1988 OPEL CALIBRA sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 204 of 525

Oil pick-up pipe bracket to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Oil pick-up pipe to oil pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Oil pipes to radiator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2216
Oil pressure switch to oil pump:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3022
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4030
Oil pressure relief valve to oil pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3022
Oil pump cover to oil pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Oil pump to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Oxygen sensor to exhaust manifold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3022
Power steering pump bracket to support:
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1813
Power steering pump to support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Right engine mounting to subframe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6548
Shackle to alternator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Spark plugs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Starter to cylinder block (M10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4533
Starter to cylinder block (M12) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
Sump:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1511
Sump drain plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5541
Support to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3526
Temperature sender to cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
Thermostat housing:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1511
Timing belt tensioner to oil pump:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5541
Timing belt cover to oil pump/camshaft housing:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .129
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Timing belt drive gear to crankshaft:
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13096
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by between 40º to 50º
Transmission to engine (M10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4533
Transmission to engine (M12) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
1General description
General
The engine is of four-cylinder, in-line single
or double overhead camshaft type (depending
on model), mounted transversely at the front
of the vehicle.
The crankshaft runs in five shell-type
bearings, and the centre bearing incorporates
a thrust bearing shell to control crankshaft
endfloat.
The connecting rods are attached to the
crankshaft by horizontally split shell-type
big-end bearings. On single overhead
camshaft (SOHC) models, the pistons are
attached to the connecting rods by gudgeon
pins, which are an interference fit in the
connecting rod small-end bore. The
aluminium alloy pistons are fitted with three
piston rings: two compression rings and an oil
control ring.
The camshaft on SOHC engines is driven
from the crankshaft by a toothed composite
rubber belt. Each cylinder has two valves (oneinlet and one exhaust), operated through
rocker arms that are supported at their pivot
ends by hydraulic self-adjusting valve lifters
(tappets).
The inlet and exhaust valves are each
closed by a single valve spring, and operate in
guides pressed into the cylinder head.
A gear-type oil pump is located in a housing
attached to the front of the cylinder block, and
is driven directly from the crankshaft. A
full-flow type oil filter is fitted.
The distributor is driven directly from the
end of the camshaft. On carburettor models,
the mechanical fuel pump is operated from
the front end of the camshaft. The coolant
pump is located at the front of the cylinder
block, and is driven by the timing belt.
Chapter 2A describes the SOHC engine
repair procedures. Many repairs and specifi-
cations to the DOHC engine are similar to the
2.0 litre SOHC. However where they differ,
details can be found in Chapter 2B.
Engine identification codes -
general
Before ordering spare parts, or carrying out
any repair or overhaul operations on the
engine, it is essential to identify the exactengine type being worked on. Later engines,
although outwardly similar in appearance,
often have significant differences in repair
procedures, even though they may be of the
same displacement and model year.
The following sub-Sections in this Chapter
are mainly specific to engine type, as will be
noted from the sub-Section headings. Check
the engine identification code first, which is
located on a horizontal surface on the exhaust
manifold side of the cylinder block, at the
distributor end. On later engines, the code is
on the cylinder block-to-transmission flange,
next to the engine oil dipstick.
2Crankcase ventilation
system - description and
maintenance
2
Description
1A crankcase ventilation system is fitted to
all models, but the systems differ in detail
depending on the model concerned.
2Oil fumes and blow-by gases (combustion
gases that have passed by the piston rings)
are drawn from the crankcase into the area of
SOHC engine procedures 2A•7
2A
Page 206 of 525
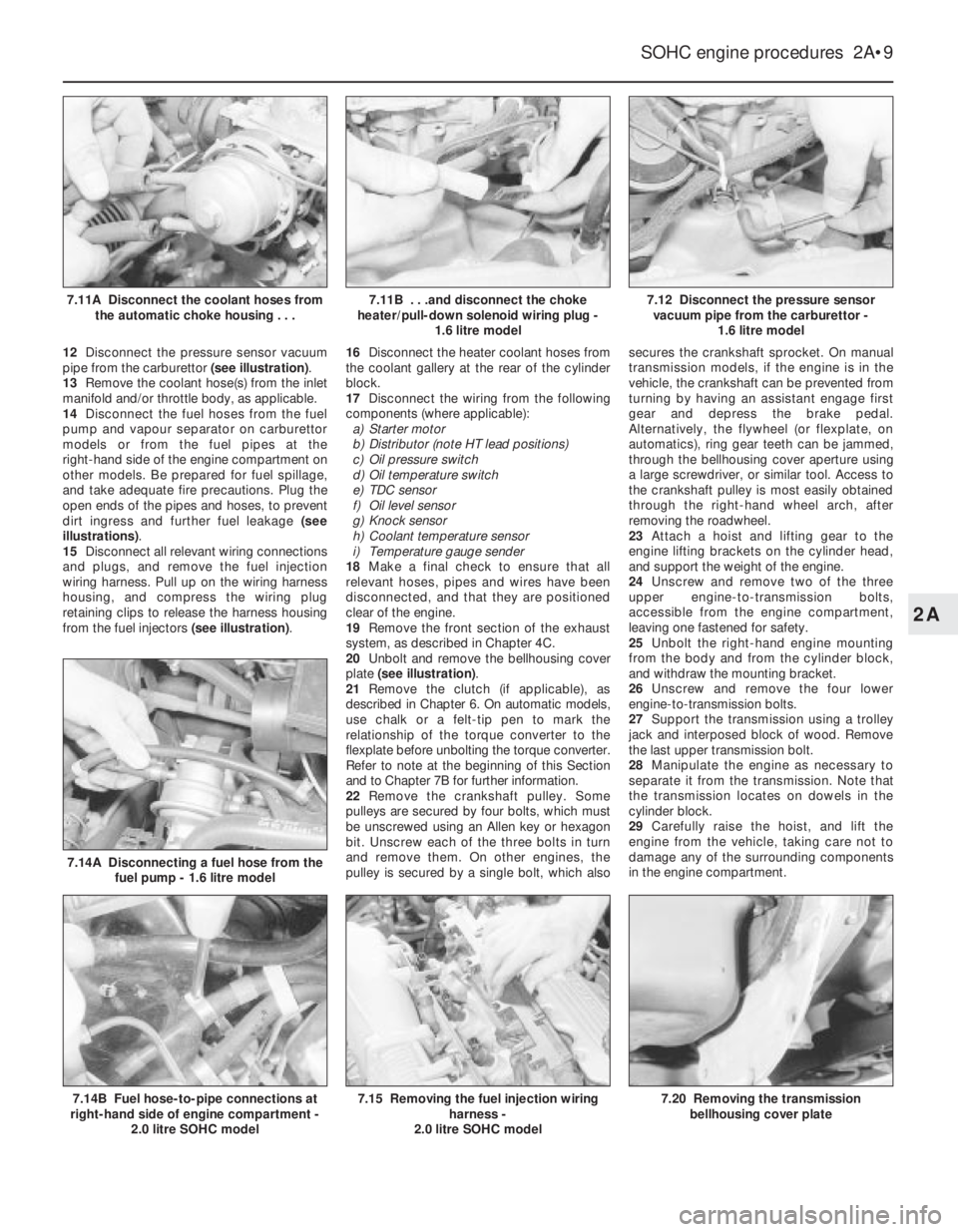
12Disconnect the pressure sensor vacuum
pipe from the carburettor (see illustration).
13Remove the coolant hose(s) from the inlet
manifold and/or throttle body, as applicable.
14Disconnect the fuel hoses from the fuel
pump and vapour separator on carburettor
models or from the fuel pipes at the
right-hand side of the engine compartment on
other models. Be prepared for fuel spillage,
and take adequate fire precautions. Plug the
open ends of the pipes and hoses, to prevent
dirt ingress and further fuel leakage (see
illustrations).
15Disconnect all relevant wiring connections
and plugs, and remove the fuel injection
wiring harness. Pull up on the wiring harness
housing, and compress the wiring plug
retaining clips to release the harness housing
from the fuel injectors (see illustration).16Disconnect the heater coolant hoses from
the coolant gallery at the rear of the cylinder
block.
17Disconnect the wiring from the following
components (where applicable):
a)Starter motor
b)Distributor (note HT lead positions)
c)Oil pressure switch
d)Oil temperature switch
e)TDC sensor
f)Oil level sensor
g)Knock sensor
h)Coolant temperature sensor
i)Temperature gauge sender
18Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant hoses, pipes and wires have been
disconnected, and that they are positioned
clear of the engine.
19Remove the front section of the exhaust
system, as described in Chapter 4C.
20Unbolt and remove the bellhousing cover
plate (see illustration).
21Remove the clutch (if applicable), as
described in Chapter 6. On automatic models,
use chalk or a felt-tip pen to mark the
relationship of the torque converter to the
flexplate before unbolting the torque converter.
Refer to note at the beginning of this Section
and to Chapter 7B for further information.
22Remove the crankshaft pulley. Some
pulleys are secured by four bolts, which must
be unscrewed using an Allen key or hexagon
bit. Unscrew each of the three bolts in turn
and remove them. On other engines, the
pulley is secured by a single bolt, which alsosecures the crankshaft sprocket. On manual
transmission models, if the engine is in the
vehicle, the crankshaft can be prevented from
turning by having an assistant engage first
gear and depress the brake pedal.
Alternatively, the flywheel (or flexplate, on
automatics), ring gear teeth can be jammed,
through the bellhousing cover aperture using
a large screwdriver, or similar tool. Access to
the crankshaft pulley is most easily obtained
through the right-hand wheel arch, after
removing the roadwheel.
23Attach a hoist and lifting gear to the
engine lifting brackets on the cylinder head,
and support the weight of the engine.
24Unscrew and remove two of the three
upper engine-to-transmission bolts,
accessible from the engine compartment,
leaving one fastened for safety.
25Unbolt the right-hand engine mounting
from the body and from the cylinder block,
and withdraw the mounting bracket.
26Unscrew and remove the four lower
engine-to-transmission bolts.
27Support the transmission using a trolley
jack and interposed block of wood. Remove
the last upper transmission bolt.
28Manipulate the engine as necessary to
separate it from the transmission. Note that
the transmission locates on dowels in the
cylinder block.
29Carefully raise the hoist, and lift the
engine from the vehicle, taking care not to
damage any of the surrounding components
in the engine compartment.
SOHC engine procedures 2A•9
7.12 Disconnect the pressure sensor
vacuum pipe from the carburettor -
1.6 litre model
7.20 Removing the transmission
bellhousing cover plate7.15 Removing the fuel injection wiring
harness -
2.0 litre SOHC model7.14B Fuel hose-to-pipe connections at
right-hand side of engine compartment -
2.0 litre SOHC model
7.14A Disconnecting a fuel hose from the
fuel pump - 1.6 litre model
7.11B . . .and disconnect the choke
heater/pull-down solenoid wiring plug -
1.6 litre model7.11A Disconnect the coolant hoses from
the automatic choke housing . . .
2A
Page 207 of 525

30With the engine removed, the
transmission can be supported by placing a
length of wood between the bellhousing and
the front suspension subframe. Once the
wooden support is in place, remove the trolley
jack from under the transmission.
Refitting
Note: New left and right-hand
engine/transmission mounting-to-body bolts
must be used on refitting.
31Use an M10 x 1.25 bottoming tap to clean
the threads in the torque converters threaded
bosses and ensure that new bolts are
available for reassembly, where applicable.
32Support the transmission with a trolley
jack and remove the length of wood from
between the bellhousing and the subframe.
33Support the engine with the hoist and
lifting tackle, and gently lower it into position
in the engine compartment.
34Mate the engine and transmission
together, ensuring that the transmission
locates on the dowels in the cylinder block,
then refit the three upper
engine-to-transmission bolts.
35Tighten all nuts and bolts to their specified
torque wrench settings. When tightening the
torque converter-to-flexplate bolts to their
specified torque wrench settings, a
commercially available adapter will be
required (see illustration).
36If the clutch is still bolted to the flywheel,
ensure that the weight of the transmission is
not allowed to hang on the input shaft as it is
engaged with the clutch friction disc.
37Refit the four lower
engine-to-transmission bolts, but again do not
fully tighten them at this stage.
38Fit the right-hand engine mounting
bracket to the cylinder block, and tighten the
securing bolts to the specified torque.39Manipulate the engine and transmission
as necessary to enable the right-hand engine
mounting-to-body bolts to be fitted, then fit
new bolts and tighten them to the specified
torque.
40Tighten all the engine-to-transmission
bolts to the specified torque, then disconnect
the lifting tackle and hoist from the engine,
and remove the trolley jack from beneath the
transmission.
41Refit the transmission bellhousing cover
plate.
42Refit the clutch, as described in Chapter
6.
43Refit the front section of the exhaust
system, as described in Chapter 4C.
44Refit the crankshaft pulley using a reversal
of the removal procedure described earlier in
paragraph 22, and tighten the securing bolt(s)
to the specified torque.
45Lower the vehicle to the ground.
46Refit all relevant wires, pipes and hoses,
etc., using a reversal of the removal
procedure described earlier.
47Where applicable, refit the power steering
pump, tension the pump drivebelt, and bleed
the hydraulic fluid circuit, as described in
Chapter 10.
48Refit the alternator and tension the
drivebelt, as described in Chapter 5.
49Refit the air cleaner components, referring
to Chapter 4A or 4B, if necessary. On
carburettor models reconnect the hot air hose
to the exhaust manifold hot air shroud.
50Fit a new oil filter (if not already replaced),
and fill the engine with oil, as described in
Chapter 1.
51Refit the radiator and refill the cooling
system, as described in Chapter 3.
52Refit the bonnet as described in Chapter
11.
53Reconnect the battery negative lead.
54Refer to Section 37
8Engine and transmission -
removal, separation,
reconnection and refitting
4
Note: A hoist and lifting tackle will be required
for this operation
Removal
1Proceed as described in Section 7,
paragraphs 1 to 18 inclusive.
2Working in the engine compartment,
remove the gear selector linkage, as
described in Chapters 7A and 7B, as
appropriate.
3On manual transmission models, remove
the retaining clip, then slide the clutch cable
from the release lever, pushing the release
lever back towards the bulkhead if necessary
to allow the cable to be disconnected. On
automatic models disconnect the selector
cable from the actuating lever, then either
unbolt the cable bracket or release the cable
from the bracket. In either case, pull the cablesupport from the bracket on the transmission
casing, then move the cable and secure to
one side out of the way, taking note of its
routing.
4Disconnect the wiring from the reversing
lamp switch, which is located at the front of
the manual transmission casing, above the
left-hand mounting bracket. On automatic
models, disconnect the transmission wiring
by unplugging the five connector plugs from
the various switches, solenoids and sensors.
Release also the wiring from any clips or ties
securing to the vehicle.
5Where applicable, withdraw the automatic
transmission breather hose from under the
battery bracket. Disconnect the oxygen
sensor wiring if fitted.
6Unscrew the securing sleeve, and
disconnect the speedometer cable from the
transmission.
7Unscrew the retaining nut, and disconnect
the earth strap from the transmission
endplate.
8Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant hoses, pipes, wires etc. have been
disconnected, and that they are positioned
clear of the engine and transmission.
9Proceed as described in Section 7,
paragraphs 19 and 22.
10Disconnect the inboard ends of the
driveshafts from the differential, referring to
the relevant paragraphs of Chapter 8. Be
prepared for oil spillage as the driveshafts are
withdrawn, and plug the apertures in the
differential, to prevent further loss of oil and
dirt ingress. Support the driveshafts by
suspending them with wire or string - do not
allow them to hang down under their own
weight.
11Attach a hoist and lifting gear to the
engine lifting brackets on the cylinder head,
and support the weight of the engine.
12Remove the left-hand transmission
mounting completely by unscrewing the two
bolts securing the rubber mounting to the
vehicle, body, and the three bolts securing the
mounting bracket to the transmission (see
illustration).
13Unbolt the right-hand engine mounting
from the body and from the cylinder block,
and withdraw the mounting bracket.
2A•10SOHC engine procedures
8.12 Left-hand transmission mounting
viewed from underside of vehicle7.35 Commercially-available torque
wrench adapter being used to tighten
torque converter bolts
If a tap is not available, cut
two slots into the threads of
one of the old flywheel bolts
and use the bolt to remove
the locking compound from the
threads.
Page 208 of 525

14Working under the vehicle, unscrew and
remove the two nuts securing the
engine/transmission rear mounting to the front
subframe, and the three bolts securing the
mounting bracket to the transmission, then
withdraw the mounting bracket (see
illustrations).
15Carefully swing the engine/transmission
assembly across the engine compartment as
necessary, to allow the assembly to be lifted
vertically from the vehicle by raising the hoist.
Take care not to damage any of the
surrounding components in the engine
compartment.
Separation
16With the engine/transmission assembly
removed, support the assembly on blocks of
wood positioned on a workbench, or failing
that, on a clean area of the workshop floor.
17Clean away any external dirt using
paraffin or a water-soluble solvent and a stiff
brush.
18Unbolt and remove the transmission
bellhousing cover plate.
19Ensure that both engine and transmission
are adequately supported, then unscrew and
remove the engine-to-transmission bolts.
20Carefully withdraw the transmission from
the engine, ensuring that the weight of the
transmission is not allowed to hang on the
input shaft while it is engaged with the clutch
friction disc. Note that the transmission
locates on dowels positioned in the cylinder
block.
21On automatic models unbolt the
transmission bellhousing cover plate (three
bolts), then use chalk or a felt-tip pen to mark
the relationship of the torque converter to the
flexplate before unbolting the torque
converter. Note:If the torque converter is
removed (even partially) from the transmission,
a considerable amount of the fluid inside it will
leak out. To prevent this, when prising the
transmission off its locating dowels and
removing it, be careful to keep the torque
converter pressed firmly into the transmission.
If the transmission is to be removed for some
time, retain the torque converter by bolting a
strip of metal across the bellhousing mating
surface. Applying a spanner to the crankshaft
pulley/sprocket bolt, rotate the crankshaft
until the first bolt appears, then use ascrewdriver or similar to jam the flexplate ring
gear teeth to prevent it from rotating as the
bolt is unscrewed. Unscrew each of the three
bolts in turn and remove them.
Reconnection
22Before beginning the refitting operations,
check that the two original bolts that secured
the left-hand transmission rubber mounting to
the vehicle body rotate freely in their threaded
bores in the body. If necessary, re-cut the
threaded bores using an M10 x 1.25 mm tap.
23Where applicable, if the clutch assembly
has been removed from the flywheel, it will
prove easier to refit after the transmission has
been refitted.
24On automatics, if any fluid was spilled from
the torque converter, be careful to refill it as
much as possible. Wipe clean the converter’s
spigot to prevent damage to the transmission’s
input shaft oil seal as the converter is installed,
and ensure that the converter engages
correctly on the fluid pump shaft.
25If the transmission has been renewed, be
careful to flush clean the radiator fluid cooler
passages. Vauxhall recommend the use of
low-pressure compressed air, but this will
require great care to avoid deforming the
radiator.
26Be very careful to ensure that all
components are scrupulously clean, to avoid
the risk of dirt getting into the system.
27Use an M10 x 1.25 bottoming tap to clean
the threads in the torque converters threaded
bosses and ensure that new bolts are
available for reassembly, where applicable.
28Tighten all nuts and bolts to their specified
torque wrench settings.
29Refer also to Section 7, paragraphs 35
and 36.
30Carefully offer the transmission to the
engine until the bellhousing is located on the
dowels in the cylinder block, then refit the
engine-to-transmission bolts, and tighten
them to the specified torque.
31Refit the transmission bellhousing cover
plate.
Refitting
32Working under the vehicle, refit the rear
engine/transmission mounting to the
transmission, using new locking plates under
the bolt heads, and tighten the bolts to the
specified torque.
33Fit the two bolts securing the engine/
transmission rear mounting to the front
subframe, but do not fully tighten at this stage.
34Fit the right-hand engine mounting
bracket to the cylinder block, and tighten the
securing bolts to the specified torque.
35Fit new right-hand engine
mounting-to-body bolts, but do not fully
tighten them at this stage.
36Fit the left-hand transmission mounting
bracket to the transmission, and tighten the
securing bolts to the specified torque.
37Fit new left-hand transmission
mounting-to-body bolts, and tighten them to
the specified torque.
38Tighten the right-hand engine mounting-
to-body bolts and the engine/transmission
rear mounting-to-front subframe bolts to their
specified torques, then remove the lifting
tackle and hoist from the engine.
39Where applicable, the clutch can now be
fitted, and the transmission input shaft can be
pressed into engagement with the splined hub
of the clutch friction disc, (see Chapter 5).
40Reconnect the inboard ends of the
driveshafts to the differential, with reference
to the relevant paragraphs of Chapter 8, and
using new snap rings.
41Refit the front section of the exhaust
system, as described in Chapter 4C.
42Refit the crankshaft pulley, using a
reversal of the removal procedure described
in Section 7, paragraph 22, and tighten the
securing bolt(s) to the specified torque.
43On automatic models, connect the wires
to the various switches, solenoids and
sensors. Replace the transmission breather
hose and oxygen sensor (if fitted).
44Reconnect the transmission earth strap,
and tighten the securing nut.
45Lower the vehicle to the ground.
46Reconnect the speedometer cable to the
transmission, and tighten the securing sleeve.
47Reconnect the reversing lamp wiring.
48On manual transmission models, refit the
clutch cable to the bracket on the
transmission casing, then reconnect the cable
to the release lever, and adjust the cable as
described in Chapter 6. Ensure that the cable
is routed as noted during removal.
49Refit the gear selector linkage, as
described in Chapter 7A, if applicable.
50Proceed as described in Section 7,
paragraphs 41 to 52 inclusive.
51Top-up the transmission oil level, as
described in Chapters 7A and 7B.
52Adjust the selector cable on completion,
and refill the transmission with fluid (see
above).
53Reconnect the battery negative lead.
54Refer to Section 37
SOHC engine procedures 2A•11
8.14B Rear engine/transmission mounting-
to-transmission bolts (arrowed)8.14A Rear engine/transmission
mounting-to-front subframe nuts
2A
If a tap is not available, cut
two slots into the threads of
one of the old flywheel bolts
and use the bolt to remove
the locking compound from the threads.
Page 210 of 525
a)Inlet and exhaust manifolds (where
applicable)
b)Starter motor
c)Rear coolant gallery and hoses
d)Oil pressure switch
e)Oil temperature switch (where applicable)
f)Oil level sensor (where applicable)
g)Knock sensor (where applicable)
h)TDC sensor (where applicable)
i)Distributor components
j)Fuel pump (where applicable)
k)Thermostat/housing (N 16 NZ2, 1.8 and
2.0 litre models)
l)Power steering pump and mounting
bracket (where applicable)
m)Alternator mounting bracket
n)Engine lifting brackets
o)Dipstick/crankcase breather tube
p)Inlet manifold mounting bracket (where
applicable)
13To ensure maximum life, with minimum
trouble, from a rebuilt engine, not only must
everything be correctly assembled, but it must
also be spotlessly clean. All oilways and
coolant passages must be clear, and all
washers must be fitted in their original
positions. Oil all bearings and other moving
surfaces thoroughly with clean engine oil
during assembly.
14Before assembly begins, renew any bolts
or studs with damaged threads.
15Obtain a torque wrench, an angle-torque
gauge, sockets and bits, an oil can, clean
lint-free rag, and a set of engine gaskets and
oil seals, together with a new oil filter.16If they have been removed, new cylinder
head bolts, flywheel bolts, big-end bearing
cap bolts and main bearing cap bolts will also
be required.
17On completion of reassembly, refit the
applicable ancillary components listed in
paragraph 12.
18Follow procedure shown in Section 37.
11Timing belt and sprockets
(without automatic tensioner) -
removal, refitting and adjustment
3
Note: A two-legged puller may be required to
remove the crankshaft sprocket on N 16 NZ2,
1.8 and 2.0 litre models.Some of the later 1.4
and 1.6 litre engines, identifiable by the
squared-off top surfaces of the timing belt
covers, are fitted with spring-loaded auto-matic timing belt tensioners to ensure correct
belt tensioning on assembly.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2On models with power steering, remove the
pump drivebelt, see Chapters 1 and 10.
3Remove the alternator drivebelt, as
described in Chapter 5.
4On C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models,
disconnect the wiring from the temperature
gauge sender.
5Release the securing clips (or hexagon-
headed screws, if fitted), and remove the main
outer timing belt cover, then unclip the smaller
outer timing belt cover from the coolant pump.
Where applicable, three screws retain the lower
(small) outer cover to the rear cover, the fourth
secures the tensioner (see illustrations).
6On 1.6 litre models with power steering,
remove the power steering pump, as
described in Chapter 10.
7Turn the crankshaft using a socket or
spanner on the crankshaft sprocket bolt, until
the timing mark on the camshaft sprocket is
aligned with the notch in the rear timing belt
cover, and the notch in the crankshaft pulley
is aligned with the pointer on the rear timing
belt cover (see illustrations). Note that on 1.4
litre engine there are two notches in the
crankshaft pulley, representing 5°and 10°
BTDC, and the 10°BTDC notch should be
aligned with the pointer (see illustration).
8Loosen the three coolant pump securing
bolts (see illustration), and turn the pump to
relieve the tension in the timing belt, then slide
the belt from the camshaft sprocket.
SOHC engine procedures 2A•13
11.5C Timing belt lower (small) outer
cover screws (A), tensioner screw (B),
ignition timing fixed reference mark (C)
11.8 Loosening a coolant pump securing
bolt - 2.0 litre engine11.7C Crankshaft pulley 10°BTDC notch
aligned with pointer on rear timing belt
cover - 1.4 litre engine11.7B . . .and notch in crankshaft pulley
aligned with pointer on rear timing belt
cover - 2.0 litre engine
11.7A Camshaft sprocket TDC mark
aligned with notch in rear timing belt
cover . . .
11.5B . . .and the smaller cover from the
coolant pump - 2.0 litre engine11.5A Remove the main outer timing belt
cover . . .
2A
Page 211 of 525

9The crankshaft pulley must now be
removed. On 1.4 and 1.6 litre engines (except
C 16 NZ2), the pulley is secured by a single
bolt, which also secures the crankshaft
sprocket. On C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre
engines, the pulley is secured by four bolts,
which must be unscrewed using an Allen key
or hexagon bit. On manual transmission
models, if the engine is in the vehicle, the
crankshaft can be prevented from turning by
having an assistant engage first gear and
depress the brake pedal. Alternatively, the
flywheel ring gear teeth can be jammed using
a large screwdriver or similar tool.
10With the crankshaft pulley removed, the
timing belt can be withdrawn.
11If desired, the sprockets and the rear
timing belt cover can be removed as follows,
otherwise go on to paragraph 23.
12To remove the camshaft sprocket, firstdisconnect the breather hose(s) from the
camshaft cover, then unscrew the securing
bolts noting the locations of the HT lead
brackets and any other wiring brackets, and
remove the camshaft cover.
13Recover the gasket. Prevent the camshaft
from turning by holding it with a spanner on
the flats provided between No’s 3 and 4
camshaft lobes, and unscrew the camshaft
sprocket bolt.
14Withdraw the sprocket from the end of the
camshaft.
15To remove the crankshaft sprocket on 1.4
and 1.6 litre engines (except C 16 NZ2), if
necessary, remove the lower securing bolts
from the main rear timing belt cover and use
two large screwdrivers behind the cover to
lever off the sprocket. Remove the Woodruff
key if it is loose.
16To remove the crankshaft sprocket on C
16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre engines, it will benecessary to prevent the crankshaft from
turning, as described in paragraph 9. Take
care when unscrewing the sprocket bolt, as it
is very tight. If necessary, use a two-legged
puller to remove the sprocket. Recover the
Woodruff key and the thrustwasher from the
end of the crankshaft.
17To remove the main rear timing belt cover
on C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models
disconnect the TDC sensor wiring plug and
unclip the wiring from the belt cover. Then
unscrew the two upper securing bolts and the
lower securing bolt(s) (one in the case of C 16
NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre engines, two on other
SOHC engines). Withdraw the cover,
manipulating it from the smaller rear belt
cover on the coolant pump (see illustrations).
18If desired, the smaller rear belt cover can
be removed from the coolant pump, after
unscrewing the securing bolt (see
illustration), by rotating it to disengage it from
the retaining flange on the pump.
Refitting
19Refit the rear timing belt cover(s) using a
reversal of the removal procedure, and
ensuring that the main cover engages correctly
with the smaller cover on the coolant pump.
20On C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre engines,
refit the thrustwasher and the Woodruff key to
the end of the crankshaft. Then refit the
crankshaft sprocket, and tighten the securing
bolt to the specified torque in the two stages
given in the Specifications. Ensure that the
washer is in place under the bolt head, and
prevent the crankshaft from turning as during
removal (see illustrations).
2A•14SOHC engine procedures
11.17A Loosening the main rear timing
belt cover lower securing bolt -
2.0 litre engine11.18 Unscrewing the coolant pump rear
belt cover securing bolt - 2.0 litre engine
11.20E Tighten the bolt to the specified
torque . . .11.20D . . .and the washer and bolt11.20C . . .the crankshaft sprocket . . .
11.20B . . . the Woodruff key . . .11.20A Refit the thrustwasher . . .
11.17B Main rear timing belt cover lower
securing bolts (arrowed) - 1.6 SV engine
Page 224 of 525

28Crankshaft rear oil seal -
renewal
4
Renewal
1With the engine removed from the vehicle,
remove the flywheel, or flexplate (as
applicable) as described in Sections 25 and
26.
2Punch or drill a small hole in the centre of
the now-exposed oil seal. Screw in a
self-tapping screw, and pull on the screw with
pliers to extract the seal. Several attempts
may be necessary. Be careful not to damage
the sealing face of the crankshaft.
3Clean the oil seal seat with a wooden or
plastic scraper.4Grease the lips of the new seal, then tap the
seal into position using a tube, until flush with
the outer faces of the cylinder block and rear
main bearing cap (see illustration).
5Refit the flywheel or flexplate (if applicable),
as described in Sections 25 or 26.
29Sump - removal and refitting
4
Note: The sump gasket(s) must be renewed
on refitting and sealer will be required for use
on the oil pump and rear main bearing
cap-to-cylinder block joints
Removal
1If the engine is in the vehicle, continue as
follows, otherwise go on to paragraph 9.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Drain the engine oil, referring to Chapter 1 if
necessary, then refit and tighten the drain
plug.
4Apply the handbrake, then jack up the front
of the vehicle, and support securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”).
5Remove the front section of the exhaust
system, as described in Chapter 4C.
6Where applicable, disconnect the wiring
from the oil level sensor.
7Unscrew the securing bolts and remove the
engine-to-transmission blanking plate from
the bellhousing.8Remove the securing bolts, and withdraw
the sump. Note that on most models, the
sump baffle will probably be pulled away from
the cylinder block with the sump, but cannot
be removed until the oil pick-up pipe has been
removed.
9On 1.6, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models, to remove
the sump baffle, it is necessary to unbolt the
bracket securing the oil pick-up pipe to the
cylinder block. The baffle can then be
manipulated over the oil pick-up pipe. On C
16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models, prise the
rubber gasket from the sump baffle.
10If need be, the oil pick-up pipe can be
removed by unscrewing the single bolt
securing the support bracket to the cylinder
block (if not already done). Then remove the
two bolts securing the end of the pipe to the
oil pump. Recover the O-ring.
11Clean all traces of old gasket and sealing
compound from the mating faces of the
cylinder block, sump baffle (where
applicable), and sump.
Refitting
12Begin refitting by applying sealing
compound (Vauxhall part No 90485251 or
equivalent) to the joints between the oil pump
and cylinder block, and the rear main bearing
cap and cylinder block (see illustrations).
13On C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre locate a
new rubber gasket over the sump baffle
flange, ensuring that it is seated correctly (see
illustration).
14On 1.6, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models, offer the
sump baffle up to the cylinder block,
manipulating it over the oil pick-up pipe where
applicable.
15If the oil pick-up pipe has been removed,
refit it to the oil pump using a new O-ring and
tighten bolts to the specified torque (see
illustrations).
16Where applicable, refit the bracket
securing the oil pick-up pipe to the cylinder
block, ensuring that it passes through the
relevant hole in the sump baffle, if applicable
(see illustration).
17Coat the sump securing bolts with
thread-locking compound (i.e. Vauxhall part
No. 90167347), then refit the sump, and
tighten the bolts to the specified torque (see
illustrations).
SOHC engine procedures 2A•27
29.12B Applying sealing compound to the
joint between the oil pump and cylinder
block - 2.0 litre engine
29.15B . . .and tighten the securing bolts
to the specified torque - 2.0 litre engine29.15A Fit a new O-ring to the oil pick-up
pipe . . .29.13 Locate a new rubber gasket over
the sump baffle flange - 2.0 litre engine
29.12A Apply sealing compound (arrowed)
to oil pump and rear main bearing cap
joints before refitting sump
28.4 Fitting a new crankshaft rear oil seal -
2.0 litre engine
2A
Page 228 of 525

7If any of the ring end gaps exceed the
specified tolerance, the relevant rings will have
to be renewed, and if the ring grooves in the
pistons are worn, new pistons may be required.
8Clean out the piston ring grooves using a
piece of old piston ring as a scraper. Take
care not to scratch the surface of the pistons.
Protect your fingers, piston ring edges are
sharp. Also probe the groove oil return holes,
to ensure that they are not blocked.
9Check the cylinder bores for signs of wear
ridges towards the top of the bores. If wear
ridges are evident, and new piston rings are
being fitted, the top ring must be stepped to
clear the wear ridge, or the bore must be
de-ridged using a scraper.
10Fit the oil control ring sections with the
lower steel ring gap offset 25 to 50 mm to the
right of the spreader ring gap, and the upper
steel ring gap offset by the same distance to
the left of the spreader ring gap.
11Fit the lower compression ring, noting that
the ring is tapered or stepped. The ring should
be fitted with the word “TOP” uppermost.
12Fit the upper compression ring, and offset
the ring gap by 180°to the lower compression
ring gap. If a stepped ring is being fitted, fit
the ring with the smaller diameter of the step
uppermost.
13If new pistons are to be fitted, they must
be selected from the grades available, after
measuring the cylinder bores as described in
Section 36.
14Normally the appropriate oversize pistons
are supplied by the dealer when the block is
rebored.15Whenever new piston rings are being
installed, the glaze on the original cylinder
bores should be “broken”, using either
abrasive paper or a glaze-removing tool in an
electric drill. If abrasive paper is used, use
strokes at 60°to the bore centre line, to create
a cross-hatching effect.
34Crankshaft and bearings -
removal and refitting
4
Note: New main bearing cap bolts must be
used on refitting
Removal
1With the engine removed from the vehicle,
continue as follows.
2Remove the cylinder head, as described
previously in Section 20.
3Remove the sump, oil pick-up pipe and
sump baffle (where applicable), as described
in Section 29.
4Remove the oil pump, as described in
Section 30.
5Remove the flywheel or flexplate (if
applicable), as described in Sections 25 and
26.
6Remove the pistons and connecting rods,
as described in Section 32.
7Invert the engine so that it is standing on
the top face of the cylinder block.
8The main bearing caps are numbered 1 to 4
from the timing belt end of the engine. The
rear (flywheel end) cap is not marked. Toensure that the caps are refitted the correct
way round, note that the numbers are read
from the coolant pump side of the engine with
the engine inverted (see illustration).
9Unscrew and remove the main bearing cap
bolts, and tap off the bearing caps. If the
bearing shells are to be re-used, tape them to
their respective caps.
10Note that the centre bearing shell
incorporates thrust flanges to control
crankshaft endfloat.
11Lift the crankshaft (complete with timing
sensor wheel, if fitted), from the crankcase.
12Extract the upper bearing shells, and
identify them for position if they are to be
re-used.
13The crankshaft, bearings and sensor
wheel can be examined for wear and damage,
as described in Section 35, and the cylinder
block and bores can be examined as
described in Section 36.
Refitting
14Begin refitting by ensuring that the
crankcase and crankshaft are thoroughly
clean, and that all oilways are clear. If
possible, blow through the oil drillings with
compressed air, and inject clean engine oil
into them.
15If the crankshaft is being replaced, where
applicable, transfer the timing sensor wheel
and tighten to correct torque.
16Wipe clean the bearing shell seats in the
crankcase and the bearing caps, then fit the
upper bearing shells to their seats.
17Note that there is a tag on the back of
each bearing shell, which engages with a
groove in the relevant seat in the crankcase or
bearing cap (see illustration).
18If new bearing shells are being fitted, wipe
away all traces of protective grease.
SOHC engine procedures 2A•31
33.6 Measuring a piston ring end gap
using a feeler blade34.8 Main bearing cap identification mark
(arrowed) - 1.6 litre engine34.17 Main bearing shell tag (arrowed)
engages with groove in cylinder block -
2.0 litre SOHC engine
33.5C Sectional view showing correct
orientation of piston rings - all engines33.5B Removing the centre section of the
oil control ring - 2.0 litre SOHC engine
2A
A good alternative to
compressed air, is to use a
water dispersing lubricant
spray into each hole, using
the spout provided.