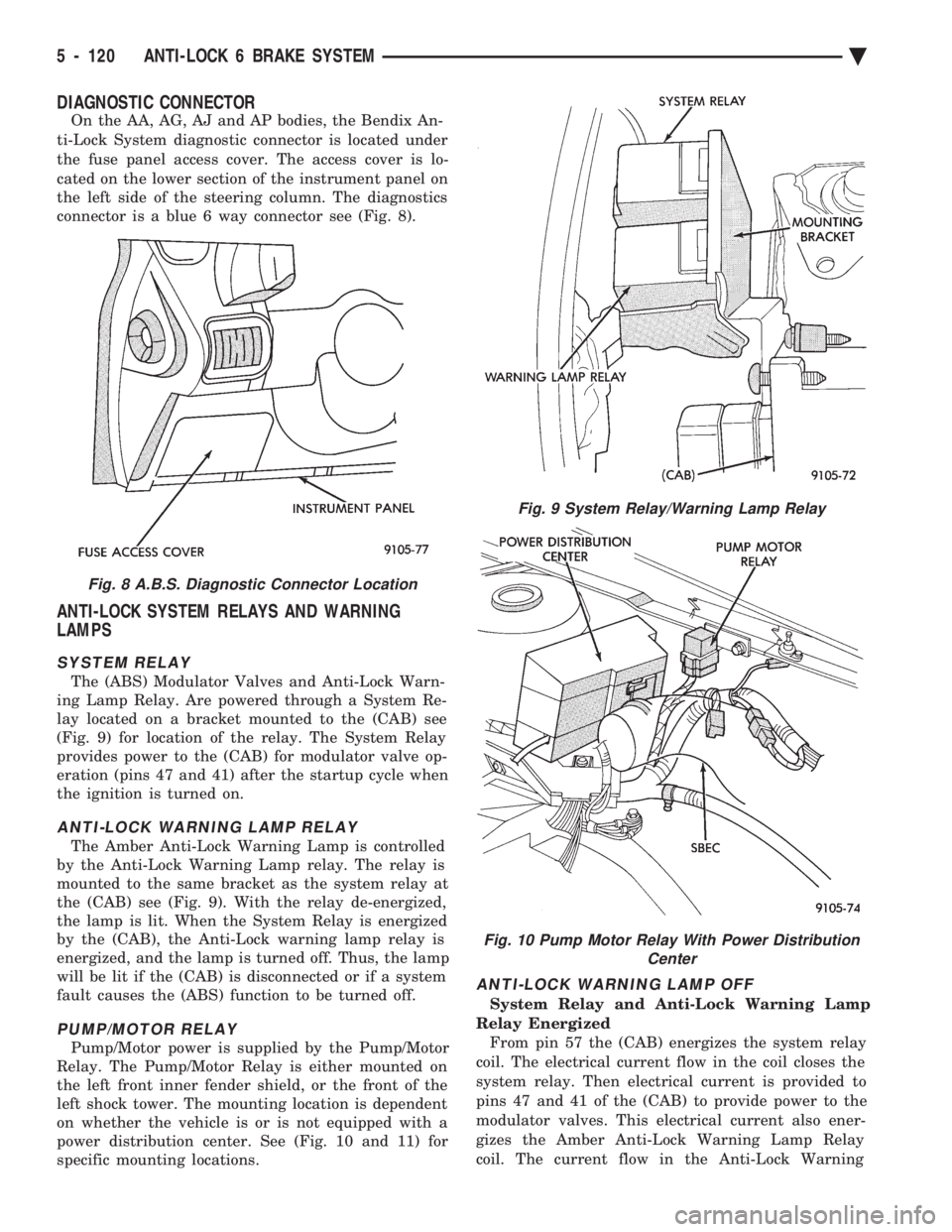
SYSTEM RELAY
The (ABS) Modulator Valves and Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp Relay. Are powered through a System Re-
lay located on a bracket mounted to the (CAB) see
(Fig. 9) for location of the relay. The System Relay
provides power to the (CAB) for modulator valve op-
eration (pins 47 and 41) after the startup cycle when
the ignition is turned on.
