1988 OPEL VECTRA air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 127 of 525

2Exhaust gas recirculation
(EGR) system - general
The system reintroduces small amounts of
exhaust gas into the combustion cycle to
reduce the generation of oxides of nitrogen
(NOx).
On C16 NZ, C16 NZ2 and C18 NZ engines,
the volume of exhaust gas reintroduced is
governed by manifold vacuum, through the
EGR valve mounted on the inlet manifold.
When the valve is opened small amounts of
exhaust gas are allowed to enter the inlet
tract, passing through ports in the cylinder
head.
On X16 SZ engines the EGR valve is
operated by an EGR module, mounted on the
left-hand side of the engine compartment
behind the battery. This module amplifies
signals received from the fuel system ECU
and operates the EGR valve electronically
providing precise control of exhaust gas
recirculation under all engine conditions.
3EGR valve (Multec system
models) - testing, removal and
refitting
2
Testing
1On C16 NZ, C16 NZ2 and C18 NZ engines,
it is recommended that the system is checked
annually, by checking the movement of the
valve’s diaphragm carrier plate as follows.
Note that the carrier plate is visible only
through the apertures in the underside of the
valve, so a battery-operated torch and small
mirror may be useful. On X16 SZ engines,
Vauxhall test equipment is necessary to check
the EGR system.
2With the engine fully warmed up to normal
operating temperature and idling, briefly open
and close the throttle. The carrier plate should
move upwards as the manifold vacuum
changes. When the engine is idling smoothly
again, press the carrier plate upwards (do this
very carefully, so that the plate is not distorted or
the diaphragm damaged). The idle speed should
drop significantly (approximately 100 rpm).
3If the valve does not respond as described,
it must be cleaned.
Removal
4Pull off the hose from the valve, then unbolt
the valve and remove it (see illustrations).
Clean away all carbon using a wire brush and
a pointed tool, but take care not to damage
the valve seat. Renew the valve gasket to
prevent induction leaks.
Refitting
5Refit the valve and reconnect the hose,
then recheck the system’s performance; if
there is no improvement, the valve must be
renewed.
4EGR valve (Simtec system) -
testing, removal and refitting
3
Note: A new gasket will be required when
refitting the valve.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove wiring harness and vacuum hose.
3Mark position of the valve, to ensure
correct relocation.
4Undo the 3 bolts, and remove the valve
from the dual spark ignition coil’s coolant
flange.
Refitting
5Clean the sealing surfaces of the valve and
flange.
6Refit the valve with a new gasket and line
up the marks made before removal (see
illustration).
5EGR module (X16 SZ
models) - removal and
refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the knock module from its
bracket (refer to Chapter 4B, if necessary),
and place to one side.
2Remove wiring plug from module. Remove
module from bracket.
Refitting
3Refitting is a reversal of removal.
6AIR pump assembly (Simtec
system) - removal and refitting
3
Removal
1Chock the rear wheels, jack up the front of
the vehicle and support it on axle stands
placed under the body side members (see
“Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
2Remove the left hand front wheel and inner
wheel arch lining.
3Loosen the hose clamp and remove the air
duct hose from the pump.
4Disconnect the battery negative lead.
5Undo the securing nuts and remove the
pump assembly from its location. Disconnect
the wiring plug.
6Remove the wiring plug from the pump’s
bracket.
7Mark the position of the pump on it’s
bracket before separating.
8Remove the fixing bolts and disconnect the
pump from it’s insulator.
9The insulator can also be checked by
removing the 3 nuts, securing the protective
shield. Before removing, mark the shield and
insulator. Replace if necessary.
10Check the pump’s air cleaner for damage.
Refitting
11Refitting is a reversal of removal. Ensure
correct alignment of the components.
7AIR cut-off valve - removal,
testing and refitting
3
Removal
1Before removal, mark on the cut-off valve,
the direction of flow towards the non-return
valve (see illustration).
2Disconnect and remove the air duct and
vacuum hoses.
3Undo the switchover valve’s bolts and
move to one side.
4C•2Fuel and exhaust systems - exhaust and emissions
3.4 Disconnecting the vacuum hose from
the exhaust gas recirculation valve
4.6 EGR valve
1 Valve 2 Gasket
3.4B Withdrawing the exhaust gas
recirculation valve
Page 140 of 525

11Remove the wood and carefully withdraw
the piston.
12Carefully prise the seal from the groove in
the caliper piston bore, using a plastic or
wooden instrument.
13Inspect the surfaces of the piston and its
bore in the caliper for scoring, or evidence of
metal-to-metal contact. If evident, renew the
complete caliper assembly.
14If the piston and bore are in good
condition, discard the seals and obtain a
repair kit, which will contain all the necessary
renewable items.
15Clean the piston and cylinder bore with
brake fluid or methylated spirit, nothing else!
16Begin reassembly by fitting the seal into
the caliper bore.
17Locate the dust seal in its groove in the
piston. Dip the piston in clean brake fluid and
insert it squarely into the cylinder. Check that
the cutaway recesses in the piston are
positioned horizontally. If necessary, carefully
turn the piston to its correct position.
18When the piston has been partially
depressed, engage the dust seal with the rim
of the caliper bore, and fit the retaining clip.
19Push the piston further into its bore, but
not as far as the stop, ensuring that it does
not jam.
20If desired, the caliper body locating pin
rubbers can be renewed. Extract the nylon
compression sleeve from within each rubber,
then carefully compress the rubber shoulder,
and push the rubber through the hole in the
caliper body to remove it from the inboard
end (see illustrations).
21Fit the new rubbers using a reversal of the
removal procedure.
22Secure the caliper bracket in a soft-jawed
vice, and refit the guide springs in the
positions noted before removal.
23Engage the caliper body with the locating
pins on the bracket, then press the caliper
body into position until the locating pin
rubbers in the caliper body rest against the
bracket.
Refitting
24Refit the caliper bracket to the hub carrier,
and tighten the securing bolts to the specified
torque. Refit the dust caps to the bolts.25Reconnect the brake fluid hose union,
using new sealing rings on the union bolt.
26Refit the disc pads, as described in
Section 4.
27Remove the polythene from the brake
fluid reservoir filler neck, and bleed the
relevant brake hydraulic circuit, as described
in Section 3.
28Refit the roadwheel and lower the vehicle
to the ground. Do not fully tighten the
roadwheel bolts until the vehicle is resting on
its wheels.
Models with ventilated discs
Removal
29Proceed as described in paragraphs 1 to 4
inclusive.
30Withdraw the caliper body from the
vehicle.
31If desired, the caliper bracket can be
removed from the hub carrier by unscrewing
the two securing bolts (see illustration).
Overhaul
32To overhaul the caliper, continue as
follows. Otherwise, go on to paragraph 42 for
details of refitting.
33Brush the dirt and dust from the caliper,
but take care not to inhale it.
34Using a screwdriver, carefully prise the
dust seal from the end of the piston and the
caliper body, and remove it.
35Proceed as described in paragraphs 10
to 15 inclusive.
36Begin reassembly by fitting the seal into
the caliper bore.
37Locate the dust seal in its groove in the
piston. Dip the piston in clean brake fluid and
insert it squarely into the cylinder. Check that
the cutaway recesses in the piston are
positioned vertically. If necessary, carefully
turn the piston to its correct position.
38When the piston has been partially
depressed, engage the dust seal with the rim
of the caliper bore.
39Push the piston further into its bore, but
not as far as the stop, ensuring that it does
not jam.
40If desired, the guide bolt sleeves can be
renewed. Extract the nylon compression
sleeve from within each rubber, then carefullycompress the rubber shoulder, and push the
rubber through the hole in the caliper body to
remove it from the inboard end.
41Fit the new sleeves using a reversal of the
removal procedure.
Refitting
42Where applicable, refit the caliper bracket
to the hub carrier, and tighten the securing
bolts to the specified torque.
43Proceed as described in paragraphs 25
to 28 inclusive.
9Rear disc caliper - removal,
overhaul and refitting
3
Note: Refer to the note at the beginning of
Section 3 before proceeding. Before
dismantling a caliper, check that replacement
parts can be obtained, and retain the old
components to compare them with the new
ones
Removal
1Where applicable, remove the wheel trim,
then loosen the relevant rear roadwheel bolts
and check the front wheels. Jack up the rear
of the vehicle, and support on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
Remove the roadwheel.
2Remove the disc pads, as described in
Section 5.
3Working under the bonnet, remove the
brake fluid reservoir cap and secure a piece of
polythene over the filler neck with a rubber
band, or by refitting the cap. This will reduce
the loss of fluid during the following
procedure.
4Unscrew the brake fluid pipe union nut from
the rear of the caliper, and disconnect the
pipe. Take care not to strain the pipe. Be
prepared for fluid spillage, and plug the open
ends to prevent dirt ingress and further fluid
loss.
5Unscrew the two mounting bolts and
withdraw the caliper from the vehicle, noting
that on DOHC models, the caliper securing
bolts also secure the ABS sensor bracket (see
illustrations). Take care not to strain the ABS
sensor wiring, where applicable.
Braking system 9•9
8.31 Caliper bracket securing bolts
(arrowed) - model with ventilated discs8.20B . . . then withdraw the caliper
locating pin rubber - model with
solid discs8.20A Extract the nylon compression
sleeve (arrowed) . . .
9
Page 141 of 525

Overhaul
6If desired, the caliper can be overhauled as
follows. Otherwise, go on to paragraph 20 for
details of refitting.
7Brush the dirt and dust from the caliper, but
take care not to inhale it.
8Note that no attempt must be made to
separate the two halves of the caliper.
9Using a screwdriver, prise the dust seal
retaining clips from the piston dust seals, then
carefully prise off the dust seals.
10Using a clamp, secure one of the pistons
in its fully retracted position. Then apply low
air pressure (e.g. from a foot pump), to the
hydraulic fluid union hole in the rear of the
caliper body, to eject the remaining piston
from its bore. Take care not to drop the
piston, which may result in damage.
11Temporarily close off the bore of the
removed piston, using a flat piece of wood or
similar improvised tool. Then remove the
clamp from the remaining piston, and again
apply air pressure to the caliper union to eject
the piston.
12Carefully prise the seals from the grooves
in the caliper piston bores, using a plastic or
wooden instrument.
13Inspect the surfaces of the pistons and
their bores in the caliper for scoring, or
evidence of metal-to-metal contact. If evident,
renew the complete caliper assembly.
14If the pistons and bores are in good
condition, discard the seals and obtain a
repair kit, which will contain all the necessary
renewable items. Also obtain a tube of brake
cylinder paste.
15Clean the piston and cylinder bore with
brake fluid or methylated spirit - nothing else!
16Apply a little brake cylinder paste to the
pistons, cylinder bores and piston seals.
17Begin reassembly by fitting the seals to
the grooves in the caliper bores.
18Locate the dust seals in their grooves in
the pistons, then insert the pistons carefully
into their bores until they enter the seals. It
may be necessary to rotate the pistons to
prevent them from jamming in the seals.
19When the pistons have been partially
depressed, engage the dust seals with the
rims of the caliper bores, and fit the retaining
clips.
Refitting
20Refit the caliper and tighten the securing
bolts to the specified torque, ensuring that the
ABS sensor bracket is in position, where
applicable.
21Reconnect the brake fluid pipe to the
caliper, and tighten the union nut.
22Refit the disc pads, as described in
Section 5.
23Remove the polythene from the brake
fluid reservoir filler neck and bleed the
relevant brake hydraulic circuit, as described
in Section 3.
24Refit the roadwheel and lower the vehicle
to the ground. Do not fully tighten the
roadwheel bolts until the vehicle is resting on
its wheels.
10Brake disc - inspection,
removal and refitting
3
Inspection
1Where applicable, remove the wheel trim,
then loosen the relevant roadwheel bolts. If
checking a front disc, apply the handbrake,
and if checking a rear disc, chock the front
wheels, then jack up the relevant end of the
vehicle and support on axle stands (see
“Jacking and Vehicle Support”) positioned
under the body side members. Remove the
roadwheel.
2Where applicable, check that the brake disc
securing screw is tight. Then fit a spacer
approximately 10.0 mm (0.4 in) thick to one of
the roadwheel bolts, and refit and tighten the
bolt in the hole opposite the disc securing
screw (see illustration).
3Rotate the brake disc, and examine it for
deep scoring or grooving. Light scoring is
normal, but if excessive, the disc should be
removed and either renewed or machined
(within the specified limits) by an engineering
works.
4Using a dial gauge, or a flat metal block and
feeler blades, check that the disc run-out does
not exceed the figure given in the Specifications.
Measure the run-out 10.0 mm (0.4 in) in from the
outer edge of the disc. 5On all SOHC models, if the rear disc run-
out is excessive, check the rear wheel bearing
adjustment, as described in Chapter 10.
6If the front disc run-out (all models), or the
rear disc run-out (DOHC models), is
excessive, remove the disc as described later
in this Section. Check that the disc-to-hub
surfaces are perfectly clean. Refit the disc and
check the run-out again.
7If the run-out is still excessive, the disc
should be renewed.
8To remove a disc, continue as follows.
Front disc
Removal
9Where applicable, remove the roadwheel
bolt and spacer used when checking the disc.
10Remove the disc pads, (Section 4).
11On 2.0 litre models, unscrew the two
securing bolts and remove the caliper
bracket.
12Remove the securing screw and withdraw
the disc from the hub, where applicable tilting
it to clear the brake caliper (see illustration).
Refitting
13Refitting is a reversal of removal, but
make sure that the mating faces of the disc
and hub are perfectly clean, and apply a little
locking fluid to the threads of the securing
screw. Refit the disc pads, (Section 4).
Rear disc - SOHC models
14On these models, the disc is integral with
the rear hub, and removal and refitting is
described in Chapter 10.
9•10Braking system
9.5A Withdrawing a rear caliper mounting
bolt . . .10.2 Refit a wheel bolt and spacer
(arrowed) opposite the disc securing screw
(A) before checking brake disc run-out
10.12 Removing a disc securing screw -
SOHC model
9.5B . . . which also secures the ABS
sensor bracket - DOHC model
Page 143 of 525
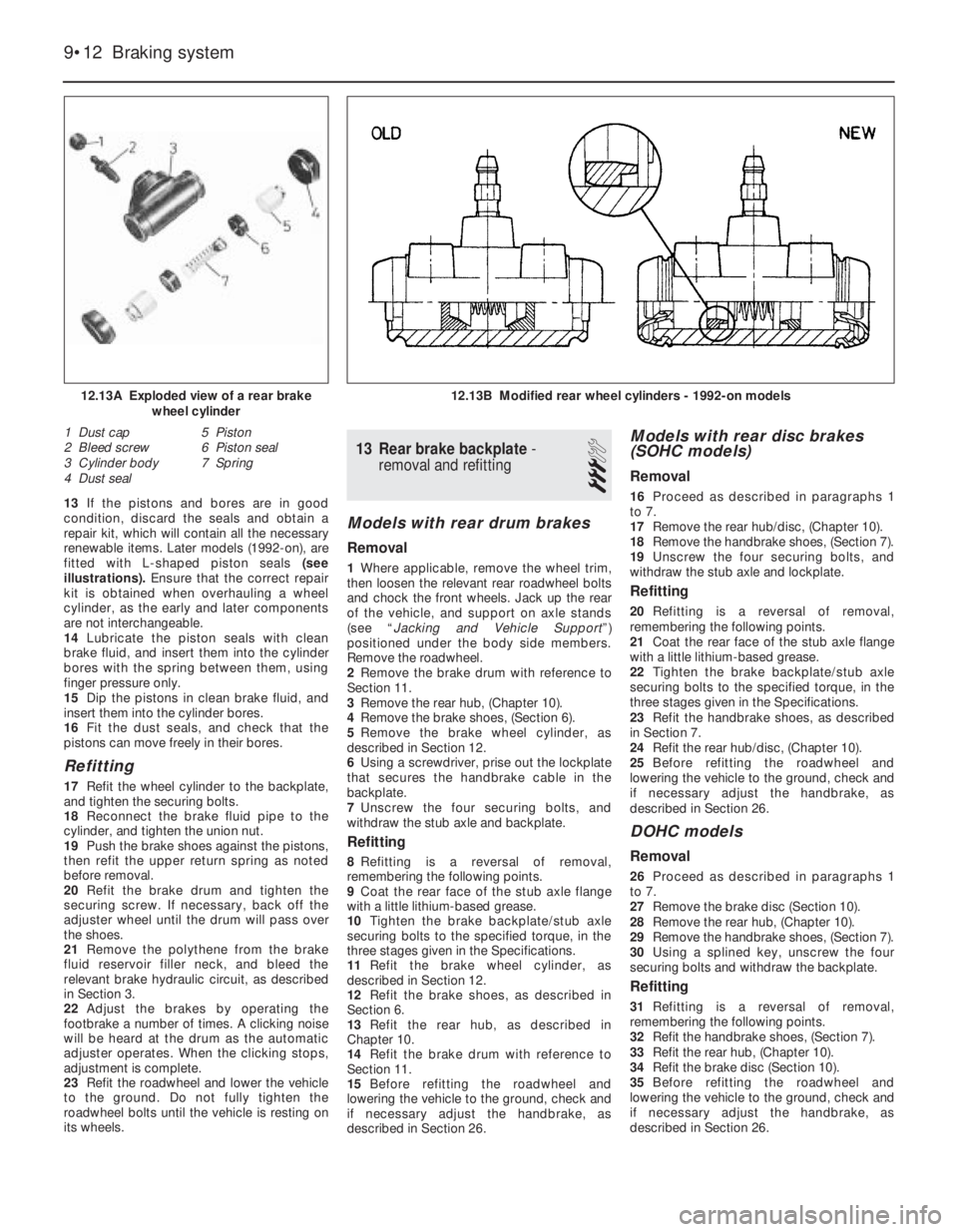
13If the pistons and bores are in good
condition, discard the seals and obtain a
repair kit, which will contain all the necessary
renewable items. Later models (1992-on), are
fitted with L-shaped piston seals (see
illustrations). Ensure that the correct repair
kit is obtained when overhauling a wheel
cylinder, as the early and later components
are not interchangeable.
14Lubricate the piston seals with clean
brake fluid, and insert them into the cylinder
bores with the spring between them, using
finger pressure only.
15Dip the pistons in clean brake fluid, and
insert them into the cylinder bores.
16Fit the dust seals, and check that the
pistons can move freely in their bores.
Refitting
17Refit the wheel cylinder to the backplate,
and tighten the securing bolts.
18Reconnect the brake fluid pipe to the
cylinder, and tighten the union nut.
19Push the brake shoes against the pistons,
then refit the upper return spring as noted
before removal.
20Refit the brake drum and tighten the
securing screw. If necessary, back off the
adjuster wheel until the drum will pass over
the shoes.
21Remove the polythene from the brake
fluid reservoir filler neck, and bleed the
relevant brake hydraulic circuit, as described
in Section 3.
22Adjust the brakes by operating the
footbrake a number of times. A clicking noise
will be heard at the drum as the automatic
adjuster operates. When the clicking stops,
adjustment is complete.
23Refit the roadwheel and lower the vehicle
to the ground. Do not fully tighten the
roadwheel bolts until the vehicle is resting on
its wheels.
13Rear brake backplate -
removal and refitting
3
Models with rear drum brakes
Removal
1Where applicable, remove the wheel trim,
then loosen the relevant rear roadwheel bolts
and chock the front wheels. Jack up the rear
of the vehicle, and support on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
Remove the roadwheel.
2Remove the brake drum with reference to
Section 11.
3Remove the rear hub, (Chapter 10).
4Remove the brake shoes, (Section 6).
5Remove the brake wheel cylinder, as
described in Section 12.
6Using a screwdriver, prise out the lockplate
that secures the handbrake cable in the
backplate.
7Unscrew the four securing bolts, and
withdraw the stub axle and backplate.
Refitting
8Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
9Coat the rear face of the stub axle flange
with a little lithium-based grease.
10Tighten the brake backplate/stub axle
securing bolts to the specified torque, in the
three stages given in the Specifications.
11Refit the brake wheel cylinder, as
described in Section 12.
12Refit the brake shoes, as described in
Section 6.
13Refit the rear hub, as described in
Chapter 10.
14Refit the brake drum with reference to
Section 11.
15Before refitting the roadwheel and
lowering the vehicle to the ground, check and
if necessary adjust the handbrake, as
described in Section 26.
Models with rear disc brakes
(SOHC models)
Removal
16Proceed as described in paragraphs 1
to 7.
17Remove the rear hub/disc, (Chapter 10).
18Remove the handbrake shoes, (Section 7).
19Unscrew the four securing bolts, and
withdraw the stub axle and lockplate.
Refitting
20Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
21Coat the rear face of the stub axle flange
with a little lithium-based grease.
22Tighten the brake backplate/stub axle
securing bolts to the specified torque, in the
three stages given in the Specifications.
23Refit the handbrake shoes, as described
in Section 7.
24Refit the rear hub/disc, (Chapter 10).
25Before refitting the roadwheel and
lowering the vehicle to the ground, check and
if necessary adjust the handbrake, as
described in Section 26.
DOHC models
Removal
26Proceed as described in paragraphs 1
to 7.
27Remove the brake disc (Section 10).
28Remove the rear hub, (Chapter 10).
29Remove the handbrake shoes, (Section 7).
30Using a splined key, unscrew the four
securing bolts and withdraw the backplate.
Refitting
31Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
32Refit the handbrake shoes, (Section 7).
33Refit the rear hub, (Chapter 10).
34Refit the brake disc (Section 10).
35Before refitting the roadwheel and
lowering the vehicle to the ground, check and
if necessary adjust the handbrake, as
described in Section 26.
9•12Braking system
12.13A Exploded view of a rear brake
wheel cylinder
1 Dust cap
2 Bleed screw
3 Cylinder body
4 Dust seal5 Piston
6 Piston seal
7 Spring
12.13B Modified rear wheel cylinders - 1992-on models
Page 144 of 525

14Front brake disc shield -
removal and refitting
3
Removal
1Where applicable, remove the wheel trim,
then loosen the relevant front roadwheel bolts
and apply the handbrake. Jack up the front of
the vehicle, and support on axle stands (see
“Jacking and Vehicle Support”) positioned
under the body side members. Remove the
roadwheel.
2Remove the brake disc, as described in
Section 10.
3Using a screwdriver inserted through the
holes in the hub flange, extract the three
screws securing the disc shield to the hub
carrier.
4Using plate shears or an alternative tool, cut
a section of metal from the rear edge of the
shield to enable the shield to be withdrawn
over the hub, then remove the shield (see
illustration).
Refitting
5If a new shield is to be fitted, cut out a
section of metal, as during removal of the old
shield, to enable the shield to be fitted.
Smooth the cut edges, and coat them with
anti-corrosion paint.
6Further refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
7Refit the brake disc, as described in
Section 10.
8Do not fully tighten the roadwheel bolts until
the vehicle is resting on its wheels.
15Master cylinder - removal and
refitting
4
Note: Refer to the note at the beginning of
Section 3 before proceeding
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Depress the footbrake pedal several times
to dissipate the vacuum in the servo unit.3Disconnect the wiring plug from the brake
fluid level sensor in the reservoir filler cap.
4If possible, use a teat pipette or an old
hydrometer to remove the brake fluid from the
reservoir. This will reduce the loss of fluid later
in the procedure.
5Locate a container beneath the master
cylinder, to catch the brake fluid that will be
released.
6Identify the brake fluid pipes for position,
then unscrew the union nuts and disconnect
the pipes from the master cylinder.
7Unscrew the two securing nuts, and
withdraw the master cylinder from the studs
on the vacuum servo unit (see illustration).
8Clean the external surfaces of the cylinder,
then using a screwdriver carefully prise the
fluid reservoir and its seals from the top of the
cylinder.
9If desired, on models without ABS, the
master cylinder can be overhauled, as
described in Section 16.
10No overhaul of the master cylinder is
possible on models with ABS, see Section 17.
Refitting
11Refitting is a reversal of removal, but use
new seals when fitting the brake fluid
reservoir, and on completion, bleed the
complete brake hydraulic system, as
described in Section 3.
16Master cylinder (non-ABS) -
overhaul
4
Note: Before dismantling the master cylinder,
check that replacement parts can be obtained
and retain the old components to compare
them with the new ones
1With the master cylinder removed as
described in Section 15, continue as follows,
according to type.
GMF type master cylinder
2Clamp the master cylinder in a soft-jawed
vice.
3Where applicable, unscrew the pressure-
proportioning valves from the base of the
cylinder.4Carefully prise out the sealing ring from the
end of the cylinder bore.
5Depress the primary piston slightly using a
piece of wood or plastic. Then hold the piston
in the depressed position by inserting a
smooth pin or rod of 3.0 mm (0.12 in) diameter
through the primary fluid reservoir port in the
cylinder (see illustration).
6Extract the circlip from the end of the
cylinder bore using a screwdriver. Take care
not to damage the piston or cylinder bore.
7Withdraw the pin or rod retaining the piston.
8Withdraw the primary piston assembly from
the cylinder, if necessary tapping the cylinder
on a wooden block to free the piston from the
bore.
9Apply low air pressure - e.g. from a foot
pump - to the front fluid reservoir port in the
cylinder, to eject the secondary piston
assembly.
10Clean all the components, in clean brake
fluid or methylated spirit only, and examine
them for wear and damage. In particular,
check the surfaces of the pistons and cylinder
bore for scoring and corrosion. If the bore
shows signs of wear, renew the complete
master cylinder assembly (see illustration).
11If the cylinder bore is in good condition,
obtain a repair kit, which will contain all the
necessary renewable items. A Vauxhall dealer
will supply a pre-assembled kit of parts, which
should be fitted as follows.
12Lubricate the cylinder bore with clean
brake fluid or brake grease, then clamp the
cylinder in a soft-jawed vice, with the bore
horizontal.
13Remove the plug from the end of the
assembly tube, and insert the short part of the
tube into the cylinder bore as far as the
shoulder on the tube.
14Use a piece of wood or plastic to push the
components out of the tube and into the
cylinder bore. Then hold the primary piston in
the depressed position by inserting the pin or
rod used during dismantling through the
cylinder primary fluid reservoir port.
15Fit a new circlip to the end of the cylinder
bore, ensuring that it seats correctly, and that
the piston is free to move.
16Depress the primary piston, and withdraw
the pin or rod from the fluid reservoir port.
Braking system 9•13
16.5 Holding the primary piston depressed
while extracting the circlip from the
cylinder body - GMF type master cylinder15.7 Master cylinder securing nut
(arrowed)14.4 Cutting a section of metal from a new
front brake disc shield prior to fitting
9
Page 145 of 525
17Fit a new sealing ring to the end of the
cylinder bore.
18Where applicable, screw the pressure-
proportioning valves into the base of the
cylinder.
19Refit the master cylinder, as described in
Section 15.
ATE type master cylinder
20Clamp the master cylinder in a soft-jawed
vice.
21Where applicable, unscrew the pressure-
proportioning valves from the base of the
cylinder.
22Carefully prise out the sealing ring from
the end of the cylinder bore.
23Depress the primary piston slightly using
a piece of wood or plastic, then extract the
circlip from the end of the cylinder bore.
24Withdraw the primary piston assembly,
noting the location of the stop washers.
25Depress the secondary piston, again
using a piece of wood or plastic, and
withdraw the stop screw from the cylinder
body (see illustration).
26Withdraw the secondary piston assembly
from the cylinder, if necessary tapping the
cylinder on a wooden block to free the piston
from the bore.
27Clean all the components, in clean brake
fluid or methylated spirit only, and examine
them for wear and damage. In particular,
check the surfaces of the pistons and cylinder
bores for scoring and corrosion. If the bore
shows signs of wear, renew the complete
master cylinder assembly (see illustration).28If the cylinder bore is in good condition,
obtain a repair kit, which will contain all the
necessary renewable items. A Vauxhall dealer
will supply a complete kit of parts, which
should be fitted as follows.
29Lubricate the cylinder bore with clean
brake fluid or brake grease, then clamp the
cylinder in a soft-jawed vice, with the bore
horizontal.
30Fit a new sealing ring to the stop screw,
then screw it into the cylinder body a little
way, but not so far that it protrudes into the
bore.
31Remove the plugs from the ends of the
assembly tube, then remove all the
components from the short part of the tube,
and push the short part into the long part until
they are flush.
32Insert the assembly tube into the cylinder
bore as far as the collar on the short sleeve.
Then use a piece of wood or plastic to push
the secondary piston assembly into the bore
until it contacts the end of the cylinder.
33Lightly tighten the stop screw, then
withdraw the piece of wood or plastic and the
assembly tube, and fully tighten the stop
screw.
34Reposition the master cylinder in the vice,
with the bore facing upwards.
35Smear the primary piston skirt and the
seal grooves with the special grease provided
in the repair kit. Fit the stop washer to the
piston.
36Adjust the assembly tube so that the end
of the long part is flush with the inner shoulder
of the short part.37Fit the front seal to the primary piston,
with the open end of the seal facing the front
of the master cylinder.
38Place the assembly tube over the cylinder
to compress the seal, insert the piston and
tube part way into the bore, and withdraw the
tube.
39Place the intermediate ring on the primary
piston, then fit the remaining seal using the
assembly tube as described previously.
40Place the stop washer as the primary
piston, then depress the piston slightly using
a piece of wood or plastic, and fit a new circlip
to the end of the cylinder bore. Ensure that the
circlip is correctly seated, and that the piston
is free to move.
41Fit a new sealing ring to the end of the
cylinder bore.
9•14Braking system
16.25 Depressing the secondary piston
while extracting the stop screw - ATE type
master cylinder
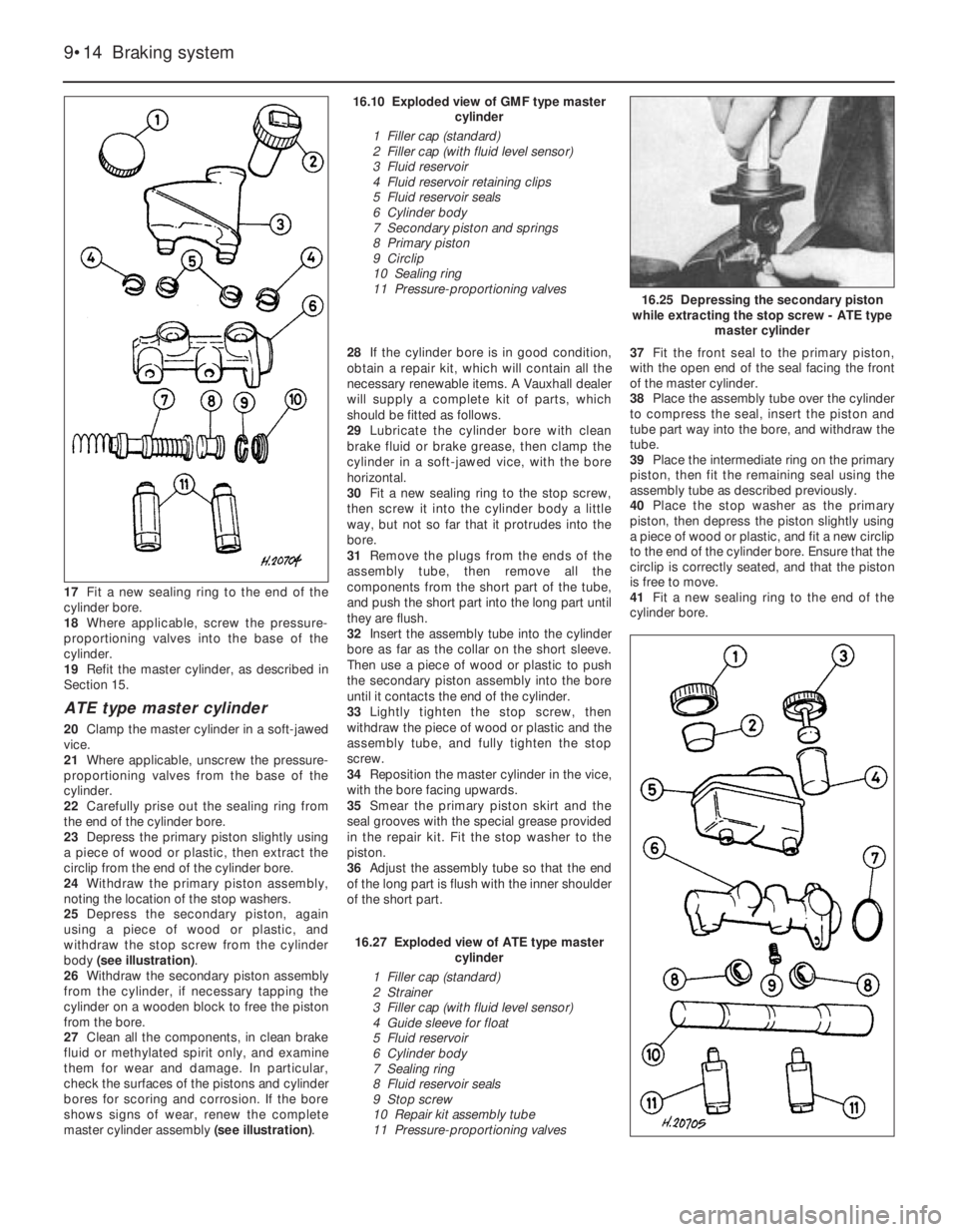
16.27 Exploded view of ATE type master
cylinder
1 Filler cap (standard)
2 Strainer
3 Filler cap (with fluid level sensor)
4 Guide sleeve for float
5 Fluid reservoir
6 Cylinder body
7 Sealing ring
8 Fluid reservoir seals
9 Stop screw
10 Repair kit assembly tube
11 Pressure-proportioning valves
16.10 Exploded view of GMF type master
cylinder
1 Filler cap (standard)
2 Filler cap (with fluid level sensor)
3 Fluid reservoir
4 Fluid reservoir retaining clips
5 Fluid reservoir seals
6 Cylinder body
7 Secondary piston and springs
8 Primary piston
9 Circlip
10 Sealing ring
11 Pressure-proportioning valves
Page 149 of 525

8Disconnect the battery negative lead.
9Unclip the lid and open the relay box, then
pull out the relay (see illustration).
Refitting
10Refitting is a reversal of removal, with
reference to paragraph 6.
24Rear brake pressure-
proportioning valves -
removal and refitting
4
Note: Refer to the note at the beginning of
Section 3 before proceeding. Note also that
the valve must only be renewed in pairs, and
both valves must be of the same calibration.
Ensure that correct type of valves are fitted.
The bodies have been stamped for easier
identification.
Master cylinder-mounted valves
Removal
1Remove the brake fluid reservoir cap, and
secure a piece of polythene over the filler
neck with a rubber band, or by refitting the
cap. This will reduce the loss of fluid during
the following procedure.
2Locate a container beneath the master
cylinder, to catch the brake fluid that will be
released.
3Identify the two lower brake pipes for
position, then unscrew the union nuts and
disconnect the pipes from the proportioning
valves in the base of the master cylinder. Plug
the open ends of the pipes to prevent dirt
ingress.
4Unscrew the proportioning valves from the
master cylinder, and plug the open ends of
the cylinder to prevent dirt ingress.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal, but on
completion, remove the polythene from the
brake fluid reservoir filler neck, and bleed the
complete hydraulic system, as described in
Section 3.
Rear underbody-mounted valves
Removal
6Proceed as described in paragraph 1.
7Chock the front wheels, then jack up the
rear of the vehicle, and support securely on
axle stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle
Support”) positioned under the body side
members.
8Working under the rear of the vehicle,
unscrew the union nut and disconnect the
brake pipe from one of the valves. Be
prepared for fluid spillage, and plug the open
end of the pipe to prevent dirt ingress and
further fluid spillage.
9Similarly, disconnect the flexible hose from
the valve.
10Pull the valve retaining clip from the
bracket on the underbody, noting that on
certain models, the retaining clip also secures
the ABS sensor wiring, and withdraw the valve
(see illustration).
11Repeat the procedure for the other valve.
Refitting
12Proceed as described in paragraph 5.
25Brake fluid pipes and hoses
- general, removal and refitting
4
Note: Refer to the note at the beginning of
Section 3, before proceeding.
General
1When checking the condition of the
system’s pipes and/or hoses, carefully check
that they do not foul other components such
as the power steering gear pipes (where
applicable), so that there is no risk of the
pipes chafing. If necessary use clips or ties to
secure braking system pipes and hoses well
clear of other components.
Rigid pipes
Removal
2Some of the commonly used brake pipes
can be obtained from Vauxhall parts dealers,
ready-formed and complete with unions, but
other brake pipes must be prepared using
4.75 mm (0.19 in) diameter brake pipe. Kits for
making the brake pipes can be obtained from
certain motor accessory shops.
3Before removing a brake pipe, remove the
brake fluid reservoir cap, and secure a piece
of polythene over the filler neck with a rubber
band, or by refitting the cap. This will reduce
the loss of fluid when the pipe is
disconnected.4Jack up the vehicle, and support securely
on axle stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle
Support”) positioned under the body side
members.
5To remove a brake pipe, unscrew the
unions at each end, and release the pipe from
the retaining clips.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal, taking
care not to overtighten the unions.
7On completion, remove the polythene from
the brake fluid reservoir filler neck, and bleed
the relevant hydraulic circuit(s), as described
in Section 3.
Flexible hoses
Removal
8Proceed as described previously for the
rigid pipes, but note that a flexible pipe must
never be installed twisted, although a slight
“set” is permissible to give it clearance from
adjacent components.
Refitting
9When reconnecting a flexible hose to a
front brake caliper, note that the sealing rings
on the union bolt must be renewed.
26Handbrake - adjustment
2
Models with rear drum brakes
1The handbrake will normally be kept in
correct adjustment by the self-adjusting
action of the rear brake shoes. However, due
to cable stretch over a period of time, the
travel of the handbrake lever may become
excessive, in which case the following
operations should be carried out.
2Chock the front wheels, jack up the rear of
the vehicle, and support securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
3Fully release the handbrake.
4Turn the knurled nut on the cable adjuster
(mounted on the torsion beam), until the brake
shoes can just be heard to rub when the rear
wheels are turned by hand in the normal
direction of rotation (see illustration).
9•18Braking system
23.9 ABS surge arrester relay (arrowed)
26.4 Handbrake cable adjuster. Knurled
nut arrowed - all SOHC models24.10 Brake pressure-proportioning valve
on rear underbody - DOHC model
1 Valve 2 Retaining clip
Page 156 of 525

4B
cruising and accelerating. The injector earth is
also switched off on the overrun to improve
fuel economy and reduce exhaust emissions.
Additionally, on the X16 SZ engine, the ECU
also controls the operation of the charcoal
canister purge valve in the evaporative
emission control system.
10The oxygen sensor screwed into the
exhaust manifold provides the ECU with a
constant feedback signal. This enables it to
adjust the mixture (closed-loop control) to
provide the best possible conditions for the
catalytic converter to operate effectively.
11Until the oxygen sensor is fully warmed up
it gives no feedback so the ECU uses
pre-programmed values (open-loop control) to
determine the correct injector pulse width.
When the sensor reaches its normal operating
temperature, its tip (which is sensitive to
oxygen) sends the ECU a varying voltage
depending on the amount of oxygen in the
exhaust gases. If the inlet air/fuel mixture is too
rich, the exhaust gases are low in oxygen so the
sensor sends a low-voltage signal. The voltage
rises as the mixture weakens and the amount of
oxygen rises in the exhaust gases. Peak
conversion efficiency of all major pollutants
occurs if the inlet air/fuel mixture is maintained
at the chemically correct ratio for the complete
combustion of petrol of 14.7 parts (by weight) of
air to 1 part of fuel (the “stoichiometric” ratio).
The sensor output voltage alters in a large step
at this point, the ECU using the signal change
as a reference point and correcting the inlet
air/fuel mixture accordingly by altering the fuel
injector pulse width.
12In addition, the ECU senses battery
voltage, incorporates diagnostic capabilities,
and can both receive and transmit information
by way of the diagnostic connector, thus
permitting engine diagnosis and tuning by
Vauxhall’s TECH1, test equipment.
Motronic system
13The Motronic type is available in several
different versions, depending on model. The
system is under the overall control of the
Motronic engine management system (Chapter
5), which also controls the ignition timing.
14Fuel is supplied from the rear-mounted
fuel tank by an electric fuel pump mounted
under the rear of the vehicle, through a
pressure regulator, to the fuel rail. The fuel rail
acts as a reservoir for the four fuel injectors,
which inject fuel into the cylinder inlet tracts,
upstream of the inlet valves. On SOHC
engines, the fuel injectors receive an electrical
pulse once per crankshaft revolution, which
operates all four injectors simultaneously. On
DOHC engines, sequential fuel injection is
used, whereby each injector receives an
individual electrical pulse allowing the four
injectors to operate independently, which
enables finer control of the fuel supply to each
cylinder. The duration of the electrical pulse
determines the quantity of fuel-injected, and
pulse duration is computed by the Motronic
module, based on the information received
from the various sensors.15On SOHC engines, inlet air passes from
the air cleaner through a vane type airflow
meter, before passing to the cylinder inlet
tracts through the throttle valve. A flap in the
vane airflow meter is deflected in proportion
to the airflow; this deflection is converted into
an electrical signal, and passed to the
Motronic module. A potentiometer screw
located on the airflow meter provides the
means of idle mixture adjustment, by altering
the reference voltage supplied to the Motronic
module.
16On DOHC engines, inlet air passes from
the air cleaner through a hot wire type air
mass meter, before passing to the cylinder
inlet tracts through a two-stage throttle body
assembly. The electrical current required to
maintain the temperature of the hot wire in the
air mass meter is directly proportional to the
mass flow rate of the air trying to cool it. The
current is converted into a signal, which is
passed to the Motronic module. The throttle
body contains two throttle valves that open
progressively, allowing high torque at part
throttle, and full-throttle, high-speed
“breathing” capacity. A potentiometer screw
located on the air mass meter provides the
means of idle mixture adjustment, by altering
the reference voltage supplied to the Motronic
module.
17A throttle position sensor enables the
Motronic module to compute the throttle
position, and on certain models, its rate of
change. Extra fuel can thus be provided for
acceleration when the throttle is opened
suddenly. Information from the throttle
position sensor is also used to cut off the fuel
supply on the overrun, thus improving fuel
economy and reducing exhaust gas
emissions.
18Idle speed is controlled by a variable-
orifice solenoid valve, which regulates the
amount of air bypassing the throttle valve. The
valve is controlled by the Motronic module;
there is no provision for direct adjustment of
the idle speed.
19Additional sensors inform the Motronic
module of engine coolant temperature, air
temperature, and on models fitted with a
catalytic converter, exhaust gas oxygen
content.
20A fuel filter is incorporated in the fuel
supply line, to ensure that the fuel supplied to
the injectors is clean.
21A fuel pump cut-off relay is controlled by
the Motronic module, which cuts the power to
the fuel pump should the engine stop with the
ignition switched on, if there is an accident. All
1993-onwards models equipped with
Motronic systems, have their fuel pump
located inside the fuel tank.
22The later M2.8 system is basically the
same as the earlier M2.5 system apart from
the following:
a)Hot Film Mass Airflow Meter - The hot
wire type unit used previously is replaced
on the M2.8 system by a hot film mass
airflow meter. The operation is the sameexcept that a thin, electrically heated plate
rather than a wire is used. The plate is
maintained at a constant temperature by
electric current as the inlet air mass
passing over the plate tries to cool it. The
current required to maintain the
temperature of the plate is directly
proportional to the mass flow rate of the
inlet air. The current is converted to a
signal that is passed to the Motronic
module.
b)Inlet Air Temperature Sensor -The sensor
is located in the hose between the hot
film mass airflow meter and the air cleaner
for precise monitoring of inlet air
temperature. Signals from the sensor are
used in conjunction with other sensors to
indicate the occurrence of a hot start
condition. The Motronic module then
interprets these signals to alter injector
duration accordingly.
c)Throttle Valve Potentiometer -On the
M2.8 system a throttle valve
potentiometer replaces the throttle valve
switch used previously.
Simtec system
23An increased amount of electronic
components are used instead of mechanical
parts as sensors and actuators with the
Simtec engine management system. This
provides more precise operating data as well
as greater problem free motoring.
24The control unit is equipped with
electronic ignition control. Called ‘Micropro-
cessor Spark Timing System, inductive
triggered’, (or MSTS-i), and means that the
mechanical high voltage distributor is no
longer needed. It is located behind the trim
panel, on the right-hand side footwell (door
pillar).
25The ignition coil is replaced by a dual
spark ignition coil, which is switched directly
by the output stages in the control unit.
26A camshaft sensor will maintain
emergency operation, should the crankshaft
inductive pulse pick-up, malfunction. These
sense TDC (‘Top Dead Centre’), crankshaft
angle and engine speed. The signals are used
by the control unit to calculate ignition point
and for fuel injection.
27The ‘hot film airflow meter’ determines the
mass of air taken in by the engine. The system
uses this information to calculate the correct
amount of fuel needed for injection in the
engine.
28The air inlet temperature sensor (NTC), is
fitted in the air inlet duct between the air
cleaner and the hot mass air flow meter.
29A controlled canister purge valve is
actuated by the system. The tank ventilation is
monitored closely with the Lambda control (or
oxygen sensor) and adaptation by the
computer within the control unit.
30A knock control system is also fitted. This
eliminates the need for octane number
adjustment, as it is performed automatically
through the control unit.
Fuel and exhaust systems - fuel injection models 4B•3