1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM steering wheel
[x] Cancel search: steering wheelPage 18 of 2438

GROUP TAB LOCATOR
Introduction
0Lubrication and Maintenance
2Suspension/Driveshafts
5Brakes
6Manual Transaxle Clutch
7Cooling System
9Engine
11Exhaust System and Intake Manifold
13Frame and Bumpers
19Steering
21Transaxle
22Wheels/Tires
23Body
24Heating/Air Conditioning
Component and System Index
Service Manual Comment Forms (Rear of Manual)
Page 31 of 2438

COMPONENT AND SYSTEM INDEX
Name Group-page Name Group-page
BODY ................................... 23-1
AA-VEHICLE BODY COMPONENT SERVICE .......23-11
AC-VEHICLE BODY COMPONENT SERVICE .......23-37
AG-VEHICLE BODY COMPONENT SERVICE .......23-52
AJ/27-VEHICLE CONVERTIBLE BODY COMPONENT SERVICE ............................ 23-86
AJ-VEHICLE BODY COMPONENT SERVICE .......23-71
AP-VEHICLE BODY COMPONENT SERVICE .......23-97
AY-VEHICLE BODY COMPONENT SERVICE .......23-133
BODY DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES .............23-2
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION .............23-1
PAINT ................................. 23-4
POWER SUNROOF ........................ 23-6
WINDSHIELD ............................ 23-9
BRAKES ..................................5-1
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEMÐBENDIX ANTI-LOCK 10 AC/Y BODY ......................... 5-72
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEMÐBENDIX ANTI-LOCK 6 AA,AG,AJ,AP BODY .................... 5-113
BRAKE DISC (ROTOR) ...................... 5-53
BRAKE SUPPORT ASSEMBLY .................5-25
FRONT DISC BRAKES ...................... 5-31
GENERAL INFORMATION .....................5-1
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM CONTROL VALVES .........5-26
KELSEY HAYES DOUBLE PIN FAMILY CALIPER .....5-35
KELSEY HAYES DOUBLE PIN NON-FAMILY CALIPER ............................. 5-38
MASTER CYLINDER ....................... 5-66
PARKING BRAKES ........................ 5-57
POWER BRAKES ......................... 5-68
REAR DISC BRAKES ....................... 5-45
REAR WHEEL DRUM BRAKES ................5-18
SERVICE ADJUSTMENTS .....................5-4
WHEEL BEARINGS ........................ 5-70
WHEEL CYLINDERS ....................... 5-23
COOLING SYSTEM ...........................7-1
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS ................... 7-24
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER .................... 7-28
GENERAL INFORMATION .....................7-1
SERVICE PROCEDURES ..................... 7-10
SPECIFICATIONS ......................... 7-29
ENGINE ..................................9-1
2.2/2.5L ENGINES .........................9-8
3.0L ENGINE ............................ 9-66
3.3/3.8L ENGINE ......................... 9-98
STANDARD SERVICE PROCEDURES .............9-1
EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD .........11-1
GENERAL INFORMATION .................... 11-1
SERVICE PROCEDURES ..................... 11-4
TORQUE SPECIFICATION ................... 11-25
FRAME AND BUMPERS ....................... 13-1
BUMPER AND FASCIA ...................... 13-1
FRAME ................................ 13-9
HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING ...............24-1
AUTOMATIC TEMPERATURE CONTROL (ATC) .....24-66 COMPONENT SERVICE PROCEDURES
..........24-47
FIXED DISPLACEMENT COMPRESSORÐMODEL 10PA17............................. 24-24
FIXED DISPLACEMENT COMPRESSORÐMODEL SD709P ............................. 24-38
FIXED DISPLACEMENT COMPRESSORÐMODEL TR105 .............................. 24-32
GENERAL INFORMATION .................... 24-1
HEATER AND A/C PERFORMANCE TESTS .........24-6
REFRIGERANT SERVICE PROCEDURES ..........24-8
VACUUM CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS .........24-4
VARIABLE DISPLACEMENT COMPRESSORÐMODEL 6C17 ............................... 24-13
INTRODUCTION .......................... Intro.-1
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE ................0-1
CHASSIS AND BODY ....................... 0-19
DRIVETRAIN ............................ 0-16
ENGINE ................................0-8
GENERAL INFORMATION .....................0-1
MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH ...................6-1
STEERING ................................ 19-1
ACUSTAR STANDARD AND TILT STEERING COLUMN ............................ 19-28
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION SHIFTER/IGNITION INTERLOCK .......................... 19-36
GENERAL INFORMATION .................... 19-1
POWER STEERING GEAR ................... 19-25
POWER STEERING PUMPS ..................19-1
SPECIFICATIONS AND TIGHTENING REFERENCE . . . 19-42
SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS .................2-1
AUTOMATIC AIR LOAD LEVELING SYSTEM ........2-59
AUTOMATIC AIR SUSPENSION ................2-73
DRIVESHAFTS ........................... 2-25
FRONT SUSPENSION .......................2-2
FRONT SUSPENSION SERVICE PROCEDURES .......2-5
GENERAL INFORMATION .....................2-1
REAR (STUB) AXLE ALIGNMENT ALL MODELS .....2-89
REAR SUSPENSION ....................... 2-50
SPECIFICATIONS ......................... 2-91
TRANSAXLE .............................. 21-85
41TE FOUR SPEED AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE ......21-85
41TE FOUR SPEED TRANSAXLE HYDRAULIC SCHEMATICS ........................ 21-170
41TE ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS .............21-145
A-523, A-543, and A-568 MANUAL TRANSAXLE ....21-1
SPECIFICATIONS ........................ 21-183
THREE SPEED TORQUEFLITE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE .......................... 21-35
THREE SPEED TRANSAXLE HYDRAULIC SCHEMATICS ........................ 21-162
WHEELSÐTIRES ........................... 22-1
SPECIFICATIONS ......................... 22-8
TIRE SERVICE PROCEDURES .................22-1
WHEELS SERVICE PROCEDURES ..............22-6
Page 40 of 2438

LUBRICANTS AND GREASES
Lubricating grease is rated for quality and usage
by the NLGI. All approved products have the NLGI
symbol on the label. At the bottom NLGI symbol is the usage and qual-
ity identification letters. Wheel bearing lubricant is
identified by the letter ``G''. Chassis lubricant is iden-
tified by the letter ``L''. The letter following the us-
age letter indicates the quality of the lubricant. The
following symbols indicate the highest quality.
FLUID CAPACITIES
Fuel Tank
AP,AG and AJ ......................................53 L (14 gal.)
AA,AC and AY .....................................60 L (16 gal.)
AA-Flexible Fuel ..................................68 L (18 gal.)
Engine Oil
All.........................................................3.8 L (4.5 qts.)
Cooling System
2.2L ......................................................8.5 L (9.0 qts.)
2.5L ......................................................8.5 L (9.0 qts.)
3.0L ......................................................9.0 L (9.5 qts.)
3.3L ......................................................9.0 L (9.5 qts.)
3.8L ......................................................9.0 L (9.5 qts.)
Includes heater and coolant recovery bottle
Automatic Transaxle
Estimated Service Fill
ALL ......................................................3.8 L (4.0 qts.)
Overhaul Fill Capacity with Torque Converter
Empty
3-speed Fleet .......................................8.7 L (9.2 qts.)
3-speed .................................................8.2 L (8.8 qts.)
4-speed Electronic ................................9.4L (9.9 qts.)
Manual Transaxle
All ..........................................................9.4L (9.9 qts.)
Fill to bottom of fill hole.
Power Steering
All ...........................................................75L (1.5 pts.)
PARTS REQUIRING NO LUBRICATION
Many components on a Chrysler Corporation vehi-
cle require no periodic maintenance. Some compo-
nents are sealed and permanently lubricated. Rubber
bushings can deteriorate or limit damping ability if
lubricated. The following list of components require
no lubrication: ²
Air Pump
² Generator Bushings
² Drive Belts
² Drive Belt Idler/Tensioner Pulley
² Front Wheel Bearings
² Rubber Bushings
² Starter Bearings/Bushings
² Suspension Strut Bearings
² Throttle Control Cable
² Throttle Linkage
² Water Pump Bearings
JUMP STARTING PROCEDURE
WARNING: REVIEW ALL SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
AND WARNINGS IN GROUP 8A, BATTERY/START-
ING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS. DO NOT JUMP START A FROZEN BATTERY, PER-
SONAL INJURY CAN RESULT. DO NOT JUMP START WHEN BATTERY INDICA-
TOR DOT IS YELLOW OR BRIGHT COLOR. DO NOT ALLOW JUMPER CABLE CLAMPS TO
TOUCH EACH OTHER WHEN CONNECTED TO A
BOOSTER SOURCE. DO NOT USE OPEN FLAME NEAR BATTERY.
REMOVE METALLIC JEWELRY WORN ON HANDS
OR WRISTS TO AVOID INJURY BY ACCIDENTAL
ARCHING OF BATTERY CURRENT. WHEN USING A HIGH OUTPUT BOOSTING DE-
VICE, DO NOT ALLOW BATTERY VOLTAGE TO EX-
CEED 16 VOLTS. REFER TO INSTRUCTIONS
PROVIDED WITH DEVICE BEING USED.
CAUTION: When using another vehicle as a
booster, do not allow vehicles to touch. Electrical
systems can be damaged on either vehicle.
TO JUMP START A DISABLED VEHICLE:
(1) Raise hood on disabled vehicle and visually in-
spect engine compartment for:
² Battery cable clamp condition, clean if necessary.
² Frozen battery.
² Yellow or bright color test indicator, if equipped.
² Low battery fluid level.
² Generator drive belt condition and tension.
² Fuel fumes or leakage, correct if necessary.
CAUTION: If the cause of starting problem on dis-
abled vehicle is severe, damage to booster vehicle
charging system can result.
(2) When using another vehicle as a booster
source, turn off all accessories, place gear selector in
park or neutral, set park brake and operate engine
at 1200 rpm.
NLGI SYMBOL
0 - 4 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE Ä
Page 43 of 2438

TOWING RECOMMENDATIONS
RECOMMENDED TOWING EQUIPMENT
To avoid damage to bumper fascia and air dams
use of a wheel lift or flat bed towing device (Fig. 8) is
recommended. When using a wheel lift towing de-
vice, be sure the unlifted end of disabled vehicle has
at least 100 mm (4 in.) ground clearance. If mini-
mum ground clearance cannot be reached, use a tow-
ing dolly. If a flat bed device is used, the approach
angle should not exceed 15 degrees.
GROUND CLEARANCE
CAUTION: If vehicle is towed with wheels removed,
install lug nuts to retain brake drums or rotors.
A towed vehicle should be raised until lifted wheels
are a minimum 100 mm (4 in) from the ground. Be
sure there is adequate ground clearance at the oppo-
site end of the vehicle, especially when towing over
rough terrain or steep rises in the road. If necessary,
remove the wheels from the lifted end of the vehicle
and lower the vehicle closer to the ground, to in-
crease the ground clearance at the opposite end of
the vehicle. Install lug nuts on wheel attaching studs
to retain brake drums or rotors.
LOCKED VEHICLE TOWING
When a locked vehicle must be towed with the
front wheels on the ground, use a towing dolly or flat
bed hauler.
FLAT TOWING WITH TOW BAR
² 4-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be flat
towed at speeds not to exceed 72 km/h (44 mph) for
not more than 160 km (100 miles). The steering col-
umn must be unlocked and gear selector in neutral.
² 3-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be flat
towed at speeds not to exceed 40 km/h (25 mph) for
not more than 25 km (15 miles). The steering column
must be unlocked and gear selector in neutral.
² Manual transaxle vehicles can be flat towed at any
legal highway speed with no distance restrictions.
The steering column must be unlocked and gear se-
lector in neutral. WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW TOWING ATTACH-
MENT DEVICES TO CONTACT THE FUEL TANK OR
LINES, FUEL LEAK CAN RESULT. DO NOT LIFT OR TOW VEHICLE BY FRONT OR
REAR BUMPER, OR BUMPER ENERGY ABSORBER
UNITS. DO NOT VENTURE UNDER A LIFTED VEHICLE IF
NOT SUPPORTED PROPERLY ON SAFETY
STANDS. DO NOT ALLOW PASSENGERS TO RIDE IN A
TOWED VEHICLE. USE A SAFETY CHAIN THAT IS INDEPENDENT
FROM THE TOWING ATTACHMENT DEVICE.
CAUTION: Do not damage brake lines, exhaust sys-
tem, shock absorbers, sway bars, or any other un-
der vehicle components when attaching towing
device to vehicle. Remove or secure loose or protruding objects
from a damaged vehicle before towing. Refer to state and local rules and regulations be-
fore towing a vehicle. Do not allow weight of towed vehicle to bear on
lower fascia, air dams, or spoilers.
TOWINGÐFRONT WHEEL LIFT
Chrysler Corporation recommends that a vehicle be
towed with the front end lifted, whenever possible.
TOWINGÐREAR WHEEL LIFT
If a front wheel drive vehicle cannot be towed with
the front wheels lifted, the rear wheels can be lifted
provided the following guide lines are observed.
CAUTION: Do not use steering column lock to se-
cure steering wheel during towing operation.
² Unlock steering column and secure steering wheel
in straight ahead position with a clamp device de-
signed for towing.
² Verify that front drive line and steering compo-
nents are in good condition.
² 4-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be towed
at speeds not to exceed 72 km/h (44 mph) for not
more than 160 km (100 miles). The gear selector
must be in neutral position.
² 3-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be towed
at speeds not to exceed 40 km/h (25 mph) for not
more than 25 km (15 miles). The gear selector must
be in neutral position.
² 3-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be towed
at speeds not to exceed 40 km/h (25 mph) for not
more than 25 km (15 miles). The gear selector must
be in neutral position.
Fig. 8 Recommended Towing Devices
Ä LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 7
Page 55 of 2438

CHASSIS AND BODY INDEX
page page
Body Lubrication ......................... 22
Brakes ................................ 21
Headlamps ............................. 22
Lower Ball Joints ......................... 19 Power Steering
.......................... 19
Rear Wheel Bearings ..................... 20
Steering Linkage ......................... 19
STEERING LINKAGE
INSPECTION
The steering linkage and steering gear should be in-
spected for wear, leaks or damage when other under ve-
hicle service is performed. The rack and pinion steering
gear end boots should not have excess oil or grease res-
idue on the outside surfaces or surrounding areas
(Fig.1). If boot is leaking, it should be repaired. For
proper service procedures, see Group 19, Steering.
The tie rod end seal should fit securely between the
steering knuckle and tie rod end (Fig.2). The steering
linkage should be lubricated at the time and distance
intervals described in the Lubrication and Mainte-
nance Schedules. Refer to General Information sec-
tion of this group.
TIE ROD END LUBRICATION
Lubricate the steering linkage with Mopar, Multi-
mileage Lube or equivalent. Using a wiping cloth,
clean grease and dirt from around grease fitting and
joint seal. Using a grease gun, fill tie rod end until
lubricant leaks from around the tie rod end side of
the seal (Fig.2). When lube operation is complete,
wipe off excess grease.
LOWER BALL JOINTS
INSPECTION
The front suspension lower ball joints should be in-
spected for wear, leaks or damage when other under ve- hicle service is performed. The ball joint seal should fit
securely between the steering knuckle and lower control
arm (Fig. 3). The ball joints should be lubricated at the
time and distance intervals described in the Lubrication
and Maintenance Schedules. Refer to the General Infor-
mation section of this group.
BALL JOINT LUBRICATION
CAUTION: Do not over fill ball joint with grease,
damage to seal can result.
Lubricate the ball joints with Mopar, Multi-mile-
age Lube or equivalent. Using a wiping cloth, clean
grease and dirt from around grease fitting and joint
seal. Using a grease gun, fill ball joint until seal
starts to swell (Fig. 3). When lube operation is com-
plete, wipe off excess grease.
POWER STEERING
The power steering fluid level should be inspected
when other under hood service is performed. If the
fluid level is low and system is not leaking, use Mo-
par, Power Steering Fluid or equivalent. The power
steering system should be inspected for leaks when
other under vehicle service is performed. For proper
service procedures, refer to Group 19, Steering.Fig. 1 Inspect Steering Linkage
Fig. 2 Tie Rod End Lubrication
Ä LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 19
Page 56 of 2438

The power steering pump drive belt should be in-
spected at the time and distance interval described in
the Lubrication and Maintenance Schedules. Refer to
the General Information section of this group.
POWER STEERING FLUID INSPECTION
WARNING: ENGINE MUST NOT BE RUNNING WHEN
INSPECTING POWER STEERING FLUID LEVEL,
PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: Do not over fill power steering reservoir
when adding fluid, seal damage and leakage can re-
sult.
TO INSPECT FLUID LEVEL:
(1) Position vehicle on a level surface with engine
at normal running temperature. (2) Turn OFF engine and remove ignition key.
(3) Using a wiping cloth, clean oil and dirt residue
from around power steering reservoir cap. (4) Remove reservoir cap or dipstick and wipe off
fluid. (5) Install cap or dipstick.
(6) Remove cap or dipstick. Holding handle or cap
above tip of dipstick, read fluid level (Fig. 4, 5, or 6).
Add fluid if reading is below cold level mark on dip-
stick.
REAR WHEEL BEARINGS
INSPECTION
The rear wheel bearings should be packed with
new lubricant at the distance interval described in the Lubrication and Maintenance Schedules. Refer to
the General Information section of this group. The
bearings should be inspected for contamination and
wear before they are cleaned. Slight discoloration of
bearing rollers and race cup is normal. If metal
Fig. 3 Ball Joint Lubrication
Fig. 4 Power Steering Reservoir DipstickÐ2.2L or 2.5L Engine
Fig. 5 Power Steering Reservoir DipstickÐ3.0L Engine
Fig. 6 Power Steering Reservoir DipstickÐ3.3L or3.8L Engine
0 - 20 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE Ä
Page 60 of 2438

FRONT SUSPENSION
FRONT SUSPENSION MAJOR COMPONENTS (FIG. 2)
STRUT SUPPORT
The system is supported by coil springs positioned
offset around the struts. The springs are contained
between an upper seat, located just below the top
strut mount assembly (Fig. 2) and a lower spring
seat on the strut lower housing. The top of each strut assembly is bolted to the up-
per fender reinforcement (shock tower) through a
rubber isolated mount. The bottom attaches to the top of the steering
knuckle with two through bolts. On some vehicles,
one bolt has an eccentric cam located below the head
of the bolt for camber adjustment. On the other ve-
hicles the camber adjustment is done by manually
moving the steering knuckle within the strut assem-
bly. Caster is a fixed setting on all vehicles and is
not adjustable.
STEERING KNUCKLE
The steering knuckle is a single casting with legs
machined for attachment to the strut damper, steer-
ing linkage, brake adaptor, and lower control arm
ball joint. The knuckle also holds the front drive hub
bearing. The hub is positioned through the bearing
and knuckle, with the constant velocity stub shaft
splined through the hub.
LOWER CONTROL ARM
The lower control arm is a steel casting with 2
large spool type rubber pivot bushings. The lower
control arm is bolted to the crossmember with pivot
bolts through the center of the rubber pivot bush-
ings. The ball joint is pressed into the control arm and
has a non-tapered stud with a notch for clamp bolt
clearance. The stud is clamped and locked into the
steering knuckle leg with a clamp bolt. The lower control arms are inter-connected through
a rubber isolated sway bar (Fig. 2).
DRIVESHAFTS
A left and right driveshaft is attached inboard to
the transaxle differential side gears, and outboard to
the driven wheel hub. To deliver driving force from the transaxle to the
front wheels during turning maneuvers and suspen-
sion movement. Both shafts are constructed with con-
stant velocity universal joints at both ends. Both shafts have a Tripod (sliding) joint at the
transaxle end and Rzeppa joints (with splined stub
shafts) on the hub ends. Due to the transaxle loca-
tion the connecting shafts between the C/V joints are
of different length and construction. The right shaft
is longer and of tubular construction. The left shaft
is solid.
2 - 2 SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS Ä
Page 62 of 2438
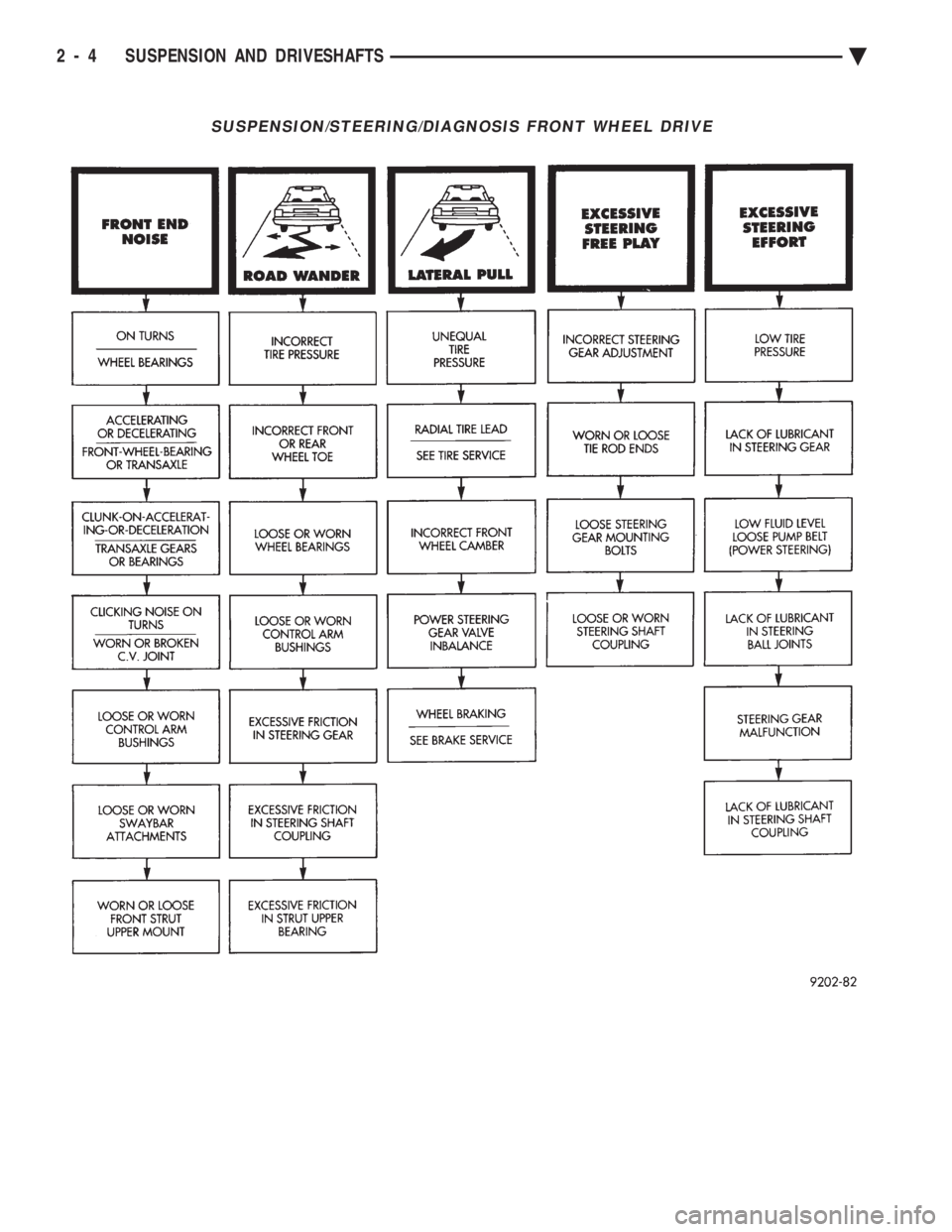
SUSPENSION/STEERING/DIAGNOSIS FRONT WHEEL DRIVE
2 - 4 SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS Ä