ANTI-LOCK WARNING LAMP RELAY
The Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp is controlled
by the Anti-Lock Warning Lamp relay. The relay is
mounted to the same bracket as the system relay at
the (CAB) see (Fig. 9). With the relay de-energized,
the lamp is lit. When the System Relay is energized
by the (CAB), the Anti-Lock warning lamp relay is
energized, and the lamp is turned off. Thus, the lamp
will be lit if the (CAB) is disconnected or if a system
fault causes the (ABS) function to be turned off.
PUMP/MOTOR RELAY
Pump/Motor power is supplied by the Pump/Motor
Relay. The Pump/Motor Relay is either mounted on
the left front inner fender shield, or the front of the
left shock tower. The mounting location is dependent
on whether the vehicle is or is not equipped with a
power distribution center. See (Fig. 10 and 11) for
specific mounting locations.
ANTI-LOCK WARNING LAMP OFF
System Relay and Anti-Lock Warning Lamp
Relay Energized From pin 57 the (CAB) energizes the system relay
coil. The electrical current flow in the coil closes the
system relay. Then electrical current is provided to
pins 47 and 41 of the (CAB) to provide power to the
modulator valves. This electrical current also ener-
gizes the Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp Relay
coil. The current flow in the Anti-Lock Warning
Fig. 8 A.B.S. Diagnostic Connector Location
Fig. 9 System Relay/Warning Lamp Relay
Fig. 10 Pump Motor Relay With Power Distribution Center
5 - 120 ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 274 of 2438

In order to effectively diagnose an Anti-Lock Brake
System (ABS) condition. It is important to read Anti-
Lock Brake System Description. And to follow the
diagnostic procedures outlined in this section. Many conditions that generate customer complaints
may be normal operating conditions, but are judged to
be a problem due to not being familiar with the ABS
system. These conditions can be recognized without
performing extensive diagnostic work. Given adequate
understanding of the operating principles and perfor-
mance characteristics of the ABS system. See Section 1
of this manual to familiarize yourself with the operat-
ing principles of the ABS system.
DEFINITIONS
Several abbreviations are used in this manual. They
are presented here for reference.
² CABÐController Anti-Lock Brake
² ABSÐAnti-Lock Brake System
² PSIÐPounds per Square Inch (pressure)
² WSSÐWheel Speed Sensor
ABS COMPUTER SYSTEM SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
The ABS system uses an electronic control module,
the (CAB). This module is designed to withstand nor-
mal current draws associated with vehicle operation.
However care must be taken to avoid overloading the
(CAB) circuits. In testing for open or short circuits,
do not ground or apply voltage to any of the
circuits unless instructed to do so by the appro-
priate diagnostic procedure. These circuits should
only be tested using a high impedance multi-meter,
special tools or the DRB II tester as described in this
section. Power should never be removed or applied to
any control module with the ignition in the ON posi-
tion. Before removing or connecting battery cables,
fuses, or connectors, always turn the ignition to the
OFF position.
ABS GENERAL SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
TEST DRIVING ABS COMPLAINT VEHICLES
Most ABS complaints will require a test drive as a
part of the diagnostic procedure. The purpose of the
test drive is to duplicate the condition. Remember conditions that result in the turn-
ing on of the Red Brake Warning Lamp may
indicate reduced braking ability. The following
procedure should be used to test drive an ABS
complaint vehicle. Before test driving a brake complaint vehicle, note
whether the Red or Amber Brake Warning Lamp is
turned on. If it is the Red Brake Warning Lamp, refer
to the standard brake, Control Valves Section in the
brake group of this manual. If the Amber Anti-Lock
Warning light was/is on, read record and erase the
fault. While the Amber ABS Warning Lamp is on the
ABS system is not functional. When the Am- ber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp is on only the Anti-Lock
function of the brake system if affected. The standard
brake system and the ability to stop the car is not be
affected if only the Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp is
on. (1) Turn the key to the off position and then back to
the on position. Note whether the Amber ABS Warning
Lamp continues to stay on. If it does refer to the 1993
M.Y. Bendix Anti-Lock 6 Diagnostic Manual for the
required test procedures. (2) If the Amber ABS Warning Lamp goes out, shift
into gear and drive the car to a speed of 5 mph to
complete the ABS start up cycle. If at this time the
Amber ABS Warning Lamp goes on refer to the Bendix
Anti-Lock 6 Diagnostic Manual. (3) If the Amber ABS Warning Lamp remains OUT,
drive the vehicle a short distance. During this test
drive be sure that the vehicle achieves at least 25 mph.
Brake to at least one complete stop and again acceler-
ate to 25 mph. (4) If a functional problem with the A.B.S. system is
determined while test driving a vehicle. Refer to the
Bendix Anti-Lock 6 Diagnostics Manual for required
test procedures and proper use of the DRB II tester.
ABS BRAKE SYSTEM ON VEHICLE SERVICE
The following are general precautions which
should be observed when servicing and diagnos-
ing the ABS system and/or other vehicle systems.
Failure to observe these precautions may result
in ABS system damage. (1) If welding work is to be performed on a vehicle
using an arc welder, the (CAB) should be disconnected
before the welding operation begins. (2) The (CAB) and modulator assembly 10 way con-
nector should never be connected or disconnected with
the ignition in the on position. (3) Some components of the ABS system are not
serviced separately and must be serviced as complete
assemblies. Do not disassemble any component which
is designated as non-serviceable.
CAUTION: Brake fluid will damage painted surfaces.
If brake fluid is spilled on any painted surfaces, wash
off with water immediately.
WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CABLES
Proper installation of the Wheel Speed Sensor Cables
is critical to continued system operation. Be sure that
cables are installed, routed and clipped properly. Fail-
ure to install speed sensor cables as shown in the on
car service section of this manual. May result in
contact with moving parts or over extension of cables,
resulting in component failure and an open circuit.
5 - 124 ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 275 of 2438

MECHANICAL DIAGNOSTICS AND SERVICE
PROCEDURES
SPECIAL SERVICE TOOL
Some diagnostic procedures in this section require
the use of the DRB II diagnostics tester. The proper
application and procedures for the use of this tool are
described below.
DRB II DIAGNOSTIC TESTER Some of the diagnostic procedures that are ex-
plained in this section require the use of the DRB II
Diagnostics Tester to insure that proper diagnostics
are performed. Refer to those sections for proper test-
ing procedures and the DRB II operators manual for
its proper operational information.
INTERMITTENT FAULTS
As with virtually any electronic system, intermit-
tent faults in the ABS system may be difficult to ac-
curately diagnose. Most intermittent faults are caused by faulty elec-
trical connections or wiring. When an intermittent
fault is encountered, check suspect circuits for: (1) Poor mating of connector halves or terminals
not fully seated in the connector body. (2) Improperly formed or damaged terminals. All
connector terminals in a suspect circuit should be
carefully reformed to increase contact tension. (3) Poor terminal to wire connection. This requires
removing the terminal from the connector body to in-
spect. (4) Pin presence in the connector assembly
If a visual check does not find the cause of the
problem, operate the car in an attempt to duplicate
the condition and record the Fault code. Most failures of the ABS system will disable Anti-
Lock function for the entire ignition cycle even if the
fault clears before key-off. There are some failure
conditions, however, which will allow ABS operation
to resume during the ignition cycle in which a fail-
ure occurred. If the failure conditions are no longer
present. The following conditions may result in inter-
mittent illumination of the Amber Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp. All other failures will cause the lamp to
remain on until the ignition switch is turned off. Cir-
cuits involving these inputs to the (CAB) should be
investigated if a complaint of intermittent warning
system operation is encountered. (1) Low system voltage. If Low System Voltage is
detected by the (CAB), the (CAB) will turn on the
Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp until normal sys-
tem voltage is achieved. Once normal voltage is seen
at the (CAB), normal operation resumes. (2) Anti-Lock relay. If the relay fails to make the
ground circuit connection or is an intermittent
ground. The (CAB) will turn on the Amber Anti-Lock
Warning Light. (3) Excess decay, an extended pressure decay pe-
riod, will turn on the Amber Anti-Lock Warning
Light until the vehicle comes to a complete stop. Additionally, any condition which results in inter-
ruption of electrical current to the (CAB) or modula-
tor assembly. May cause the Amber Anti-Lock
Warning Lamp to turn on intermittently.
ABS BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES
ABS SYSTEM SELF DIAGNOSIS
The ABS system is equipped with a self diagnostic
capability which may be used to assist in isolation of
ABS faults. The features of the self diagnostics sys-
tem are described below.
START-UP CYCLE
The self diagnostic ABS start up cycle begins when
the ignition switch is turned to the on position. An
electrical check is completed on the ABS components.
Such as Wheel Speed Sensor Continuity and System
and other Relay continuity. During this check the
Amber Anti-Lock Light is turned on for approxi-
mately 1- 2 seconds. Further Functional testing is accomplished once
the vehicle is set in motion.
² The solenoid valves and the pump/motor are acti-
vated briefly to verify function.
² The voltage output from the wheel speed sensors is
verified to be within the correct operating range. If the vehicle is not set in motion within 3 minutes
from the time the ignition switch is set in the on po-
sition. The solenoid test is bypassed but the pump/
motor is activated briefly to verify that it is
operating correctly.
CONTROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (CAB)
Fault codes are kept in a Non-Volatile memory un-
til either erased by the technician using the DRB II
or erased automatically after 50 ignition cycles (key
ON-OFF cycles). The only fault that will not be
erased after 50 (KEY CYCLES) is the (CAB) fault. A
(CAB) fault can only be erased by the technician us-
ing the DRB II diagnostic tester. More than one fault
can be stored at a time. The number of key cycles
since the most recent fault was stored is also dis-
played. Most functions of the (CAB) and ABS system
can be accessed by the technician for testing and di-
agnostic purposes by using the DRB II.
LATCHING VERSUS NON-LATCHING ABS FAULTS
Some faults detected by the (CAB) are latching; the
fault is latched and (ABS) is disabled until the igni-
tion switch is reset. Thus ABS is disabled even if the
original fault has disappeared. Other faults are non-
latching; any warning lights that are turned on, are
only turned on as long as the fault condition exists.
Ä ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 125
Page 276 of 2438

As soon as the condition goes away, the Anti-Lock
Warning Light is turned off. Although a fault code
will be set in most cases.
BENDIX ABS SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS
Bendix Anti-Lock 6 Brake System Diagnostics, be-
yond basic mechanical diagnostics, covered earlier in
this section. Are accomplished by using the DRB II
scan tool. See testing procedures outlined in the Ben-
dix Anti-Lock 6 Diagnostics Manual for the 1992
M.Y. vehicles. Please refer to the above mentioned manual for
any further electronic diagnostics and service proce-
dures that are required on the Bendix Anti-Lock 6
Brake System.
ON-CAR ABS BRAKE SYSTEM SERVICE
GENERAL SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
The following are general cautions which should be
observed when servicing the Anti-Lock brake system
and/or other vehicle systems. Failure to observe
these precautions may result in Anti-Lock Brake
System component damage. If welding work is to be performed on the vehicle,
using an electric arc welder, the (CAB) connector
should be disconnected during the welding operation. The (CAB) connector should never be connected or
disconnected with the ignition switch in the ON po-
sition. Many components of the Anti-Lock Brake System
are not serviceable and must be replaced as an as-
sembly. Do not disassemble any component which is
not designed to be serviced.
CHECKING BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
CAUTION: Only use brake fluid conforming to DOT
3 specifications, such as Mopar or Equivalent. Do
not use any fluid which contains a petroleum base.
Do not use a container which has been used for pe-
troleum based fluids or a container which is wet
with water. Petroleum based fluids will cause swell-
ing and distortion of rubber parts in the hydraulic
brake system. Water will mix with brake fluid, low-
ering the fluid boiling point. Keep all brake fluid
containers capped to prevent contamination. Re-
move the front cap of the master cylinder reservoir
and fill to the bottom of the split ring.
For the specific procedure for the inspection of
brake fluid level and adding of brake to the reser-
voir. Refer to the Service Adjustments Section in this
group of the service manual.
BLEEDING BENDIX ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM
The Anti-Lock Brake System must be bled anytime
air is permitted to enter the hydraulic system, due to
disconnection of brake lines, hoses of components. If the Modulator Assembly is removed from the ve-
hicle, both the Base Brake System and the Anti-Lock
Brake System must be bled using the appropriate
procedures. It is important to note that excessive air
in the brake system will cause a soft or spongy feel-
ing brake pedal. During bleeding operations, be sure that the brake
fluid level remains close to the FULL level in the
reservoir. Check the fluid level periodically during
the bleeding procedure and add DOT 3 brake fluid as
required. The Bendix Anti-Lock 6 Brake System must be
bled as two independent braking systems. The non
ABS portion of the brake system is to be bled the
same as any non ABS system. Refer to the Service
Adjustments section in this manual for the proper
bleeding procedure to be used. This brake system can
be either pressure bled or manually bled. The Anti-Lock portion of brake system MUST be
bled separately. This bleeding procedure requires the
use of the DRB II Diagnostic tester and the bleeding
sequence procedure outlined below.
ABS BLEEDING PROCEDURE (FIG. 1)
(1) Assemble and install all brake system compo-
nents on vehicle making sure all hydraulic fluid
lines are installed and properly torqued. (2) Bleed the base brake system. Using the stan-
dard pressure or manual bleeding procedure as out-
lined in the Service Adjustments section of this
service manual. To perform the bleeding procedure on the ABS
unit. The battery and acid shield must be removed
from the vehicle. Reconnect the vehicles battery, to
the vehicles positive and negative battery cables us-
ing jumper cables. This is necessary to allow access
to the 4 bleeder screws located on the top of the Mod-
ulator assembly. (3) Connect the DRB II Diagnostics Tester to the
diagnostics connector. Located behind the Fuse Panel
access cover on the lower section of the dash panel to
the left of the steering column. (It is a blue 6 way
connector). (4) Using the DRB II check to make sure the
(CAB) does not have any fault codes stored. If it does
remove them using the DRB II.
5 - 126 ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 280 of 2438
junction block. Torque both lower mounting bracket
bolts to 28 N Im (250 in. lbs.)
(4) Reinstall the 4 hydraulic brake tubes to the
Modulator Assembly and torque the fittings to 16
N Im (145 in. lbs.).
(5) Reconnect the 10 way Modulator assembly con-
nector, and the delta P switch connector. (6) Lower the vehicle and install the 2 master cyl-
inder supply tubes to the Modulator Assembly.
Torque the Modulator Assembly fittings and the
master cylinder fittings to 16 N Im (145 in.lbs.).
(7) Torque the Modulator to fender splash shield
attaching bolt to 28 N Im (250 in. lbs.)
(8) Bleed the brake system. Refer to the Bleeding
Bendix Anti 6 Brake System in this section of the
manual for proper bleeding procedure. (9) Reinstall the acid shield and battery tray. Re-
install battery and connect battery cables.
MASTER CYLINDER AND POWER BOOSTER
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
If the Master Cylinder or the Power Booster need
to be serviced or replaced. Refer to Master Cylinder
or Power Brake Service section in this group of the
service manual. After servicing the Master Cylinder. Refer back to
this section of the service manual. For the appropri-
ate procedure and sequence, used to bleed the base
and ABS portion of the brake system
