1988 OPEL CALIBRA checking oil
[x] Cancel search: checking oilPage 69 of 525

Wiring diagrams 12•55
12
Key to wiring diagrams for 1992 and later models
NoDescriptionTrackNoDescriptionTrack
E1Left parking lamp506
E2Left tail lamp507, 745
E3Licence plate lamp513
E4Right parking lamp509
E5Right tail lamp510, 746
E6Engine compartment lamp515
E7Left high beam 535
E8Right high beam536
E9Left low beam537, 747
E10Right low beam538, 748
E11Instrument lights728, 729
E12Selector lever lamp 498, 499
E13Boot lamp585
E14Passenger compartment lamp587
E15Glove box lamp677
E16Cigarette lighter lamp676
E17Left reversing lamp597
E18Right reversing lamp598
E19Heated back window652
E20Left fog lamp553
E21Right fog lamp554
E24Left rear fog lamp548
E25Left front heating mat660
E27Left rear reading lamp680, 681
E28Right rear reading lamp683, 684
E30Right front heating mat664
E32Clock lamp863
E37Left mirror make-up lamp686
E38Computer lamp854
E39Right rear foglamp549
E40Right mirror make-up lamp688
E41Passenger compartment delay lamp 588 to 590
E50Driver door lamp866
E51Passenger door lamp884
F1 onFusesVarious
F35Voltage stabilizer702
G1Battery101
G2Alternator114
G6Diesel alternator 402 to 405
H1Radio784 to 798
H3Turn signal lamp telltale716, 718
H4Oil pressure telltale710
H5Brake fluid telltale712
H6Telltale hazard warning system570
H7Charging indicator lamp710
H8High beam telltale722
H9Left stop lamp561, 749
H10Right stop lamp562, 750
H11Left front turn signal lamp572
H12Left rear turn signal lamp573
H13Right front turn signal lamp581
H14Right rear turn signal lamp582
H15Fuel telltale705, 706
H16Preheating time telltale715
H17Trailer turn signal lamp telltale717
H18Horn670
H19Headlamps on warning buzzer594, 595
H21Parking brake telltale713
H23Airbag telltale719
H25Heated back window & mirror telltale642, 765
H26ABS telltale721
H27Safety checking warning buzzer996 to 998
H28Seat belt warning telltale723
H30Engine telltale724H33Left auxiliary turn signal lamp576
H34Right auxiliary turn signal lamp578
H36Additional stop lamp563
H37Left front loudspeaker788 to 790
H38Right front loudspeaker794 to 796
H39Left rear loudspeaker788, 789
H40Right rear loudspeaker791, 792
H42Automatic program power telltale725
H45Four wheel drive telltale727
H46Catalytic converter temperature telltale729
H47Anti-theft warning unit horn838
H48Horn671
H51Traction control telltale720
H52Left front tweeter787 to 791
H53Right front tweeter793 to 797
K3Starter relay anti-theft warning unit109, 110
K5Fog lamps relay554 to 555
K6Air conditioning relay901, 902
K7Four stage air conditioning blower relay904, 905
K8Windshield wiper interval relay603 to 606
K9Headlamps washer unit relay619, 620
K10Flasher unit567 to 569
K20Ignition coil module149, 150, 171, 172, 241, 242, 302 to 305,
361 to 364, 1001 to 1005, 1055 to 1061
K22Coolant pump relay133, 134, 969, 970
K25Glow time relay440 to 443
K26Radiator blower relays972 to 974
K27Radiator blower relay137 to 139
K30Back window wiper interval relay613 to 615
K31Airbag control unit1191 to 1198
K34Radiator blower time delay relay356 to 358, 956 to 958
K35Heated back window & mirror time delay relay650 to 652
K37Central locking control unit805 to 812
K51Radiator blower relay430, 431, 942, 943, 956, 957
K52Radiator blower relay145 to 147, 433,435,
982 to 984, 960 to 962
K57Multec unit control211 to 230, 244 to 262
K58Fuel pump relay231, 232, 262, 263
K59Running light relay520 to 525
K60Compressor relay931,932
K61Motronic control unit270 to 294, 307 to 337,
366 to 396, 1007 to 1037, 1063 to 1096
K63Horn relay671, 672
K641 stage air conditioning blower relay913, 914
K67Radiator blower relay142, 143, 436, 437, 948,
949, 964, 965, 986, 987
K68Fuel injection unit relay295 to 299, 393 to 397,
334 to 338, 1093 to 1097, 1034 to 1038
K73High beam relay (Calibra)530, 531
K76Glow time control unit413 to 417
K77Glow plugs relay419, 420
K78Preresistor relay (70A)422, 423
K79Charge indicator relay406 to 408
K80Filter heating relay426, 427, 452, 453
K82Engine revolution relay447, 448
K83Four wheel drive unit control342 to 349
K84EZ Plus control unit155 to 166, 177 to 191
K85Automatic transmission control unit473 to 496
K86Check control unit736 to 752
K87Radiator blower relay945, 946, 953, 954, 977, 978
K88Catalytic converter temperature control unit462 to 464
K89Rear fog lamp relay543 to 545
K90Compressor relay (automatic transmission only)930, 931
K94Anti-theft warning unit control unit833 to 847
Page 88 of 525
5
System type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 volt, negative earth
Battery capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36, 44, 55 or 66 Ah
Alternator
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bosch or Delco-Remy
Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55 or 70 A, depending upon model
Minimum brush length:
Bosch type alternator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.0 mm protrusion
Delco-Remy type alternator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.0 mm overall length
Starter motor
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pre-engaged, Bosch or Delco-Remy
Minimum brush length:
Bosch DF type starter motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11.5 mm
Bosch DM type starter motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 mm
Bosch DW type starter motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.5 mm
Delco-Remy type starter motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.0 mm
System type
14 NV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . HEI (High Energy Ignition) system
16 SV and 18 SV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . MSTS-i (Microprocessor Spark Timing System)
C16 NZ, C16 NZ2 and C18 NZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Multec, with MSTS-i
X16 SZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Multec, with DIS (Direct Ignition System)
20 NE, C20 NE and 20 SEH, (up to 1990) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motronic M4.1
20 NE, C20 NE and 20 SEH, (from 1990) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motronic M1.5
20 XEJ and C20 XE, (up to 1993) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motronic M2.5
C20 XE (from 1993) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motronic M2.8
X20 XEV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Simtec 56.1
Coil
Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16.0 to 20.0 kilovolts
Primary winding resistance (DOHC models only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.2 to 0.34 ohms
Secondary winding resistance (DOHC models only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.2 to 8.2 ohms
Chapter 5
Engine electrical systems
Alternator - description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Alternator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Alternator - testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Alternator brushes - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Alternator drivebelt - removal, refitting and adjusting . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Battery - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Battery - testing and charging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Camshaft phase sensor (C20 XE engine) - removal and refitting . . . .27
DIS module - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Distributor - dismantling, inspection and reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Distributor (DOHC models) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Distributor (SOHC models) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Distributor cap and rotor arm - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Electrical system - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1Electrical system - precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Electronic modules - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Ignition coil - removal, testing and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Ignition system - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Ignition system testing - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Ignition timing - adjustment for use with unleaded petrol . . . . . . . . .22
Ignition timing - checking and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Motronic system components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . .25
MSTS-i components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Starter motor - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Starter motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Starter motor - overhaul . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Starter motor - testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
5•1
Specifications Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
Page 91 of 525

28The system also incorporates a separate
ignition amplifier module that transmits
amplified signals from the main system
module to trigger the HT pulse from the
ignition coil. The module is mounted on the
ignition coil’s bracket/baseplate.
29Additionally, the Motronic module
receives information from a cylinder
block-mounted knock sensor, which senses
“knocking” (or pre-ignition) just as it begins to
occur, enabling the module to retard the
ignition timing, thus preventing engine
damage.
Simtec 56.1
30This system uses increased amount of
electronic components instead of mechanical
parts as sensors and actuators with the
Simtec engine management system. This
provides more precise operating data as well
as greater problem free motoring.
31The control unit is equipped with
electronic ignition control. Called ‘Micropro-
cessor Spark Timing System, inductive
triggered’, (or MSTS-i), and means that the
mechanical high voltage distributor is no
longer needed. It is located behind the trim
panel, on the right-hand side footwell (door
pillar).
32The ignition coil is replaced by a dual
spark ignition coil, which is switched directly
by the output stages in the control unit.
33A camshaft sensor will maintain
emergency operation, should the crankshaft
inductive pulse pick-up, malfunction. These
sense TDC (‘Top Dead Centre’), crankshaft
angle and engine speed. The signals are used
by the control unit to calculate ignition point
and for fuel injection.
34The ‘hot film airflow meter’ determines the
mass of air taken in by the engine. The system
uses this information to calculate the correct
amount of fuel needed for injection in the
engine.
35The air inlet temperature sensor (NTC), is
fitted in the air inlet duct between the air
cleaner and the hot mass air flow meter.
36A controlled canister purge valve is
actuated by the system. The tank ventilation is
monitored closely with the Lambda control (or
oxygen sensor) and adaptation by the
computer within the control unit.
37A knock control system is also fitted. This
eliminates the need for octane number
adjustment, as it is performed automatically
through the control unit.
3Electrical system -
precautions
1It is necessary to take extra care when
working on the electrical system, to avoid
damage to semi-conductor devices (diodes
and transistors), and to avoid the risk of
personal injury. Along with the precautions
given in the “Safety first!” Section at the
beginning of this manual, take note of the
following points when working on the system.
2Always remove rings, watches, etc. before
working on the electrical system. Even with
the battery disconnected, discharge could
occur if a component live terminal is earthed
through a metal object. This could cause a
shock or nasty burn.
3Do not reverse the battery connections.
Components such as the alternator, or any
other component having semi-conductor
circuitry, could be irreparably damaged.
4If the engine is being started using jump
leads and a slave battery, connect the
batteries positive to positive and negative to
negative. This also applies when connecting a
battery charger.
5Never disconnect the battery terminals, or
alternator multi-plug connector, when the
engine is running.
6The battery leads and alternator wiring
must be disconnected before carrying out any
electric welding on the vehicle.
7Never use an ohmmeter of the type
incorporating a hand-cranked generator for
circuit or continuity testing.
8Engine management modules are very
sensitive components, and certain
precautions must be taken, to avoid damage
to the module when working on a vehicle
equipped with an engine management
system, as follows.
9When carrying out welding operations on
the vehicle using electric welding equipment,
the battery and alternator should be
disconnected.
10Although underbonnet-mounted modules
will tolerate normal underbonnet conditions,
they can be adversely affected by excess heat
or moisture. If using welding equipment or
pressure washing equipment near the
module, take care not to direct heat, or jets of
water or steam, at the module. If this cannot
be avoided, remove the module from the
vehicle, and protect its wiring plug with a
plastic bag.
11Before disconnecting any wiring, or
removing components, always ensure that the
ignition is switched off.
12Do not attempt to improvise fault
diagnosis procedures using a test lamp or
multimeter, as irreparable damage could be
caused to the module.13After working on ignition/engine
management system components, ensure
that all wiring is correctly reconnected before
reconnecting the battery or switching on the
ignition.
14Any ignition system that uses a
“Hall-effect” generator in the distributor,
cannot be tested. Test equipment that uses
its own power source (e.g. an ohmmeter),
when connected to the distributor or the
“Hall-effect” generator, will be damaged.
4Ignition system testing -
general
3
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding.
Always switch off the ignition before
disconnecting or connecting any component
and when using a multi-meter to check
resistances. Any voltmeter or multi-meter
used to test ignition system components must
have an impedance of 10 meg ohms or
greater
1Electronic ignition system components are
normally very reliable. Most faults are far more
likely to be due to loose or dirty connections,
or to “tracking” of HT voltage due to dirt,
dampness or damaged insulation than to
component failure. Always check all wiring
thoroughly before condemning an electrical
component and work methodically to
eliminate all other possibilities before deciding
that a particular component is faulty.
2The old practice of checking for a spark by
holding the live end of a HT lead a short
distance away from the engine is not
recommended. Not only is there a high risk of
a powerful electric shock, but the ignition coil
or amplifier module will be damaged.
Similarly, never try to “diagnose” misfires by
pulling off one HT lead at a time. Note also
that the ECU is at risk if the system is
triggered with an open (i.e., not properly
earthed) HT circuit; ECU’s are very expensive
to replace, so take care!
3If you are in any doubt as to your skill and
ability to test an ignition system component or
if you do not have the required equipment,
take the vehicle to a suitably equipped
Vauxhall dealer. It is better to pay the labour
charges involved in having the vehicle
checked by an expert than to risk damage to
the system or to yourself.
4If the engine either will not turn over at all,
or only turns very slowly, check the battery
and starter motor. Connect a voltmeter across
the battery terminals (meter positive probe to
battery positive terminal) and disconnect the
ignition coil HT lead from the distributor cap
and earth. Note the voltage reading obtained
while turning over the engine on the starter for
(no more than) ten seconds. If the reading
obtained is less than approximately 9.5 volts,
check the battery, battery connections, starter
motor and charging system.
5•4Engine electrical systems
Warning: The HT voltage
generated by an electronic
ignition system is extremely
high and, in certain
circumstances, could prove fatal. Take
care to avoid receiving electric shocks
from the HT side of the ignition system.
Do not handle HT leads, or touch the
distributor or coil, when the engine is
running. If tracing faults in the HT circuit,
use well-insulated tools to manipulate live
leads
Page 100 of 525
Inspection
17Examine the distributor cap and rotor arm,
as described in paragraphs 6 and 7. Examine
the O-rings at the rear of the distributor body,
and on the rear of the shaft, and renew if
necessary.
Reassembly
18Reassembly is a reversal of dismantling,
ensuring that the thrustwashers are correctly
located. Note that the drive collar should be
refitted so that the drive peg on the collar is
aligned with the groove in the top of the
distributor shaft (it is possible to fit the drive
collar 180°out of position).
19Refit the distributor as described in
Section 18, and then check and if necessary
adjust the ignition timing, as described in
Section 21.
DOHC models (where
applicable)
20The distributor cap and rotor arm can be
examined as described in paragraphs 6 and 7.
21Ignition timing -checking and
adjustment
4
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding. A
tachometer and a timing light will be required
during this procedure. For details of ignition
timing adjustment required to operate vehicles
on unleaded petrol, refer to Section 22.
14 NV and 16 SV models
Checking
1Start the engine and run it until it reaches
normal operating temperature, then switch
off.
2On 14 NV models, disconnect the vacuum
pipe from the distributor vacuum diaphragm
unit.
3On all models use a spanner applied to the
crankshaft pulley bolt to rotate the crankshaft
clockwise until the notch in the pulley’s
inboard rim aligns with the pointer protruding
from the oil pump housing. On 14 NV models,
where two notches (indicating 10°and 5°
BTDC respectively) are found, rotate the
crankshaft until the second notch (in thedirection of rotation -i.e. 5°BTDC) aligns. Use
white paint or similar to emphasise the pointer
and notch, to make them easier to see.
4Connect a timing light to No 1 cylinder
(nearest the timing belt end of the engine) HT
lead, also a tachometer; follow the equipment
manufacturer’s instructions for connection.
5Start the engine and allow it to idle -the
speed should be between 700 and 1000 rpm.
6On 14 NV models, aim the timing light at the
pointer and check that it is aligned with the
crankshaft pulley notch.
7On early 16 SV models, disconnect the
ignition timing basic adjustment coding plug.
This can be identified by a length of Black
wire joining Brown/Red and Brown/Yellow
wires in a connector plug clipped to the wiring
or heater/cooling system hoses beneath the
battery/ignition coil (see illustration, 16.1). This
causes the MSTS-i module to adopt its basic
adjustment mode, sending a constant firing
signal corresponding to 10°BTDC and
eliminating any advance below 2000 rpm. Aim
the timing light at the pointer and check that it
is aligned with the crankshaft pulley notch.
8On later 16 SV, C 16 NZ and C 16 NZ2
models, the coding plugs are no longer fitted.
For accurate checking, special Vauxhall test
equipment must be used which causes the
MSTS module to adopt its basic adjustment
mode.
9Without access to such equipment, it is
possible to check and adjust the ignition
timing, accurate results cannot be
guaranteed. Owners are therefore advised to
have this work carried out by a suitably
equipped Vauxhall dealer; at the very least,
make the initial setting yourself and then have
it checked as soon as possible.
10If you do attempt to check the ignition
timing yourself, note that the fixed reference
mark is now an extended line embossed on
the timing belt lower outer cover.
Adjustment
11If the notch and pointer are not aligned,
loosen the distributor clamp nut and turn the
distributor body slightly in the required
direction to align.
12Tighten the distributor clamp nut, and
check that the notch and pointer are still
aligned. 13Stop the engine, and disconnect the
timing light and tachometer.
14On 16 SV models, reconnect the basic
adjustment coding plug. On 14 NV models,
reconnect the vacuum pipe to the distributor
vacuum diaphragm unit.
Other models
15No adjustment of the ignition timing is
possible on 1.8 and 2.0 litre models, as the
adjustment is carried out automatically by the
electronic control module.
16The ignition timing can be checked by a
Vauxhall dealer using specialist dedicated test
equipment, if a fault is suspected.
22Ignition timing -adjustment
for use with unleaded petrol
3
14 NV models
1All models with the 14 NV engine have the
ignition timing adjusted for use with 95 RON
unleaded petrol before they leave the factory,
and no further adjustment is required.
2Leaded petrol (98 RON) can be used if
desired, with no adverse effects.
1.6, 1.8 and 2.0 SOHC models
Note: Models equipped with a catalytic
converter must be operated on 95 R0N
unleaded petrol at all times, and although an
octane coding plug may be fitted, it should
not be tampered with
3Models, other than 14 NV, are equipped
with an octane coding plug, which is located
Engine electrical systems 5•13
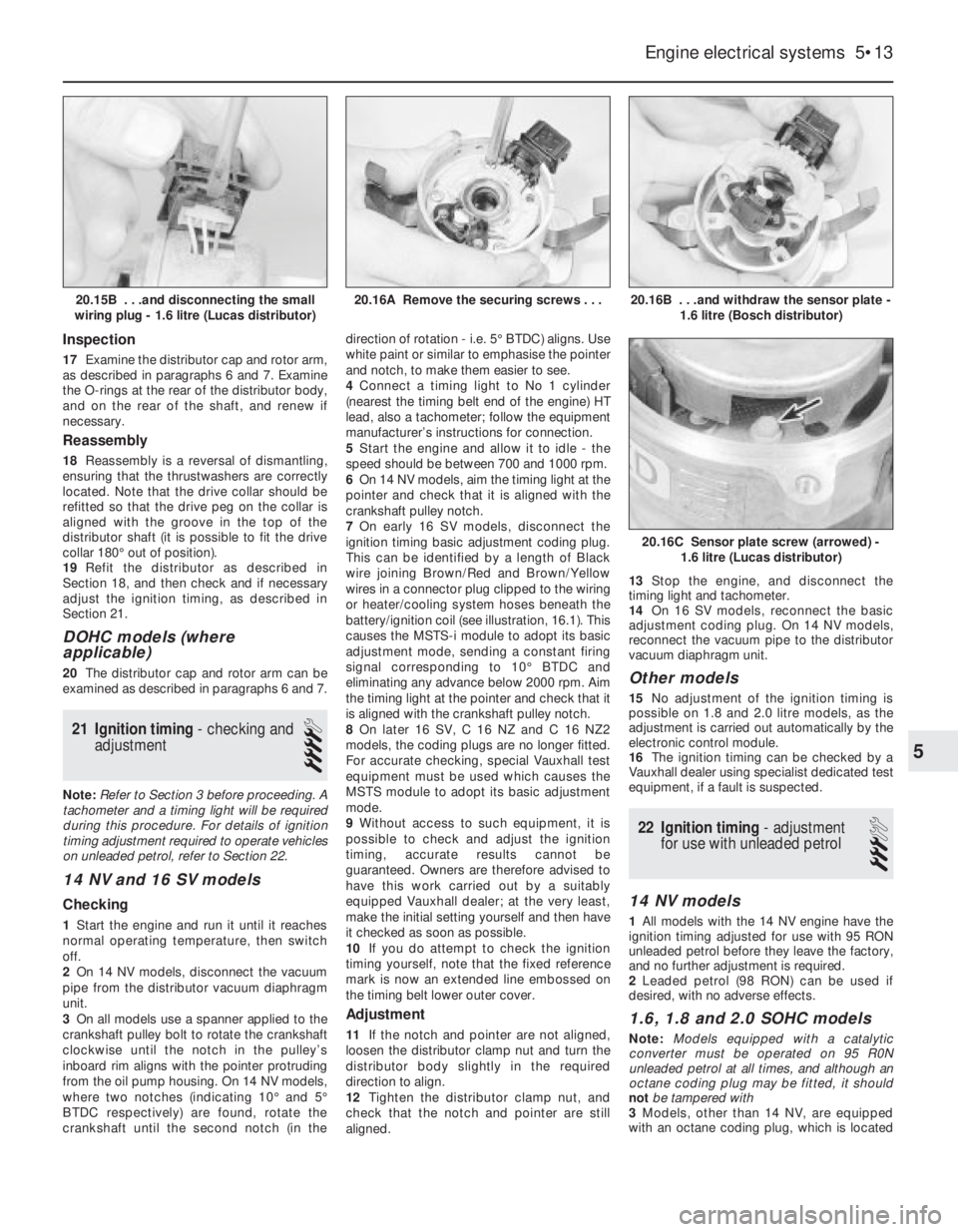
20.16B . . .and withdraw the sensor plate -
1.6 litre (Bosch distributor)
20.16C Sensor plate screw (arrowed) -
1.6 litre (Lucas distributor)
20.16A Remove the securing screws . . .20.15B . . .and disconnecting the small
wiring plug - 1.6 litre (Lucas distributor)
5
Page 127 of 525

2Exhaust gas recirculation
(EGR) system - general
The system reintroduces small amounts of
exhaust gas into the combustion cycle to
reduce the generation of oxides of nitrogen
(NOx).
On C16 NZ, C16 NZ2 and C18 NZ engines,
the volume of exhaust gas reintroduced is
governed by manifold vacuum, through the
EGR valve mounted on the inlet manifold.
When the valve is opened small amounts of
exhaust gas are allowed to enter the inlet
tract, passing through ports in the cylinder
head.
On X16 SZ engines the EGR valve is
operated by an EGR module, mounted on the
left-hand side of the engine compartment
behind the battery. This module amplifies
signals received from the fuel system ECU
and operates the EGR valve electronically
providing precise control of exhaust gas
recirculation under all engine conditions.
3EGR valve (Multec system
models) - testing, removal and
refitting
2
Testing
1On C16 NZ, C16 NZ2 and C18 NZ engines,
it is recommended that the system is checked
annually, by checking the movement of the
valve’s diaphragm carrier plate as follows.
Note that the carrier plate is visible only
through the apertures in the underside of the
valve, so a battery-operated torch and small
mirror may be useful. On X16 SZ engines,
Vauxhall test equipment is necessary to check
the EGR system.
2With the engine fully warmed up to normal
operating temperature and idling, briefly open
and close the throttle. The carrier plate should
move upwards as the manifold vacuum
changes. When the engine is idling smoothly
again, press the carrier plate upwards (do this
very carefully, so that the plate is not distorted or
the diaphragm damaged). The idle speed should
drop significantly (approximately 100 rpm).
3If the valve does not respond as described,
it must be cleaned.
Removal
4Pull off the hose from the valve, then unbolt
the valve and remove it (see illustrations).
Clean away all carbon using a wire brush and
a pointed tool, but take care not to damage
the valve seat. Renew the valve gasket to
prevent induction leaks.
Refitting
5Refit the valve and reconnect the hose,
then recheck the system’s performance; if
there is no improvement, the valve must be
renewed.
4EGR valve (Simtec system) -
testing, removal and refitting
3
Note: A new gasket will be required when
refitting the valve.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove wiring harness and vacuum hose.
3Mark position of the valve, to ensure
correct relocation.
4Undo the 3 bolts, and remove the valve
from the dual spark ignition coil’s coolant
flange.
Refitting
5Clean the sealing surfaces of the valve and
flange.
6Refit the valve with a new gasket and line
up the marks made before removal (see
illustration).
5EGR module (X16 SZ
models) - removal and
refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the knock module from its
bracket (refer to Chapter 4B, if necessary),
and place to one side.
2Remove wiring plug from module. Remove
module from bracket.
Refitting
3Refitting is a reversal of removal.
6AIR pump assembly (Simtec
system) - removal and refitting
3
Removal
1Chock the rear wheels, jack up the front of
the vehicle and support it on axle stands
placed under the body side members (see
“Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
2Remove the left hand front wheel and inner
wheel arch lining.
3Loosen the hose clamp and remove the air
duct hose from the pump.
4Disconnect the battery negative lead.
5Undo the securing nuts and remove the
pump assembly from its location. Disconnect
the wiring plug.
6Remove the wiring plug from the pump’s
bracket.
7Mark the position of the pump on it’s
bracket before separating.
8Remove the fixing bolts and disconnect the
pump from it’s insulator.
9The insulator can also be checked by
removing the 3 nuts, securing the protective
shield. Before removing, mark the shield and
insulator. Replace if necessary.
10Check the pump’s air cleaner for damage.
Refitting
11Refitting is a reversal of removal. Ensure
correct alignment of the components.
7AIR cut-off valve - removal,
testing and refitting
3
Removal
1Before removal, mark on the cut-off valve,
the direction of flow towards the non-return
valve (see illustration).
2Disconnect and remove the air duct and
vacuum hoses.
3Undo the switchover valve’s bolts and
move to one side.
4C•2Fuel and exhaust systems - exhaust and emissions
3.4 Disconnecting the vacuum hose from
the exhaust gas recirculation valve
4.6 EGR valve
1 Valve 2 Gasket
3.4B Withdrawing the exhaust gas
recirculation valve
Page 137 of 525

outboard pad and anti-squeal shim that fits
between the pad and the caliper body.
7Withdraw the inboard pad and anti-squeal
shim.
Refitting
8Proceed as described in Section 4,
paragraphs 10 and 11.
9Check that the cutaway recesses in the
pistons are positioned downwards, at
approximately 23°to the horizontal. A
template made of card may be used to check
the setting (see illustration). If necessary,
carefully turn the pistons to their correct
positions.
10Apply a little brake grease to the top and
bottom edges of the backplates on the new
brake pads.
11Locate the new pads and the anti-squeal
shims in the caliper. Ensure that the friction
material faces the disc, and check that the
pads are free to move slightly.
12Locate the anti-rattle spring on the pads,
then insert the pad retaining pins from the
inside edge of the caliper, while depressing
the spring. Tap the pins firmly into the caliper.
13Repeat the operations on the remaining
side of the vehicle.
14Proceed as described in Section 4,
paragraphs 17 to 20 inclusive.
6Rear brake shoes (drum
brakes) - inspection, removal
and refitting
3
Note: When working on the brake
components, take care not to disperse brake
dust into the air, or to inhale it, since it may
contain asbestos, which can damage your
health.
Inspection
1It is recommended that the brake shoes are
inspected when necessary by removing the
drums. This will enable a proper inspection of
the linings to be made, and additionally, the
wheel cylinders can be inspected for leaks. If
preferred, however, a provisional inspection of
the state of wear of the rear shoe linings can
be made by removing the plugs from the
inspection holes in the brake backplates.2Use a torch or inspection lamp, and if
necessary a mirror, to check that the friction
material has not worn down to less than the
specified minimum.
3If any one of the shoes has worn below the
specified limit, all four rear brake shoes must
be renewed as a set, as follows.
Removal
4Where applicable, remove the wheel trims,
then loosen the rear roadwheel bolts and
chock the front wheels. Jack up the rear of the
vehicle, and support on axle stands (see
“Jacking and Vehicle Support”) positioned
under the body side members. Remove the
roadwheels.
5Fully release the handbrake.
6Extract the drum securing screw and
remove the drum. If the drum is tight, remove
the plug from the inspection hole in the brake
backplate, and push the handbrake operating
lever towards the brake shoe to move the
shoes away from the drum. If necessary,
slacken the handbrake cable adjuster (see
illustrations).
7Note the location and orientation of all
components before dismantling, as an aid to
reassembly.
8Clean the dust and dirt from the drum and
shoes, but take care not to inhale it.
9Remove the shoe hold-down pins, springs
and cups by depressing the cups and turning
them through 90°using a pair of pliers (see
illustrations). Note that the hold-down pins
are removed through the rear of the brake
backplate.
10Disconnect the handbrake cable from the
operating lever.11The upper and lower return springs may
now be unhooked and the shoes removed
separately, or the assembly of shoes, adjuster
strut and springs may be removed together.
Remove the hub, refer to Chapter 10, if
necessary. Take care not to damage the
wheel cylinder rubber boots. Before removing
the return springs, note the position and
orientation of the springs and adjuster strut.
12If the shoes are to be removed for some
time, fit a stout rubber band or a spring clip to
the wheel cylinder, to prevent the pistons from
being pushed out of their bores. In any event,
do not press the brake pedal while the drum is
removed.
Refitting
13Clean the dust and dirt from the brake
backplate, but take care not to inhale it.
14Apply a small amount of brake grease to
the shoe rubbing areas on the backplate.
15Investigate and rectify any source of
contamination of the linings (wheel cylinder or
hub bearing oil seal leaking).
16Although linings are available separately
(without shoes), renewal of the shoes
complete with linings is to be preferred,
unless the reader has the necessary skills and
equipment to fit new linings to the old shoes.
17If not already done, dismantle the shoes,
strut and springs. Note the position and
orientation of the components. On later
models (1992-on), the brake shoe lower
anchorage has been modified so that it is now
rectangular, necessitating modified brake
shoes and a modified lower return spring (see
illustration).
9•6Braking system
5.9 Checking a rear caliper piston cut
away recess angle with a card template6.6B Push the handbrake operating lever
to move the shoes away from the drum
6.9B . . . then withdraw the cup and spring6.9A Release the shoe hold-down cup . . .
6.6A Extracting a brake drum securing
screw
Page 142 of 525

Rear disc - DOHC models
Removal
15Where applicable, remove the roadwheel
bolt and spacer used when checking the disc.
16Remove the disc pads, as described in
Section 5.
17Remove the brake caliper with reference
to Section 9, but leave the hydraulic fluid pipe
connected. Move the caliper to one side, and
suspend it using wire or string to avoid
straining the pipe.
18Remove the securing screw and withdraw
the disc from the hub (see illustration). If the
disc is tight, collapse the handbrake shoes by
inserting a screwdriver through the adjuster
hole in the disc and turning the adjuster
wheel.
Refitting
19Refitting is a reversal of removal, but
make sure that the mating faces of the disc
and hub are perfectly clean, and apply a little
locking fluid to the threads of the securing
screw. Refit the disc pads, as described in
Section 5.
11Brake drum - removal,
inspection and refitting
3
Note: When working on the brake
components, take care not to disperse brake
dust into the air, or to inhale it, since it may
contain asbestos, which can damage your
health.
Removal
1Where applicable, remove the wheel trim,
then loosen the relevant rear roadwheel bolts
and chock the front wheels. Jack up the rear
of the vehicle, and support on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
Remove the roadwheel.
2Fully release the handbrake.
3Extract the drum securing screw and
remove the drum. If the drum is tight, remove
the plug from the inspection hole in the brake
backplate, and push the handbrake operating
lever towards the brake shoe to move theshoes away from the drums. If necessary,
slacken the handbrake cable adjuster.
Inspection
4Brush the dirt and dust from the drum,
taking care not to inhale it.
5Examine the internal friction surface of the
drum. If they are deeply scored, or so worn
that the drum has become ridged to the width
of the shoes, then both drums must be
renewed.
6Regrinding of the friction surface is not
recommended, since the internal diameter of
the drum will no longer be compatible with the
shoe friction material contact diameter.
Refitting
7Refit the brake drum and tighten the
securing screw. If necessary, back off the
adjuster wheel until the drum will pass over
the shoes.
8Adjust the brakes by operating the
footbrake a number of times. A clicking noise
will be heard at the drum as the automatic
adjuster operates. When the clicking stops,
adjustment is complete.
9Refit the roadwheel and lower the vehicle to
the ground. Do not fully tighten the roadwheel
bolts until the vehicle is resting on its wheels.
12Rear wheel cylinder (drum
brakes) - removal, overhaul
and refitting
3
Note: Refer to the notes at the beginning of
Sections 3 and 11 before proceeding. Before
dismantling a wheel cylinder, check that
replacement parts can be obtained, and retain
the old components to compare them with the
new ones
Removal
1Where applicable, remove the wheel trim,
then loosen the relevant rear roadwheel bolts
and chock the front wheels. Jack up the rear
of the vehicle and support on axle stands (see
“Jacking and Vehicle Support”) positioned
under the body side members. Remove the
roadwheel.
2Fully release the handbrake.3Extract the drum securing screw and
remove the drum. If the drum is tight, remove
the plug from the inspection hole in the brake
backplate, and push the handbrake operating
lever towards the brake shoe to move the
shoes away from the drum. If necessary,
slacken the handbrake cable adjuster.
4Using a pair of pliers, unhook the upper
return spring from the brake shoes, noting its
orientation, then push the upper ends of the
shoes apart until they are clear of the wheel
cylinder (see illustration).
5Working under the bonnet, remove the
brake fluid reservoir cap and secure a piece of
polythene over the filler neck with a rubber
band, or by refitting the cap. This will reduce
the loss of fluid during the following
procedure.
6Unscrew the brake fluid pipe union nut from
the rear of the wheel cylinder, and disconnect
the pipe (see illustration). Take care not to
strain the pipe. Be prepared for fluid spillage,
and plug the open ends to prevent dirt ingress
and further fluid loss.
7Unscrew the two securing bolts from the
rear of the brake backplate, and withdraw the
wheel cylinder.
Overhaul
8If desired, the wheel cylinder can be
overhauled as follows. Otherwise, go on to
paragraph 17 for details of refitting.
9Brush the dirt and dust from the wheel
cylinder, but take care not to inhale it.
10Pull the rubber dust seals from the ends of
the cylinder body.
11The pistons will normally be ejected by
the pressure of the coil spring. If they are not,
tap the end of the cylinder body on a piece of
wood, or apply low air pressure (e.g. from a
foot pump), to the hydraulic fluid union hole in
the rear of the cylinder body, to eject the
pistons from their bores.
12Inspect the surfaces of the pistons and
their bores in the cylinder body for scoring, or
evidence of metal-to-metal contact. If evident,
renew the complete wheel cylinder assembly.
Note that the later type of wheel cylinder can
be used to replace the early type as a
complete unit.
Braking system 9•11
12.6 Unscrewing rear wheel cylinder brake
fluid pipe union12.4 Rear brake assembly
1 Wheel cylinder
2 Upper shoe return spring (note
orientation)
10.18 Withdrawing the rear brake disc -
DOHC model
9
Page 186 of 525

3When refitting the distributor cap, check
that the ends of the HT leads are fitted
securely to the cap, plugs and coil. Also make
sure that the spring-tensioned carbon brush
in the centre of the distributor cap moves
freely, and that the HT segments are not worn
excessively.
4Inspect the electrical and vacuum
connections of the ignition/engine
management systems, and make sure that
they are clean and secure.
32Clutch cable check
2
Check the clutch cable adjustment, as
described in Chapter 6.
Check also, the condition of the cable.
Inspect the cable strands for fraying, and
ensure that the cable is correctly routed, to
avoid chafing against surrounding
components. Renew the cable, as described
in Chapter 6, if excessive wear or damage is
evident.
33Manual transmission fluid
check
2
Note:Models built after 1994 it is no longer
necessary to check levels.
1Ensure that the vehicle is on level ground.
2Unscrew the transmission oil level plug,
which is located in the rear left of the
differential housing on F10 and F13
transmissions, and in the rear right of the
differential housing on F16 and F20
transmissions (see illustrations). The oil level
should be up to the bottom of the level plug
orifice.
3If necessary, top-up the oil level through the
breather/filler orifice in the gear selector
cover. Unscrew the breather/filler plug, and
top-up with the specified grade of oil, until oil
just begins to run from the level plug orifice.
Refit the level plug and the breather/filler plug
on completion (see illustrations).
4Renewal of the transmission oil is not
specified by the manufacturers, and no drain
plug is provided. If it is desired to renew the oil
as a precaution, the oil may be drained by
removing the differential cover plate. Use a
new gasket when refitting the cover plate. Fillthe transmission through the breather/filler
orifice, as described previously in this
Section.
5Periodically inspect the transmission for oil
leaks, and check the gear selector linkage
components for wear and smooth operation.
34Automatic transmission
check
2
1Carry out a thorough road test, ensuring
that all gearchanges occur smoothly, without
snatching and with no increase in engine
speed between changes.
2Check the operation of the kickdown.
Check that all gear positions can be engaged
at the appropriate movement of the selector
lever and with the vehicle at rest, check that
the operation of the parking pawl in position
“P” prevents it from being moved. Ensure that
the starter motor will work only with the
selector lever in positions “P” or “N”, and thatthe reversing lamps light only when position
“R” is selected.
3The manufacturer’s schedule calls for a
regular check of the electrical control system
using the special Vauxhall test equipment;
owners will have to have this check carried
out by a Vauxhall dealer.
4Periodically inspect the transmission
casing, checking all joint surfaces and seals
for signs of fluid leaks. If any are found, the
fault must be rectified immediately.
5Check also that the transmission breather
hose (under the battery mounting bracket) is
clear and not blocked, kinked or twisted.
35Brake shoe check
2
Note:On models fitted with rear brake pads,
the handbrake operates brake shoes that are
located inside the rear brake discs.
Refer to Chapter 9, for details.
Every 18 000 miles or 24 months 1•15
33.3A Transmission breather/filler plug
(arrowed) - F16 type transmission33.3B Topping-up the transmission oil
level - F13 type transmission
33.2B Transmission oil level plug
(arrowed) - F16 type transmission (viewed
from below, with driveshaft removed)33.2A Transmission oil level plug
(arrowed) - F13 type transmission (viewed
from above)
1