Page 1256 of 4087
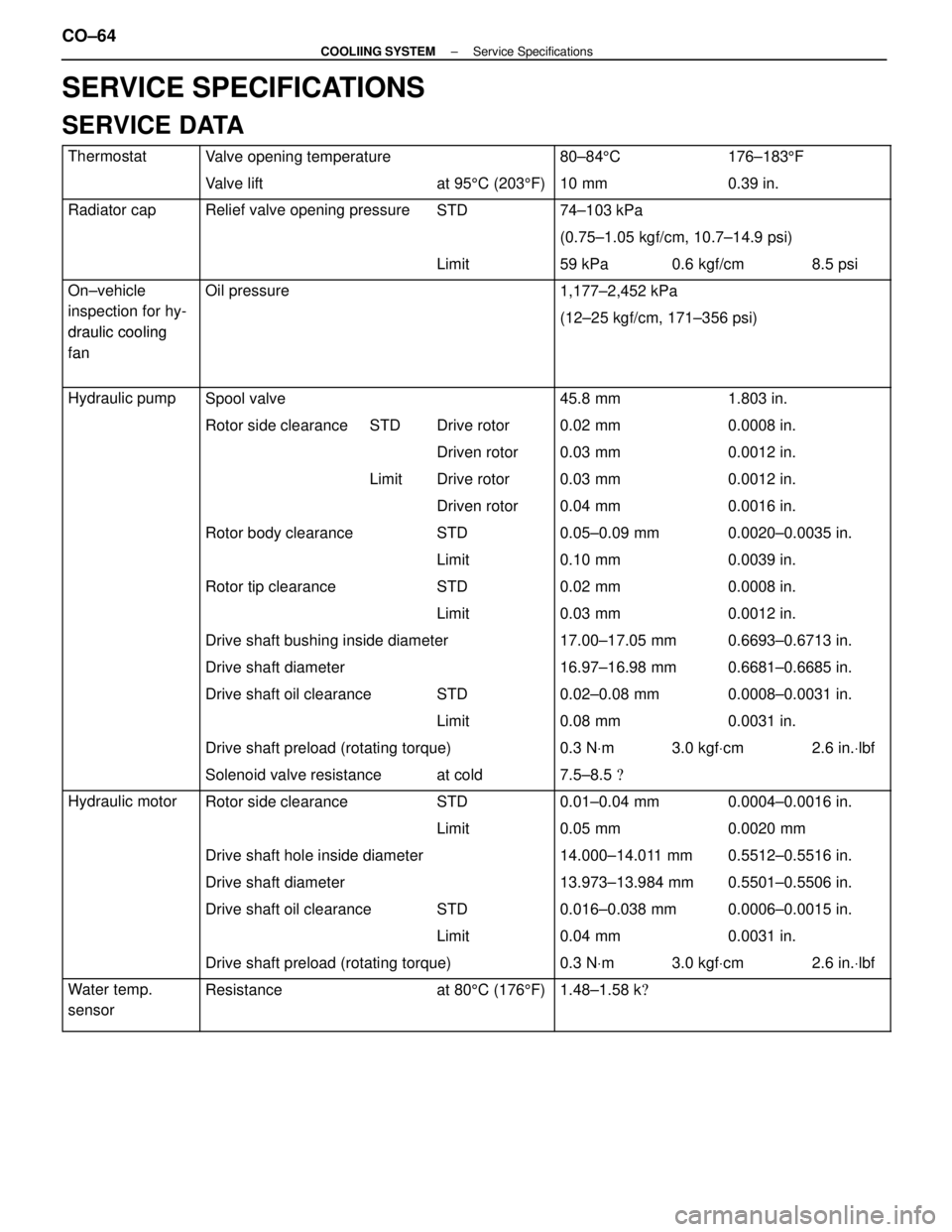
SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS
SERVICE DATA
ThermostatValve opening temperature80±845C176±183 5F
Valve liftat 95 5C (203 5F) 10 mm0.39 in.
Radiator capRelief valve opening pressureSTD74±103 kPa
(0.75±1.05 kgf/cm, 10.7±14.9 psi)
Limit 59 kPa 0.6 kgf/cm 8.5 psi
On±vehicle
itifh
Oil pressure1,177±2,452 kPa
inspection for hy-
draulic cooling(12±25 kgf/cm, 171±356 psi)draulic cooling
fan
fan
Hydraulic pumpSpool valve45.8 mm1.803 in.
Rotor side clearanceSTD Drive rotor 0.02 mm0.0008 in.
Driven rotor 0.03 mm0.0012 in.
Limit Drive rotor 0.03 mm0.0012 in.
Driven rotor 0.04 mm0.0016 in.
Rotor body clearanceSTD 0.05±0.09 mm0.0020±0.0035 in.
Limit 0.10 mm0.0039 in.
Rotor tip clearanceSTD 0.02 mm0.0008 in.
Limit 0.03 mm0.0012 in.
Drive shaft bushing inside diameter17.00±17.05 mm0.6693±0.6713 in.
Drive shaft diameter16.97±16.98 mm0.6681±0.6685 in.
Drive shaft oil clearanceSTD 0.02±0.08 mm0.0008±0.0031 in.
Limit 0.08 mm0.0031 in.
Drive shaft preload (rotating torque)0.3 N Vm 3.0 kgf Vcm 2.6 in. Vlbf
Solenoid valve resistanceat cold 7.5±8.5 �
Hydraulic motorRotor side clearanceSTD0.01±0.04 mm0.0004±0.0016 in.
Limit 0.05 mm0.0020 mm
Drive shaft hole inside diameter14.000±14.011 mm0.5512±0.5516 in.
Drive shaft diameter13.973±13.984 mm0.5501±0.5506 in.
Drive shaft oil clearanceSTD 0.016±0.038 mm0.0006±0.0015 in.
Limit 0.04 mm0.0031 in.
Drive shaft preload (rotating torque)0.3 NVm 3.0 kgf Vcm 2.6 in. Vlbf
Water temp. Resistanceat 80 5C (176 5F)1.48±1.58 k �
sensor
CO±64±
COOLIING SYSTEM Service Specifications
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 1259 of 4087
DESCRIPTION
This engine utilizes a pressurized forced circulation cooling system which i\
ncludes a hermostat equipped
with a by±pass valve mounted on the inlet side. The cooling system is composed of the water jacket (inside the cylinder bl\
ock and cylinderhead), radiator,
water pump, thermostat, cooling fan, hoses and other components.
OPERATION
CO±2±
COOLIING SYSTEM Description
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 1260 of 4087
DESCRIPTION
This engine utilizes a pressurized forced circulation cooling system whi\
ch includes a hermostat equipped
with a by±pass valve mounted on the inlet side. The cooling system is composed of the water jacket (inside the cylinder bl\
ock and cylinderhead), radiator,
water pump, thermostat, cooling fan, hoses and other components.
OPERATION
CO±2±
COOLIING SYSTEM Description
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 1261 of 4087

Coolant which is heated in the water jacket is pumped to the radiator, through which a cooling fan blows
air to cool the coolant as it passes through. Coolant which has been coo\
led is then sent back to the engine by
the water pump, where it cools the engine. The water jacket is a network of channels in the shell of the cylinder bloc\
k and cylinderhead through which
coolant passes. It is designed to provide adequate cooling through the cylinders and combus\
tion chambers
which become heated during engine operation.
RADIATOR The radiator performs the function of cooling the coolant which has pass\
ed through the waterjacket and
become hot, and it is mounted in the front of the vehicle. The radiator consis\
ts of an upper tank and lower tank,
and a core which connects the two tanks. The upper tank contains the inlet \
for coolant from the water jacket
and the filler inlet. It also has a hose attached through which excess cool\
ant or steam can flow. The lower tank
contains the outlet for coolant and drain plug. The core contains many t\
ubes through which coolant flows from
the upper tank to the lower tank as well as cooling fins which radiate heat\
away from the coolant in the tubes.
The air sucked through the radiator by the cooling fan, as well as the wind generated by the ve\
hicle's travel,
passes through the radiator, cooling the coolant. Models with automatic transmission include an aut\
omatic
transmission fluid cooler built into the lower tank of the radiator. A cooling fan is mounted behind radiator to assist
the flow of air through the radiator. When the coolant temperature is low, the fan operates slowly to help the warm
up, and when the coolant temperature becomes high, the fan speed is increas\
ed to provide the air flow required
for cooling.
RADIATOR CAP (on Reservoir Tank)
The radiator cap is a pressure type cap which seals the radiator, resulting in pressurization of the radiator
as the coolant expands. The pressurization prevents the coolant from boi\
ling even when the coolant tempera-
ture exceeds 100 5C (212 5F). A relief valve (pressurization valve) and a vacuum valve (negati\
ve pressure valve)
are built into the radiator cap. The relief valve opens and lets steam esca\
pe through the overflow pipe when
the pressure generated inside the cooling system exceeds the limit (coolant temperature: 110±120 5C
(230±248 5F) pressure; 29.4±98.1 kPa (0.3±1.0 kgf/cm2, 4.3±14.2 psi)). The vacuum v\
alve opens to alleviate
the vacuum which develops in the coolant system after the engine is stopped\
and the coolant temperature
drops.
RESERVOIR TANK The purpose of the reservoir tank is to catch coolant overflows created by \
volumetrix expansion when the
coolant temperature increases. The cap of the reservoir tank is a pressure type\
which prevents deterioration
of the LLC (Long Life Coolant) caused by contact with atmospheric air, increases vaporization performance and
reduces loss of the coolant volume.
WATER PUMP The water pump is mounted on the front of the cylinder block and driven by t\
he reverse side of the timing
belt.
THERMOSTAT The thermostat has a wax type by±pass valve and is mounted in the wat\
er inlet housing. The thermostat
begins to open at the temperature of 80 5C (180 5F). When the coolant temperature is low, the valve closes to
prevent coolant flow to the radiator, thus permitting the engine to warm up rapidly. When the by±pass valve
opens the by±pass circuit, the engine coolant continues to circulate \
inside the engine, quickly and uniformly
warming up to the appropriate temperature. When the coolant temperature is high\
, the valve opens and coolant
flows to the radiator where it is cooled. When the wax inside the thermostat \
is heated, it expands and thus
creates pressure which overpowers the force of the spring which keeps the valve\
closed. When the wax cools,
its contraction causes the force of the spring to take effect once more, closing the valve.
ELECTRONICALLY CONTROLLED HYDRAULIC COOLING FAN (See page CO±22)
±
COOLIING SYSTEM DescriptionCO±3
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 1271 of 4087
THERMOSTAT
HINT: Removing the thermostat would decrease the cooling
efficiency. Do not remove the thermostat, even if it tends to
overheat.
COMPONENTS
REMOVAL OF THERMOSTAT
1. DRAIN ENGINE COOLANT (See page CO±5)
2. REMOVE THERMOSTAT (a) Remove the two nuts holding the water inlet to the water
pump, and disconnect the water inlet from the water
pump.
(b) Remove the thermostat.
(c) Remove the gasket from the thermostat.
CO±10
±
COOLING SYSTEM Thermostat
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 1272 of 4087
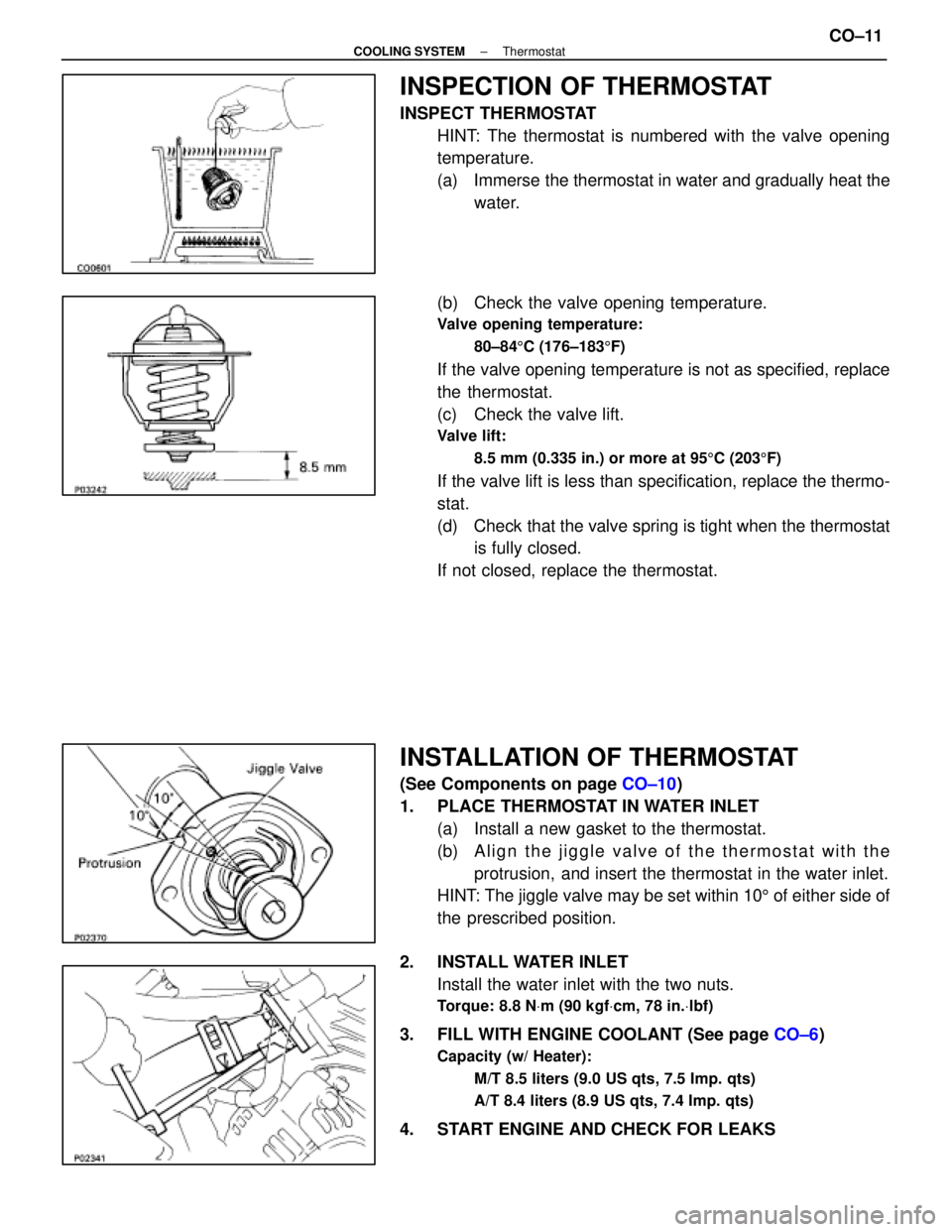
INSPECTION OF THERMOSTAT
INSPECT THERMOSTATHINT: The thermostat is numbered with the valve opening
temperature.
(a) Immerse the thermostat in water and gradually heat thewater.
(b) Check the valve opening temperature.
Valve opening temperature: 80±84 5C (176±183 5F)
If the valve opening temperature is not as specified, replace
the thermostat.
(c) Check the valve lift.
Valve lift:
8.5 mm (0.335 in.) or more at 95 5C (203 5F)
If the valve lift is less than specification, replace the thermo-
stat.
(d) Check that the valve spring is tight when the thermostat
is fully closed.
If not closed, replace the thermostat.
INSTALLATION OF THERMOSTAT
(See Components on page CO±10)
1. PLACE THERMOSTAT IN WATER INLET (a) Install a new gasket to the thermostat.
(b) A l i g n t h e j i g g l e v a l v e o f t h e t h e r m o s t a t w i t h t h eprotrusion, and insert the thermostat in the water inlet.
HINT: The jiggle valve may be set within 10 5 of either side of
the prescribed position.
2. INSTALL WATER INLET Install the water inlet with the two nuts.
Torque: 8.8 N Vm (90 kgf Vcm, 78 in. Vlbf)
3. FILL WITH ENGINE COOLANT (See page CO±6)
Capacity (w/ Heater):
M/T 8.5 liters (9.0 US qts, 7.5 Imp. qts)
A/T 8.4 liters (8.9 US qts, 7.4 Imp. qts)
4. START ENGINE AND CHECK FOR LEAKS
±
COOLING SYSTEM ThermostatCO±11
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 1273 of 4087
THERMOSTAT
HINT: Removal of the thermostat would have an adverse ef-
fect, causing a lowering of cooling efficiency. Do not remove
the thermostat, even if the tends to overheat.
COMPONENTS FOR REMOVAL AND
INSTALLATION
REMOVAL OF THERMOSTAT
1. DRAIN ENGINE COOLANT (See page CO±6)
2. REMOVE THERMOSTAT (a) Remove the two nuts holding the water inlet to the inlethousing, and disconnect the water inlet from the inlet
housing.
(b) Remove the thermostat.
(c) Remove the gasket from the thermostat.
CO±12
±
COOLIING SYSTEM Thermostat
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 1274 of 4087
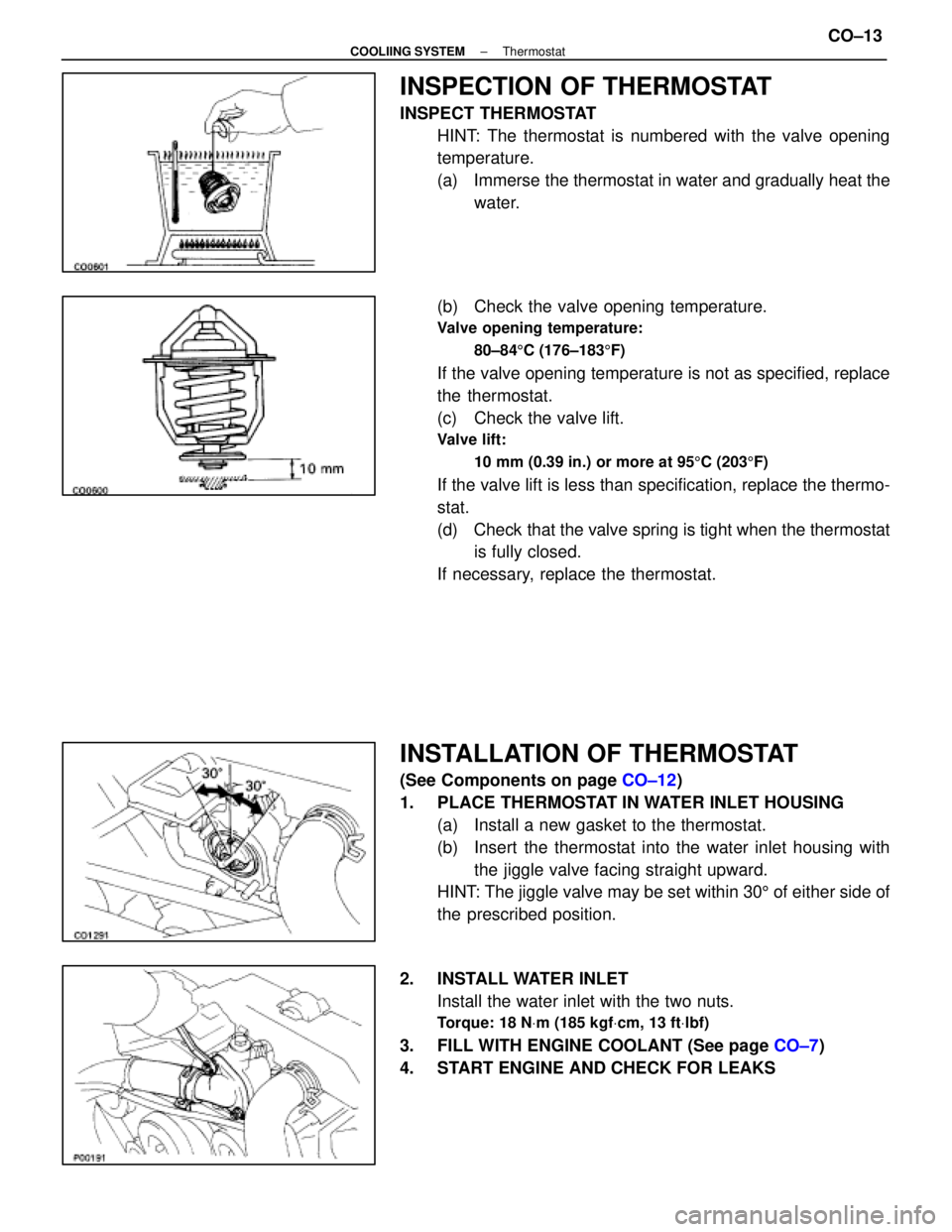
INSPECTION OF THERMOSTAT
INSPECT THERMOSTATHINT: The thermostat is numbered with the valve opening
temperature.
(a) Immerse the thermostat in water and gradually heat thewater.
(b) Check the valve opening temperature.
Valve opening temperature: 80±84 5C (176±183 5F)
If the valve opening temperature is not as specified, replace
the thermostat.
(c) Check the valve lift.
Valve lift:
10 mm (0.39 in.) or more at 95 5C (203 5F)
If the valve lift is less than specification, replace the thermo-
stat.
(d) Check that the valve spring is tight when the thermostat
is fully closed.
If necessary, replace the thermostat.
INSTALLATION OF THERMOSTAT
(See Components on page CO±12)
1. PLACE THERMOSTAT IN WATER INLET HOUSING (a) Install a new gasket to the thermostat.
(b) Insert the thermostat into the water inlet housing withthe jiggle valve facing straight upward.
HINT: The jiggle valve may be set within 30 5 of either side of
the prescribed position.
2. INSTALL WATER INLET Install the water inlet with the two nuts.
Torque: 18 N Vm (185 kgf Vcm, 13 ft Vlbf)
3. FILL WITH ENGINE COOLANT (See page CO±7)
4. START ENGINE AND CHECK FOR LEAKS
±
COOLIING SYSTEM ThermostatCO±13
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName