Page 3579 of 4087
OKNG
OKNG
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
1Check ISC value.
C
OK
P
P
OK
C
Disconnect ISC connector.
Measure resistance between terminals shown below.
Remove ISC Valve
(2) Connect the battery positive lead to terminals B1and B2, and the negative lead to terminals
S1±S2±S3±S4 in that order.
(2) Connect the battery positive lead to terminals B1 and B2, and the negative lead to terminals
S4±S3±S2±S1 in that order.
(2) The valve moves in the closing direction.
(2) The value moves in the opening direction.
Replace ISC valve.
2Check for open and short in harness and connector between EFI main relay and \
ISC valve, ISC
valve and engine & ECT ECU (See page IN±27).
Repair or replace harness or connector.
Proceed to next circuit inspection shown on ma-
trix chart (See page TR±35).
±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit InspectionTR±141
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3580 of 4087
Fuel Pressure Control VSV Circuit
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The ECU turns on a VSV (Vacuum Switching Valve)
to draw the air into the diaphragm chamber of the
pressure regulator if it detects that the temperature of
the coolant is too high during engine starting.
The air drawn into the chamber increases the fuel
pressure to prevent fuel vapor lock at high engine
temperature in order to help the engine start when it
is warm.
Fuel pressure control ends approx. 100 secs. after
the engine is started.
DIAGNOSTIC CHARTDIAGNOSTIC CHART
Check operation for fuel pressure control
VSV.Replace fuel pressure control VSV.
Repair or replace harness or
connector.
Proceed to next circuit inspection
shown on matrix chart (See page
TR±35).
Check for open and short in harness and
connector between main relay and ECU.
Check voltage of VSV power source.
Check and replace ECU.
WIRING DIAGRAM
TR±142±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit Inspection
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3581 of 4087
OKNG
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
1Check fuel pressure control VSV.
C
OK
P
OK
C
(2) Remove fuel pressure control VSV.
(2) Disconnect fuel pressure control VSV connector.
(2) Measure resistance between terminals.
(2) Measure resistance between each terminal and thebody.
1. Resistance: 30 ± 50 at 20C (68F)
2. Resistance: 1M or higher
Check operation of fuel pressure control VSV when bat-
tery voltage is applied to the terminals of fuel pressure
control VSV connector or not.
Battery voltage is applied:
The air from pipe E is flowing out through the air fil-
ter.
Battery voltage is not applied:
The air from pipe E is flowing out through pipe G.
Replace fuel pressure control VSV.
Go to step 2.
±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit InspectionTR±143
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3582 of 4087
NGOK
OKNG
2Check voltage between terminal FPU of engine & ECT ECU connector and body gro\
und.
C
OK
Hint
P(2) Connect the Check Harness A.(See page TR±30)
(2) Turn ignition switch on.
Measure voltage between terminal FPU of engine &
ECT ECU connector and body ground.
Voltage: 10 ± 14 V
Proceed to next circuit inspection shown on matrix chart
(See page TR±35).
3
Check for open and short in harness and connector between engine & ECT ECU an\
d VSV, VSV
and EFI main relay (See page IN±27).
Repair or replace harness or connector
Check and replace engine & ECT ECU.
