Page 3457 of 4087
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION (Cont'd)
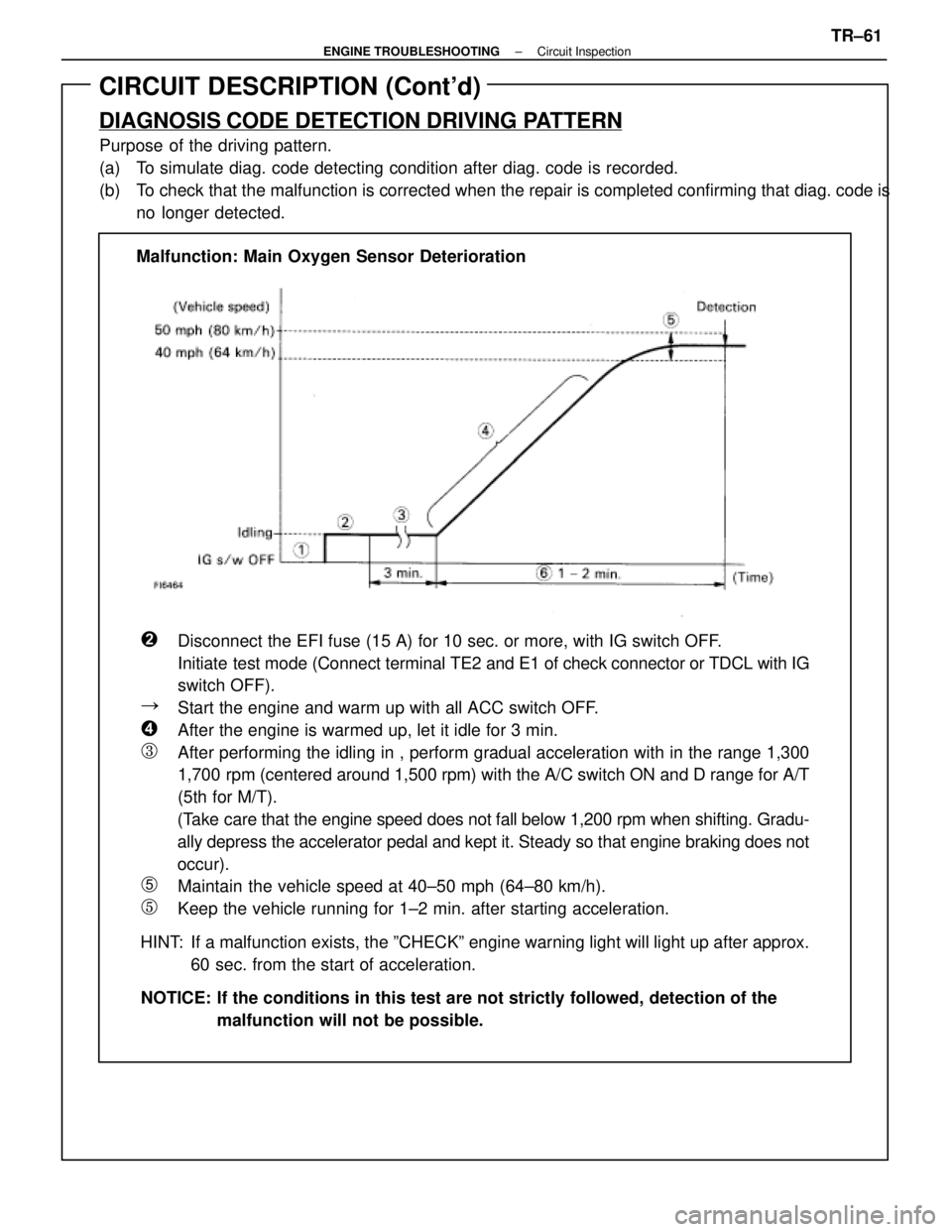
DIAGNOSIS CODE DETECTION DRIVING PATTERN
Purpose of the driving pattern.
(a) To simulate diag. code detecting condition after diag. code is recorded.
(b) To check that the malfunction is corrected when the repair is completed co\
nfirming that diag. code isno longer detected.
�Disconnect the EFI fuse (15 A) for 10 sec. or more, with IG switch OFF\
.
Initiate test mode (Connect terminal TE2 and E1 of check connector or TDCL with IG
switch OFF).
�Start the engine and warm up with all ACC switch OFF.
�After the engine is warmed up, let it idle for 3 min.
�After performing the idling in , perform gradual acceleration with in th\
e range 1,300
1,700 rpm (centered around 1,500 rpm) with the A/C switch ON and D range fo\
r A/T
(5th for M/T).
(Take care that the engine speed does not fall below 1,200 rpm when shifting.\
Gradu-
ally depress the accelerator pedal and kept it. Steady so that engine br\
aking does not
occur).
�Maintain the vehicle speed at 40±50 mph (64±80 km/h).
�Keep the vehicle running for 1±2 min. after starting acceleration.
HINT: If a malfunction exists, the ºCHECKº engine warning light will light\
up after approx. 60 sec. from the start of acceleration.
NOTICE: If the conditions in this test are not strictly followed, detection of t\
he malfunction will not be possible.
Malfunction: Main Oxygen Sensor Deterioration
±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit InspectionTR±61
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3458 of 4087
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Are there any other codes (Besides 21 or
28) being output?
Replace oxygen sensor.
Go to relevant diag. code chart.
HINT: If diag. code 21 is output, replace the front side main oxygen sensor.If diag. code 28 is output, replace the rear side main oxygen sensor.
WIRING DIAGRAM
TR±62±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit Inspection
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3459 of 4087
Reference INSPECTION USING OSCILLOSCOPE
wWith the engine racing (4,000 rpm) measure
between terminals OX1, OX2 and E1 of engine (&
ECT) ECU.
HINT: The correct waveform appears as shown in the
illustration on the left, oscillating between approx.
0.1 V and 0.9 V
If the oxygen sensor is deteriorated, the amplitude
of the voltage is reduced as shown on the left.
±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit InspectionTR±63
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3461 of 4087
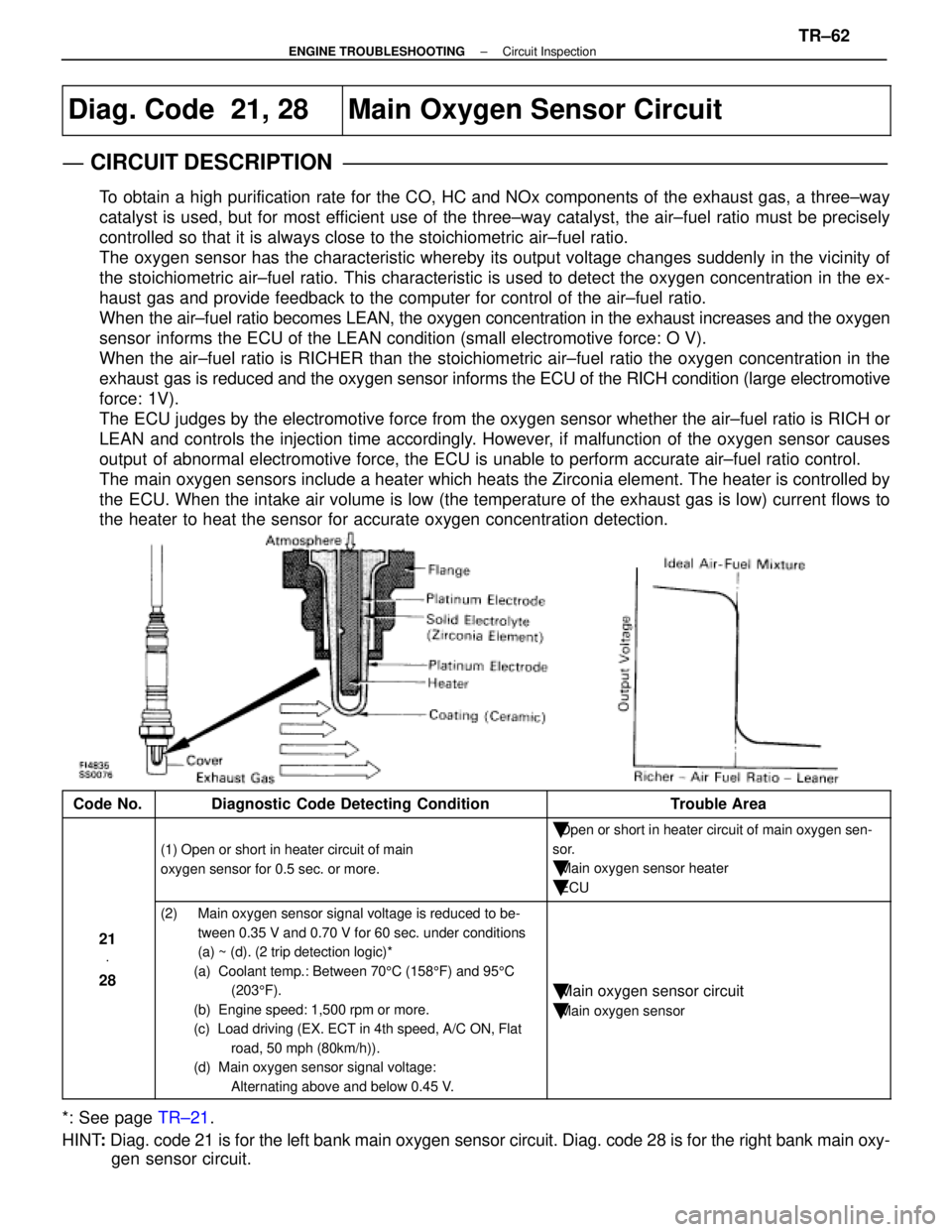
Diag. Code 21, 28Main Oxygen Sensor Circuit
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
To obtain a high purification rate for the CO, HC and NOx components of th\
e exhaust gas, a three±way
catalyst is used, but for most efficient use of the three±way catalyst, the air±fuel ratio must be \
precisely
controlled so that it is always close to the stoichiometric air±fuel \
ratio.
The oxygen sensor has the characteristic whereby its output voltage chan\
ges suddenly in the vicinity of
the stoichiometric air±fuel ratio. This characteristic is used to det\
ect the oxygen concentration in the ex-
haust gas and provide feedback to the computer for control of the air±\
fuel ratio.
When the air±fuel ratio becomes LEAN, the oxygen concentration in the exh\
aust increases and the oxygen
sensor informs the ECU of the LEAN condition (small electromotive force: O V)\
.
When the air±fuel ratio is RICHER than the stoichiometric air±fuel\
ratio the oxygen concentration in the
exhaust gas is reduced and the oxygen sensor informs the ECU of the RICH condition (large electromotive
force: 1V).
The ECU judges by the electromotive force from the oxygen sensor whether th\
e air±fuel ratio is RICH or
LEAN and controls the injection time accordingly. However, if malfunction of the oxygen sensor causes
output of abnormal electromotive force, the ECU is unable to perform accurate \
air±fuel ratio control.
The main oxygen sensors include a heater which heats the Zirconia element. The heater is controlled by
the ECU. When the intake air volume is low (the temperature of the exhaust\
gas is low) current flows to
the heater to heat the sensor for accurate oxygen concentration detectio\
n.
Code No.Diagnostic Code Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
(1) Open or short in heater circuit of main
oxygen sensor for 0.5 sec. or more.
�Open or short in heater circuit of main oxygen sen-
sor.
�Main oxygen sensor heater
�ECU
21 V
28
(2) Main oxygen sensor signal voltage is reduced to be-
tween 0.35 V and 0.70 V for 60 sec. under conditions
(a) ~ (d). (2 trip detection logic)*
(a) Coolant temp.: Between 70 5C (158 5F) and 95 5C
(203 5F).
(b) Engine speed: 1,500 rpm or more.
(c) Load driving (EX. ECT in 4th speed, A/C ON, Flat road, 50 mph (80km/h)).
(d) Main oxygen sensor signal voltage:
Alternating above and below 0.45 V.
�Main oxygen sensor circuit
�Main oxygen sensor
*: See page TR±21.
HINT : Diag. code 21 is for the left bank main oxygen sensor circuit. Diag. co\
de 28 is for the right bank main oxy-
gen sensor circuit.
±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit InspectionTR±62
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3463 of 4087
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
DIAGNOSTIC
CHART
WIRING DIAGRAM
HINT: If diag. code º21º is output, check the left bank main oxygen sens\
or circuit. If diag. code º28º is output, check the right bank main oxygen sensor circuit.
Check voltage of terminals HTL1, HTR1.
Check resistance of oxygen sensor heater.
Check and repair oxygen sensor heater circuit.
Check operation of oxygen sensor heater.
Check and replace ECU. Replace main oxygen sensor.
*: In this case, oxygen sensor can be deteriorated.
Replace main oxygen sensor.*
±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit InspectionTR±64
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3464 of 4087
OKNG
OKNG
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
1Disconnect the engine & ECT ECU connector, check voltage between terminals HTL1, HTR1 of
engine & ECT ECU connector and body ground.
C
OK
P(2) Connect the Check Harness A.(See page TR±30)
(2) Disconnect engine & ECT ECU connector.
(2) Turn ignition switch on.
Measure voltage beween terminals HTL1, HTR1 of en-
gine & ECT ECU connector and body ground.
Voltage: 10 ± 14 V
Go to step [3].
2Check main oxygen sensor heater.
C
OK
PDisconnect main oxygen sensor connector.
Measure resistance between terminals 1 and 2 of main
oxygen sensor connector.
Resistance: 5.1 ± 6.3 � at 20 �C (68 �F)
Replace main oxygen sensor.
Check and repair harness or connector between
main relay and main oxygen sensor, main oxygen
sensor and engine & ECT ECU.
TR±65±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit Inspection
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3465 of 4087
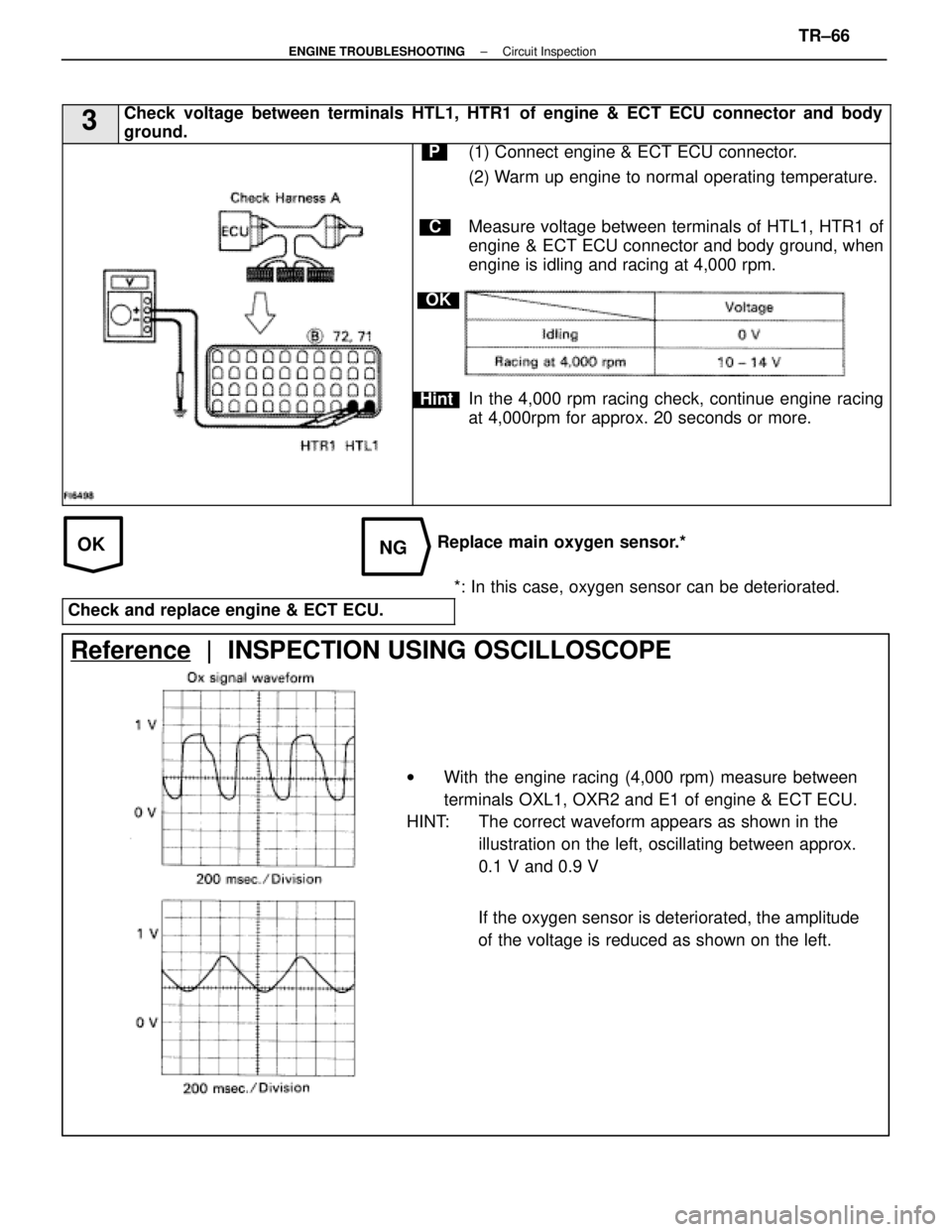
OKNG
3Check voltage between terminals HTL1, HTR1 of engine & ECT ECU connector and \
body
ground.
C
OK
Hint
P(1) Connect engine & ECT ECU connector.
(2) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
Measure voltage between terminals of HTL1, HTR1 of
engine & ECT ECU connector and body ground, when
engine is idling and racing at 4,000 rpm.
In the 4,000 rpm racing check, continue engine racing
at 4,000rpm for approx. 20 seconds or more.
Replace main oxygen sensor.**: In this case, oxygen sensor can be deteriorated.
Check and replace engine & ECT ECU.
Reference | INSPECTION USING OSCILLOSCOPE
w With the engine racing (4,000 rpm) measure between
terminals OXL1, OXR2 and E1 of engine & ECT ECU.
HINT: The correct waveform appears as shown in the
illustration on the left, oscillating between approx.
0.1 V and 0.9 V
If the oxygen sensor is deteriorated, the amplitude
of the voltage is reduced as shown on the left.
±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit InspectionTR±66
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3467 of 4087
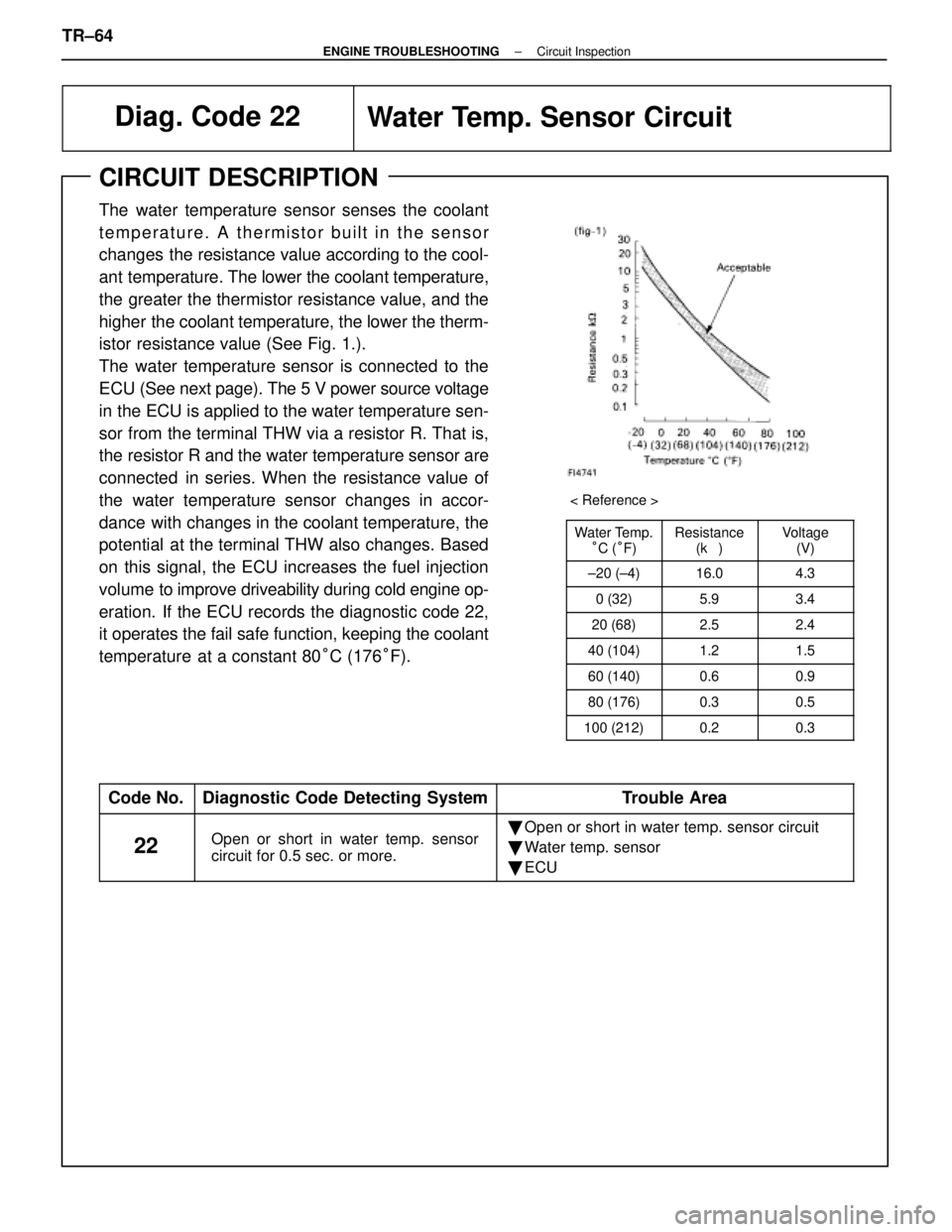
Diag. Code 22Water Temp. Sensor Circuit
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Water Temp.°C ( °F)Resistance
(k�)Voltage
(V)
±20 (±4)16.04.3
0 (32)5.93.4
20 (68)2.52.4
40 (104)1.21.5
60 (140)0.60.9
80 (176)0.30.5
100 (212)0.20.3
Code No.Diagnostic Code Detecting SystemTrouble Area
22Open or short in water temp. sensor
circuit for 0.5 sec. or more.� Open or short in water temp. sensor circuit
� Water temp. sensor
� ECU
< Reference >
TR±64±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit Inspection
The water temperature sensor senses the coolant
temperature. A thermistor built in the sensor
changes the resistance value according to the cool-
ant temperature. The lower the coolant temperature,
the greater the thermistor resistance value, and the
higher the coolant temperature, the lower the therm-
istor resistance value (See Fig. 1.).
The water temperature sensor is connected to the
ECU (See next page). The 5 V power source voltage
in the ECU is applied to the water temperature sen-
sor from the terminal THW via a resistor R. That is,
the resistor R and the water temperature sensor are
connected in series. When the resistance value of
the water temperature sensor changes in accor-
dance with changes in the coolant temperature, the
potential at the terminal THW also changes. Based
on this signal, the ECU increases the fuel injection
volume to improve driveability during cold engine op-
eration. If the ECU records the diagnostic code 22,
it operates the fail safe function, keeping the coolant
temperature at a constant 80 °C (176 °F).
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName