1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 2003 of 2438

(3) Move selector lever on transaxle one detent
forward from full rearward position. This is selector
2 position.
(4) Read pressures on both gauges as throttle lever
on transaxle is moved from full clockwise position to
full counterclockwise position. (5) Line pressure should read 52 to 58 psi with
throttle lever clockwise and gradually increase, as le-
ver is moved counterclockwise, to 80 to 88 psi. (6) Lubrication pressure should be 10 to 25 psi
with lever clockwise and 10 to 35 psi with lever full
counterclockwise. (7) This tests pump output, pressure regulation,
and condition of rear clutch and lubrication hydrau-
lic circuits.
TEST THREE (SELECTOR IN D)
(1) Attach gauges to lineandkickdown release
ports (Fig. 3). (2) Operate engine at 1600 rpm for test.
(3) Move selector lever on transaxle two detents
forward from full rearward position. This is selector
D position.
(4) Read pressures on both gauges as throttle lever
on transaxle is moved from full clockwise position to
full counterclockwise position. (5) Line pressure should read 52 to 58 psi with
throttle lever clockwise and gradually increase, as le-
ver is moved counterclockwise to 80 to 88 psi. (6) Kickdown release is pressurized only in direct
drive and should be same as line pressure within 3
psi, up to kickdown point. (7) This tests pump output, pressure regulation,
and condition of rear clutch, front clutch, and hy-
draulic circuits.
TEST FOUR (SELECTOR IN REVERSE)
(1) Attach 300 psi gauge to low-reverseport (Fig.
3). (2) Operate engine at 1600 rpm for test.
(3) Move selector lever on transaxle four detents
forward from full rearward position. This is selector
R position.
(4) Low-reverse pressure should read 180 to 220
psi with throttle lever clockwise and gradually in-
crease, as lever is moved counterclockwise to 260 to
300 psi. (5) This tests pump output, pressure regulation,
and condition of front clutch and rear servo hydraulic
circuits. (6) Move selector lever on transaxle to Dposition
to check that low-reverse pressure drops to zero. (7) This tests for leakage into rear servo, due to
case porosity, which can cause reverse band burn
out.
TEST RESULT INDICATIONS
(1) If proper line pressure, minimum to maximum, is
found in any one test, the pump and pressure regulator
are working properly. (2) Low pressure in D, 1, and 2but correct pressure
in Rindicates rear clutch circuit leakage.
(3) Low pressure in D and Rbut correct pressure in
1 indicates front clutch circuit leakage.
(4) Low pressure in R and 1but correct pressure in
2 indicates rear servo circuit leakage.
(5) Low line pressure in all positions indicates a
defective pump, a clogged filter, or a stuck pressure
regulator valve.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE
Test only if transaxle shifts at wrong vehicle speeds
when throttle cable is correctly adjusted. (1) Connect a 0-150 psi pressure gauge to governor
pressure take-off point, located at lower right side of
case, below differential cover (Fig. 3). (2) Operate transaxle in third gear to read pres-
sures. The governor pressure should respond smoothly
to changes in mph and should return to 0 to 3 psi when vehicle is stopped. High pressure at
standstill (above 3 psi) will prevent the transaxle from
downshifting.
THROTTLE PRESSURE
No gauge port is provided for throttle pressure.
Incorrect throttle pressure should only be suspected if
part throttle upshift speeds are either delayed or occur
too early, with a correctly adjusted throttle cable.
Engine runaway on either upshifts or downshifts can
also be an indicator of incorrect (low) throttle pressure
setting, or misadjusted throttle cable. In no case should throttle pressure be adjusted until
the transaxle throttle cable adjustment has been veri-
fied to be correct.
CLUTCH AND SERVO AIR PRESSURE TESTS
A no drive condition might exist even with correct
fluid pressure, because of inoperative clutches or
bands. The inoperative units, clutches, bands, and
servos can be located through a series of tests by
substituting air pressure for fluid pressure (Fig. 4). The front and rear clutches, kickdown servo, and
low-reverse servo may be tested by applying air pres-
sure to their respective passages after the valve body assembly has been removed. To make
air pressure tests, proceed as follows: Compressed air supply must be free of all dirt
or moisture. Use a pressure of 30 psi. Remove oil pan and valve body See Disassembly-
Subassembly Removal .
FRONT CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to front clutch applypassage and
listen for a dull thudwhich indicates that front
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 43
Page 2004 of 2438

clutch is operating. Hold air pressure on for a few
seconds and inspect system for excessive oil leaks.
REAR CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to rear clutch applypassage
and listen for a dull thudwhich indicates that rear
clutch is operating. Also inspect for excessive oil
leaks. If a dull thudcannot be heard in the clutches,
place finger tips on clutch housing and again apply
air pressure. Movement of piston can be felt as the
clutch is applied.
KICKDOWN SERVO (FRONT)
Direct air pressure into kickdown servo ONpas-
sage. Operation of servo is indicated by a tightening
of front band. Spring tension on servo piston should
release the band.
LOW AND REVERSE SERVO (REAR)
Direct air pressure into LOW-REVERSE SERVO
APPLY passage. Operation of servo is indicated by a
tightening of rear band. Spring tension on servo pis-
ton should release the band. If clutches and servos operate properly, no upshift
or erratic shift conditions indicate that malfunctions
exist in the valve body.
FLUID LEAKAGE-TRANSAXLE TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING AREA
(1) Check for Source of Leakage.
Since fluid leakage at or around the torque con-
verter area may originate from an engine oil leak,
the area should be examined closely. Factory fill
fluid is dyed red and, therefore, can be distinguished
from engine oil. (2) Prior to removing the transaxle, perform the
following checks:
² When leakage is determined to originate from the
transaxle, check fluid level prior to removal of the
transaxle and torque converter.
² High oil level can result in oil leakage out the
vent in the dipstick. If the fluid level is high, adjust
to proper level. After performing this operation, inspect for leak-
age. If a leak persists, perform the following opera-
tion on the vehicle to determine if it is the torque
converter or transaxle that is leaking.
LEAKAGE TEST PROBE
(1) Remove torque converter housing dust shield.
(2) Clean the inside of torque converter housing
(lower area) as dry as possible. A solvent spray fol-
lowed by compressed air drying is preferable.
Fig. 4 Air Pressure Tests
21 - 44 TRANSAXLE Ä
Page 2005 of 2438
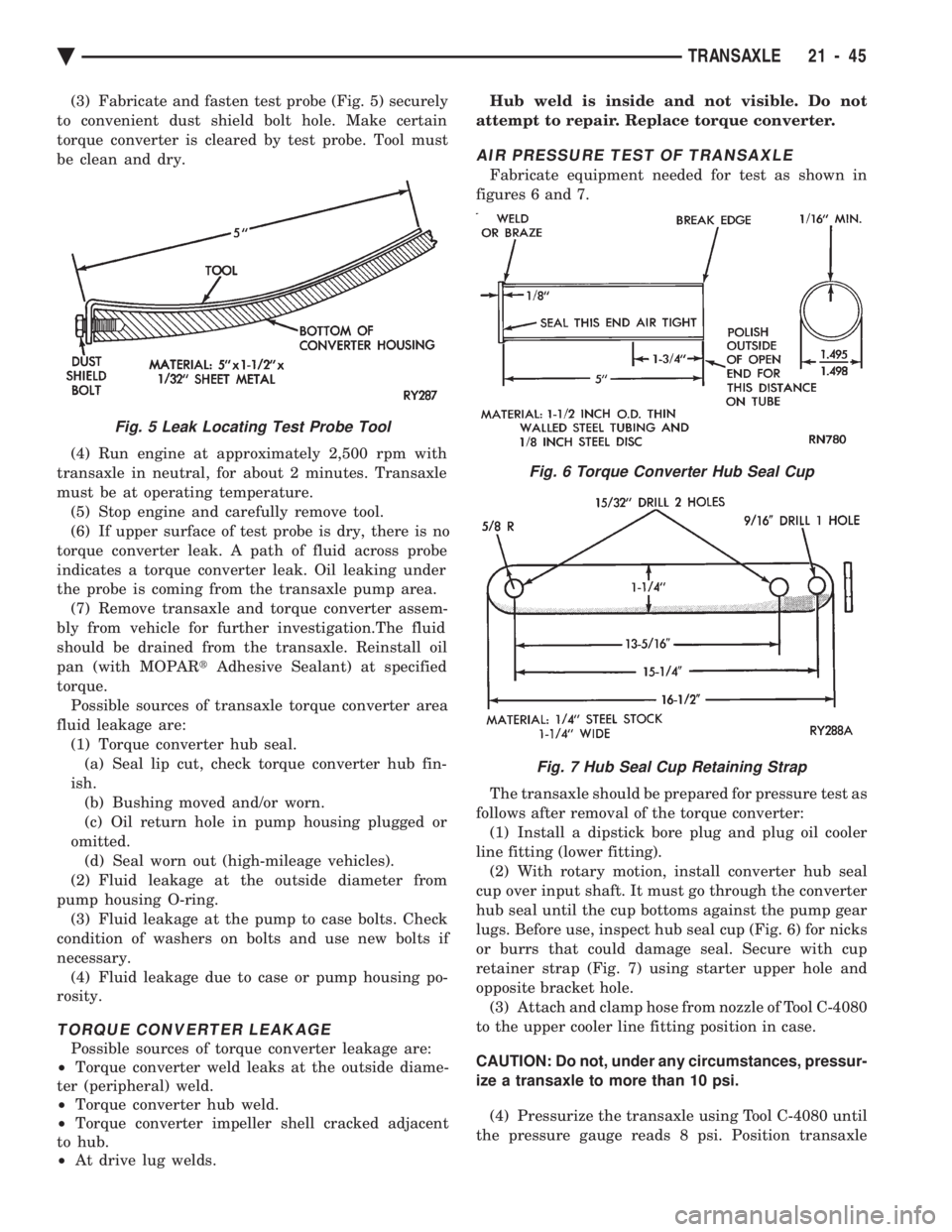
(3) Fabricate and fasten test probe (Fig. 5) securely
to convenient dust shield bolt hole. Make certain
torque converter is cleared by test probe. Tool must
be clean and dry.
(4) Run engine at approximately 2,500 rpm with
transaxle in neutral, for about 2 minutes. Transaxle
must be at operating temperature. (5) Stop engine and carefully remove tool.
(6) If upper surface of test probe is dry, there is no
torque converter leak. A path of fluid across probe
indicates a torque converter leak. Oil leaking under
the probe is coming from the transaxle pump area. (7) Remove transaxle and torque converter assem-
bly from vehicle for further investigation.The fluid
should be drained from the transaxle. Reinstall oil
pan (with MOPAR tAdhesive Sealant) at specified
torque. Possible sources of transaxle torque converter area
fluid leakage are: (1) Torque converter hub seal.(a) Seal lip cut, check torque converter hub fin-
ish. (b) Bushing moved and/or worn.
(c) Oil return hole in pump housing plugged or
omitted. (d) Seal worn out (high-mileage vehicles).
(2) Fluid leakage at the outside diameter from
pump housing O-ring. (3) Fluid leakage at the pump to case bolts. Check
condition of washers on bolts and use new bolts if
necessary. (4) Fluid leakage due to case or pump housing po-
rosity.
TORQUE CONVERTER LEAKAGE
Possible sources of torque converter leakage are:
² Torque converter weld leaks at the outside diame-
ter (peripheral) weld.
² Torque converter hub weld.
² Torque converter impeller shell cracked adjacent
to hub.
² At drive lug welds. Hub weld is inside and not visible. Do not
attempt to repair. Replace torque converter.
AIR PRESSURE TEST OF TRANSAXLE
Fabricate equipment needed for test as shown in
figures 6 and 7.
The transaxle should be prepared for pressure test as
follows after removal of the torque converter: (1) Install a dipstick bore plug and plug oil cooler
line fitting (lower fitting). (2) With rotary motion, install converter hub seal
cup over input shaft. It must go through the converter
hub seal until the cup bottoms against the pump gear
lugs. Before use, inspect hub seal cup (Fig. 6) for nicks
or burrs that could damage seal. Secure with cup
retainer strap (Fig. 7) using starter upper hole and
opposite bracket hole. (3) Attach and clamp hose from nozzle of Tool C-4080
to the upper cooler line fitting position in case.
CAUTION: Do not, under any circumstances, pressur-
ize a transaxle to more than 10 psi. (4) Pressurize the transaxle using Tool C-4080 until
the pressure gauge reads 8 psi. Position transaxle
Fig. 5 Leak Locating Test Probe Tool
Fig. 6 Torque Converter Hub Seal Cup
Fig. 7 Hub Seal Cup Retaining Strap
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 45
Page 2006 of 2438

so that pump housing and case front may be covered
with soapy solution or water. Leaks are sometimes
caused by porosity in the case or pump housing.If a leak source is located, that part and all associ-
ated seals, O-rings, and gaskets should be replaced
with new parts.
GEARSHIFT LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT
Normal operation of the Park/Neutral Position
Switch provides a quick check to confirm proper
manual linkage adjustment. Move the selector level slowly upward until it
clicks into the ``P'' Park notch in the selector gate. If
the starter will operate the ``P'' position is correct. After checking ``P'' position, move selector slowly
toward ``N'' Neutral position until lever drops in the
``N'' stop. If the starter will also operate at this point
the gearshift linkage is properly adjusted. If the
starter fails to operate in either position, linkage ad-
justment is required.
CAUTION: When it is necessary to disassemble
linkage cable from levers, which use plastic grom-
mets as retainers, the grommets should be replaced
with new grommets. Use a prying tool to force rod
from grommet in lever, then cut away old grommet.
Use pliers to snap new grommet into lever and rod
into grommet.
(1) Set parking brake.
(2) Place gearshift lever in P(PARK) position.
(3) Loosen clamp bolt on gearshift cable bracket.
(4) Column shift: Insure that preload adjustment
spring engages fork on transaxle bracket. (5) Pull the shift lever by hand to the front detent
position (PARK) and tighten lock. Tighten screw to
11 N Im (100 in. lbs.). Gearshift linkage should now
be properly adjusted. (6) Check adjustment as follows:(a) Detent position for neutral and drive should
be within limits of hand lever gate stops. (b) Key start must occur only when shift lever is
in park or neutral positions.
THROTTLE PRESSURE LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT
The throttle pressure cable adjustment is very im-
portant to proper transaxle operation. This adjust-
ment positions a valve which controls shift speed,
shift quality, and part throttle downshift sensitivity.
If the setting is too long, early shifts and slippage be-
tween shifts may occur. If the setting is too short,
shifts may be delayed and part throttle downshifts
may be very sensitive.
CABLE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE (4-CYL.)
(1) Perform transaxle throttle pressure cable ad-
justment while engine is at normal operating tem-
perature. (2) Loosen cable mounting bracket lock screw.
(3) Bracket should be positioned with both bracket
alignment tabs touching the transaxle cast surface.
Tighten lock screw to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.) see Fig-
ure 8.
(4) Release cross-lock on the cable assembly (pull
cross-lock upward) see Figure 7. (5) To insure proper adjustment, the cable must be
free to slide all the way toward the engine, against
its stop, after the cross-lock is released. (6) Move transaxle throttle control lever fully
clockwise, against its internal stop, and press cross-
lock downward into locked position (Fig. 7). (7) The adjustment is complete and transaxle
throttle cable backlash was automatically removed. (8) Test cable freedom of operation by moving the
transaxle throttle lever forward (counterclockwise).
Then slowly release it to confirm it will return fully
rearward (clockwise). (9) No lubrication is required for any component of
the throttle cable system.
ROD ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE (6-CYL.)
(1) Perform transaxle throttle pressure cable ad-
justment while engine is at normal operating tem-
perature. (2) Loosen adjustment swivel lock screw.
(3) To insure proper adjustment, swivel must be
free to slide along flat end of throttle rod so that pre-
load spring action is not restricted. Disassemble and
clean or repair parts to assure free action, if neces-
sary. (4) Hold transaxle throttle lever firmly toward en-
gine, against its internal stop and tighten swivel lock
screw to 11 N Im (100 in. lbs.)
(5) The adjustment is finished and linkage back
lash was automatically removed by the preload
spring. (6) If lubrication is required see Lubrication,
Group 0.
Fig. 8 Throttle Pressure CableÐTypical
21 - 46 TRANSAXLE Ä
Page 2008 of 2438

GOVERNOR
To service the governor assembly in the vehicle, it
is not necessary to remove the transfer gear cover,
transfer gear, and governor support. The governor
may be serviced by removing the transaxle oil pan
and valve body assembly. With the oil pan and valve
body removed, the governor may be unbolted from
the governor support and removed. When cleaning or assembling the governor, make
sure the governor valves move freely in the bores of
the governor body.
ALUMINUM THREAD REPAIR
Damaged or worn threads in the aluminum tran-
saxle case and valve body can be repaired by the use
of Heli-Coils, or equivalent. This repair consists of
drilling out the worn-out damaged threads. Then tap-
ping the hole with a Heli-Coil tap, or equivalent, and
installing a Heli-Coil insert, or equivalent, into the
hole. This brings the hole back to its original thread
size. Heli-Coil, or equivalent, tools and inserts are
readily available from most automotive parts suppli-
ers.
OIL COOLERS AND TUBES REVERSE FLUSHING
When a transaxle failure has contaminated the
fluid, the oil cooler(s) must be flushed. The torque
converter must be replaced with an exchange unit.
This will insure that metal particles or sludged oil
are not transferred back into the reconditioned (or
replaced) transaxle.
CAUTION: If vehicle is equipped with two oil cool-
ers (one in the radiator tank, one in front of the ra-
diator) they must be flushed separately. Do not
attempt to flush both coolers at one time.
(1) Disconnect the cooler lines at the transmission.
(2) Using a hand suction gun filled with mineral
spirits, reverse flush the cooler. Force mineral spirits
into the From Cooler line of the cooler (Fig. 9) and
catch the exiting spirits from the To Coolerline.
Observe for the presence of debris in the exiting
fluid. Continue until fluid exiting is clear and free
from debris. (3) Using compressed air in intermittent spurts,
blow any remaining mineral spirits from the cooler,
again in the reverse direction. (4) To remove any remaining mineral spirits from
the cooler, one (1) quart of automatic transmission
fluid should be pumped through the cooler before re-
connecting. (5) If at any stage of the cleaning process, the
cooler does not freely pass fluid, the cooler must be
replaced.
OIL COOLER FLOW CHECK
After the new or repaired transmission has been
installed and filled to the proper level with auto-
matic transmission fluid. The flow should be checked
using the following procedure: (1) Disconnect the From coolerline at the trans-
mission and place a collecting container under the
disconnected line. (2) Run the engine at curb idle speed , with the
shift selector in neutral. (3) If the fluid flow is intermittent or it takes more
than 20 seconds to collect one quart of automatic
transmission fluid, the cooler should be replaced.
CAUTION: With the fluid set at the proper level,
fluid collection should not exceed (1) quart or inter-
nal damage to the transmission may occur.
(4) If flow is found to be within acceptable limits,
reconnect the cooler line. Then fill transmission to
the proper level, using the approved type of auto-
matic transmission fluid.
TRANSAXLE AND TORQUE CONVERTER REMOVAL
Transaxle removal does NOT require engine
removal. (1) The transaxle and torque converter must be re-
moved as an assembly; otherwise, the torque con-
verter drive plate, pump bushing, or oil seal may be
damaged. The drive plate will not support a load;
therefore, none of the weight of the transaxle should
be allowed to rest on the plate during removal. (2) Disconnect battery negative cable .
(3) Disconnect throttle linkage and shift linkage
from transaxle.
Fig. 9 Cooler Line Identification
21 - 48 TRANSAXLE Ä
Page 2048 of 2438

ing to each new reading. This provides the precise
and sophisticated friction element control needed to
make smooth clutch-to-clutch shifts for all gear
changes. The use of overrunning clutches or other
shift quality aids are not required. As with most au-
tomatic transaxles, all shifts involve releasing one el-
ement and applying a different element. In simplified
terms, the upshift logic allows the releasing element
to slip back wards slightly to ensure that it does not
have excess capacity; the apply element is filled until
it begins to make the speed change to the higher
gear; its apply pressure is then controlled to main-
tain the desired rate of speed change until the shift
is complete. The key to providing excellent shift
quality is precision; for example, as mentioned, the
release element for upshifts is allowed to slip back-
wards slightly; the amount of that slip is typically
less than a total of 20 degrees. To achieve that pre-
cision, the transmission control module learns the
characteristics of the particular transaxle that it is
controlling. It learns the release rate of the releasing
element and the apply time of the applying element.
It also learns the rate at which the apply element
builds pressure sufficient to begin making the speed
change. This method achieves more precision than
would be possible with exacting tolerances. It can
also adapt to any changes that occur with age or en-
vironment, for example, altitude, temperature, en-
gine output, etc. For kickdown shifts, the control logic allows the re-
leasing element to slip and then controls the rate at
which the input (and engine) accelerate; when the
lower gear speed is achieved, the releasing element
reapplies to maintain that speed until the apply ele-
ment is filled. This provides quick response since the
engine begins to accelerate immediately and a
smooth torque exchange since the release element
can control the rate of torque increase. This control
can make any powertrain feel more responsive with-
out in creasing harshness. Adaptive controls respond to input speed changes. They compensate for changes in engine or friction el-
ement torque and provide good, consistent shift qual-
ity for the life of the transaxle.
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
These controls provide comprehensive, on-board
transaxle diagnostics. The information available can
aid in transaxle diagnosis. For example, apply ele-
ment buildup rate indicates solenoid performance.
Also included are self diagnostic functions. Self diag-
nostics allow the technician to test the condition of
the electronic controls. The transmission control
module continuously monitors its critical functions.
It also records any malfunctions, and the number of
engine starts since the last malfunction. This allows
the technician to use the information in the event of
a customer complaint.
41TE TRANSAXLE GENERAL DIAGNOSIS
CAUTION: Before attempting any repair on a 41TE
four speed automatic transaxle, check for diagnos-
tic trouble codes with the DRB II scan tool. Always
use the Powertrain Diagnostic Test Procedure Man-
ual.
Transaxle malfunctions may be caused by these
general conditions:
² Poor engine performance
² Improper adjustments
² Hydraulic malfunctions
² Mechanical malfunctions
² Electronic malfunctions
Diagnosis of these problems should always begin
by checking the easily accessible variables: fluid
level and condition, gearshift cable adjustment. Then
perform a road test to determine if the problem has
been corrected or that more diagnosis is necessary. If
the problem exists after the preliminary tests and
corrections are completed, hydraulic pressure checks
should be performed.
21 - 88 TRANSAXLE Ä
Page 2053 of 2438

FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION
The transmission and differential sump have a
common oil sump with a communicating opening
between the two. The torque converter fills in both the PPark and N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in PPark to
check the fluid level. The engine should be running
at idle speed for at least one minute, with the
vehicle on level ground. This will assure com-
plete oil level stabilization between differential
and transmission. The fluid should be at normal
operating temperature (approximately 82 C. or 180 F.).
The fluid level is correct if it is in the HOTregion
(cross-hatched area) on the oil level indicator. Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with the
fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles make the
fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be low and build
up slowly. Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the gears
churn up foam and cause the same conditions which
occur with a low fluid level. In either case, the air bubbles can cause over heat-
ing, fluid oxidation, and varnishing, which can inter-
fere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator opera-
tion. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping from the
transaxle vent where it may be mistaken for a leak. Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle overhaul is needed. Be
sure to examine the fluid on the dipstick closely. If
there is any doubt about its condition, drain out a
sample for a double check. After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
SELECTION OF LUBRICANT
It is important that the proper lubricant be used in
the 41TE transaxle. MOPAR tATF PLUS (Automatic
Transmission FluidÐtype 7176) should be used to aid
in assuring optimum transmission performance. Flu-
ids of the type labeled DEXRON II Automatic Trans-
mission Fluid are not recommended . DEXRON II
can be used only if the recommended fluid is not
available. If more than a small amount of DEXRON II
is used shudder or shift quality problems may result. It
is important that the transmission fluid be maintained
at the prescribed level using the recommended fluids.
SPECIAL ADDITIVES
Chrysler Corporation does not recommend the addi-
tion of any fluids to the transaxle, other than the
automatic transmission fluid listed above. An excep- tion to this policy is the use of special dyes to aid in
detecting fluid leaks. The use of transmission sealers
should be avoided, since they may adversely affect
seals.
FLUID AND FILTER CHANGES
When the factory fill fluid is changed, only fluids
labeled MOPAR tATF PLUS (Automatic Transmis-
sion fluid) Type 7176 should be used. A filter change
should be made at the time of the oil change. Also
the magnet (on the inside of the oil pan) should be
cleaned with a clean, dry cloth. If the transaxle is disassembled for any reason, the
fluid and filter should be changed.
FLUID DRAIN AND REFILL
(1) Raise vehicle on a hoist (See Lubrication,
Group 0). Place a drain container with a large open-
ing, under transaxle oil pan. (2) Loosen pan bolts and tap the pan at one corner
to break it loose allowing fluid to drain, then remove
the oil pan. (3) Install a new filter and O-ring on bottom of the
valve body. (4) Clean the oil pan and magnet. Reinstall pan
using new MOPAR tAdhesive Sealant. Tighten oil
pan bolts to 19 N Im (165 in. lbs.).
(5) Pour four quarts of MOPAR tATF PLUS (Au-
tomatic Transmission Fluid) Type 7176 through the
fill tube. (6) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes ap-
plied, move selector lever momentarily to each posi-
tion, ending in the park or neutral position. (7) Add sufficient fluid to bring level to 1/8 inch
below the ADD mark. Recheck fluid level after transaxle is at normal op-
erating temperature. The level should be in the HOT
region (Fig. 3).
To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make cer-
tain that dipstick is seated into the dipstick fill tube
(Fig. 4).
ROAD TEST
Prior to performing a road test, be certain that the
fluid level and condition, and control cable adjust-
ment have been checked and approved.
Fig. 3 Oil Level Indicator
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 93
Page 2054 of 2438
During the road test, the transaxle should be oper-
ated in each position to check for slipping and any
variation in shifting. If vehicle operates properly at highway speeds, but
has poor acceleration, the torque converter stator
overrunning clutch may be slipping. If through-gear
acceleration is normal, but high throttle opening is
required to maintain highway speeds, the torque con-
verter stator clutch may have seized. Both of these
stator defects require replacement of the torque con-
verter. The clutch that is slipping can be determined by
noting the transaxle operation in all selector posi-
tions. Then comparing which internal units are ap-
plied in those positions. The Elements in Use Chart
provides a basis for road test analysis. The process of elimination can be used to detect
any unit which slips and to confirm proper operation
of good units. Road test analysis can usually diag-
nose slipping units, but the actual cause of the mal-
function usually can not be decided. Practically any
condition can be caused by leaking hydraulic circuits
or sticking valves.
HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TESTS
Pressure testing is a very important step in the di-
agnostic procedure. These tests usually reveal the
cause of most transaxle problems. Before performing pressure tests, be certain that
fluid level and condition, and shift cable adjustments
have been checked and approved. Fluid must be at
operating temperature (150 to 200 degrees F.). Install an engine tachometer, raise vehicle on hoist
which allows front wheels to turn, and position ta-
chometer so it can be read. Attach 150 psi gauges to ports required for test be-
ing conducted. A 300 psi gauge (C-3293) is required
for reverse pressure test. Test port locations are shown in (Figure 1).
TEST ONE-SELECTOR IN LOW 1ST GEAR
(1) Attach pressure gauge to the low/reverse clutch
tap. (2) Move selector lever to the L position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle
speed to 20 mph. (4) Low/reverse clutch pressure should read 115 to
145 psi.
ELEMENTS IN USE AT EACH POSITION OF THE SELECTOR LEVER
Fig. 4 Oil Level Indicator Location
21 - 94 TRANSAXLE Ä