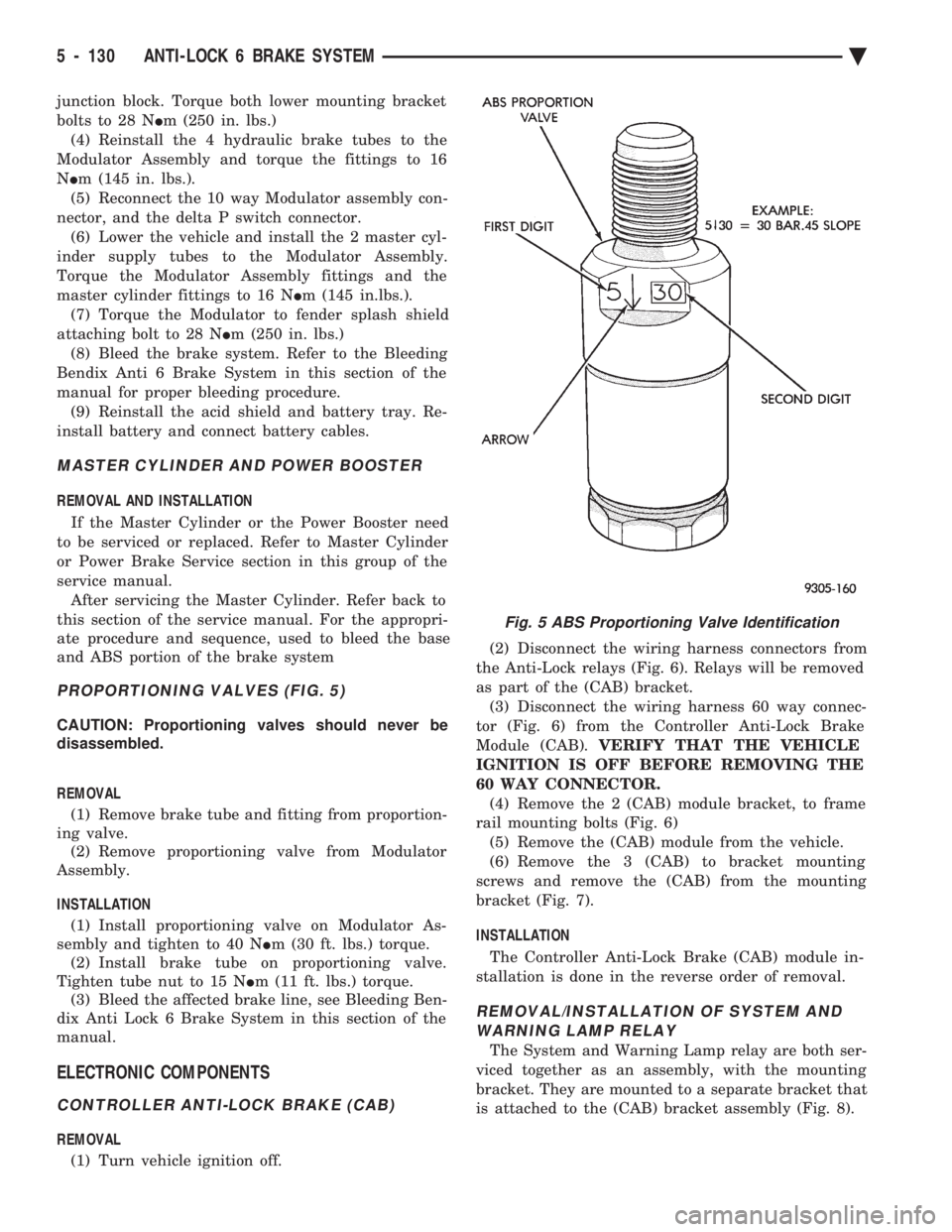
PROPORTIONING VALVES (FIG. 5)
CAUTION: Proportioning valves should never be
disassembled.
REMOVAL (1) Remove brake tube and fitting from proportion-
ing valve. (2) Remove proportioning valve from Modulator
Assembly.
INSTALLATION (1) Install proportioning valve on Modulator As-
sembly and tighten to 40 N Im (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install brake tube on proportioning valve.
Tighten tube nut to 15 N Im (11 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Bleed the affected brake line, see Bleeding Ben-
dix Anti Lock 6 Brake System in this section of the
manual.
ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS
CONTROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (CAB)
REMOVAL
(1) Turn vehicle ignition off. (2) Disconnect the wiring harness connectors from
the Anti-Lock relays (Fig. 6). Relays will be removed
as part of the (CAB) bracket. (3) Disconnect the wiring harness 60 way connec-
tor (Fig. 6) from the Controller Anti-Lock Brake
Module (CAB). VERIFY THAT THE VEHICLE
IGNITION IS OFF BEFORE REMOVING THE
60 WAY CONNECTOR. (4) Remove the 2 (CAB) module bracket, to frame
rail mounting bolts (Fig. 6) (5) Remove the (CAB) module from the vehicle.
(6) Remove the 3 (CAB) to bracket mounting
screws and remove the (CAB) from the mounting
bracket (Fig. 7).
INSTALLATION
The Controller Anti-Lock Brake (CAB) module in-
stallation is done in the reverse order of removal.
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION OF SYSTEM AND WARNING LAMP RELAY
The System and Warning Lamp relay are both ser-
viced together as an assembly, with the mounting
bracket. They are mounted to a separate bracket that
is attached to the (CAB) bracket assembly (Fig. 8).
Fig. 5 ABS Proportioning Valve Identification
5 - 130 ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 297 of 2438

The instrument panel bulb can be checked each
time the ignition switch is turned to the start posi-
tion or the parking brake is set.
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURES
BRAKE WARNING SYSTEM
CHECKING BRAKE WARNING SWITCH UNIT
The Red Brake Warning light will come on when the
parking brake is applied with the ignition key turned
ON. The same light will also illuminate should one of
the two service brake hydraulic systems fail.
CAUTION:Make sure air does not enter the hydraulic
system during this test procedure. See bleeding with-
out a pressure bleeder at the beginning of this section
for master cylinder fluid level checking procedures.
To test the service brake warning system lamp.
Raise vehicle on a hoist and open a wheel cylinder
bleeder while a helper depresses the brake pedal and
observes the warning light.
If light fails to come on, inspect for a burned out bulb,
disconnected socket, or a broken or disconnected wire at
the switch. If the bulb is not burned out and the wire
continuity is not interrupted. Check the service brake
warning switch operation with a test lamp between the
switch terminal and a known good ground. Be sure to
fill master cylinder and bleed brake system after correc-
tion has been made, if necessary.
TESTING ANTILOCK PROPORTIONING VALVES
(1) Install one gauge and (TEE) between modula-
tor assembly and male end (Inlet) of proportioning
valve (Fig. 4). (2) Install second gauge at female end (Outlet) of
proportioning valve (Fig. 4).
(3) Have a helper exert pressure on brake pedal to
obtain and hold required pressure reading on the
valve inlet gauge. (4) Check reading on outlet gauge. If inlet and out-
let pressures do not agree with the following chart,
replace the valve. See (Fig. 3) for proportioning valve
identification.
BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 PROPORTIONING VALVE APPLICATIONS
BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 PROPORTIONING VALVE PRESSURES
Fig. 4 Tube Connections for ABS
Ä BRAKES 5 - 11
Page 301 of 2438

ANTILOCK BRAKES OPERATION AND
PERFORMANCE
The Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System represents
the current state-of-the-art in vehicle brake systems
and offers the driver increased safety and control
during braking. This is accomplished by a sophisti-
cated system of electrical and hydraulic components.
As a result, there are a few performance characteris-
tics that may at first seem different but should be
considered normal. These characteristics are dis-
cussed below. More technical details are discussed
further in this section.
PEDAL FEEL
Since the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System uses the
vehicle's conventional brake system power booster
and master cylinder. The brake pedal feel during
normal braking is the same as on a conventional
Non ABS equipped vehicle. When the Antilock system becomes activated dur-
ing hard braking due to a wheel lockup tendency.
The brake pedal effort will increase do to the master
cylinder pressure being isolated from the brake sys-
tem. Some brake pedal movement and associated
noises may be felt and heard by the driver. This is
normal operation of the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake
System due to pressurized brake fluid being trans-
ferred to and from the wheel brakes.
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATION
During Antilock Brake system operation, brake
pressures are modulated by cycling electric solenoid
valves. The cycling of these valves can be heard as a
series of popping or ticking noises. In addition, the
cycling may be felt as a pulsation in the brake pedal.
If Antilock operation occurs during a hard applica-
tion of the brakes, some pulsation may be felt in the
vehicle body due to fore and aft movement of vehicle
suspension components. Although ABS operation is available at virtually
all vehicle speeds, it will automatically turn off at
speeds below 3 to 5 mph. Wheel lockup may be per-
ceived at the very end of an anti lock stop and is con-
sidered normal.
TIRE NOISE & MARKS
Although the ABS system prevents complete wheel
lock-up, some wheel slip is desired in order to
achieve optimum vehicle braking performance. During brake fluid pressure modulation, as the
brake fluid pressure is increased, wheel slip is al-
lowed to reach up to 30%. This means that wheel
rolling speed is 30% less than that of a free rolling
wheel at a given vehicle speed. This slip may result
in some tire chirping, depending on the road surface.
This sound should not be interpreted as total wheel
lock-up. Complete wheel lock up normally leaves black tire
marks on dry pavement. The Antilock Brake System
will not leave dark black tire marks since the wheel
never reaches a locked condition. Tire marks may
however be noticeable as light patched marks.
VEHICLE PERFORMANCE
Antilock Brakes provide the driver with some
steering control during hard braking, however there
are conditions where the system does not provide any
benefit. In particular, hydroplaning is still possible
when the tires ride on a film of water. This results in
the vehicles tires leaving the road surface rendering
the vehicle virtually uncontrollable. In addition, ex-
treme steering maneuvers at high speed or high
speed cornering beyond the limits of tire adhesion to
the road surface may cause vehicle skidding, inde-
pendent of vehicle braking. For this reason, the ABS
system is termed Antilock instead of Anti-Skid.
SYSTEM SELF-DIAGNOSTICS
The Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System has been de-
signed with the following self diagnostic capabilities. The self diagnostic ABS startup cycle begins when
the ignition switch is turned to the on position. At
this time an electrical check is completed on the ABS
components such as Wheel Speed Sensor Continuity
and System and other Relay continuity. During this
check the Amber Antilock Light is on for approxi-
mately 1-2 seconds. Further Antilock Brake System functional testing
is accomplished once the vehicle is set in motion,
known as drive-off. (1) The solenoid valves and the pump/motor are ac-
tivated briefly to verify function.
Fig. 5 Controller Antilock Brake CAB
Ä ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 15
Page 302 of 2438

(2) The voltage output from each of the wheel
speed sensors is verified to be within the correct op-
erating range. If a vehicle is not set in motion within 3 minutes
from the time the ignition switch is turned to the on
position. The solenoid valve test is bypassed but the
pump/motor is activated briefly to verify that it is op-
erating correctly.
WARNING SYSTEMS OPERATION
The ABS system uses an Amber Antilock Warning
Lamp, located in the instrument cluster. The purpose
of the warning lamp is discussed in detail below. The Amber Antilock Warning Light will turn on
whenever the CAB detects a condition which results
in a shutdown of the Antilock brake system. The
Amber Antilock Warning Lamp is normally on until
the CAB completes its self tests and turns the lamp
off (approximately 1-2 seconds). When the Amber
Antilock Warning Light is on, only the Antilock
brake function of the brake system if affected. The
standard brake system and the ability to stop the car
will not be affected when only the Amber Antilock
Warning Light is on.
NORMAL OPERATION OF WARNING LAMP
With ignition key turned to the Crank position, the
Red Brake Warning Lamp and Amber Antilock
Warning Lamp will turn on as a bulb check. The
Amber Antilock Warning Lamp will stay on for 1-2
seconds then turn off, once verification of Antilock
Brake System self diagnosis is completed.
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The following is a detailed description of the Ben-
dix Antilock 4 Brake System components. For infor-
mation on servicing the Four Wheel Disc Brake
System, see the standard Brake section in the Front
Wheel Drive Car, chassis service manual.
MODULATOR ASSEMBLY
WARNING: THE ONLY COMPONENTS OF THE
MODULATOR ASSSEMBLY THAT ARE SERVICE-
ABLE, ARE THE 2 PROPORTIONING VALVES,
BLEED SCREWS AND THREAD SAVERS. THE RE-
MAINING COMPONENTS OF THE MODULATOR AS-
SEMBLY ARE NOT INTENDED TO BE
SERVICEABLE ITEMS. NO ATTEMPT SHOULD BE
MADE TO REMOVE OR SERVICE ANY OTHER COM-
PONENTS OF THE MODEULATOR ASSEMBLY.
The Modulator Assembly (Fig. 1) is located under
the battery tray and is covered with an acid shield.
The Modulator Assembly contains the following com-
ponents for controlling the Antilock brake system. 4
Build/Decay Valves, 4 Shuttle Orifices, 2 Fluid
Sumps, 2 Accumulators, and a Pump/Motor assem- bly. Also attached to the Modulator Assembly are 6
brake tubes which are connected to a 12 way junc-
tion block. The junction block (Fig. 2) is mounted to
the left frame rail below the master cylinder in the
same location as the non ABS equipped combination
valve. The wheel brake lines are attached to the sys-
tem via the connector block.BUILD/DECAY VALVES
There are 4 Build/Decay valves, one for each
wheel. In the released position they provide a fluid
path direct to the wheel brakes. In the actuated (de-
cay) position, they provide a fluid path from the
wheel brakes to the sump. The Build/Decay valves
are spring loaded in the released (build) position.
SHUTTLE ORIFICE
There are 4 Shuttle Orifice Valves, one for each
wheel. The Shuttle Orifice Valve is a hydraulically
actuated valve which shuttles when the Build/Decay
valve is actuated. Actuating of the Build/Decay valve
causes a pressure differential to be created across the
Shuttle Orifice Valve. This acts like placing an ori-
Fig. 1 Modulator Assembly
Fig. 2 Antilock Brake Junction Block
5 - 16 ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä