1993 CHEVROLET DYNASTY wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 305 of 2438

(4) Provide communication to the DRB II while in
the Antilock brakes diagnostic mode. The CAB continuously monitors the speed of each
wheel, through the signals generated at the Wheel
Speed Sensors. This is used to determine if any
wheel of the vehicle is beginning to lock-up (skid)
when the brakes are applied. When a wheel locking
tendency is detected during brake apply. The CAB
commands the appropriate Build/Decay valves to
modulate brake fluid pressure in some or all of the
hydraulic circuits. The CAB continues to control
pressure in individual hydraulic circuits until a lock-
ing tendency is no longer present. The ABS system is constantly monitored by the
CAB for proper operation. If the CAB detects a fault,
it will turn on the Amber Antilock Warning Lamp
and disable the ABS brake system. The normal Non
ABS brake system will remain operational. The CAB contains a self-diagnostic program which
will turn on the Amber Antilock Warning Lamp
when a system fault is detected. Faults are stored in
a diagnostic program memory. There are 16 fault
codes which may be stored in the CAB and displayed
through the DRB II. These fault codes will remain in
the CAB memory even after the ignition has been
turned off. The fault codes can be cleared by using
the DRB II diagnostics tester, or they will be auto-
matically cleared from the memory after (50) ignition
switch on/off cycles.
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE (INPUTS)
² Four wheel speed sensors.
² Stop lamp switch.
² Ignition switch.
² System relay voltage.
² Ground.
² Pump/Motor Relay Monitor
² Diagnostics Communications
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE (OUTPUTS)
²4 Build/Decay valves.
² Antilock warning lamp.
² System relay actuation.
² Diagnostic communication.
² Pump/Motor relay actuation
DIAGNOSTIC CONNECTOR
The Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System diagnostic
connector is located under the fuse panel access
cover. The access cover is located on the lower sec-
tion of the instrument panel to the left side of the
steering column. The diagnostics connector is a blue
6 way connector see (Fig. 9).
ANTILOCK SYSTEM RELAYS AND WARNING LAMPS
SYSTEM RELAY
The ABS Modulator Valves are powered through
the System Relay which is located on a bracket
mounted to the CAB (Fig. 10). The System Relay
provides power to the CAB for modulator valve oper-
ation (pins 47 and 41) after the startup cycle when
the ignition is turned on.
Fig. 8 CAB Location
Fig. 9 Antilock Diagnostic Connector Location
Fig. 10 System Relay Location On The CAB
Ä ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 19
Page 306 of 2438

ANTILOCK WARNING LAMP DIODE
The Warning Lamp Relay on the Bendix Antilock
4 Brake System has been replaced with a diode. The
diode is used to control the function of the warning
lamp and is located inside the CAB module wiring
harness. The diode is a replaceable component of the
wiring harness, and will not require replacement of
the entire wiring harness if only the diode is diag-
nosed to have failed. When the system relay is de-energized, the Anti-
lock warning lamp will be lit. This will occur because
a ground path exists for the Antilock warning lamp
through the Antilock warning lamp diode and the
system relay armature. When the system relay is en-
ergized by the CAB, the system relay armature will
no longer provide a ground and the lamp will turn
off. Thus, the lamp will be lit if either the CAB is
disconnected or a system fault causes the Antilock to
be turned off.
PUMP/MOTOR RELAY
Pump/Motor power is supplied by the Pump/Motor
Relay. The Pump/Motor Relay is either mounted on
the left front inner fender shield, or the front of the
left shock tower. The mounting location is dependent
on whether the vehicle is or is not equipped with a
power distribution center. See (Fig. 11 and 12) for
specific mounting locations.
ANTILOCK WARNING LAMP OFF
System Relay Energized
From pin 57, the CAB energizes the Antilock sys-
tem relay coil, thus the electrical current flow in the
coil closes the system relay. Then electrical current
is provided to pins 47 and 41 of the CAB to provide
power to the modulator valves. The CAB turns off the Amber Antilock Warning
Lamp by breaking the ground path through pin 15 of
the CAB.
ANTILOCK WARNING LAMP ON
System Relay De-Energized.
When the Amber Antilock Warning Lamp is on,
there is no electrical current flow from the CAB at
pin 57 and the System Relay coil is NOT energized.
No electrical current flows to pin 47 and 41 (modula-
tor valve power), or to the Antilock Warning Lamp
diode. Thus, the Amber Antilock Warning Lamp is
not energized. The Amber Antilock Warning Lamp is
now grounded through the Antilock Warning Lamp
diode and pin 15 of the CAB turning on the Amber
Antilock Warning Lamp.
HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS AND VALVE OPERATION
Through the following operation descriptions and
diagrams. The function of the various hydraulic con-
trol valves in the ABS system will be described. The
fluid control valves mentioned below, control the flow
of pressurized brake fluid to the wheel brakes during
the different modes of Antilock braking. For explanation purposes we will assume all speed
sensors are sending the same wheel speed informa-
tion, requiring the same hydraulic fluid modulation
at the same rate.
NORMAL BRAKING
BUILD/DECAY VALVES
Closed (Fig. 1)
The brake pedal is applied. The travel of the brake
pedal closes primary and secondary circuits from the
master cylinder fluid supply. Brake fluid from the
master cylinder primary and secondary circuits flows
through the build/decay valves to the wheel brakes.
ABS BRAKING-BUILD PRESSURE
BUILD/DECAY VALVES
Open (Fig. 2)
Fig. 11 Pump Motor Relay Location On AA Body W/O Power Distribution Center
Fig. 12 Pump Motor Relay Location On AJ BodyWith Power Distribution Center
5 - 20 ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 307 of 2438
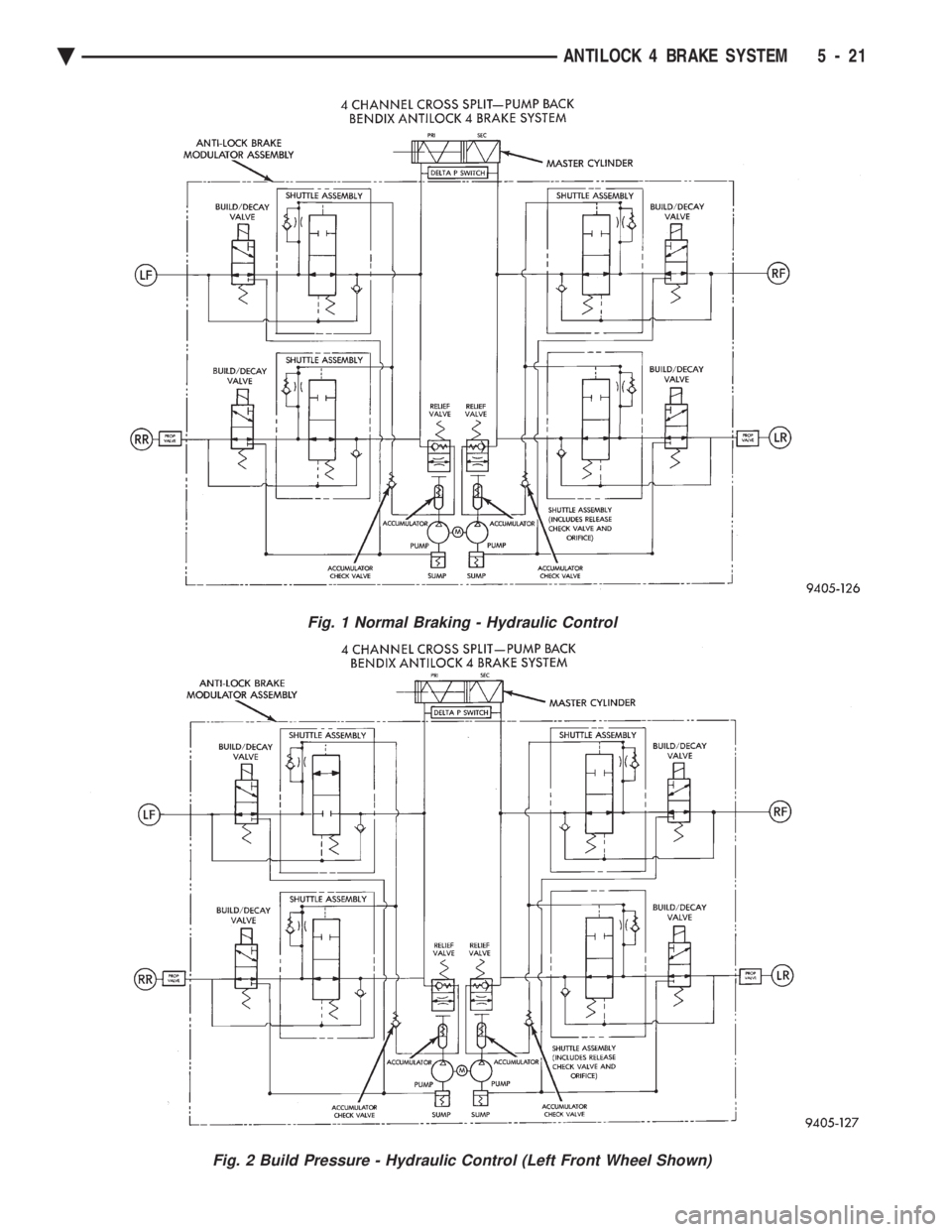
Fig. 1 Normal Braking - Hydraulic Control
Fig. 2 Build Pressure - Hydraulic Control (Left Front Wheel Shown)
Ä ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 21
Page 308 of 2438
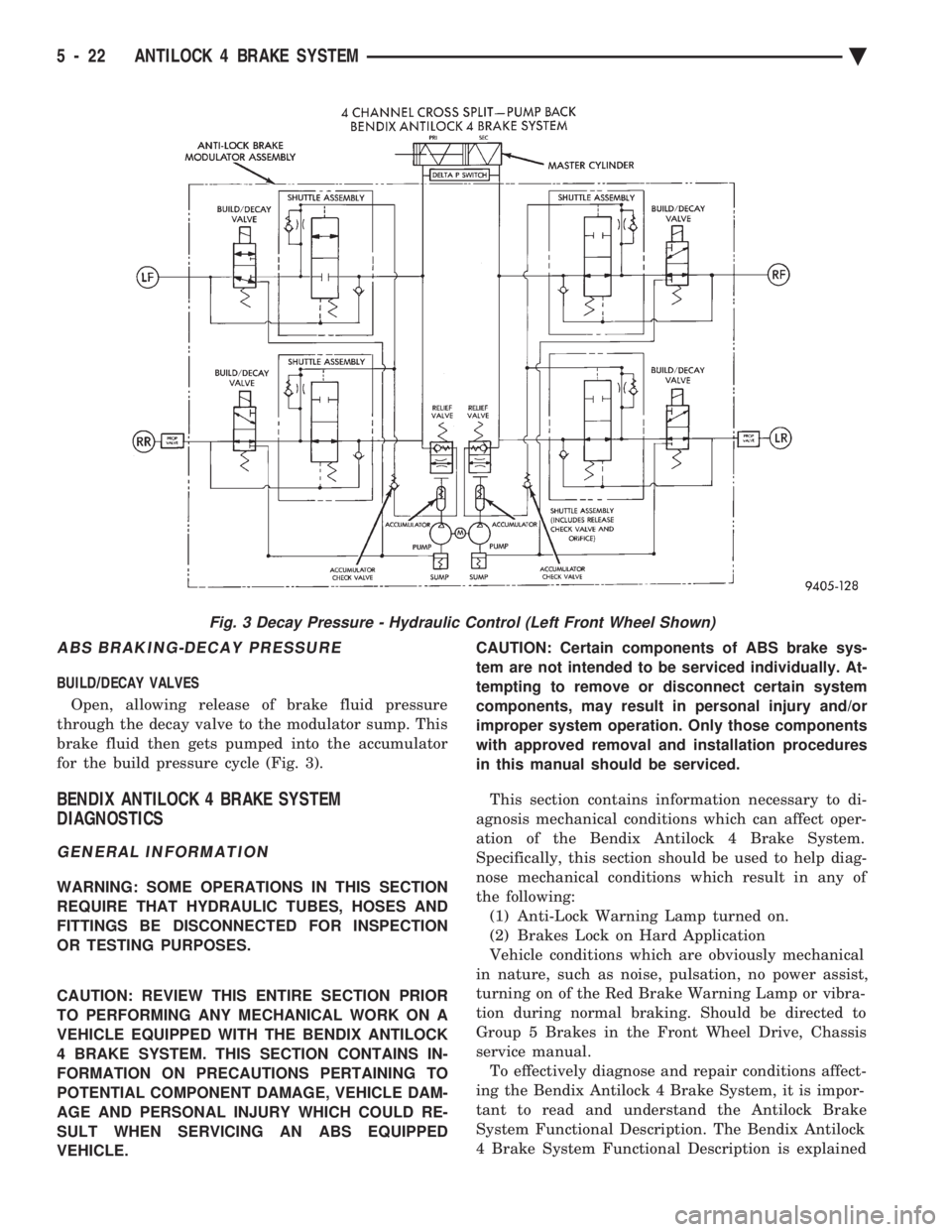
ABS BRAKING-DECAY PRESSURE
BUILD/DECAY VALVES Open, allowing release of brake fluid pressure
through the decay valve to the modulator sump. This
brake fluid then gets pumped into the accumulator
for the build pressure cycle (Fig. 3).
BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM
DIAGNOSTICS
GENERAL INFORMATION
WARNING: SOME OPERATIONS IN THIS SECTION
REQUIRE THAT HYDRAULIC TUBES, HOSES AND
FITTINGS BE DISCONNECTED FOR INSPECTION
OR TESTING PURPOSES.
CAUTION: REVIEW THIS ENTIRE SECTION PRIOR
TO PERFORMING ANY MECHANICAL WORK ON A
VEHICLE EQUIPPED WITH THE BENDIX ANTILOCK
4 BRAKE SYSTEM. THIS SECTION CONTAINS IN-
FORMATION ON PRECAUTIONS PERTAINING TO
POTENTIAL COMPONENT DAMAGE, VEHICLE DAM-
AGE AND PERSONAL INJURY WHICH COULD RE-
SULT WHEN SERVICING AN ABS EQUIPPED
VEHICLE. CAUTION: Certain components of ABS brake sys-
tem are not intended to be serviced individually. At-
tempting to remove or disconnect certain system
components, may result in personal injury and/or
improper system operation. Only those components
with approved removal and installation procedures
in this manual should be serviced.
This section contains information necessary to di-
agnosis mechanical conditions which can affect oper-
ation of the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System.
Specifically, this section should be used to help diag-
nose mechanical conditions which result in any of
the following: (1) Anti-Lock Warning Lamp turned on.
(2) Brakes Lock on Hard Application
Vehicle conditions which are obviously mechanical
in nature, such as noise, pulsation, no power assist,
turning on of the Red Brake Warning Lamp or vibra-
tion during normal braking. Should be directed to
Group 5 Brakes in the Front Wheel Drive, Chassis
service manual. To effectively diagnose and repair conditions affect-
ing the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System, it is impor-
tant to read and understand the Antilock Brake
System Functional Description. The Bendix Antilock
4 Brake System Functional Description is explained
Fig. 3 Decay Pressure - Hydraulic Control (Left Front Wheel Shown)
5 - 22 ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 309 of 2438

earlier in this service manual supplement. Then follow
the diagnostic procedures outlined in this section. Many conditions that generate customer complaints
may be normal operating conditions, but are judged to
be a problem due to not being familiar with the ABS
system. These conditions can be recognized without
performing extensive diagnostic work, given adequate
understanding of the operating principles and perfor-
mance characteristics of the ABS system.
DEFINITIONS
Several abbreviations are used in this manual. They
are presented here for reference.
² CABÐController Antilock Brake
² ABSÐAntilock Brake System
² PSIÐPounds per Square Inch (pressure)
² WSSÐWheel Speed Sensor
² ACÐAlternating Current
ABS COMPUTER SYSTEM SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
The ABS system uses an electronic control module,
the CAB. This module is designed to withstand normal
current draws associated with vehicle operation. How-
ever care must be taken to avoid overloading the CAB
circuits. In testing for open or short circuits, do
not ground or apply voltage to any of the circuits
unless instructed to do so by the appropriate
diagnostic procedure. These circuits should only be
tested using a high impedance multi-meter, special
tools or the DRB II tester as described in this section.
Power should never be removed or applied to any
control module with the ignition in the ON position.
Before removing or connecting battery cables, fuses, or
connectors, always turn the ignition to the OFF posi-
tion.
ABS GENERAL SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
TEST DRIVING ABS COMPLAINT VEHICLES
Most ABS complaints will require a test drive as a
part of the diagnostic procedure. The purpose of the
test drive is to duplicate the condition. Remember conditions that result in the turn-
ing on of the Red Brake Warning Lamp may
indicate reduced braking ability. The following
procedure should be used to test drive an ABS
complaint vehicle. Before test driving a brake complaint vehicle, note
whether the Red or Amber Brake Warning Lamp is
turned on. If the Red Brake Warning Lamp, is
turned on, refer to the base brake Control Valves
Section in the Front Wheel Drive, chassis service
manual. If the Amber Antilock Warning light was or
is on, read record and erase the faults. While the
Amber ABS Warning Lamp is on the ABS system is
not functional. The standard brake system and abil- ity to stop the car is not affected, if only the Amber
Antilock Warning Lamp is on.
(1) Turn ignition key to the off position and then
back to the on position. Note whether the Amber ABS
Warning Lamp continues to stay on. If it does refer to
the 1994 Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System Diagnostic
Manual for the required diagnostic test procedures. (2) If the Amber ABS Warning Lamp goes out, shift
vehicle into gear and drive car to a speed of 5 mph to
complete the ABS drive-off cycle. If at this time, the
Amber ABS Warning Lamp goes on refer to the 1994
Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System Diagnostic Manual. (3) If the Amber ABS Warning Lamp remains OUT,
continue to drive the vehicle a short distance. During
this test drive be sure that the vehicle achieves at least
25 mph. Brake to at least one complete stop and again
accelerate to 25 mph. (4) If a functional problem with the ABS system is
determined while test driving a vehicle. Refer to the
Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System Diagnostics Manual
for required diagnostic test procedures and proper use
of the DRB II tester.
ABS BRAKE SYSTEM ON VEHICLE SERVICE
The following are general precautions which
should be observed whenever servicing and or
diagnosing the ABS system and other vehicle
electronic systems. Failure to observe these pre-
cautions may result in ABS system damage. (1) If welding work is to be performed on a vehicle
using an arc welder. The wiring harness connector
should be disconnected from the CAB before beginning
any welding operation. (2) The CAB 60 way connector and modulator as-
sembly 10 way connector, should never be connected or
disconnected with the ignition in the on position. (3) Some components of Bendix Antilock 4 Brake
System assemblies can not be serviced separately from
the assembly and will require replacement of the
complete assembly for servicing. Do not disassemble
any component which is designated as non-serviceable.
CAUTION: Brake fluid will damage painted surfaces.
If brake fluid is spilled on any painted surfaces, wash
off with water immediately.
WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CABLES
Proper installation and routing of the Wheel Speed
Sensor Cables is critical to continued system opera-
tion. Be sure that cables are installed, routed and
clipped properly. Failure to install speed sensor ca-
bles as shown in the on car service section of this
Ä ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 23
Page 310 of 2438

manual. May result in contact with moving parts or
over extension of cables, resulting in component fail-
ure and an open circuit.
MECHANICAL DIAGNOSTICS AND SERVICE
PROCEDURES
SPECIAL SERVICE TOOL
Some diagnostic procedures in this section require
the use of the DRB diagnostics tester. The proper ap-
plication and procedures for the use of this tool are
described below.
DRB DIAGNOSTIC TESTER
Some of the diagnostic procedures that are ex-
plained in this section require the use of the DRB Di-
agnostics Tester to insure that proper diagnostics are
performed. Refer to those sections for proper testing
procedures and the DRB operators manual for its
proper operational information.
INTERMITTENT FAULTS
As with virtually any electronic system, intermit-
tent faults in the ABS system may be difficult to ac-
curately diagnose. Most intermittent faults are caused by faulty elec-
trical connections or wiring. When an intermittent
fault is encountered, check suspect circuits for: (1) Poor mating of wiring harness connector halves
or terminals not fully seated in the connector body. (2) Improperly formed or damaged terminals. All
connector terminals in a suspect circuit should be
checked and carefully reformed to increase contact
tension with its mating terminal. (3) Poor terminal to wire connection. This requires
removing the terminal from the connector body to in-
spect. (4) Pin presence in the connector assembly
(5) Connector push-in, spread, and corrosion.
If a visual check does not find the cause of the
problem, operate the car in an attempt to duplicate
the condition and record the set Fault code. Most failures of the ABS system will disable the
Antilock function for the entire ignition cycle even if
the fault clears before key-off. There are some failure
conditions, however, which will allow ABS operation
to resume during the ignition cycle in which it oc-
curred, if the failure condition is no longer present.
The following conditions may result in intermittent
illumination of the Amber Antilock Warning Lamp.
All other failures will cause the lamp to remain on
until the ignition switch is turned off. Circuits in-
volving these inputs to the CAB should be investi-
gated if a complaint of intermittent warning system
operation is encountered. (1) Low system voltage: If Low System Voltage is
detected by the CAB, the CAB will turn on the Am-
ber Antilock Warning Lamp until normal system voltage is achieved. Once normal voltage is seen at
the CAB, normal operation resumes.
(2) Antilock system and pump/motor relay. If the
relays fail to make the ground circuit connection or
has an intermittent ground. The CAB will turn on
the Amber Antilock Warning Light. (3) Excess decay, an extended pressure decay pe-
riod, will turn on the Amber Antilock Warning Light
until the vehicle comes to a complete stop. Additionally, any condition which results in inter-
ruption of electrical current to the CAB or modulator
assembly, may cause the Amber Antilock Warning
Lamp to turn on intermittently.
ABS BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES
ABS SYSTEM SELF DIAGNOSIS
The ABS system is equipped with a self diagnostic
capability which may be used to assist in isolation of
ABS faults. The features of the self diagnostics sys-
tem are described below.
START-UP CYCLE
The self diagnostic ABS start up cycle begins when
the ignition switch is turned to the on position. An
electrical check is completed on the ABS components.
Such as Wheel Speed Sensor Continuity and System
and other Relay continuity. During this check the
Amber Antilock Light is turned on for approximately
1- 2 seconds. Further Functional testing is accomplished once
the vehicle is set in motion, known as drive-off.
² The solenoid valves and the pump/motor are acti-
vated briefly to verify function.
² The voltage output from the wheel speed sensors is
verified to be within the correct operating range. If the vehicle is not set in motion within 3 minutes
from the time the ignition switch is set in the on po-
sition. The solenoid test is bypassed but the pump/
motor is activated briefly to verify that it is
operating correctly.
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE CAB
Fault codes are kept in a Non-Volatile memory un-
til either erased by the technician using the DRB or
erased automatically after 50 ignition cycles (key
ON-OFF cycles). The only fault that will not be
erased after 50 (KEY CYCLES) is the CAB fault. A
CAB fault can only be erased by the technician using
the DRB diagnostic tester. More than one fault can
be stored at a time. The number of key cycles since
the most recent fault was stored is also displayed.
Most functions of the CAB and ABS system can be
accessed by the technician for testing and diagnostic
purposes by using the DRB.
5 - 24 ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 321 of 2438

(4) If equipped, remove the 2 bolts (Fig. 4) attaching
speed control vacuum reservoir to battery tray. Then
remove vacuum reservoir (Fig. 4) from the battery tray.
Vacuum lines (Fig. 4) do not need to be removed
from vacuum reservoir. (5) Remove the 4 bolts attaching battery tray (Fig.
5) to frame rail and fender shield of the vehicle.
Then remove battery tray.
(6) Remove battery acid shield, (Fig. 6) from the
ABS modulator assembly.
(7) Remove the 6 tube nuts (Fig. 7), attaching hy-
draulic brake line tube bundle to modulator assem-
bly, thread savers and proportioning valves. Then
remove the 6 hydraulic brake lines as an assembly,
from the modulator assembly. (8) Remove electrical connector from the brake
pressure differential warning switch on hydraulic
junction block (Fig. 8). (9) Remove the primary and secondary hydraulic
brake tubes (Fig. 9) going from the master cylinder
to the junction block, from both master cylinder and
junction block. (10) Remove the brake hydraulic tube going to the
vehicle's left front wheel from the junction block. (11) Remove the 6 hydraulic brake tubes at the hy-
draulic junction block, coming from the antilock mod-
ulator assembly.
Fig. 5 Battery Tray And Attaching Bolts
Fig. 6 ABS Modulator Assembly Acid Shield
Fig. 2 Battery Heat Shield And Hold Down Clamp
Fig. 3 Battery Tray Shield
Fig. 4 Speed Control System Vacuum Reservoir
Ä ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 35
Page 324 of 2438
MASTER CYLINDER AND POWER BOOSTER
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION If the Master Cylinder or Power Booster need to be
removed for replacement or servicing of other vehicle
components. Refer to Master Cylinder or Power
Brake Service section in group 5 of the 1993 M.Y.
Front Wheel Drive Car service manual. After servicing master cylinder, refer back to this
service manual supplement for the appropriate proce-
dure and sequence used to bleed the base and Anti-
lock portion of the brake system.
PROPORTIONING VALVES (FIG. 1)
CAUTION: Proportioning valves should never be
disassembled.
REMOVAL (1) Disconnect and remove both battery cables
from battery. (2) Remove heat shield (Fig. 2) from the battery.
Then remove battery hold down clamp (Fig. 2) and
battery from battery tray.
Fig. 15 Battery Tray Installation And Attaching Bolts
Fig. 16 Vacuum Reservoir Installation And Attaching Bolts
Fig. 17 Battery Tray Access Shield Installed
Fig. 18 Battery Hold Down Clamp And Heat Shield Installed
Fig. 1 ABS Proportioning Valve Identification
5 - 38 ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä