1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM wiring
[x] Cancel search: wiringPage 216 of 2438

MASTER CYLINDER INDEX
page page
Brake Fluid Level Sensor .................. 66
General Information ....................... 66 Master Cylinder Service Procedures
.......... 67
Testing the Master Cylinder ................. 66
GENERAL INFORMATION
The tandem master cylinder (Fig. 1) has a glass re-
inforced nylon reservoir and an anodized aluminum
body. Do not hone the bore of the cylinder, as this will
remove the anodized surface. The reservoir is indexed to prevent installation in
the wrong direction (Fig. 2). The cap diaphragms are
slit to allow atmospheric pressure to equalize on both
sides of the diaphragm. The primary and secondary outlet tubes from the
master cylinder are connected to the valve mounted
under the master cylinder. The front part of this
block connects to the secondary outlet tube and sup-
plies the right rear and left front brakes. The rear
portion of the block connects to the primary outlet
tube and supplies the right front and left rear
brakes.
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SENSOR
The Brake Fluid Level sensor is found only in the
AJ body vehicles with the visual electronic message
center. The purpose of the sensor is to provide the
driver with an early warning message that brake
fluid in master cylinder reservoir has dropped to a
below normal. As the fluid drops below the design level the sensor
closes the warning message circuit. Approximately
15 seconds later the message BRAKE FLUID LOW
appears on the instrument panel. At this time the master cylinder reservoir should be checked and filled
to the bottom of the rings with DOT 3 brake fluid. To check the operation of the Brake Fluid Level
sensor, with ignition on and wiring still attache-
d,remove sensor from master cylinder and hold in
upright position. Within 30 seconds the instrument
panel message BRAKE FLUID LOW should appear.
Next invert the sensor. The instrument panel message
should turn off immediately. If the above sequence
occurs the sensor is operating properly. If the message
does not appear remove the wiring from the sensor and
using a jumper wire connect both sides of the plug. The
instrumental panel message BRAKE FLUID LOW
should appear within 30 seconds. If the message does
not appear a problem exists in the wiring or instru-
mentation. If the message does appear the sensor is
faulty and must be replaced. The Brake Fluid Level
sensor is not a repairable item (Fig. 2).
TESTING THE MASTER CYLINDER
Be sure master cylinder vents at both ports.
Apply pedal lightly with engine running and look for
fluid squirting or swirling into reservoirs. In this master cylinder, a special baffle reduces the
amount of fluid entering the secondary reservoir only a
small disturbance may be seen.
Fig. 1 Aluminum Master Cylinder (Cutaway View)
Fig. 2 Brake Fluid Level Sensor
5 - 66 BRAKES Ä
Page 228 of 2438

pared by the (CAB) and used to detect brake system
faults that would require Anti -Lock Braking to be
disabled.The Boost Pressure Transducer is mounted on the
bottom of the hydraulic assembly, (Fig. 1) and moni-
tors booster servo pressure. The Primary Pressure
Transducer is mounted on the left side of the hydrau-
lic assembly and monitors primary master cylinder
pressure.
DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SWITCH
A non-latching Differential Pressure Switch is used
to detect a pressure difference greater than 2,068
kPa (300 psi.) between the primary and secondary
master cylinder hydraulic circuits. If detected, the
Differential Pressure Switch grounds the output of
the primary pressure transducer (circuit B-218). This
results in a 0.0 volt signal from the Primary Pres-
sure Transducer that is sensed by the (CAB) as a dif-
ferential pressure fault. The (CAB) will then light
the Red Brake Warning Lamp and the Amber Anti-
Lock Warning Lamp and disable the Anti-Lock brak-
ing function. See Fig. 1 for location of the differential
pressure switch.
PROPORTIONING VALVES
The ABS system uses screw-in Proportioning
Valves in place of the conventional Height Sensing Proportioning Valve. Each rear brake circuit has its
own screw-in Proportioning Valve that is attached to
the rear brake outlet ports of the hydraulic assembly
(Fig. 1). These valves limit brake pressure to the
rear brakes after a certain brake pressure is reached.
This improves front to rear wheel brake balance dur-
ing normal braking.
FILTERS-SERVICEABILITY
There is a screen filter in each of the two master
cylinder fill ports. There is also a low pressure filter
for the pump/motor. The filter is integral to the
Pump/Motor low pressure hose.
FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
A Low Fluid Switch is located in the hydraulic as-
sembly fluid reservoir, (Fig. 1). The switch consists of
a float and magnetic reed switch that closes when
low fluid is detected. The Low Fluid Switch is used
as an input, to the Red Brake Warning Lamp, the
(CAB), and the EVIC (if so equipped). When a low
fluid condition exists the switch will close, grounding
the low fluid circuit and illuminating the Red Brake
Warning Lamp. The (CAB) will disable the Anti-
Lock Function and light the Amber Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp if vehicle is in motion above 3 mph. If
vehicle is not in motion, the Amber Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp will NOT be lit.
DUAL FUNCTION PRESSURE SWITCH WIRING DIAGRAM
5 - 78 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 229 of 2438
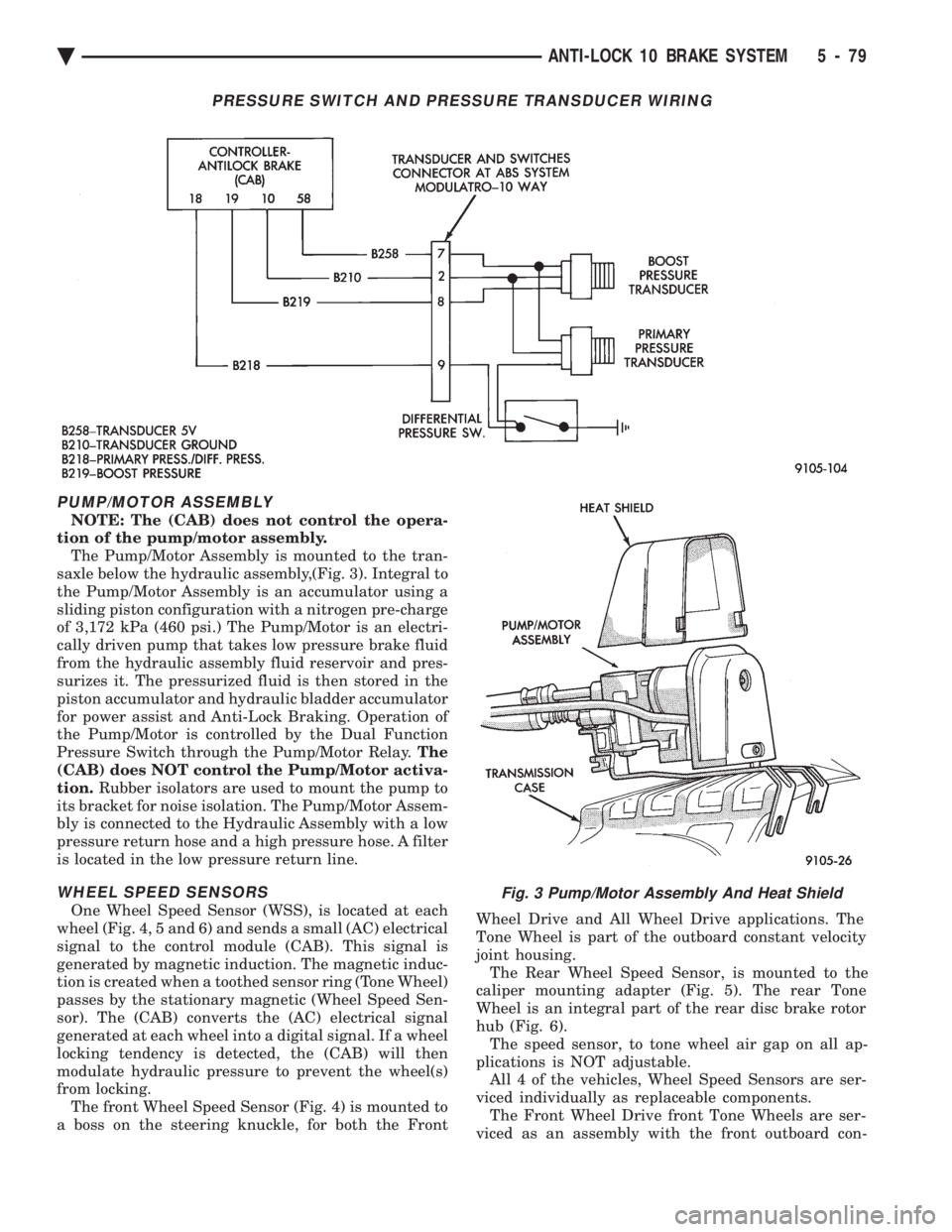
PUMP/MOTOR ASSEMBLY
NOTE: The (CAB) does not control the opera-
tion of the pump/motor assembly. The Pump/Motor Assembly is mounted to the tran-
saxle below the hydraulic assembly,(Fig. 3). Integral to
the Pump/Motor Assembly is an accumulator using a
sliding piston configuration with a nitrogen pre-charge
of 3,172 kPa (460 psi.) The Pump/Motor is an electri-
cally driven pump that takes low pressure brake fluid
from the hydraulic assembly fluid reservoir and pres-
