1990 VOLKSWAGEN CORRADO coolant temperature
[x] Cancel search: coolant temperaturePage 445 of 906
D - ADJUSTMENTS
Article Text (p. 8)
1990 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Thursday, March 23, 2000 09:43PM
1) Check idle and adjust if needed. The idle air by-pass
screw is located in the throttle valve. Adjusting the screw changes
the amount of air by-passing the throttle plate raising or lowering
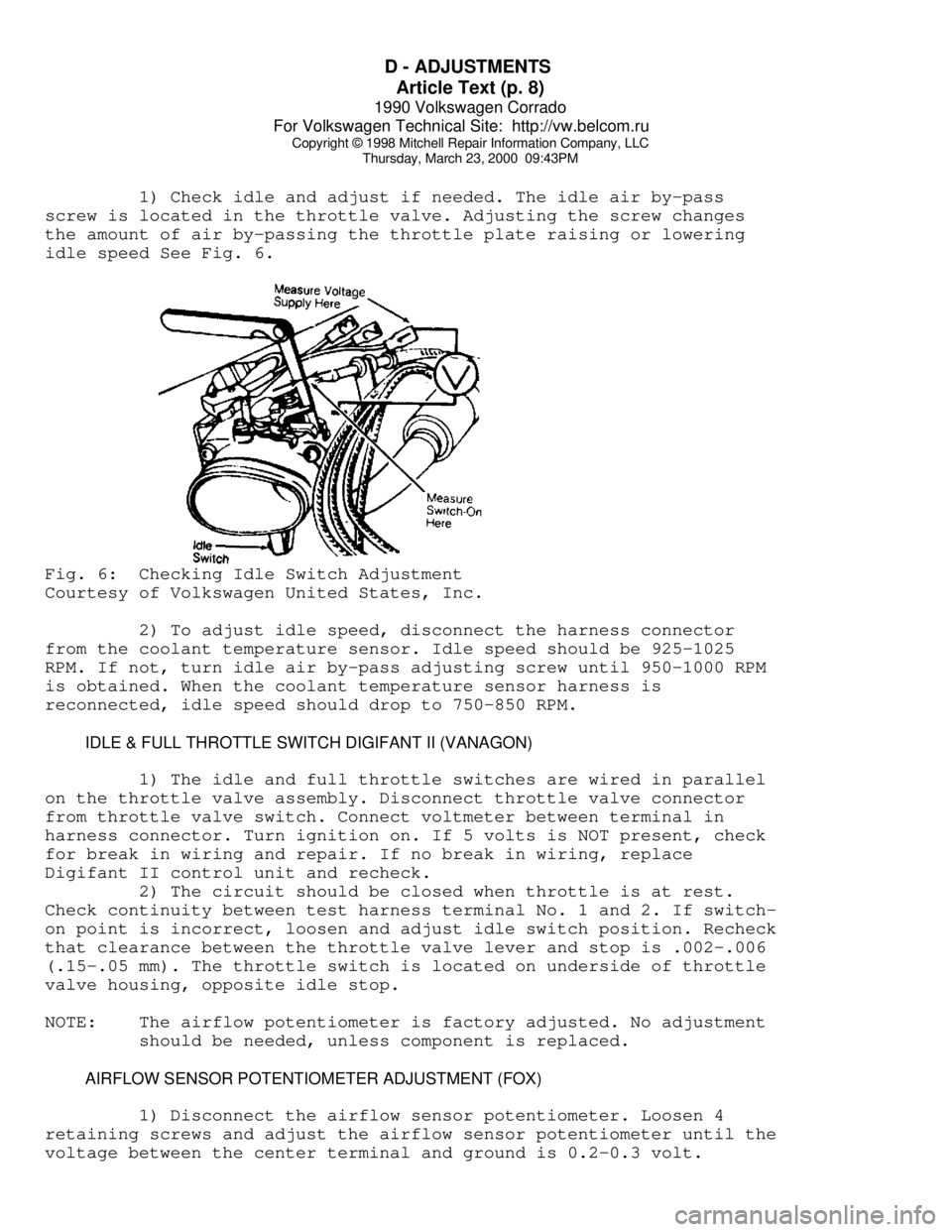
idle speed See Fig. 6.Fig. 6: Checking Idle Switch Adjustment
Courtesy of Volkswagen United States, Inc.
2) To adjust idle speed, disconnect the harness connector
from the coolant temperature sensor. Idle speed should be 925-1025
RPM. If not, turn idle air by-pass adjusting screw until 950-1000 RPM
is obtained. When the coolant temperature sensor harness is
reconnected, idle speed should drop to 750-850 RPM.
IDLE & FULL THROTTLE SWITCH DIGIFANT II (VANAGON)
1) The idle and full throttle switches are wired in parallel
on the throttle valve assembly. Disconnect throttle valve connector
from throttle valve switch. Connect voltmeter between terminal in
harness connector. Turn ignition on. If 5 volts is NOT present, check
for break in wiring and repair. If no break in wiring, replace
Digifant II control unit and recheck.
2) The circuit should be closed when throttle is at rest.
Check continuity between test harness terminal No. 1 and 2. If switch-
on point is incorrect, loosen and adjust idle switch position. Recheck
that clearance between the throttle valve lever and stop is .002-.006
(.15-.05 mm). The throttle switch is located on underside of throttle
valve housing, opposite idle stop.
NOTE: The airflow potentiometer is factory adjusted. No adjustment
should be needed, unless component is replaced.
AIRFLOW SENSOR POTENTIOMETER ADJUSTMENT (FOX)
1) Disconnect the airflow sensor potentiometer. Loosen 4
retaining screws and adjust the airflow sensor potentiometer until the
voltage between the center terminal and ground is 0.2-0.3 volt.
Page 453 of 906

E - THEORY/OPERATION - DIGIFANT
Article Text (p. 3)
1990 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Thursday, March 23, 2000 09:43PM
the following:
* Coolant Temperature Sensor
* ECU Control Relay
* ECU
* Oxygen Sensor
* Power Steering Oil Pressure Switch
NOTE: Components are grouped into 2 categories. The first category
covers INPUT DEVICES, which control or produce voltage
signals monitored by the control unit. The second category
covers OUTPUT SIGNALS, which are components controlled by
the control unit.
INPUT DEVICES
AIRFLOW SENSOR (EXCEPT CORRADO)
All intake air is drawn through the airflow sensor. The
airflow sensor contains a tunnel with a measuring flap and dampening
flap. The measuring flap swings with intake air stream against
pressure of a spiral spring and is connected to a potentiometer.
The potentiometer transmits an electrical signal determined
by measuring flap position to inform ECU of engine load. At idle, the
measuring flap is almost closed due to spring pressure. See Fig. 3.
The potentiometer within the airflow sensor prevents loss of
engine power during engine load or sudden acceleration (along with
engine speed and coolant temperature) by signaling the ECU of
necessary enrichment and timing requirements.
The airflow sensor contains an intake air temperature sensor.
An adjustable idle air by-pass screw influences CO levels at low
engine speeds. A tamper-proof plug is installed over this screw.Fig. 3: Cross-Sectional View of Airflow Meter
Courtesy of Volkswagen United States, Inc.
Page 454 of 906

E - THEORY/OPERATION - DIGIFANT
Article Text (p. 4)
1990 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Thursday, March 23, 2000 09:43PM
COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Is a temperature sensitive variable resistor sensor (less
resistance as temperature increases). This sensor returns signals to
the ECU to determine amount of cold start enrichment, ignition timing
and idle stabilization during warm-up. The sensor return signal has
input to the ECU when the oxygen sensor, idle stabilization, and full
throttle enrichment functions are activated.
CO POTENTIOMETER (CORRADO)
The CO potentiometer adjusts CO mixture. Located on the
intake air duct before the throttle housing. The adjustment screw has
a tamper-proof plug. An air temperature sensor located within the
potentiometer housing is used to calculate air density.
ECU CONTROL RELAY
When energized by ignition switch, the ECU control relay
provides battery voltage to ECU.
FULL THROTTLE (FUEL) ENRICHMENT SWITCH
The full throttle enrichment switch supplies the control unit
with information to increase amount of fuel injected during full
throttle operation.
HALL EFFECT SENSOR
See ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM under IGNITION SYSTEM in this
article.
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Intake air temperature sensor is a thermistor-type variable
resistor (resistance decreases with increase of temperature). This
sensor voltage signal varies to ECU in relation to engine air
temperature. Sensor is located inside the airflow meter.
KNOCK SENSOR(S)
Pick-up engine vibrations before knock occurs. The ECU
compensates timing as needed and controls timing advance or retard for
maximized engine performance.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR (CORRADO)
MAP is located inside the ECU. The MAP sensor signal is used
by ECU to determine engine load and manifold boost pressure. This
signal along with RPM and intake air temperature is used to calculate
fuel injection quantity.
Page 457 of 906

E - THEORY/OPERATION - DIGIFANT
Article Text (p. 7)
1990 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Thursday, March 23, 2000 09:43PM
The idle air stabilizer valve is ECU controlled. On Vanagon
idle stabilizer valve is controlled by a separate idle stabilizer
controller. The idle air stabilizer operates to continuously maintains
engine idle at a computed engine idle speed.
IGNITION SYSTEM
The Hall Effect sending unit in the distributor, uses a
shutter window wheel mounted on the distributor shaft. The shutter
blades pass in and out of the air gap of the hall effect sender
resulting in signal pulses (engine speed signal). There is one shutter
window for each engine cylinder. Signals from distributor hall sender
are sent to the ECU.
ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM
IGNITION COIL CONTROL
Signals from distributor hall sender are sent to the ECU,
which produces a pulsating signal to the ignition coil. This computed
signal from ECU to ignition coil, control ignition timing according to
engine load (airflow sensor signal), engine speed (Hall Effect signal)
and engine coolant temperature.
IGNITION TIMING ADVANCE CONTROL SYSTEM
Timing is ECU controlled.
EMISSION SYSTEMS
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS SYSTEM
Fuel vapors are collected in the expansion tank. Any liquid
gasoline collect in expansion tank flows back to the fuel tank through
vent lines. See Fig. 4. Fuel vapors are drawn from tops of the
expansion tanks and flow into the carbon canister where the vapors are
stored. When the engine is not running.
After engine is started, the control valve is opened by
throttle vacuum. Fresh air is drawn into bottom of the canister. Fuel
vapors from the canister are drawn into the intake manifold.
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION
Information is not available. See M - VACUUM DIAGRAMS for
system components and vacuum hose routings.
Page 486 of 906
ELECTRICAL COMPONENT LOCATOR
Article Text (p. 27)
1990 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Thursday, March 23, 2000 09:44PM
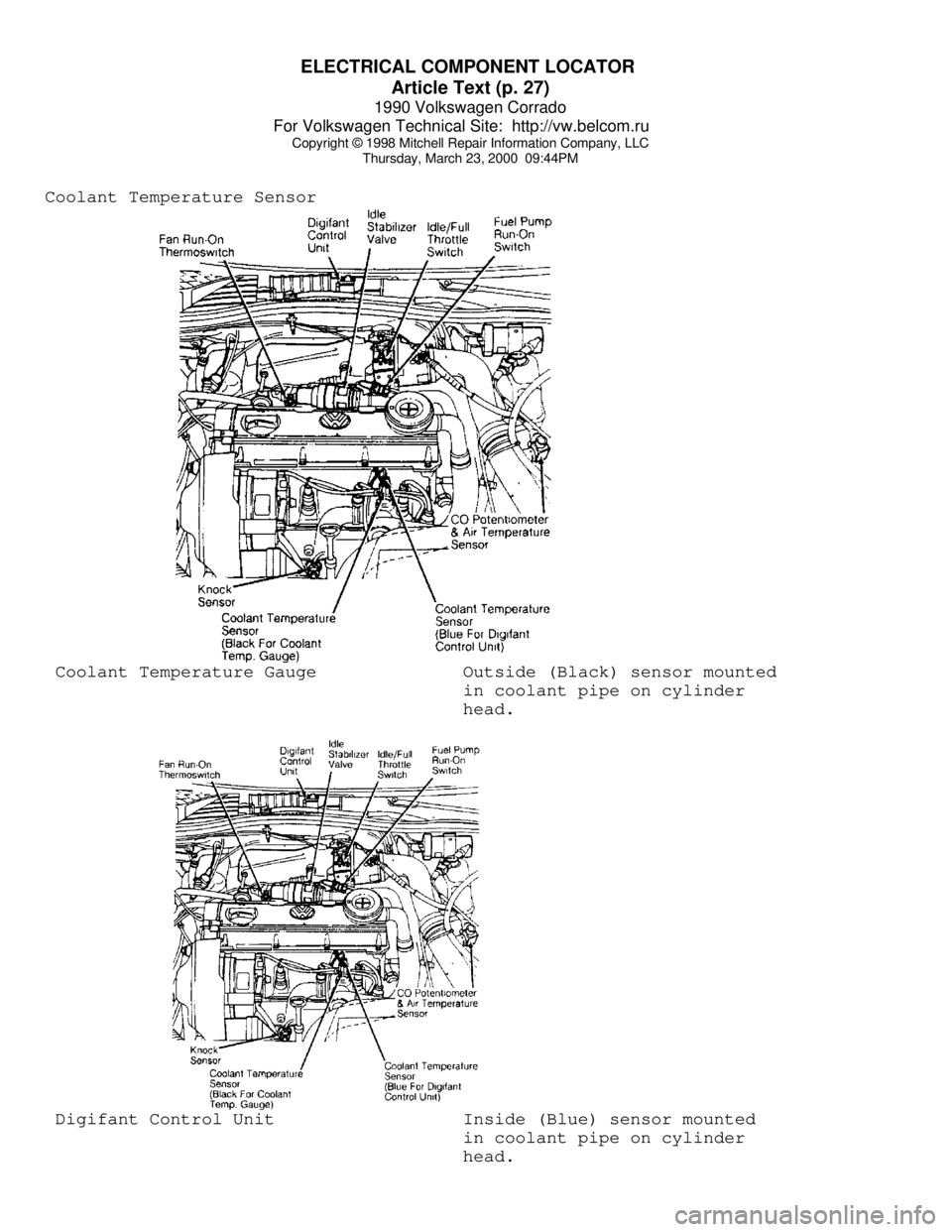
Coolant Temperature Sensor Coolant Temperature Gauge Outside (Black) sensor mounted
in coolant pipe on cylinder
head. Digifant Control Unit Inside (Blue) sensor mounted
in coolant pipe on cylinder
head.
Page 503 of 906

EMISSION CONTROL VISUAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
Article Text (p. 9)
1990 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Thursday, March 23, 2000 09:44PMFig. 10: Typical Negative Backpressure EGR Valve
Courtesy of General Motors Corp.
Digital EGR Valve
The digital EGR valve operates independently of engine
manifold vacuum. This valve controls EGR flow through 3 orifices.
These 3 orifices are opened and closed by electric solenoids. The
solenoids are, in turn, controlled by the Electronic Control Module
(ECM). When a solenoid is energized, the armature with attached shaft
and swivel pintle is lifted, opening the orifice. See Fig. 11.
The ECM uses inputs from the Coolant Temperature Sensor
(CTS), Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) and Mass Airflow (MAF) sensors
to control the EGR orifices to make 7 different combinations for
precise EGR flow control. At idle, the EGR valve allows a very small
amount of exhaust gas to enter the intake manifold. This EGR valve
normally operates above idle speed during warm engine operation.
Verify EGR valve is present and not modified or purposely
damaged. Ensure thermal vacuum switches, pressure transducers, speed
switches, etc., (if applicable) are not by-passed or modified. Ensure
vacuum hose(s) to EGR valve is not plugged. Ensure electrical
connector to EGR valve is not disconnected.
Page 545 of 906

ENGINE OVERHAUL PROCEDURES - GENERAL INFORMATION
Article Text (p. 36)
1990 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Thursday, March 23, 2000 09:44PM
to ensure correct amount of oil has filled crankcase. Check oil level
while pre-oiling.
If pressure oiler is not available, disconnect ignition
system. Remove oil pressure sending unit and replace with oil pressure
test gauge. Using starter motor, rotate engine starter until gauge
shows normal oil pressure for several seconds. DO NOT crank engine
for more than 30 seconds to avoid starter motor damage.
Ensure oil pressure has reached the most distant point from
the oil pump. Reinstall oil pressure sending unit. Reconnect ignition
system.
INITIAL START-UP
Start the engine and operate engine at low speed while
checking for coolant, fuel and oil leaks. Stop engine. Recheck coolant
and oil level. Adjust if necessary.
CAMSHAFT
Break-in procedure is required when a new or reground
camshaft has been installed. Operate and maintain engine speed between
1500-2500 RPM for approximately 30 minutes. Procedure may vary due to
manufacturers recommendations.
PISTON RINGS
Piston rings require a break-in procedure to ensure seating
of rings to cylinder walls. Serious damage may occur to rings if
correct procedures are not followed.
Extremely high piston ring temperatures are produced obtained
during break-in process. If rings are exposed to excessively high RPM
or high cylinder pressures, ring damage can occur. Follow piston ring
manufacturer's recommended break-in procedure.
FINAL ADJUSTMENTS
Check or adjust ignition timing and dwell (if applicable).
Adjust valves (if necessary). Adjust carburetion or injection idle
speed and mixture. Retighten cylinder heads (if required). If
cylinder head or block is aluminum, retighten bolts when engine is
cold. Follow the engine manufacturer's recommended break-in procedure
and maintenance schedule for new engines.
NOTE: Some manufacturer's require that head bolts be retightened
after specified amount of operation. This must be done to
prevent head gasket failure.
END OF ARTICLE
Page 558 of 906

F - BASIC TESTING
Article Text (p. 13)
1990 Volkswagen Corrado
For Volkswagen Technical Site: http://vw.belcom.ru
Copyright © 1998 Mitchell Repair Information Company, LLC
Thursday, March 23, 2000 09:44PM
DISTRIBUTOR
HALL EFFECT SENDER
1) Remove coil secondary and attach to ground. Disconnect
Hall Effect sender wire at the distributor. Using a LED Test Light (US
1115), check for voltage between outer terminals of connector. See
Fig. 5 or 8. With ignition on, light should be on. If not, check
wiring for short or open circuit. If wiring is okay, replace Digifant
control unit.
2) If light came on in step 1), reconnect Hall Effect sender
harness connector. Pull back Hall Effect sender boot to expose contact
terminals. Apply LED Test Light (US 1115) probe to center contact and
battery positive terminal. See Fig. 5. Observe test light while
cranking engine. If test light blinks, Hall Effect sender is okay. If
not, replace Hall Effect-sender.
IDLE SPEED, CO LEVEL & IGNITION TIMING
Ensure idle speed, CO level and base ignition timing are set
to specification. If necessary, see ON-VEHICLE ADJUSTMENTS article.
IDLE SPEED & CO LEVEL TABLEÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄApplication Idle RPM CO Level %
All Models ............ 800-1000 .............. 0.3-1.2%
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄIGNITION TIMING TABLE (Degrees BTDC @ RPM)
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄApplication Checking Adjusting
1.8L ............... 4-8 @ 2250-2350 . 5-7 @ 2250-2350
2.0L ................ 4-8 @ 770-830 ...... 5-7 @ 770-830
2.1L (1) ........... 4-8 @ 2250-2350 . 5-7 @ 2250-2350
(1) - With coolant temperature sensor disconnected.
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ SUMMARY
If no faults were found while performing F - BASIC TESTING,
proceed to H - TESTS W/CODES article for diagnosis by symptom (i.e.,
ROUGH IDLE, NO START, etc.) or intermittent diagnostic procedures.
END OF ARTICLE