Page 1784 of 4087
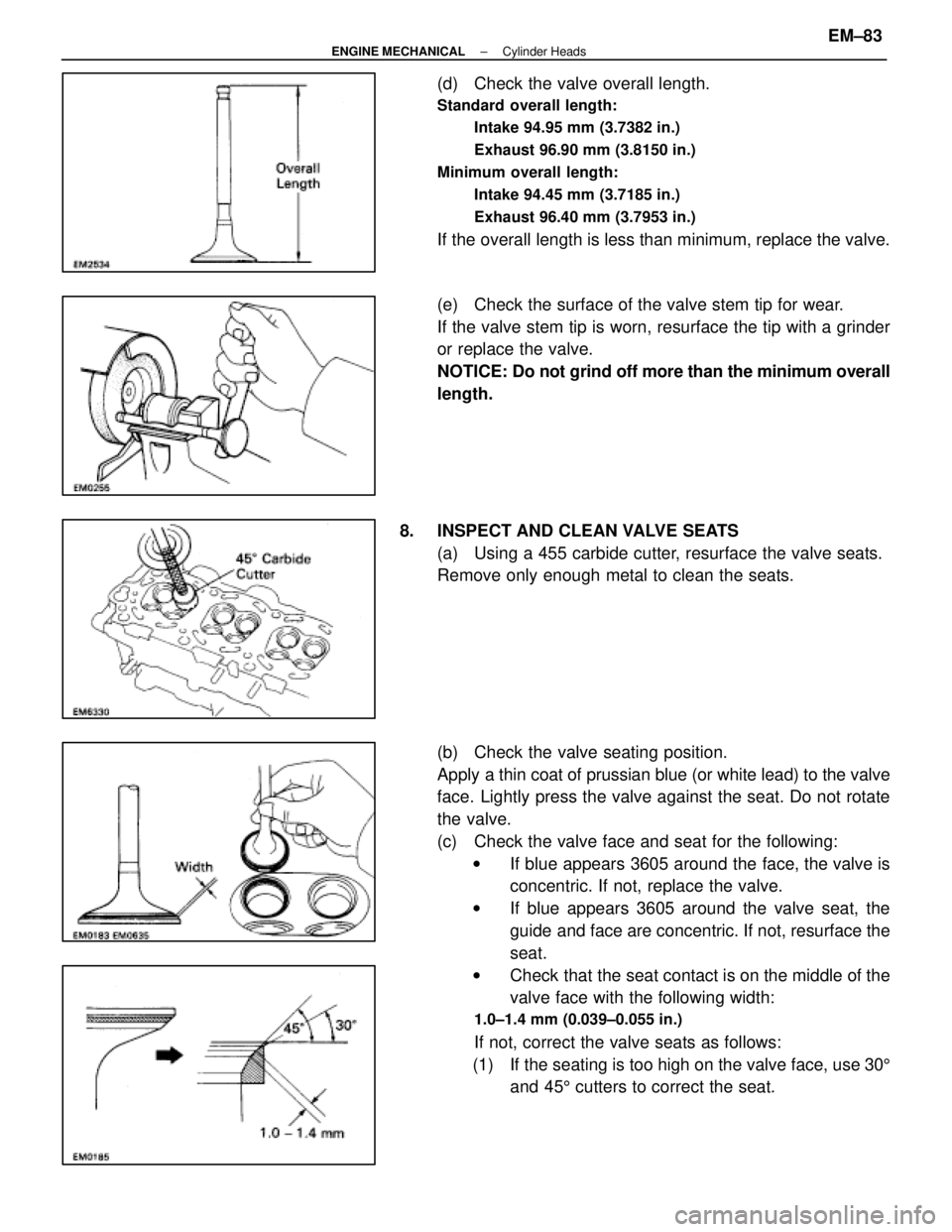
(d) Check the valve overall length.
Standard overall length:Intake 94.95 mm (3.7382 in.)
Exhaust 96.90 mm (3.8150 in.)
Minimum overall length: Intake 94.45 mm (3.7185 in.)
Exhaust 96.40 mm (3.7953 in.)
If the overall length is less than minimum, replace the valve.
(e) Check the surface of the valve stem tip for wear.
If the valve stem tip is worn, resurface the tip with a grinder
or replace the valve.
NOTICE: Do not grind off more than the minimum overall
length.
8. INSPECT AND CLEAN VALVE SEATS (a) Using a 455 carbide cutter, resurface the valve seats.
Remove only enough metal to clean the seats.
(b) Check the valve seating position.
Apply a thin coat of prussian blue (or white lead) to the valve
face. Lightly press the valve against the seat. Do not rotate
the valve.
(c) Check the valve face and seat for the following:w If blue appears 3605 around the face, the valve is
concentric. If not, replace the valve.
w If blue appears 3605 around the valve seat, the
guide and face are concentric. If not, resurface the
seat.
w Check that the seat contact is on the middle of the
valve face with the following width:
1.0±1.4 mm (0.039±0.055 in.)
If not, correct the valve seats as follows:
(1) If the seating is too high on the valve face, use 30 5
and 45 5 cutters to correct the seat.
±
ENGINE MECHANICAL Cylinder HeadsEM±83
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 1791 of 4087
2. INSTALL VALVES(a) Using SST, push in a new oil seal.
SST 09201±41020
(b) Install the following parts:(1) Valve
(2) Spring seat
(3) Valve spring
(4) Spring retainer
(c) Using SST, compress the valve spring and place the two
keepers around the valve stem.
SST 09202±70010
(d) Using a plastic±faced hammer, lightly tap the valve stem
tip to assure proper fit.
3. INSTALL VALVE LIFTERS AND SHIMS Check the valve lifter rotates smoothly by hand.
EM±90
±
ENGINE MECHANICAL Cylinder Heads
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 1794 of 4087
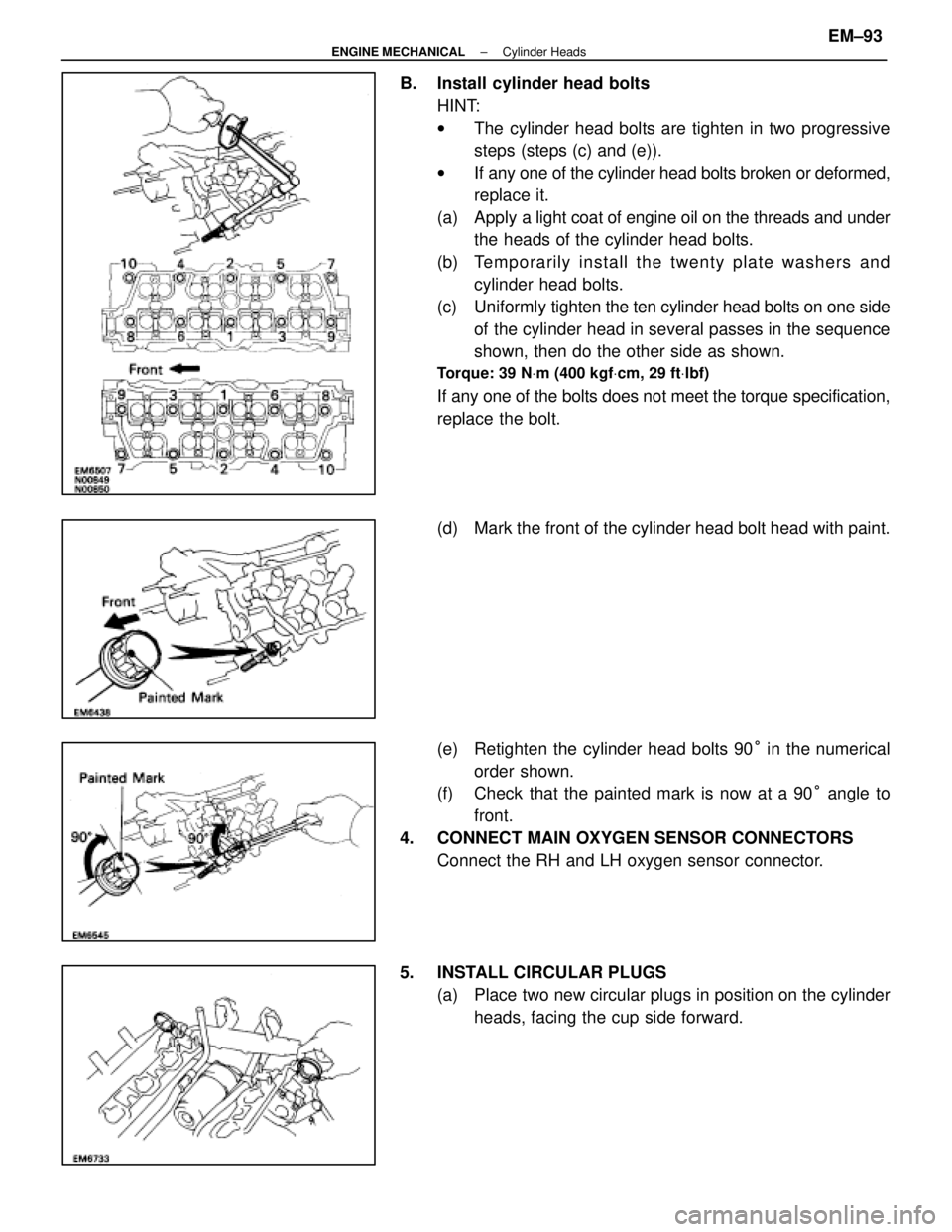
B. Install cylinder head boltsHINT:
wThe cylinder head bolts are tighten in two progressive
steps (steps (c) and (e)).
w If any one of the cylinder head bolts broken or deformed,
replace it.
(a) Apply a light coat of engine oil on the threads and under
the heads of the cylinder head bolts.
(b) Te mp o ra rily in sta ll th e twe n ty pla te wa sh e rs an d cylinder head bolts.
(c) Uniformly tighten the ten cylinder head bolts on one side
of the cylinder head in several passes in the sequence
shown, then do the other side as shown.
Torque: 39 N Vm (400 kgf Vcm, 29 ft Vlbf)
If any one of the bolts does not meet the torque specification,
replace the bolt.
(d) Mark the front of the cylinder head bolt head with paint.
(e) Retighten the cylinder head bolts 90 ° in the numerical
order shown.
(f) Check that the painted mark is now at a 90 ° angle to
front.
4. CONNECT MAIN OXYGEN SENSOR CONNECTORS Connect the RH and LH oxygen sensor connector.
5. INSTALL CIRCULAR PLUGS (a) Place two new circular plugs in position on the cylinderheads, facing the cup side forward.
±
ENGINE MECHANICAL Cylinder HeadsEM±93
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 1798 of 4087
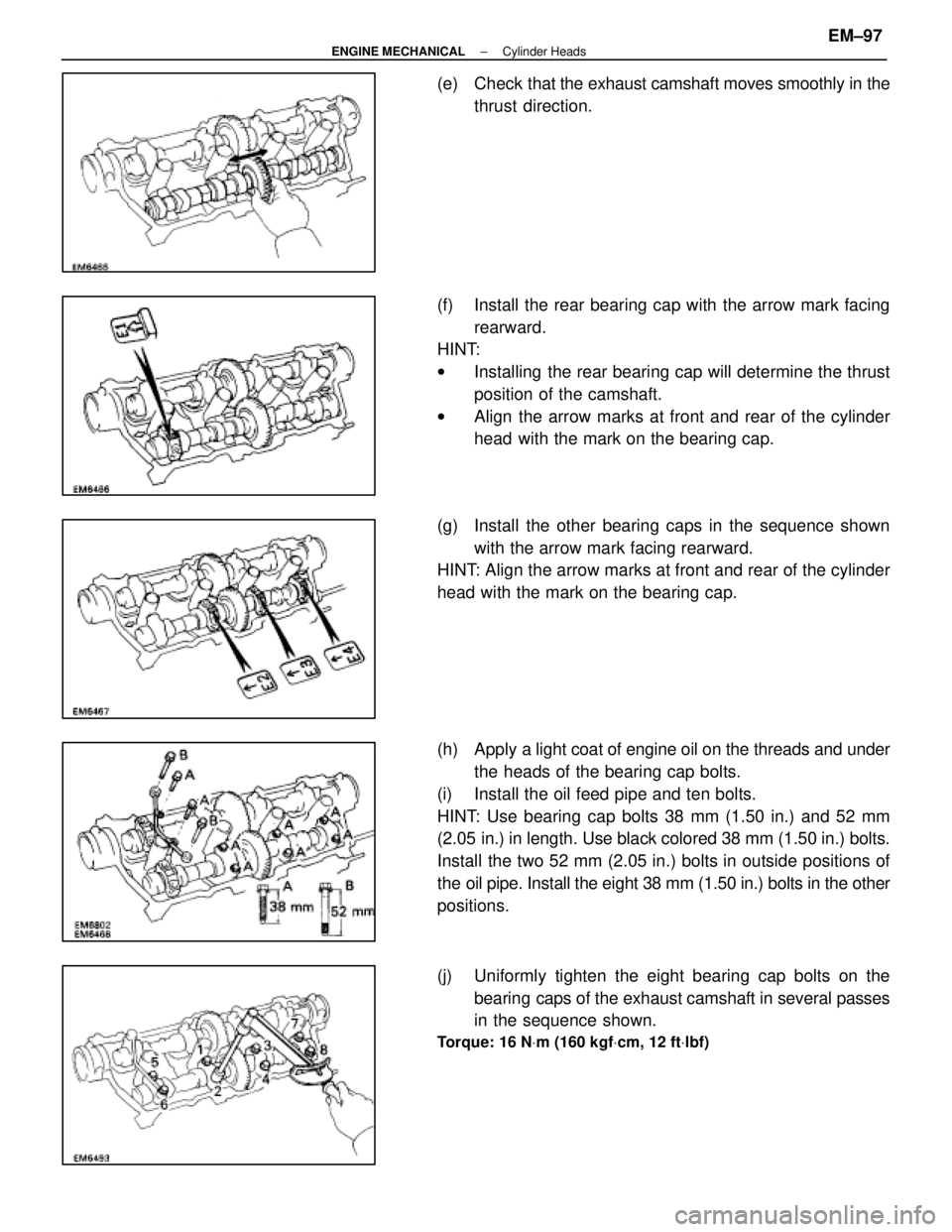
(e) Check that the exhaust camshaft moves smoothly in the
thrust direction.
(f) Install the rear bearing cap with the arrow mark facing rearward.
HINT:
w Installing the rear bearing cap will determine the thrust
position of the camshaft.
w Align the arrow marks at front and rear of the cylinder
head with the mark on the bearing cap.
(g) Install the other bearing caps in the sequence shown with the arrow mark facing rearward.
HINT: Align the arrow marks at front and rear of the cylinder
head with the mark on the bearing cap.
(h) Apply a light coat of engine oil on the threads and under
the heads of the bearing cap bolts.
(i) Install the oil feed pipe and ten bolts.
HINT: Use bearing cap bolts 38 mm (1.50 in.) and 52 mm
(2.05 in.) in length. Use black colored 38 mm (1.50 in.) bolts.
Install the two 52 mm (2.05 in.) bolts in outside positions of
the oil pipe. Install the eight 38 mm (1.50 in.) bolts in the other
positions.
(j) Uniformly tighten the eight bearing cap bolts on the bearing caps of the exhaust camshaft in several passes
in the sequence shown.
Torque: 16 N Vm (160 kgf Vcm, 12 ft Vlbf)
±
ENGINE MECHANICAL Cylinder HeadsEM±97
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 1801 of 4087
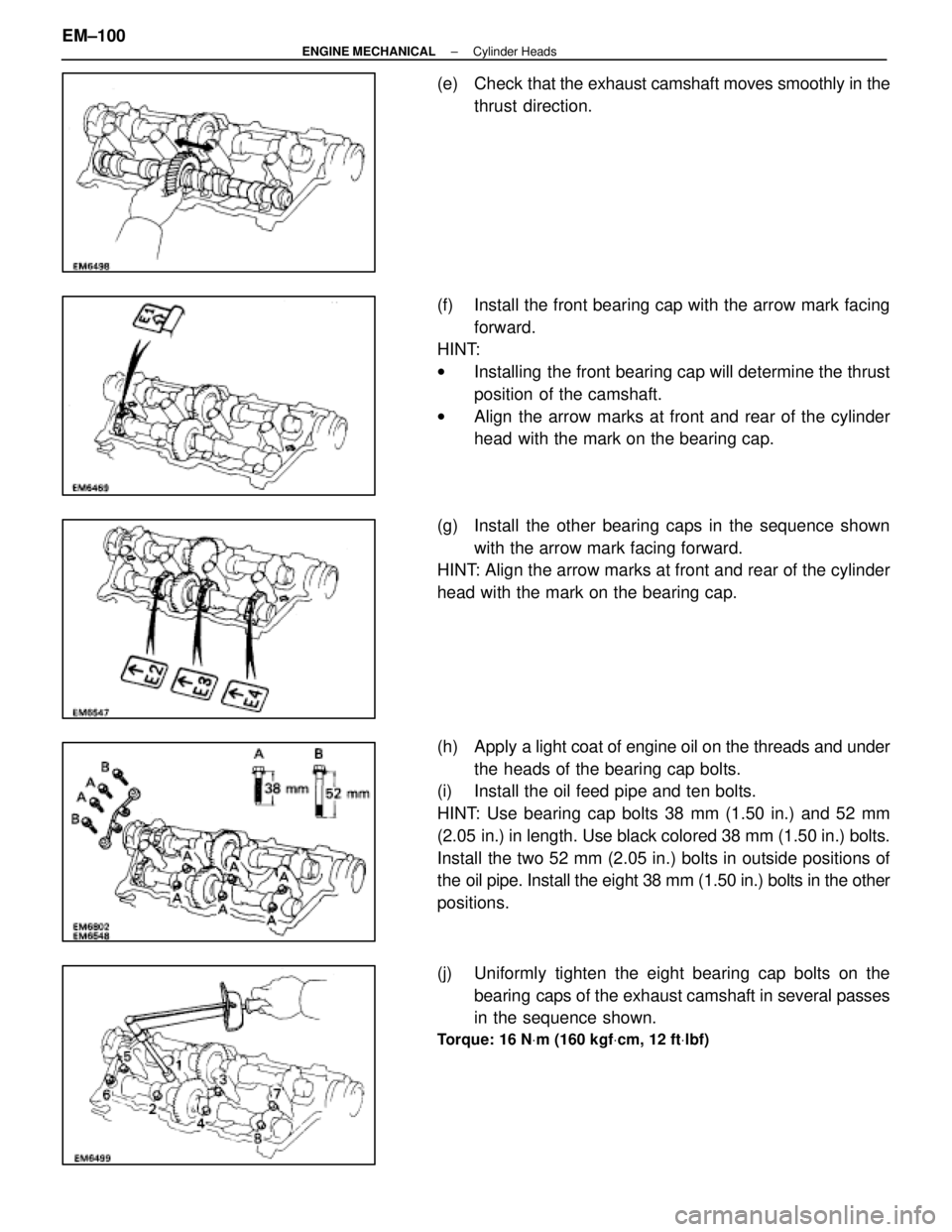
(e) Check that the exhaust camshaft moves smoothly in the
thrust direction.
(f) Install the front bearing cap with the arrow mark facing forward.
HINT:
w Installing the front bearing cap will determine the thrust
position of the camshaft.
w Align the arrow marks at front and rear of the cylinder
head with the mark on the bearing cap.
(g) Install the other bearing caps in the sequence shown with the arrow mark facing forward.
HINT: Align the arrow marks at front and rear of the cylinder
head with the mark on the bearing cap.
(h) Apply a light coat of engine oil on the threads and under
the heads of the bearing cap bolts.
(i) Install the oil feed pipe and ten bolts.
HINT: Use bearing cap bolts 38 mm (1.50 in.) and 52 mm
(2.05 in.) in length. Use black colored 38 mm (1.50 in.) bolts.
Install the two 52 mm (2.05 in.) bolts in outside positions of
the oil pipe. Install the eight 38 mm (1.50 in.) bolts in the other
positions.
(j) Uniformly tighten the eight bearing cap bolts on the
bearing caps of the exhaust camshaft in several passes
in the sequence shown.
Torque: 16 N Vm (160 kgf Vcm, 12 ft Vlbf)
EM±100±
ENGINE MECHANICAL Cylinder Heads
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 1854 of 4087
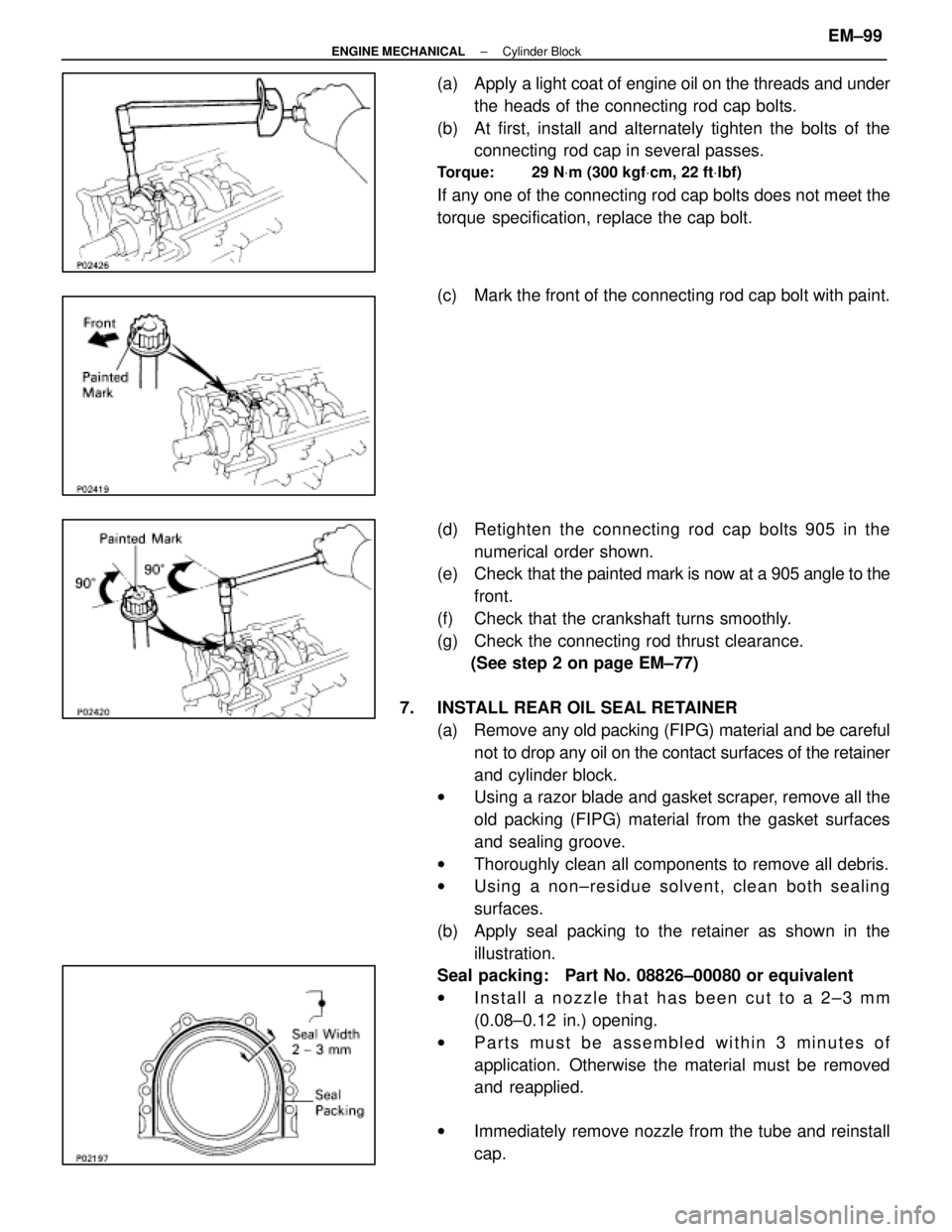
(a) Apply a light coat of engine oil on the threads and under
the heads of the connecting rod cap bolts.
(b) At first, install and alternately tighten the bolts of the connecting rod cap in several passes.
Torque: 29 N Vm (300 kgf Vcm, 22 ft Vlbf)
If any one of the connecting rod cap bolts does not meet the
torque specification, replace the cap bolt.
(c) Mark the front of the connecting rod cap bolt with paint.
(d) Retighten the connecting rod cap bolts 905 in the
numerical order shown.
(e) Check that the painted mark is now at a 905 angle to the
front.
(f) Check that the crankshaft turns smoothly.
(g) Check the connecting rod thrust clearance. (See step 2 on page EM±77)
7. INSTALL REAR OIL SEAL RETAINER (a) Remove any old packing (FIPG) material and be carefulnot to drop any oil on the contact surfaces of the retainer
and cylinder block.
w Using a razor blade and gasket scraper, remove all the
old packing (FIPG) material from the gasket surfaces
and sealing groove.
w Thoroughly clean all components to remove all debris.
w Using a non±residue solvent, clean both sealing
surfaces.
(b) Apply seal packing to the retainer as shown in the illustration.
Seal packing: Part No. 08826±00080 or equivalent
w Install a nozzle that has been cut to a 2±3 mm
(0.08±0.12 in.) opening.
w Parts must be assembled within 3 minutes of
application. Otherwise the material must be removed
and reapplied.
w Immediately remove nozzle from the tube and reinstall
cap.
±
ENGINE MECHANICAL Cylinder BlockEM±99
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 1983 of 4087
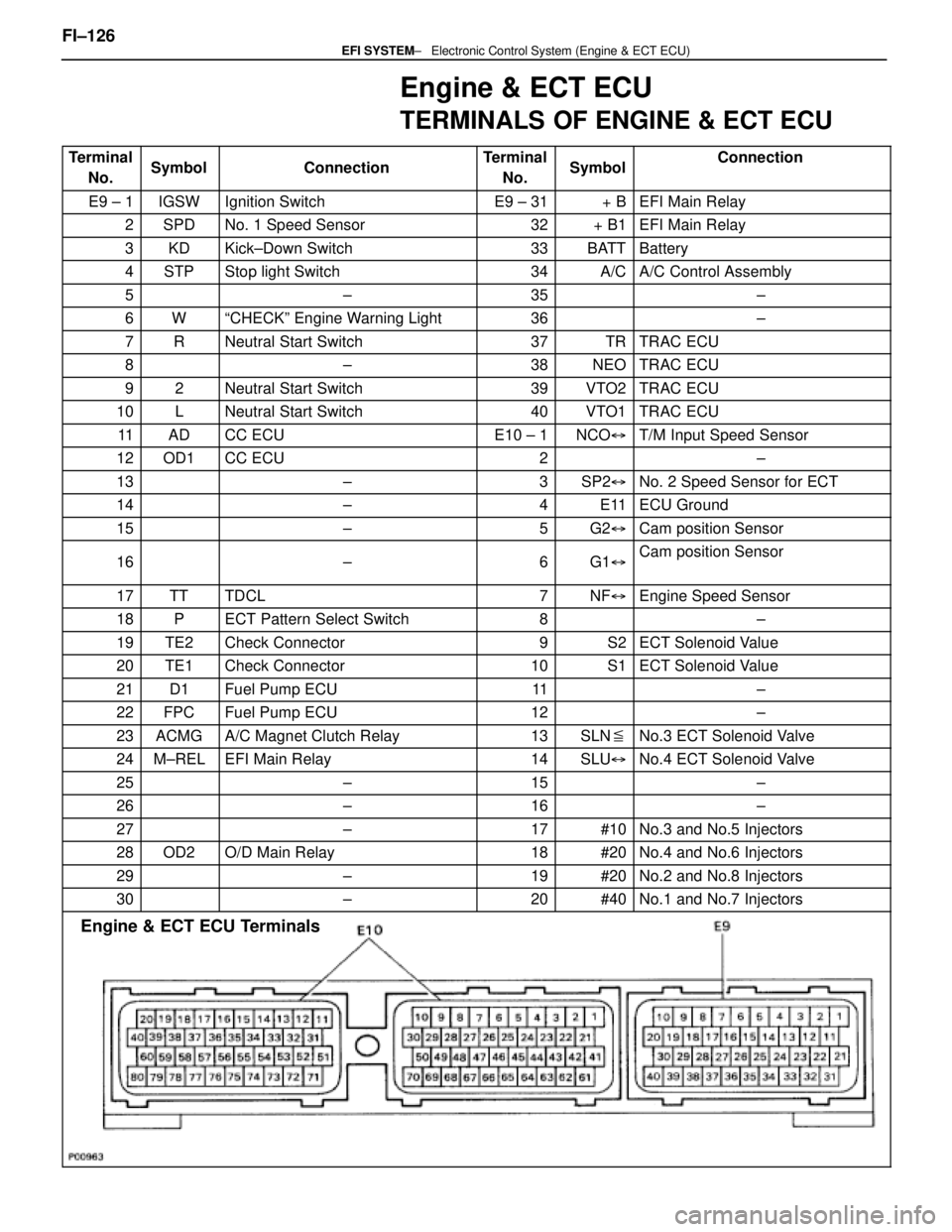
Engine & ECT ECU
TERMINALS OF ENGINE & ECT ECU
TerminalNo.SymbolConnectionTerminalNo.SymbolConnection
E9 ± 1IGSWIgnition SwitchE9 ± 31+ BEFI Main Relay
2SPDNo. 1 Speed Sensor32+ B1EFI Main Relay
3KDKick±Down Switch33BATTBattery
4STPStop light Switch34A/CA/C Control Assembly
5±35±
6WªCHECKº Engine Warning Light36±
7RNeutral Start Switch37TRTRAC ECU
8±38NEOTRAC ECU
92Neutral Start Switch39VTO2TRAC ECU
10LNeutral Start Switch40VTO1TRAC ECU
11ADCC ECUE10 ± 1NCO �T/M Input Speed Sensor
12OD1CC ECU2±
13±3SP2�No. 2 Speed Sensor for ECT
14±4E11ECU Ground
15±5G2�Cam position Sensor
16±6G1�Cam position Sensor
17TTTDCL7NF�Engine Speed Sensor
18PECT Pattern Select Switch8±
19TE2Check Connector9S2ECT Solenoid Value
20TE1Check Connector10S1ECT Solenoid Value
21D1Fuel Pump ECU11±
22FPCFuel Pump ECU12±
23ACMGA/C Magnet Clutch Relay13SLN �No.3 ECT Solenoid Valve
24M±RELEFI Main Relay14SLU�No.4 ECT Solenoid Valve
25±15±
26±16±
27±17#10No.3 and No.5 Injectors
28OD2O/D Main Relay18#20No.4 and No.6 Injectors
29±19#20No.2 and No.8 Injectors
30±20#40No.1 and No.7 Injectors
Engine & ECT ECU Terminals
FI±126 ± Electronic Control \
System (Engine & ECT ECU)EFI SYSTEM
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 2003 of 4087

The EFI system is composed of three basic sub±systems: Fuel, Air Induction and Elect\
ronic Control
Systems.
FUEL SYSTEM
An electric pump fuel pressure supplies sufficient fuel, under a constant pressure, to the EFI injectors. In
accordance with signals from the ECU (Electronic Control Unit), these \
injectors inject the quantity of fuel most
appropriate for the engine condition into the intake manifold.
AIR INDUCTION SYSTEM
The air induction system provides sufficient air for engine operation.
ELECTRONIC CONTROL SYSTEM
The 1UZ±FE engine (ECU±formerly EFI computer) with a microcomputer \
centrally controls the EFI, ESA,
ISC and Diagnosis system, etc. The ECU controls the following functions:
1. Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI)
The ECU receives signals from various sensors indicating changing engine op\
eration conditions such as:Intake air volume
Intake air temperature
Coolant temperature
Engine rpm
Acceleration/deceleration
Exhaust oxygen content etc.
The signals are utilized by the ECU to determine the injection duration nec\
essary for an optimum air±fuel
ratio.
2. Electronic Spark Advance (ESA) The ECU is programmed with data for optimum ignition timing under any and all opera\
ting conditions. Using
data provided by sensors which monitor various engine functions (rpm, coola\
nt temperature, etc.), the
Electronic Control Unit (ECU) triggers the spark at precisely right instant. (S\
ee IG section)
3. Idle Speed Control (ISC) The ECU is programmed with idle speed data for various engine conditions (\
coolant temperature, air condi-
tioner ON/OFF, etc.).
The air volume flowing through the throttle valve by±pass passage is adj\
usted according to the signal from
each sensor and the idle speed is kept at the set value.
4. Diagnosis Function When the ECU detects any malfunctions or abnormalities in the sensor network\
, it lights the ºCHECKº en-
gine warning light in the combination meter. At the same time, the trouble is identified and a diagnostic code
is recorded by the ECU. The diagnostic code can be read by the number of\
blinks of the ºCHECKº engine
warning light when terminals TE1 and E1 are connected. The diagnostic co\
des are refer to the later page.
(See TR section)
5. Self±Correction Function If any sensor malfunctions, an average value recorded in the back±up ci\
rcuit is substituted to make driving
possible.
If danger is predicted, the engine is stopped and the ºCHECKº engine\
warning light will light up.
6. Fail±Safe Function Even if an abnormality occurs in the ECU, the back±up circuit uses a specifie\
d fuel injection and ignition
timing to provide vehicle driveability, and also lightsup the ºCHECKº engine warning light.
FI±4
EFI SYSTEM
± Description
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName