1991 FORD FESTIVA ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 176 of 454
specified, go to next step.
2. Unplug VSS connector at instrument cluster. Measure resistance between VSS and GND terminals on instrument cluster. Rotate
speedometer cable. If resistance drops to less than 5 ohms 4 times for each revolution of speedometer cable, repair VSS signal wire to
4EAT. If resistance does not drop as specified, replace speedometer assembly.
PINPOINT TEST VAF - VANE AIRFLOW METER
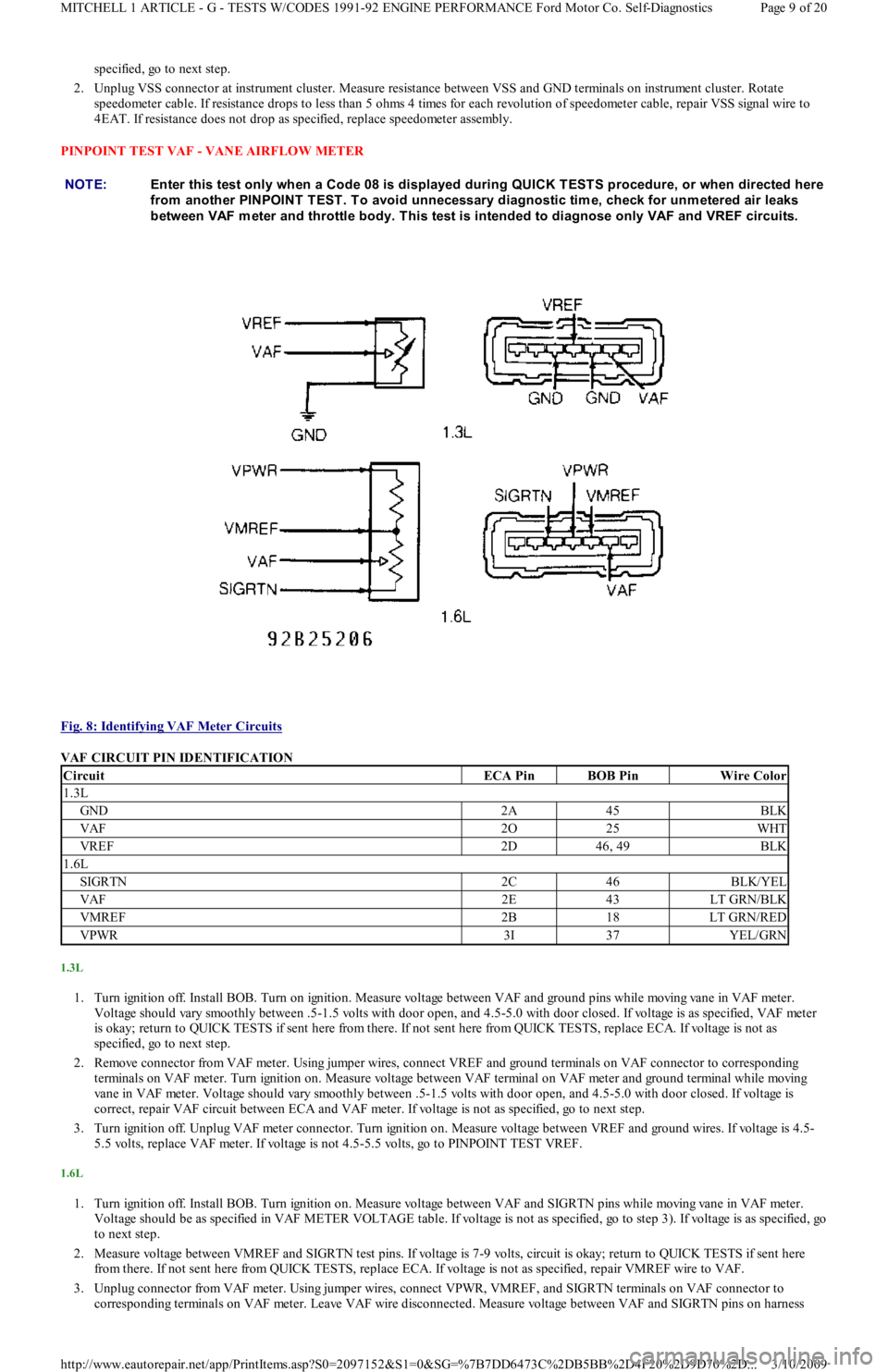
Fig. 8: Identifying VAF Meter Circuits
VAF CIRCUIT PIN IDENTIFICATION
1.3L
1. Turn ignition off. Install BOB. Turn on ignition. Measure voltage between VAF and ground pins while moving vane in VAF meter.
Voltage should vary smoothly between .5-1.5 volts with door open, and 4.5-5.0 with door closed. If voltage is as specified, VAF met er
is okay; return to QUICK TESTS if sent here from there. If not sent here from QUICK TESTS, replace ECA. If voltage is not as
specified, go to next step.
2. Remove connector from VAF meter. Using jumper wires, connect VREF and ground terminals on VAF connector to corresponding
terminals on VAF meter. Turn ignition on. Measure voltage between VAF terminal on VAF meter and ground terminal while moving
vane in VAF meter. Voltage should vary smoothly between .5-1.5 volts with door open, and 4.5-5.0 with door closed. If voltage is
correct, repair VAF circuit between ECA and VAF meter. If voltage is not as specified, go to next step.
3. Turn ignition off. Unplug VAF meter connector. Turn ignition on. Measure voltage between VREF and ground wires. If voltage is 4.5-
5.5 volts, replace VAF meter. If voltage is not 4.5-5.5 volts, go to PINPOINT TEST VREF.
1.6L
1. Turn ignition off. Install BOB. Turn ignition on. Measure voltage between VAF and SIGRTN pins while moving vane in VAF meter.
Voltage should be as specified in VAF METER VOLTAGE table. If voltage is not as specified, go to step 3). If voltage is as specified, go
to next step.
2. Measure voltage between VMREF and SIGRTN test pins. If voltage is 7-9 volts, circuit is okay; return to QUICK TESTS if sent here
from there. If not sent here from QUICK TESTS, replace ECA. If voltage is not as specified, repair VMREF wire to VAF.
3. Unplug connector from VAF meter. Using jumper wires, connect VPWR, VMREF, and SIGRTN terminals on VAF connector to
corresponding terminals on VAF meter. Leave VAF wire disconnected. Measure voltage between VAF and SIGRTN pins on harness NOTE:Enter this test only when a Code 08 is displayed during QUICK TESTS procedure, or when directed here
from another PINPOINT T EST . T o avoid unnecessary diagnostic tim e, check for unm etered air leaks
between VAF m eter and throttle body. T his test is intended to diagnose only VAF and VREF circuits.
CircuitECA PinBOB PinWire Color
1.3L
GND2A45BLK
VAF2O25WHT
VREF2D46, 49BLK
1.6L
SIGRTN2C46BLK/YEL
VAF2E43LT GRN/BLK
VMREF2B18LT GRN/RED
VPWR3I37YEL/GRN
Page 9 of 20 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - G - TESTS W/CODES 1991-92 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Ford Motor Co. Self-Diagnostics
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B7DD6473C%2DB5BB%2D4F20%2D9D70%2D
...
Page 177 of 454
connector while moving vane in VAF meter. Voltage should be as specified in VAF METER VOLTAGE table. If voltage is okay,
repair VAF wire to ECA. If voltage is not okay, go to next step.
VAF METER VOLTAGE
4. Unplug connector from VAF. Using jumper wires, connect VPWR and SIGRTN terminals on VAF connector to corresponding terminals
on VAF meter. Leave VAF and VMREF wires disconnected. Measure voltage between VAF terminal at VAF meter, and SIGRTN pin at
harness connector while moving vane in VAF meter. Voltage should be as specified in VAF METER VOLTAGE
table. If voltage is
okay, repair VMREF wire to ECA. If voltage is not okay, go to next step.
5. Unplug connector from VAF meter. Turn ignition on. Measure voltage between SIGRTN and VPWR wire. If voltage is more than 10
volts, replace VAF meter. If voltage is not more than 10 volts, go to next step.
6. Unplug VAF meter connector. Turn ignition on. Measure voltage between VAF meter VPWR wire and ground. If voltage is more than
10 volts, repair VAF wire to ECA. If voltage is not more than 10 volts, go to PINPOINT TEST VPWR.
PINPOINT TEST ECT - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
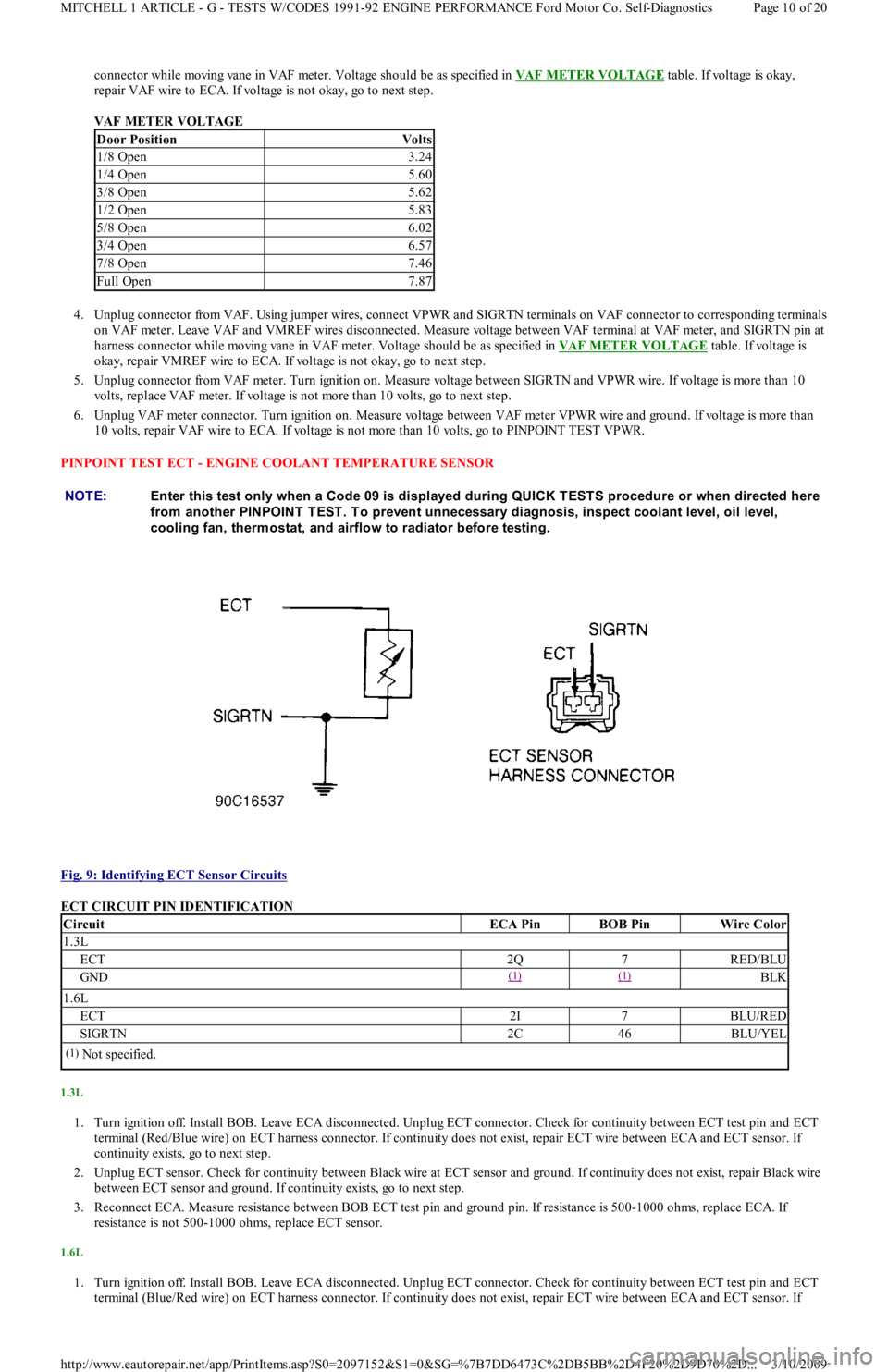
Fig. 9: Identifying ECT Sensor Circuits
ECT CIRCUIT PIN IDENTIFICATION
1.3L
1. Turn ignition off. Install BOB. Leave ECA disconnected. Unplug ECT connector. Check for continuity between ECT test pin and ECT
terminal (Red/Blue wire) on ECT harness connector. If continuity does not exist, repair ECT wire between ECA and ECT sensor. If
continuity exists, go to next step.
2. Unplug ECT sensor. Check for continuity between Black wire at ECT sensor and ground. If continuity does not exist, repair Black wire
between ECT sensor and ground. If continuity exists, go to next step.
3. Reconnect ECA. Measure resistance between BOB ECT test pin and ground pin. If resistance is 500-1000 ohms, replace ECA. If
resistance is not 500-1000 ohms, replace ECT sensor.
1.6L
1. Turn ignition off. Install BOB. Leave ECA disconnected. Unplug ECT connector. Check for continuity between ECT test pin and ECT
terminal (Blue/Red wire) on ECT harness connector. If continuity does not exist, repair ECT wire between ECA and ECT sensor. If
Door PositionVolts
1/8 Open3.24
1/4 Open5.60
3/8 Open5.62
1/2 Open5.83
5/8 Open6.02
3/4 Open6.57
7/8 Open7.46
Full Open7.87
NOTE:Enter this test only when a Code 09 is displayed during QUICK T EST S procedure or when directed here
from another PINPOINT T EST . T o prevent unnecessary diagnosis, inspect coolant level, oil level,
cooling fan, therm ostat, and airflow to radiator before testing.
CircuitECA PinBOB PinWire Color
1.3L
ECT2Q7RED/BLU
GND(1) (1) BLK
1.6L
ECT2I7BLU/RED
SIGRTN2C46BLU/YEL
(1)Not specified.
Page 10 of 20 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - G - TESTS W/CODES 1991-92 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Ford Motor Co. Self-Diagnostics
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B7DD6473C%2DB5BB%2D4F20%2D9D70%2D
...
Page 180 of 454

connector to corresponding terminals on TP sensor connector. Turn ignition on. Measure voltage between TP and SIGRTN terminals on
TP sensor while opening throttle. Compare voltage to specification in TP SENSOR OUTPUT VOLTAGE
table. If voltage is within
specification, repair TP wire to ECA. Go to next step if voltage is not within specification.
3. Turn ignition off. Unplug TP harness connector. Turn ignition on. Measure voltage between VREF and SIGRTN wires on TP harness
connect-or. If voltage is 4-5 volts, replace TP sensor. If voltage is not 4.5-5.5 volts, go to next step.
4. Measure voltage between VREF wire on TP harness connector and ground. If voltage is 4-5 volts, adjust or replace throttle position
sensor. If voltage is not 4-5 volts, go to PINPOINT TEST VREF
.
PINPOINT TEST BP - BAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSOR
Fig. 12: Identifying BP Sensor Circuits
1.3L
BP sensor is incorporated into ECA; it cannot be checked or serviced separately. If Code 14 is set and cannot be cleared, replace ECA.
1.6L
Turn ignition off. Connect BOB. Remove dust cover from BP sensor, located on passenger side cowl. Turn ignition on. Connect vacuum pump
to BP sensor. Measure voltage between pins BP and SIGRTN on BOB while applying vacuum to BP sensor. See BAROMETRIC
PRESSURE SENSOR OUTPUT VOLTAGE table. Replace BP sensor if voltage is not as specified.
BAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSOR OUTPUT VOLTAGE
PINPOINT TEST EGO - EXHAUST GAS OXYGEN SENSOR
EGO CIRCUIT PIN IDENTIFICATION
1. Warm engine to operating temperature, and let idle. Unplug EGO sensor. Measure voltage between EGO sensor connector (sensor side) NOTE:Enter this procedure only when a Code 14 is displayed during QUICK T EST S procedure or when
directed here from another PINPOINT T EST . T o prevent unnecessary replacem ent of com ponents, note
following non-EEC item s m ay be at fault: unusually high or low atm ospheric pressure, blocked vacuum
lines, or basic m echanical engine com ponents.
Vacuum (In. Hg.)(1) Voltage
03.84
53.36
102.66
151.93
201.26
25.58
(1)Voltage may vary by 15 percent.
NOTE:Enter this test only when a Code 15 (lean) or Code 17 (rich) is displayed during QUICK TESTS
procedure.
CircuitECA PinBOB PinWire Color
EGO
1.3L2N29BLU
1.6L2D29BLK
Page 13 of 20 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - G - TESTS W/CODES 1991-92 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Ford Motor Co. Self-Diagnostics
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B7DD6473C%2DB5BB%2D4F20%2D9D70%2D
...
Page 185 of 454
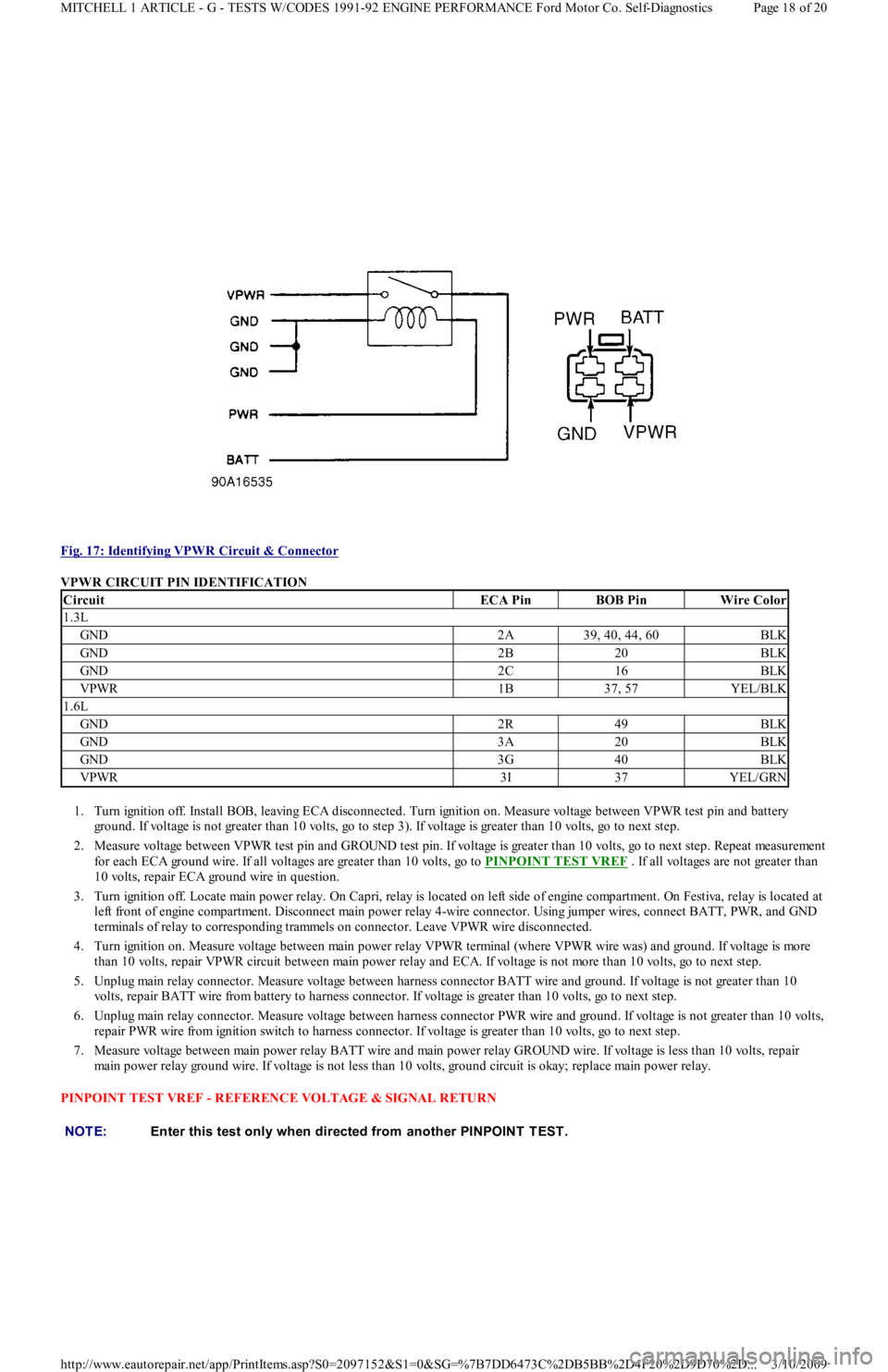
Fig. 17: Identifying VPWR Circuit & Connector
VPWR CIRCUIT PIN IDENTIFICATION
1. Turn ignition off. Install BOB, leaving ECA disconnected. Turn ignition on. Measure voltage between VPWR test pin and battery
gr o u n d . If vo l t a ge is n o t gr e a t e r t h a n 1 0 vo l t s, go t o st e p 3). If voltage is greater than 10 volts, go to next step.
2. Measure voltage between VPWR test pin and GROUND test pin. If voltage is greater than 10 volts, go to next step. Repeat measurement
for each ECA ground wire. If all voltages are greater than 10 volts, go to PINPOINT TEST VREF
. If all voltages are not greater than
10 volts, repair ECA ground wire in question.
3. Turn ignition off. Locate main power relay. On Capri, relay is located on left side of engine compartment. On Festiva, relay is located at
left front of engine compartment. Disconnect main power relay 4-wire connector. Using jumper wires, connect BATT, PWR, and GND
terminals of relay to corresponding trammels on connector. Leave VPWR wire disconnected.
4. Turn ignition on. Measure voltage between main power relay VPWR terminal (where VPWR wire was) and ground. If voltage is more
than 10 volts, repair VPWR circuit between main power relay and ECA. If voltage is not more than 10 volts, go to next step.
5. Unplug main relay connector. Measure voltage between harness connector BATT wire and ground. If voltage is not greater than 10
volts, repair BATT wire from battery to harness connector. If voltage is greater than 10 volts, go to next step.
6. Unplug main relay connector. Measure voltage between harness connector PWR wire and ground. If voltage is not greater than 10 volts,
repair PWR wire from ignition switch to harness connector. If voltage is greater than 10 volts, go to next step.
7. Measure voltage between main power relay BATT wire and main power relay GROUND wire. If voltage is less than 10 volts, repair
main power relay ground wire. If voltage is not less than 10 volts, ground circuit is okay; replace main power relay.
PINPOINT TEST VREF - REFERENCE VOLTAGE & SIGNAL RETURN
CircuitECA PinBOB PinWire Color
1.3L
GND2A39, 40, 44, 60BLK
GND2B20BLK
GND2C16BLK
VPWR1B37, 57YEL/BLK
1.6L
GND2R49BLK
GND3A20BLK
GND3G40BLK
VPWR3I37YEL/GRN
NOTE:Enter this test only when directed from another PINPOINT T EST .
Page 18 of 20 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - G - TESTS W/CODES 1991-92 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Ford Motor Co. Self-Diagnostics
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B7DD6473C%2DB5BB%2D4F20%2D9D70%2D
...
Page 196 of 454

gases into harmless substances.
PCV VALVE
The Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve, located in the valve cover, controls the flow of blow-by gas from the crankcase to the intake
man ifo l d .
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
The ECA monitors its inputs and outputs. When it detects a malfunction, it sets a code in the ECA and sends a signal to the CHECK ENGINE
warning light. The light remains on until the malfunction is repaired. Trouble codes may be accessed at the Self-Test Output (STO) and Self-
Test Input (STI) connectors, near the battery.
If a sensor fails, the ECA will use a substitute value in its calculations to permit continued engine operation. In this condition, the vehicle will
run, but driveability may be poor. Intermittent failures may result in the CHECK ENGINE warning light flickering or going out after the fault
goes away. The corresponding trouble code, however, will be stored in the ECA. If fault does not recur, the related code will be erased from
ECA memory.
CHECK ENGINE LIGHT
Hard failures cause the CHECK ENGINE warning light to come on and remain on until the malfunction is repaired. If the warning light comes
on and stays on during vehicle operation, determine and correct the cause of the malfunction. NOTE:For additional inform ation and operating procedures for the self-diagnostic system , refer to T EST S
W/CODES article in the ENGINE PERFORMANCE Section.
Copyr ight 2009 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Article GUID: A00022697
Page 6 of 6 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - E - THEORY/OPERATION 1991 ENGINE PERFORMANCE Ford/Mercury Theory & Operation
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B7DD6473C%2DB5BB%2D4F20%2D9D70%2D
...
Page 240 of 454
DRIVE AXLE - NOISE DIAGNOSIS
Unrelated Noises
Some driveline trouble symptoms are also common to the engine, transmission, wheel bearings, tires, and other parts of the vehicle. Ensure
cause of trouble actually is in the drive axle before adjusting, repairing, or replacing any of its parts.
Non-Drive Axle Noises
A few conditions can sound just like drive axle noise and have to be considered in pre-diagnosis. The 4 most common noises are exhaust, tires,
CV/universal joints and wheel trim rings.
In certain conditions, the pitch of the exhaust gases may e gear whine. At other times, it may be mistaken for a wheel bearing rumble.
Tires, especially radial and snow, can have a high-pitched tread whine or roar, similar to gear noise. Also, some non-standard tires with an
unusual tread construction may emit a roar or whine.
Defective CV/universal joints may cause clicking noises or excessive driveline play that can be improperly diagnosed as drive axle problems.
Trim and moldings also can cause a whistling or whining noise. Ensure none of these components are causing the noise before disassembling
the drive axle.
Gear Noise
Broken clutch return springReplace return spring
Worn splines on clutch disc or input shaftReplace clutch disc and/or input
shaft
Worn clutch release bearingReplace release bearing
Dry or worn pilot bearingLubricate or replace pilot bearing
Unequal release lever contactAlign or replace release lever
Incorrect pedal free playAdjust free play
Warped or damaged clutch discReplace damaged components
Slipping
Pressure springs worn orRelease pressure plate
Oily, greasy or worn facingsClean or replace clutch disc
Incorrect clutch alignmentRealign clutch assembly
Warped clutch disc or pressure plateReplace damaged components
Binding release levers or clutch pedalLubricate and/or replace release
components
Squeaking
Worn or damaged releaseReplace release bearing
Dry or worn pilot or release bearingLubricate or replace assembly
Pilot bearing turning in crankshaftReplace pilot bearing and/or
crankshaft
Worn input shaft bearingReplace bearing and seal
Incorrect transmission alignmentRealign transmission
Dry release fork between pivotLubricate release fork and pivot
Heavy and/or Stiff Pedal
Sticking release bearing sleeveReplace release bearing and/or
sleeve
Dry or binding clutch pedal hubLubricate and align components
Floor mat interference with pedalLay mat flat in proper area
Dry or binding ball/fork pivotsLubricate and align components
Faulty clutch cableReplace clutch cable
Noisy Clutch Pedal
Faulty interlock switchReplace interlock switch
Self-adjuster ratchet noiseLubricate or replace self-adjuster
Speed control interlock switchLubricate or replace interlock
switch
Clutch Pedal Sticks Down
Binding clutch cableSee CLUTCH article
Springs weak in pressure plateReplace pressure plate
Binding in clutch linkageLubricate and free linkage
Noisy
Dry release bearingLubricate or replace release
bearing
Dry or worn pilot bearingLubricate or replace bearing
Worn input shaft bearingReplace bearing
Transmission Click
Weak springs in pressureReplace pressure plate plate
Release fork loose on ball studReplace release fork and/or
ball stud
Oil on clutch disc damperReplace clutch disc
Broken spring in slave cylinderReplace slave cylinder
Page 27 of 36 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Trouble Shooting - Basic Procedures
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 252 of 454

Back To Article
GENERAL INFORMATION
Com puter Relearn Procedures
COMPUTER RELEARN PROCEDURES
Vehicles equipped with engine or transmission computers may require a relearn procedure after vehicle battery is disconnected. Many vehicle
computers memorize and store vehicle operation patterns for optimum driveability and performance. When vehicle battery is disconnected,
this memory is lost. The computer will use default data until new data from each key start is stored. As computer memorizes vehicle operation
for each new key start, driveability is restored. Vehicle computers may memorize vehicles operation patterns for 40 of more key starts.
Customers often complain of driveability problems during relearn stage because vehicle acts differently then before being serviced. Depending
on type and make of vehicle and how it is equipped, the following complaints (driveability problems) may exist:
Harsh Or Poor Shift Quality
Rough Or Unstable Idle
Hesitation Or Stumble
Rich Or Lean Running
Poor Fuel Mileage
These symptoms and complaints should disappear after a number of drive cycles have been memorized. To reduce the possibility of
complaints, after any service which requires battery power to be disconnected, vehicle should be road tested.
GENERIC COMPUTER RELEARN PROCEDURES
Some manufacturers identify a specific relearn procedure which will help establish suitable driveability during relearn stage. These procedures
are especially important if vehicle is equipped with and electronically controlled automatic transmission or transaxle. Always complete
procedure before returning vehicle to customer. The following general procedures are to be used if driveability problems are encountered after
power loss or battery has been disconnected. These procedures may provide an aid in eliminating these problems.
Automatic Transmission
Set parking brake, start engine in "P" or "N" position. Warm-up vehicle to normal operating temperature or until cooling fan cycles.
Allow vehicle to idle for one minute in "N" position. Select "D" and allow engine to idle for one minute.
Accelerate at normal throttle position (20-50%) until vehicle shifts into top gear.
Cruise at light to medium throttle.
Decelerate to a stop, allowing vehicle to downshift, and use brakes normally.
Process may be repeated as necessary.
Manual Transmission
Place transmission in Neutral position.
Ensure emergency brake has been set and all accessories are turned off.
Start engine and bring to normal operating temperature.
Allow vehicle to idle in Neutral for one minute.
Initial relearn is complete, and process will be completed during normal driving.
Copyr ight 2009 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Article GUID: A00012612
Page 1 of 1 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Computer Relearn Procedures
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...
Page 253 of 454

Back To Article
GENERAL INFORMATION
Drive Axle Noise Diagnosis
* PLEASE READ THIS FIRST *
UNRELATED NOISES
Some driveline trouble symptoms are also common to the engine, transmission, wheel bearings, tires and other parts of the vehicle. Make sure
that cause of trouble actually is in the drive axle before adjusting, repairing, or replacing any parts.
NON-DRIVE AXLE NOISES
A few conditions can sound just like drive axle noise and have to be considered in pre-diagnosis. The 4 most common noises are exhaust, tires,
CV/universal joints and trim moldings.
In certain conditions, the pitch of exhaust gases may sound like gear whine. At other times, it may be mistaken for a wheel bearing rumble.
Tires, especially radial and snow tires, can have a high-pitched tread whine or roar, similar to gear noise. Also, some non-standard tires with an
unusual tread construction may emit a roar or whine.
Defective CV/universal joints may cause clicking noises or excessive driveline play that can be improperly diagnosed as drive axle problems.
Trim and moldings can also cause a whistling or whining noise. Ensure that none of these components are causing the noise before
disassembling the drive axle.
GEAR NOISE
A "howling" or "whining" noise from the ring and pinion gear can be caused by an improper gear pattern, gear damage, or improper bearing
preload. It can occur at various speeds and driving conditions, or it can be continuous.
Before disassembling axle to diagnose and correct gear noise, make sure that tires, exhaust, and vehicle trim have been checked as possible
causes.
CHUCKLE
This is a particular rattling noise that sounds like a stick against the spokes of a spinning bicycle wheel. It occurs while decelerating from 40
MPH and usually can be heard until vehicle comes to a complete stop. The frequency varies with the speed of the vehicle.
A chuckle that occurs on the driving phase is usually caused by excessive clearance due to differential gear wear, or by a damaged tooth on the
coast side of the pinion or ring gear. Even a very small tooth nick or a ridge on the edge of a gear tooth is enough to cause the noise.
This condition can be corrected simply by cleaning the gear tooth nick or ridge with a small grinding wheel. If either gear is damaged or scored
badly, the gear set must be replaced. If metal has broken loose, the carrier and housing must be cleaned to remove particles that could cause
damage.
KNOCK
This is very similar to a chuckle, though it may be louder, and occur on acceleration of deceleration. Knock can be caused by a gear tooth that
is damaged on the drive side of the ring and pinion gears. Ring gear bolts that are hitting the carrier casting can cause knock. Knock can also be
due to excessive end play in the axle shafts. NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. For m odel-specific inform ation see appropriate articles where
available.
NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. For m odel-specific inform ation see appropriate articles where
available.
NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. For m odel-specific inform ation see appropriate articles where
available.
NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. For m odel-specific inform ation see appropriate articles where
available.
NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. For m odel-specific inform ation see appropriate articles where
available.
NOTE:This is GENERAL inform ation. This article is not intended to be specific to any unique situation or
individual vehicle configuration. For m odel-specific inform ation see appropriate articles where
available.
Page 1 of 2 MITCHELL 1 ARTICLE - GENERAL INFORMATION Drive Axle Noise Diagnosis
3/10/2009 http://www.eautorepair.net/app/PrintItems.asp?S0=2097152&S1=0&SG=%7B9B990D68%2D660A%2D45E9%2D8F46%2DE
...