TR±144±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit Inspection
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3584 of 4087
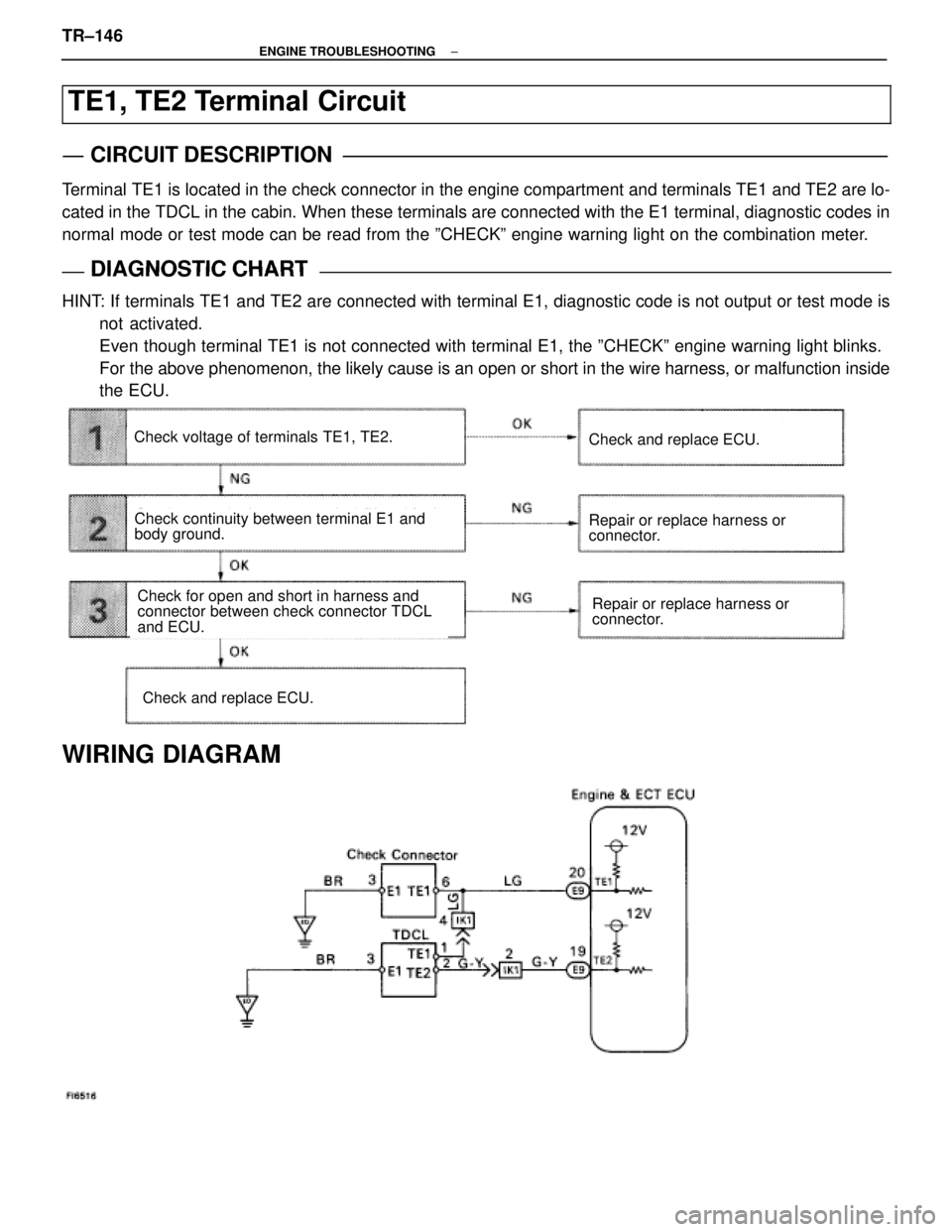
TE1, TE2 Terminal Circuit
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Terminal TE1 is located in the check connector in the engine compartment and terminals T\
E1 and TE2 are lo-
cated in the TDCL in the cabin. When these terminals are connected with \
the E1 terminal, diagnostic codes in
normal mode or test mode can be read from the ºCHECKº engine warning lig\
ht on the combination meter.
DIAGNOSTIC CHARTDIAGNOSTIC CHART
HINT: If terminals TE1 and TE2 are connected with terminal E1, diagnostic code is not output or test mode isnot activated.
Even though terminal TE1 is not connected with terminal E1, the ºCHEC\
Kº engine warning light blinks.
For the above phenomenon, the likely cause is an open or short in the wire \
harness, or malfunction inside
the ECU.
Check continuity between terminal E1 and
body ground.
Repair or replace harness or
connector.Check for open and short in harness and
connector between check connector TDCL
and ECU.
Check voltage of terminals TE1, TE2.
Check and replace ECU.
Repair or replace harness or
connector.
Check and replace ECU.
WIRING DIAGRAM
TR±146±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3585 of 4087
NGOK
OKNG
OKNG
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
1Check voltage between terminals TE1, TE2 and E1 of check connector, TDCL.
C
OK
PTurn ignition switch on.
Measure voltage between terminals TE1, TE2 and E1
of check connector, TDCL.
Voltage: 10 ± 14 V
Check and replace engine & ECT ECT.
2Check continuity between terminal E1 of check connector, TDCL and body ground.
Repair or replace harness or connector.
3
Check for open and short in harness and connector between engine & ECT ECU and che\
ck con-
nector, TDCL (See page IN±27).
Repair or replace harness or connector.
Check and replace engine & ECT ECU.
±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit InspectionTR±147
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3587 of 4087

HOW TO PROCEED WITH TROUBLESHOOTING
The Engine Control System broadly consists of the sensors, ECU and actuator\
s. The ECU receives signals from
various sensors, judges the operating conditions and determines the opti\
mum injection duration, timing, ignition
timing and idle speed.
In general, the Engine Control System is considered to be a very intricate\
system to troubleshoot. But, the fact
is that if you proceed to inspect the circuit one by one following the p\
rocedures directed in this manual, trouble-
shooting of this system is not complex.
This section explains the most ideal method of troubleshooting and tells how\
to carry out the necessary repairs.
[1] CUSTOMER PROBLEM ANALYSISUsing the customer problem analysis check sheet for reference, ask the c\
ustomer in as much details as
possible about the problem.
[2] CHECK AND CLEAR DIAGNOSTIC CODE (PRECHECK) Before confirming the problem symptom, first check the diagnostic code and mak\
e a note of any malfunc-
tion code which is output, then clear the code.
HINT: Output of the malfunction code indicates that there is a malfunction in\
the circuit indicated. However,
it does not indicate whether the malfunction is still occurring or occur\
red in the past and returned to normal.
In order to determine this, the problem symptoms should be confirmed in 4 \
first and the diagnostic code
be rechecked in [6].
Accordingly, if troubleshooting is begun based on the malfunction code only in diag\
nostic code check in
[2] , it could result in a misdiagnosis, leading to troubleshooting of circuits which are normal \
and making
it more difficult to locate the cause of the problem.
[3] SETTING THE TEST MODE DIAGNOSIS, [4] PROBLEM SYMPTOM CONFIRMATION, [5] SYMPTOM SIMULATION
In order to find out the trouble more quickly, set the diagnosis check in test mode and with higher sensing
ability of the ECU, confirm the problem symptoms. If the trouble does not reappear, use the symptom simu-
lation method to make sure the trouble is reproduced.
[6] DIAGNOSTIC CODE CHECK IN TEST MODE Check the diagnostic code in test mode. If the malfunction code is output, pr\
oceed to ºstep [8] Diagnostic
Code Chartº. If the normal code is output, proceed to ºstep [7] Basic Inspectionº.
[7] BASIC INSPECTION Carry out basic inspection such as the spark check and fuel pressure che\
ck, etc.
[8] DIAGNOSTIC CODE CHART If the malfunction code is displayed, proceed to inspect the circuit ind\
icated by the chart for each code.
[9] MATRIX CHART OF PROBLEM SYMPTOMS If the normal code is displayed in the diagnosis in test mode, perform tro\
ubleshooting according to the in-
spection order in the Matrix Chart of Problem Symptoms.
[10] PARTS INSPECTION When the Matrix Chart of Problem Symptoms instructs to check the parts, proc\
eed to parts inspection sec-
tion included in this manual.
[11] CIRCUIT INSPECTION Determine if the malfunction is the sensor, actuator, wire harness, connector or the ECU.
TR±2
±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING How to Proceed with Troubleshooting
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3588 of 4087
[12] CHECK FOR MOMENTARY INTERRUPTIONBy performing the check for momentary interruption, the place where moment\
ary interruptions or momen-
tary shorts are occurring due to poor contacts can be isolated.
[13] ADJUSTMENT, REPAIR After the cause of the problem is located, perform adjustment or repairs\
by following the inspection and
replacement procedures in this manual.
[14] CONFIRMATION TEST After completing adjustment or repairs, confirm not only that the malfunction\
is eliminated, but also conduct
a test drive, etc., to make sure the entire Engine Control System is oper\
ating normally.
±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING How to Proceed with TroubleshootingTR±3
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName