1990 MITSUBISHI SPYDER fuel type
[x] Cancel search: fuel typePage 374 of 2103

ENGINE LUBRICATION General Information/Lubricants
G E N E R A L I N F O R M A T I O N
The lubrication method is a fully force-fed, full-f low
filtration type.
ENGINE OILS
Health Warning
Prolonged and repeated contact with mineral oil
will result in the removal of natural fats from the
skin, leading to dryness, irritation and dermatitis .
In addition, used engine oil
potentially
Recommended Precautions
The most effective precaution is to adapt working
practices which prevent, as far as practicable, the
risk of skin contact with mineral oils, for example
by using enclosed systems for handling used engine
oil and by degreasing components, where
practicable, before handling them.
Other precautions:
lAvoid prolonged and repeated contact with oils,
particularly used engine oils.
l Wear protective clothing, including impervious
gloves where practicable.
l Avoid contaminating clothes, particularly
underpants, with oil.
l Do not put oily rags in packets, the use of
overalls without pockets will avoid this.
l Do not wear heavily soiled clothing and
oil-impregnated foot-wear. Overalls must be
cleaned regularly and kept separate from
personal clothing.
LUBRICANTS
harmful contaminants which may cause skin cancer.
Adequate means of skin protection and washing
facilities must
provided.
Where there is a risk of eye contact, eye protection should be worn, for example,
chemical goggles or face shields; in addition
an eye wash facility should be provided.
Obtain First Aid treatment immediately for open
cuts and wounds.
Wash regularly with soap and water to ensure
all oil is removed, especially before
cleansers and nail brushes will help). After
cleaning, the application of
containing lanolin to replace the natural
oil is advised.. .
Do not use gasoline, kerosine, diesel fuel,
oil, thinners or solvents for cleaning skin.
Use barrier creams, applying them before each
work period, to help the removal of oil from
the skin after work.
If skin disorders develop, obtain medical advice
without delay.
Items Engine oil (API classification) Quantity (qts.)
Oil filter Engine (Non-turbo)
Engine (Turbo) and
Engine
Oil cooler
Engine (Turbo)>
Total quantity
Engine (Non-turbo)
and
Engine SH or higher
0.5
0.3
0.1
4.3 (4.5)
IIIII
Engine (Turbo) 4.4 (4.6)I
EOLCS certification markENGINE OIL
Caution
use nondetergent or straight mineral oil.
Oil Identification Symbol
Use only engine oils displaying the EOLCS certifica tion mark
on the container.
. .
Revision
Page 384 of 2103

ENGINE (NON-TURBO)>
DIAGNOSTIC TEST MODE
l When an abnormality is detected in one
of the sensors or actuators related to
emission control, the CHECK
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP
nates as a warning to the driver.
l When an abnormality is detected in one
of the sensors or actuators, a diagnostic
OTHER CONTROL FUNCTIONS
t r o u b l e c o d e
a b n o r m a l i t y i s o u t p u t .
lThe RAM data inside the PCM that is
to the sensors and
by means of the scan tool.
In addition, the actuators can be controlled
under certain circumstances. . ,
1. Fuel Pump Control
Turns the fuel pump relay ON so that current
is supplied to the fuel pump while the engine
is cranking or running.
2. A/C Compressor Clutch Relay Control Turns the A/C compressor clutch ON and
OFF.
3. Fan Relay Control
The radiator fan and condenser fan speeds
are controlled in response to the engine
coolant temperature and vehicle speed. 4. Generator
Controls the generator in order
to control the generated current.
5. Engine Speedometer or Tachometer
Control.
Sends a pulse signal which ‘corresponds
to the engine speed to the’ speedometer
unit..
6. Evaporative Emission Purge
C o n t r o l
Refer to GROUP 17.
7. Electric EGR Transducer Solenoid Control Refer to GROUP 17.
Throttle body
Sensors
Actuators
Specifications
Throttle bore mm (in) 52 (2.05)
Throttle position sensor Variable resistor type
Idle air control motor
Stepper motor type [Stepper type
bypass air control system]’,
Manifold absolute pressure sensor Semiconductor type
Intake air temperature sensorT h e r m i s t o r t y p e
Engine coolant temperature sensorThermistor type .
Heated oxygen sensorZircon type .
Vehicle speed sensorElectromagnetic resistance element type
TCM output signal
Camshaft position sensor Hall element type’
Crankshaft position sensor
Hall element type
Knock sensor Piezoelectric type
Power steering pressure switch Contact switch type
fuel injection (MFI) relay (ASD relay)
Contact switch type
Fuel pump relay Contact switch type
Injector type and number Electromagnetic type, 4
Electric EGR transducer solenoid ON/OFF type solenoid valve
Evaporative emission purge solenoid Duty cycle type solenoid valve
TSB Revision
Page 520 of 2103

E N G I N E ( T U R B O )
AND
Engine (Turbo)>
Item
Throttle bodyThrottle bore mm (in.)5 4
Engine control
module (ECM)
Sensors
pressure
egulator
Volume air flow sensor
Barometric pressure sensorK a r m a n v o r t e x t y p e , ,
Intake air temperature sensor Thermistor type
Engine coolant temperature sensor
T h e r m i s t o r t y p e
Heated oxygen sensor Zircon type
Vehicle speed sensor Electromagnetic resistance elem ent ‘type
Park/neutral position switchContact switch type .
Camshaft position sensor
Crankshaft position sensorHall element type
Throttle position sensor
Idle air control motor Variable resistor type
Stepper motor type [Stepper. type ‘by-pass’ air
control system
the air
Closed throttle position switch
model No.
Rotary contact type,
,
Knock sensor Piezoelectric type
Power steering pressure switch
Contact switch type
Manifold differential pressure sensor Semiconductor type
fuel injection (MFI) relay
Contact switch type
Fuel pump relay
Injector type and number
Injector identification mark Contact switch type
Electromagnetic type, 4
solenoid Duty cycle type solenoid valve
Evaporative emission purge solenoid
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
Fuel pressure solenoid
Turbocharger waste gate solenoid ON/OFF type solenoid valve
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
Regulator
(psi) 294 (43)
TSB Revision
Page 521 of 2103

ENGINE (TURBO)
AND
ENGINE> General
Engine>
ItemSpecifications
Throttle body Throttle bore mm (in.)54 (2.13)
Throttle position sensorV a r i a b l e r e s i s t o r t y p e
Idle air control motor
DC motor type [DC by-pass air control system
with the fast idle air
Closed throttle position switch
Rotary contact type, within throttle position senso r
Idle air control valve position sensor
Hall element type
Engine control Identification model No.
module (ECM)
SensorsVolume air flow sensor Karman vortex type
Barometric pressure sensorSemiconductor type.
Intake air temperature sensorThermistor type
Engine coolant temperature sensor Thermistor type
Heated oxygen sensor Zircon type
Vehicle speed sensor Electromagnetic resistance element type
Park/neutral position switch Contact switch type
Camshaft position sensor Hall element type
Crankshaft position sensor Hall element type
Power steering pressure switch Contact type
fuel injection (MFI) relay Contact switch type
Fuel pump relay Contact switch type
Fuel pump relay module Electronic control module typ e
Injector type and number Electromagnetic type, 4
Injector identification mark
,
solenoid Duty cycle type solenoid valve
Evaporative emission purge solenoid
Duty cycle type solenoid valve
pressure Regulator (psi)335 (48)
egulator
TSB Revision
Page 608 of 2103

ENGINE (TURBO)
AND ENGINE> Troubleshooting
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 37 ,
Ignition system: Inspection when no initial occurs,
Engine (Turbo)> NGMeasure at the ignition coil connector Check ignition circuit system.
l Connect the connector. (Use the test harness:
(Refer to INSPECTION PROCEDURE 34.)
lTo inspect, connect the primary voltage detection-typetachometer to the terminal 1 (red clip) and terminal 2
(black clip).
OK: Each terminal displays a speed on the engine tachometer that is
of the cranking speed.
OK
Engine>
Measure at the ignition coil connectors
l Connect the connector.
(Use the test harness:
lTo inspect, connect the primary voltage detection-t ypetachometer to the terminal 2.OK: Each terminal displays a speed on the engine
tachometer that is of the cranking speed.
OK
NGCheck the ignition circuit system.(Refer to INSPECTION PROCEDURE 34.)
OK:
NG Check that the crankshaft position sensor are properly installed.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 38
Scan tool: Inspection when incomplete combustion oc curs.
YESINSPECTION CHART FOR DIAGNOSTIC Arediagnostic trouble code output (Refer to
SCAN TOOL Actuator te
07 Fuel pump (Refer toNG, Check the fuel pump system Engine (Turbo)>.(Refer to INSPECTION PROCEDURE 28.)Check the fuel pump system Engine>. (Refer-to IN-
SPECTION PROCEDURE 29.)
./I,’
SCAN TOOL Date list21(Refer to INSPECTION PROCEDURE TROUBLE CODE
NGSCAN TOOL Data Check the ignition switch-ST 18 Ignition switch-ST (Refer to (Refer to INSPECTION PROCEDURE 30.)
Check the ignition switch-ST andpark/neutralswitch
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 39 ,
when huntina occurs.
Clean the throttle body. (Refer to
I
Check and adiust the fixed SAS (Refer to
Check trouble symptom.
NG
Inspect air into the air intake system for vacuum l eaks.
l Broken intake manifold gasket
Broken air intake hose
l Broken vacuum hose
Page 651 of 2103

FUEL PUMP CONNECTOR”
(HOW TO REDUCE FUEL
When removing the fuel pipe, hose, etc.,
in the fuel pipe line is high, do the
as to release fuel pressure in the line and from
running out.
1.Remove the rear seat cushion.
(Refer to GROUP Seat.)
2.Remove the protector to disconnect the fuel
tor.
3.Start the engine and let it run until it stops natu rally,
off the ignition switch..
4.Connect the fuel pump connector to install the
5. the rear seat cushion. ,
FUEL PUMP OPERATION CHECK’
1.Check the operation of the fuel pump by
tool to force-drive the fuel pump.
2. If the fuel pump will not operate, check by usin g
following procedure. normal, check the fuel pump drive
circuit.
(1) Turn off the ignition switch.
(2) When the fuel,, pump
(black) is
directly to the battery, if the sound of
the fuel pump operation can be heard.
NOTE
As the fuel pump is an in-tank type, the fuel pump
sound is hard to hear, so remove the fuel tank
tube cap and check from the tank inlet.
(3) Check the fuel pressure by
the fuel hose
with the fingertips.
Page 678 of 2103

FUEL SUPPLY Fuel Tank
13500010032
(1) The fuel tank is located under the floor of the The fuel tank AWD from a high
rear seats to provide increased safety. density: pol yethylene
material and
(2)A fuel cut-off valve has been’adopted to preventblow-formed an ‘tank.
fuel from leaking out in the event of a collision.
Specifications
Fuel tank capacity (gals.)
Fuel pump type64 (16.9)
Electrical, in-tank type
ItemsStandard value.
Fuel tank differential pressure sensor output volta ge 2.0 3.0 ,
Test harness set pressure sensor
TSB Revision
Page 1174 of 2103
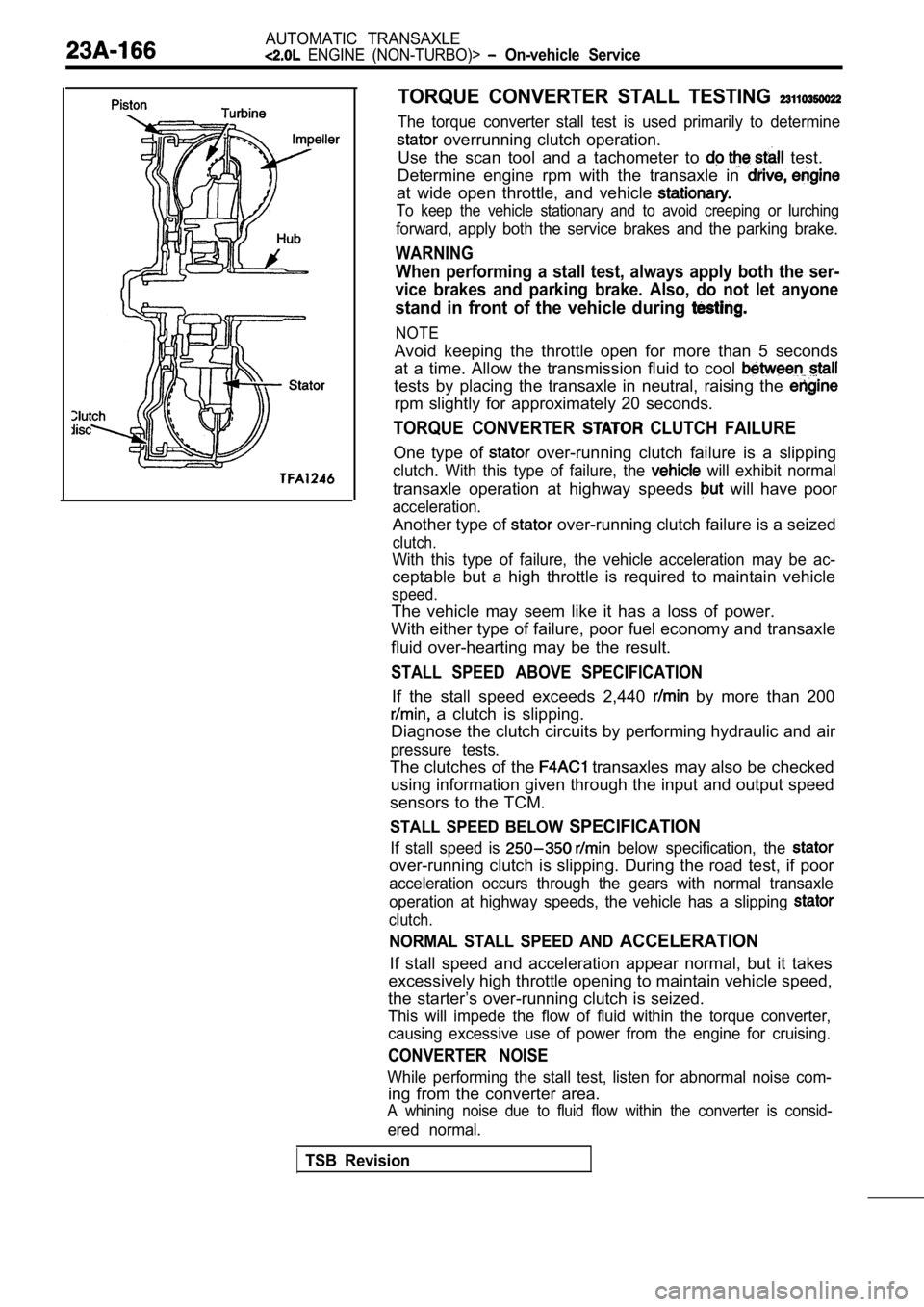
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
ENGINE (NON-TURBO)> On-vehicle Service
TORQUE CONVERTER STALL TESTING
The torque converter stall test is used primarily to determine
overrunning clutch operation.
Use the scan tool and a tachometer to
test.
Determine engine rpm with the transaxle in
at wide open throttle, and vehicle
To keep the vehicle stationary and to avoid creepin g or lurching
forward, apply both the service brakes and the parking brake.
WARNING
When performing a stall test, always apply both the ser-
vice brakes and parking brake. Also, do not let any one
stand in front of the vehicle during
NOTE
Avoid keeping the throttle open for more than 5 seconds
at a time. Allow the transmission fluid to cool
tests by placing the transaxle in neutral, raising the
rpm slightly for approximately 20 seconds.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH FAILURE
One type of over-running clutch failure is a slipping
clutch. With this type of failure, the will exhibit normal
transaxle operation at highway speeds will have poor
acceleration.
Another type of over-running clutch failure is a seized
clutch.
With this type of failure, the vehicle acceleration may be ac-
ceptable but a high throttle is required to maintai n vehicle
speed.
The vehicle may seem like it has a loss of power.
With either type of failure, poor fuel economy and transaxle
fluid over-hearting may be the result.
STALL SPEED ABOVE SPECIFICATION
If the stall speed exceeds 2,440 by more than 200
a clutch is slipping.
Diagnose the clutch circuits by performing hydrauli c and air
pressure tests.
The clutches of the transaxles may also be checked
using information given through the input and outpu t speed
sensors to the TCM.
STALL SPEED BELOW SPECIFICATION
If stall speed is below specification, the
over-running clutch is slipping. During the road te st, if poor
acceleration occurs through the gears with normal t ransaxle
operation at highway speeds, the vehicle has a slip ping
clutch.
NORMAL STALL SPEED AND ACCELERATION
If stall speed and acceleration appear normal, but it takes
excessively high throttle opening to maintain vehic le speed,
the starter’s over-running clutch is seized.
This will impede the flow of fluid within the torqu e converter,
causing excessive use of power from the engine for cruising.
CONVERTER NOISE
While performing the stall test, listen for abnormal noise com-
ing from the converter area.
A whining noise due to fluid flow within the conver ter is consid-
ered normal.
TSB Revision