surizes it. The pressurized fluid is then stored in the
piston accumulator and hydraulic bladder accumulator
for power assist and Anti-Lock Braking. Operation of
the Pump/Motor is controlled by the Dual Function
Pressure Switch through the Pump/Motor Relay. The
(CAB) does NOT control the Pump/Motor activa-
tion. Rubber isolators are used to mount the pump to
its bracket for noise isolation. The Pump/Motor Assem-
bly is connected to the Hydraulic Assembly with a low
pressure return hose and a high pressure hose. A filter
is located in the low pressure return line.
WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
One Wheel Speed Sensor (WSS), is located at each
wheel (Fig. 4, 5 and 6) and sends a small (AC) electrical
signal to the control module (CAB). This signal is
generated by magnetic induction. The magnetic induc-
tion is created when a toothed sensor ring (Tone Wheel)
passes by the stationary magnetic (Wheel Speed Sen-
sor). The (CAB) converts the (AC) electrical signal
generated at each wheel into a digital signal. If a wheel
locking tendency is detected, the (CAB) will then
modulate hydraulic pressure to prevent the wheel(s)
from locking. The front Wheel Speed Sensor (Fig. 4) is mounted to
a boss on the steering knuckle, for both the Front Wheel Drive and All Wheel Drive applications. The
Tone Wheel is part of the outboard constant velocity
joint housing. The Rear Wheel Speed Sensor, is mounted to the
caliper mounting adapter (Fig. 5). The rear Tone
Wheel is an integral part of the rear disc brake rotor
hub (Fig. 6). The speed sensor, to tone wheel air gap on all ap-
plications is NOT adjustable. All 4 of the vehicles, Wheel Speed Sensors are ser-
viced individually as replaceable components. The Front Wheel Drive front Tone Wheels are ser-
viced as an assembly with the front outboard con-
Fig. 3 Pump/Motor Assembly And Heat Shield
PRESSURE SWITCH AND PRESSURE TRANSDUCER WIRING
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 79
Page 231 of 2438
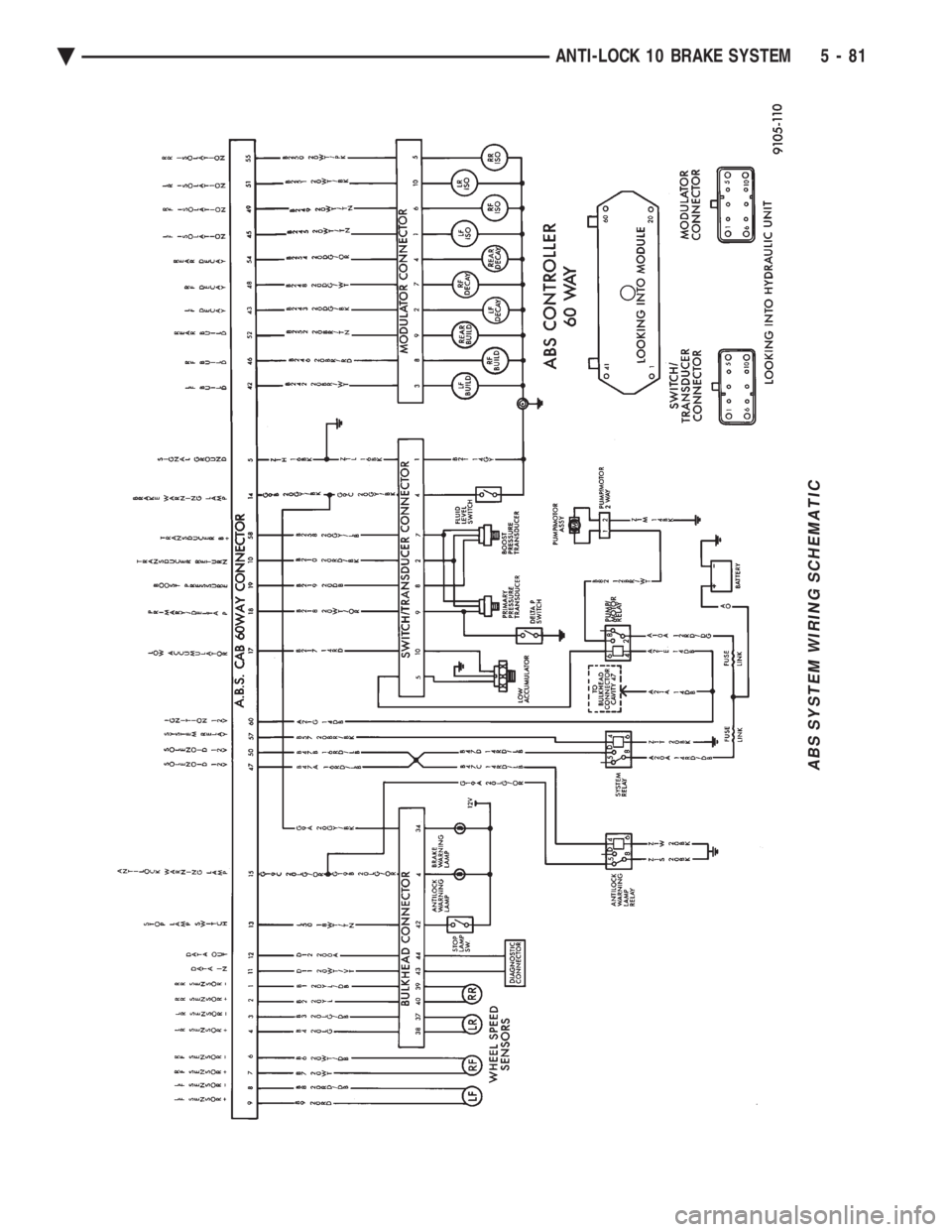
ABS SYSTEM WIRING SCHEMATIC
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 81
Page 234 of 2438
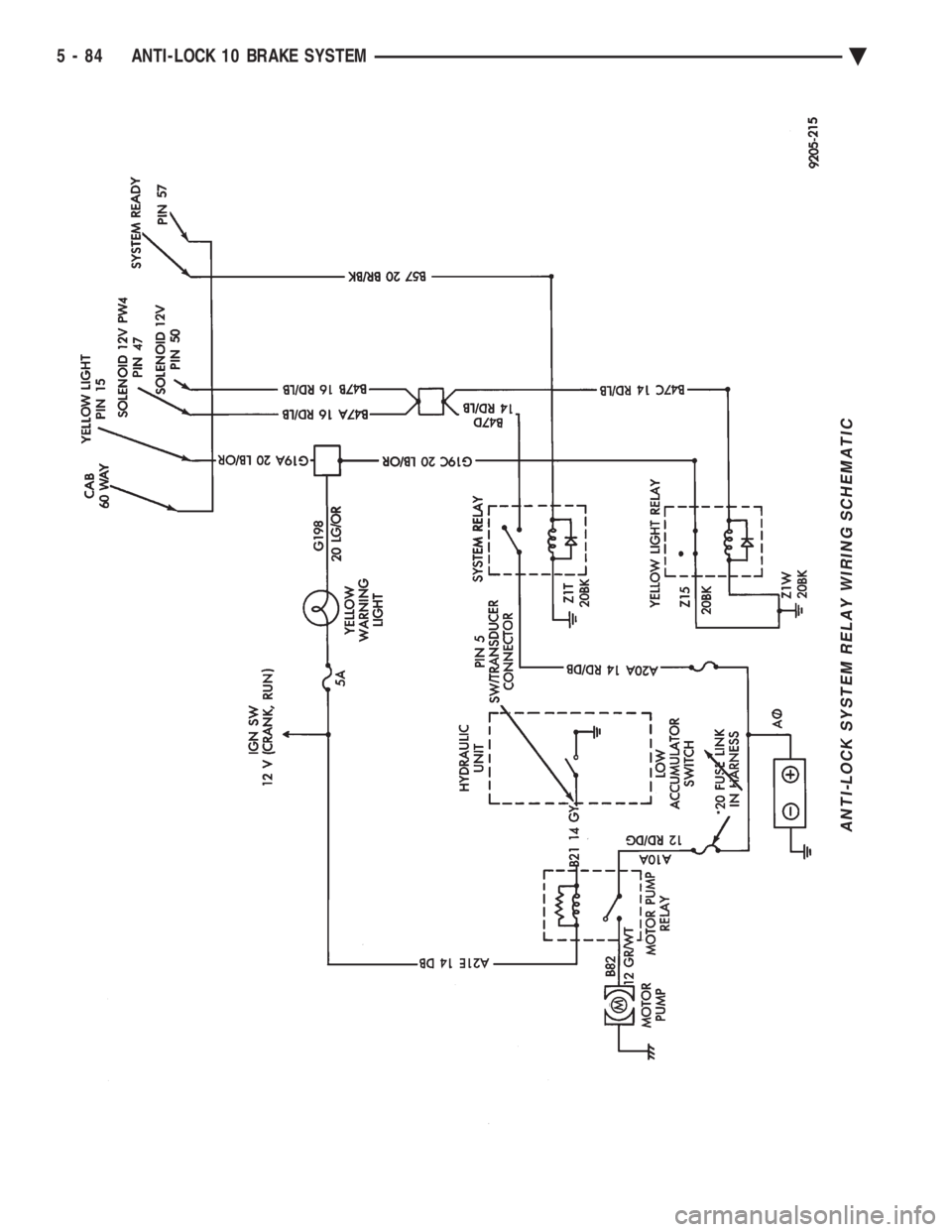
ANTI-LOCK SYSTEM RELAY WIRING SCHEMATIC
5 - 84 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 240 of 2438

WARNING: FAILURE TO DE-PRESSURIZE THE AC-
CUMULATOR PRIOR TO PERFORMING THIS OPER-
ATION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY
AND/OR DAMAGE TO PAINTED SURFACES. (2) Remove hydraulic assembly accumulator port
plug,located on right hand side of hydraulic assembly
(Fig. 1).
(3) Install pressure gauge to hydraulic assembly
adaptor into accumulator port of hydraulic assembly
(Fig. 2). Then torque adaptor to 10 N Im (7.5 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install adaptor onto the pressure gauge hose
(Fig. 2) and tighten the fitting to 15 N Im (11 ft. lbs.)
torque. (5) Install pressure gauge and hose adaptor assem-
bly onto the adaptor installed in the hydraulic as-
sembly accumulator port. Then install the retaining
clip into the grove on the accumulator port adaptor
(Fig. 2). MAKE SURE THAT THE RETAINING
CLIP IS INSTALLED ON THE ACCUMULATOR
PORT ADAPTOR BEFORE RE-PRESSURIZING
THE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM.
WARNING: BEFORE REMOVING PRESSURE
GAUGE AND ADAPTOR, BE SURE TO DE-PRES-
SURIZE THE HYDRAULIC ASSEMBLY. THEN IN-
STALL AND TIGHTEN ACCUMULATOR PORT PLUG
TO 12 N IM (9 FT. LBS.).
It is not necessary to bleed the hydraulic assembly
or brake system after installation and removal of the
pressure gauge. Unless additional tubes, hoses, or fit-
tings were removed or loosened.
HYDRAULIC ASSEMBLY INTERNAL LEAK
CHECK
If an internal leak is suspected in the ABS hydrau-
lic circuit, Test Gauge, Special Tool 6685 has been
developed to assist in the diagnostics. This fixture
will assist in determining if there is an internal leak;
and if the leak is in the hydraulic unit or the pump
motor assembly. It can be used whether the pump
shuts off or not. Test Gauge, Special Tool 6685 installation and op-
eration procedure is detailed below. Refer to the Hy-
draulic Pressure Performance Test in the 1993
Bendix Anti-Lock 10 Diagnostic Manual for the re-
quired test procedures.
WARNING: FAILURE TO DE-PRESSURIZE THE AC-
CUMULATOR PRIOR TO PERFORMING THIS OPER-
ATION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY
AND/OR DAMAGE TO PAINTED SURFACES.
(1) De-pressurize the accumulator by pumping the
brake pedal a minimum of 40 times with the ignition
off. The procedure is fully explained under De-Pres-
surizing Hydraulic Accumulator which is described
earlier in this System Diagnosis Section. (2) Remove wiring harness connector from dual
function pressure switch on bottom of hydraulic as-
sembly. Connect wiring harness from Test Gauge,
Special Tool 6685 into wiring harness connector re-
moved from dual function pressure switch.Fig. 1 Hydraulic Assembly Accumulator Port Plug Location
Fig. 2 Pressure Gauge and Adapter Installed onHydraulic Assembly
5 - 90 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 242 of 2438

(11) Remove all special tools previously installed,
from the ABS hydraulic assembly. (12) Install accumulator port plug into hydraulic
assembly. Torque accumulator port plug to 12 N Im(9
ft. lbs.). (13) Install high pressure brake hose from the
pump motor assembly into hydraulic fitting on ABS
hydraulic assembly. Torque high pressure brake hose
tube nut to 16 N Im (145 in. lbs.).
(14) Turn ignition switch to the run position to en-
ergize the pump/motor assembly and pressurize hy-
draulic system. Check for leakage at the hydraulic
assembly to hydraulic bladder accumulator fitting. (15) Again de-pressurize accumulator by pumping
brake pedal a minimum of 40 times. Use procedure
described in De-Pressurizing Hydraulic Accumulator
in this section of the service manual. (16) Then check the brake fluid level in the hy-
draulic assembly reservoir. If brake fluid level is low,
fill reservoir to proper level with Mopar tbrake fluid
or equivalent conforming to DOT 3 requirements.
INTERMITTENT FAULTS
As with almost any electronic system, intermittent
faults in the ABS system may be difficult to accu-
rately diagnose. Most intermittent faults are caused by faulty elec-
trical connections or wiring. When an intermittent
fault is encountered, check suspect circuits for: (1) Poor mating of electrical connector halves, or
electrical terminals not fully seated in the connector
body. (2) Improperly formed or damaged electrical termi-
nals. All connector terminals in a suspect circuit
should be carefully reformed to increase contact ten-
sion. (3) Poor terminal to wire connection. This requires
removing the terminal from the connector body and
inspecting for proper terminal to wire connection. If a visual check does not find the cause of the
problem, operate the vehicle in an attempt to dupli-
cate the condition and record the Fault Code. Most failures of the ABS system will disable the
Anti-Lock function for the entire ignition cycle even
if the fault clears before ignition key-off. There are
some failure conditions however, which will allow
ABS operation to resume during the ignition cycle in
which a failure occurred. If the failure conditions are
no longer present. The following conditions may result in intermittent
illumination of the Red Brake Warning Lamp and/or
Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp. All other failures
will cause the lamp(s) to remain on until the ignition
switch is turned off. Circuits and or components in-
volving these inputs to the (CAB) should be investi-
gated if a complaint of intermittent warning system
operation is encountered. ²
Low system voltage. If low system voltage is de-
tected by the (CAB), the (CAB) will turn on the Am-
ber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp until normal system
voltage is achieved. Once normal voltage is seen at
the (CAB), normal operation resumes.
² Low Brake Fluid. A low brake fluid condition will
cause the Red Brake Warning Lamp to illuminate.
When the fluid sensor again indicates an acceptable
fluid level, the Red Brake Warning Lamp will go out.
This condition may exist during hard cornering or
while the vehicle is on a grade. If the vehicle is in
motion above 3 M.P.H. the Amber Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp will also be turned on.
² Low Accumulator Pressure. Low Accumulator
Pressure will cause both the Red Brake Warning and
Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamps to illuminate.
Once normal operating pressure is achieved, the
lamps will extinguish and the system will return to
normal operation. Additionally, any condition that results in an inter-
ruption of power to the (CAB) or hydraulic assembly.
May cause the Red Brake Warning and Amber Anti-
Lock Warning Lamps to illuminate intermittently. All the conditions (or faults) mentioned above, can
store a fault code in the (CAB) module.
ABS BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES
SYSTEM SELF DIAGNOSIS
The ABS system is equipped with a diagnostic ca-
pability that may be used to assist in isolation of
ABS faults. The features of the diagnostics system
are described below.
CONTROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (CAB)
Fault codes are kept in a Non-Volatile memory un-
til either erased by the technician using the DRB II
or erased automatically after 50 ignition cycles (key
ON-OFF cycles). The only fault that will not be
erased after 50 (KEY CYCLES) is the (CAB) fault.
The (CAB) fault can only be erased by using the
DRB II diagnostic tester. More than one fault can be
stored at a time. The number of key cycles since the
most recent fault was stored is also displayed. Most
functions of the (CAB) and (ABS) system can be ac-
cessed by the technician for testing and diagnostic
purposes by using the DRB II Diagnostic Tester.
START-UP CYCLE
The START-UP CYCLE takes place immediately
after the ignition switch is turned on. It is an elec-
trical check of basic electrical functions such as the
System Relay and Anti-Lock Warning Lamp Relay.
During this check, the Amber Anti-Lock Warning
Lamp is turned on, then turned off at the end of the
test. The test takes approximatel y1-2seconds to
complete.
5 - 92 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 246 of 2438

PUMP/MOTOR SERVICE (FIG. 4)
REMOVE (1) Fully de-pressurize the hydraulic accumulator
by pumping the pedal a minimum of 40 times. Use
the procedure described in De-Pressurizing Hydraulic
Accumulator listed earlier in this section.
WARNING: FAILURE TO DE-PRESSURIZE HYDRAU-
LIC ACCUMULATOR, BEFORE PERFORMING THIS
OPERATION, MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY
AND/OR DAMAGE TO PAINTED SURFACES.
(2) Remove the fresh air intake ducts from the en-
gine induction system. (3) Loosen the low pressure hose clamp (Fig. 5) at
the hydraulic assembly. (4) Disconnect any routing clips which attach the
high and low pressure fluid lines to the body or com-
ponents of the vehicle (Fig. 5). (5) Unclip the pump/motor assembly wiring har-
ness electrical connector from the left side engine
mount (Fig. 5). Disconnect the pump/motor assembly
wiring harness from the underhood wiring harness. (6) Loosen the high pressure hose tube nut at the
hydraulic assembly fitting (Fig. 5). (7) Remove the high and low pressure hose assem-
bly (Fig. 5) from the hydraulic assembly. Cap all
open ports on reservoir and hydraulic assembly to
prevent brake fluid from leaking out. (8) Remove the pump/motor assembly front heat
shield to mounting bracket attaching bolt, from front
of pump/motor bracket (Fig. 5). (9) Remove front heat shield from the pump/motor
assembly. (10) Lift pump/motor assembly from mounting
bracket and remove assembly from the vehicle.
INSTALL
CAUTION:Be sure all high and low pressure hose
routing clips. Are securely fastened to the vehicle
body or component they were removed from when
hose assembly is reinstalled (Fig. 5).
(1) Install pump/motor assembly in reverse order of
removal. (2) Tighten the pump/motor assembly fluid lines to
the torque values shown below.
² Low pressure hose clamp. 1 N Im (10 in. lbs.)
² High pressure hose fitting to pump/motor assembly.
16 N Im (145 in. lbs.) Fig. 5.
Note: It is not necessary to bleed the founda-
tion brakes of the vehicle when the pump/motor
assembly and high and low pressure fluid hoses
are serviced. Any other service to the brake
system unless stated otherwise will require
bleeding of the complete brake system.
BRAKE FLUID PRESSURE AND RETURN HOSES (FIG. 6)
REMOVE
(1) Remove the pump/motor assembly from its
mounting bracket, see Pump/Motor Service. (2) Cut the 4 tie straps that secure the high and low
pressure hoses and pump/motor assembly wiring har-
ness together Fig. 6. (3) Remove the banjo bolt and spray shield from the
pump/motor assembly Fig. 6.
Fig. 4 Pump/Motor Assembly MountingFig. 5 Brake Tube and Hose Routing
5 - 96 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä