1988 OPEL CALIBRA fuel cap
[x] Cancel search: fuel capPage 177 of 525

1•6Maintenance - component location
Underbonnet view of a 1989 2.0 SRi model (20 SEH engine)
1 VIN plate
2 Air cleaner casing
3 Airflow meter
4 Suspension strut top
5 Coolant expansion tank
6 Brake fluid reservoir
7 Throttle body
8 Relay box
9 Octane rating plug
10 Washer fluid reservoir
11 Battery
12 Power steering fluid reservoir
13 Power steering fluid hoses
14 Distributor cap
15 Engine oil level dipstick
16 Idle speed adjuster
17 Fuel pressure regulator
18 Oil filler cap
19 Thermostat housing
Underbonnet view of a 1990 GSi 2000 model (20 XEJ engine)
1 VIN plate
2 Air cleaner casing
3 Suspension strut top
4 Coolant expansion tank
5 Brake fluid reservoir
6 Air mass meter
7 Fuel pressure regulator
8 Relay box
9 Anti-theft alarm horn
10 ABS hydraulic modulator
11 Washer fluid reservoir
12 Power steering fluid reservoir
13 Battery
14 Distributor
15 Engine oil level dipstick
16 Oil filler cap
Page 180 of 525

test (refer to Chapter 2A) will provide valuable
information regarding the overall performance
of the main internal components. Such a test
can be used as a basis to decide on the
extent of the work to be carried out. If, for
example, a compression test indicates serious
internal engine wear, conventional
maintenance as described in this Chapter will
not greatly improve the performance of the
engine. It may also prove a waste of time and
money, unless extensive overhaul work is
carried out first.
The following series of operations are those
most often required to improve the
performance of a generally poor-running
engine:Primary operations
a)Clean, inspect and test the battery (See
“Weekly Checks”)
b)Check all the engine related fluids (See
“Weekly Checks”)
c)Check the condition and tension of the
auxiliary drivebelt (Sections 18 and 22, as
appropriate).
d)Renew the spark plugs (Sections 30 and
37, as appropriate).
e)Inspect the distributor cap, rotor arm and
HT leads, as applicable (Section 31).
f)Check the condition of the air filter, and
renew if necessary (Section 27).
g)Check the fuel filter (Section 29).
h)Check the condition of all hoses, and
check for fluid leaks (Section 4).i)Check the idle speed and mixture
settings, as applicable (Section 9).
5If the above operations do not prove fully
effective, carry out the following secondary
operations:
Secondary operations
All items listed under “Primary operations”,
plus the following:
a)Check the charging system (Chapter 5).
b)Check the ignition system (Chapter 5).
c)Check the fuel system (Chapters 4A and
4B).
d)Renew the distributor cap and rotor arm
(Section 31).
e)Renew the ignition HT leads (Section 31).
3Engine oil and filter - renewal
2
1Ideally, the oil should be drained with the
engine hot, just after the vehicle has been
driven.
2On DOHC models, remove the engine
undershield to expose the sump drain plug
and the oil filter.
3Place a container beneath the oil drain plug
at the rear of the sump.
4Remove the oil filler cap from the camshaft
cover, then using a socket or spanner,
unscrew the oil drain plug, and allow the oil to
drain (see illustration). Take care to avoid
scalding if the oil is hot.
5Allow ten to fifteen minutes for the oil to
drain completely, then move the container
and position it under the oil filter.6On 1.8 and 2.0 litre models, improved
access to the oil filter can be gained by
jacking up the front of the vehicle and
removing the right-hand roadwheel (see
illustration). Ensure that the handbrake is
applied, and that the vehicle is securely
supported on axle stands (see “Jacking and
Vehicle Support”). Note that further oil may
drain from the sump as the vehicle is raised.
7Using a strap wrench or a filter removal tool
if necessary, slacken the filter and unscrew it
from the mounting. Alternatively, if the filter is
very tight, a screwdriver can be driven
through the filter casing and used as a lever.
Discard the filter.
8Wipe the mating face on the filter mounting
with a lint-free rag, then smear the sealing ring
of the new filter with clean engine oil of the
specified grade.
9Screw the new filter into position and
tighten it by hand only, do not use any tools.
10Where applicable, refit the roadwheel and
lower the vehicle to the ground. Fully tighten
the roadwheel bolts with the vehicle resting on
its wheels.
11Examine the condition of the oil drain plug
sealing ring and renew if necessary, then refit
the drain plug and tighten it to the specified
torque. 12Refill the engine through the filler on the
camshaft cover, using the specified grade and
quantity of oil. Fill until the level reaches the
“MAX” mark on the dipstick, allowing time for
the oil to drain through the engine to the
sump.
13Refit the oil filler cap, then start the engine
and check for leaks. Note that the oil pressure
warning lamp may stay illuminated for a few
seconds when the engine is started as the oil
filter fills with oil.
14Stop the engine and recheck the oil level,
topping-up if necessary.
15On DOHC models, refit the engine
undershield.
16Dispose of the old engine oil safely; do not
pour it down a drain.
4Hose and fluid leak check
1
1Visually inspect the engine joint faces,
gaskets and seals for any signs of water or oil
leaks. Pay particular attention to the areas
around the camshaft cover, cylinder head, oil
filter and sump joint faces. Remember that,
over a period of time, some very slight
seepage from these areas is to be expected -
what you are really looking for is any
indication of a serious leak. Should a leak be
found, renew the offending gasket or oil seal
by referring to the appropriate Chapters in this
manual.
Every 9000 miles or 12 months 1•9
3.6 Oil filter viewed through right-hand
wheel arch - SOHC model3.4 Sump drain plug location -
2.0 litre DOHC model
(engine undershield removed)
1
Basic service, every 9000 miles (15 000 km) or 12 months
As the drain plug releases
from the threads, move it
away quickly so the stream
of oil, running out of the
sump, goes into the container not up
your sleeve (see illustration).
Note: It is
antisocial and
illegal to dump oil
down the drain.
To find the
location of your
local oil recycling
bank, call this
number free.
Page 181 of 525

2Also check the security and condition of all
the engine related pipes and hoses. Ensure
that all cable-ties or securing clips are in
place, and in good condition. Clips that are
broken or missing can lead to chafing of the
hoses, pipes or wiring, which could cause
more serious problems in the future.
3Carefully check the radiator hoses and
heater hoses along their entire length. Renew
any hose that is cracked, swollen or
deteriorated. Cracks will show up better if the
hose is squeezed. Pay close attention to the
hose clips that secure the hoses to the
cooling system components. Hose clips can
pinch and puncture hoses, resulting in cooling
system leaks. It is always beneficial to renew
hose clips whenever possible.
4Inspect all the cooling system components
(hoses, joint faces, etc.) for leaks.
5Where any problems are found on system
components, renew the component or gasket
with reference to Chapter 3.
6Where applicable, inspect the automatic
transmission fluid cooler hoses for leaks or
deterioration.
7With the vehicle raised, inspect the petrol
tank and filler neck for punctures, cracks and
other damage. The connection between the
filler neck and tank is especially critical.
Sometimes a rubber filler neck or connecting
hose will leak due to loose retaining clamps or
deteriorated rubber.
8Carefully check all rubber hoses and metal
fuel lines leading away from the petrol tank.
Check for loose connections, deteriorated
hoses, crimped lines, and other damage. Pay
particular attention to the vent pipes and
hoses, which often loop up around the filler
neck and can become blocked or crimped.
Follow the lines to the front of the vehicle,
carefully inspecting them all the way. Renew
damaged sections as necessary.
9From within the engine compartment,
check the security of all fuel hose attachments
and pipe unions, and inspect the fuel hoses
and vacuum hoses for kinks, chafing and
deterioration.
10Where applicable, check the condition of
the power steering fluid hoses and pipes.5Steering and suspension
check
2
Front suspension and steering
check
1Raise the front of the car, and support on
axle stands (“Jacking and Vehicle Support”).
2Visually inspect the balljoint dust covers
and the steering rack-and-pinion gaiters for
splits, chafing or deterioration. Any wear of
these components will cause loss of lubricant,
together with dirt and water entry, resulting in
rapid wear of the balljoints or steering gear.
3On vehicles with power steering, check the
fluid hoses for chafing or deterioration, and
the pipe and hose unions for fluid leaks. Also
check for signs of fluid leakage under
pressure from the steering gear rubber
gaiters, which would indicate failed fluid seals
within the steering gear.
4Grasp the roadwheel at the 12 o’clock and
6 o’clock positions, and try to rock it (see
illustration). Very slight free play may be felt,
but if the movement is appreciable, further
investigation is necessary to determine the
source. Continue rocking the wheel while an
assistant depresses the footbrake. If the
movement is now eliminated or significantly
reduced, it is likely that the hub bearings are
at fault. If the free play is still evident with the
footbrake depressed, then there is wear in the
suspension joints or mountings.
5Now grasp the wheel at the 9 o’clock and 3
o’clock positions, and try to rock it as before.
Any movement felt now may again be caused
by wear in the hub bearings or the steering
track-rod balljoints. If the inner or outer balljoint
is worn, the visual movement will be obvious.
6Using a large screwdriver or flat bar, check
for wear in the suspension mounting bushes
by levering between the relevant suspension
component and its attachment point. Some
movement is to be expected as the mountings
are made of rubber, but excessive wear
should be obvious. Also check the condition
of any visible rubber bushes, looking for splits,
cracks or contamination of the rubber.
7Inspect the front suspension lower arms for
distortion or damage (Chapter 10, Section 5).
8With the car standing on its wheels, have an
assistant turn the steering wheel back and
forth about an eighth of a turn each way.
There should be very little, if any, lost
movement between the steering wheel and
roadwheels. If this is not the case, closely
observe the joints and mountings previously
described, but in addition, check the steering
column universal joints for wear, and the rack-
and-pinion steering gear itself.
Suspension strut/shock
absorber check
Note:Suspension struts/shock absorbers
should always be renewed in pairs on the
same axle.9Check for any signs of fluid leakage around
the suspension strut/shock absorber body, or
from the rubber gaiter around the piston rod.
Should any fluid be noticed, the suspension
strut/shock absorber is defective internally,
and should be renewed.
10The efficiency of the suspension
strut/shock absorber may be checked by
bouncing the vehicle at each corner. The body
will return to its normal position and stop after
being depressed. If it rises and returns on a
rebound, the suspension strut/shock
absorber is probably suspect. Examine also
the suspension strut/shock absorber upper
and lower mountings for any signs of wear.
6Driveshaft gaiter check
2
With the vehicle raised and securely
supported on stands, turn the steering onto
full lock, then slowly rotate the roadwheel.
Inspect the condition of the outer constant
velocity (CV) joint rubber gaiters, squeezing
the gaiters to open out the folds (see
illustration). Check for signs of cracking,
splits or deterioration of the rubber, which
may allow the grease to escape, and lead to
water and grit entry into the joint. Also check
the security and condition of the retaining
clips. Repeat these checks on the inner CV
joints. If any damage or deterioration is found,
the gaiters should be renewed as described in
Chapter 8.
1•10Every 9000 miles or 12 months
6.1 Check the condition of the driveshaft
gaiters (A) and clips (B)
5.4 Check for wear in the hub bearings by
grasping the wheel and trying to rock it
A leak in the cooling system will usually
show up as white or rust coloured
deposits on the area adjoining the leak
Page 185 of 525

28Air inlet temperature control
check (carburettor models
only)
2
Refer to Chapter 4A for details.
29Fuel filter renewal
3
Fuel filters are fitted in various locations
throughout the range. Some may be ‘in-line’ in
the fuel tank itself, or fitted into the
carburettor.
Refer to Chapters 4A or 4B, as appropriate.
30Spark plug renewal (SOHC)
2
1The correct functioning of the spark plugs is
vital for the correct running and efficiency of
the engine. It is essential that the plugs fitted
are appropriate for the engine. Refer to the
specifications in Chapter 5. If this type is used
and the engine is in good condition, the spark
plugs should not need attention between
scheduled service replacement intervals.
Spark plug cleaning is rarely necessary and
should not be attempted unless specialised
equipment is available, as damage can easily
be caused to the firing ends.
2Identify each HT lead for position so that the
leads can be refitted to their correct cylinders.
Then disconnect the leads from the plugs by
pulling on the connectors, not the leads.
3Clean the area around each spark plug
using a small paintbrush, then using a plugspanner (preferably with a rubber insert),
unscrew and remove the plugs (see
illustration). Cover the spark plug holes with
a clean rag to prevent the ingress of any
foreign matter.
4The condition of the spark plugs will tell
much about the overall condition of the
engine.
5If the insulator nose of the spark plug is
clean and white, with no deposits, this is a
sign of a weak mixture, or too hot a plug (a hot
plug transfers heat away from the electrode
slowly -a cold plug transfers heat away
quickly).
6If the tip and insulator nose is covered with
hard black-looking deposits, then this is
indicative that the mixture is too rich. Should
the plug be black and oily, then it is likely that
the engine is fairly worn, as well as the mixture
being too rich.
7If the insulator nose is covered with light tan
to greyish brown deposits, then the mixture is
correct, and it is likely that the engine is in
good condition.
8The spark plug gap is of considerable
importance, because if it is either too large or
too small, the size of the spark and its
efficiency will be seriously impaired. The spark
plug gap should be set to the figure given in
the Specifications, in Chapter 5.
9To set it, measure the gap with a feeler
blade and then bend open, or close, the outer
plug electrode until the correct gap is
achieved. The centre electrode should never
be bent, as this may crack the insulation and
cause plug failure, if nothing worse (see
illustrations).10Before fitting new spark plugs check that
their threaded connector sleeves are tight.
11Screw in the plugs by hand, then tighten
them to the specified torque. Do not exceed
the torque figure.
12Push the HT leads firmly onto the spark
plugs, ensuring that they are connected to
their correct cylinders.
31Distributor cap and HT lead
check
3
1Remove the distributor cap and HT leads,
and wipe them clean.
2Also wipe clean the coil connections.
Remove the rotor arm, then visually check the
distributor cap, rotor arm and HT leads for
hairline cracks, and signs of arcing.
1•14Every 18 000 miles or 24 months
30.9A Tools required for spark plug
removal, gap adjustment and refitting30.9C Measuring the spark plug gap with
feeler blade30.9B Measuring the spark plug gap with
wire gauge
30.3 Removing a spark plugWarning: Before carrying out
the following operation, refer to
the precautions given in “Safety
first!” at the beginning of this
manual, and follow them implicitly. Petrol
is a highly dangerous and volatile liquid,
and the precautions necessary when
handling it cannot be overstressed.
It is very often difficult to insert spark
plugs into their holes without cross-
threading them. To avoid this, fit a
short length of 8 mm (internal
diameter), rubber hose over the end of
the spark plug. The flexible hose acts
as a universal joint to help align the
plug correctly. Should the plug begin to
cross-thread, the hose will slip on the
spark plug, preventing damage to the
thread in the cylinder head.
Number the HT leads before
removal to ensure correct
refitting.
Page 194 of 525

pitting. If evident, the cylinder head and all
bearing caps must be renewed as a matched
set, as there is no provision for refacing if the
bearing caps cannot be renewed individually.
8The camshaft(s) should show no marks or
scoring on the journal or cam lobe surfaces. if
evident, renew the camshaft(s).
9It is advisable to renew the camshaft front
oil seal(s) as a matter of course. Prise the old
seal(s) from the front of the camshaft(s) and
discard them.
Refitting
10Begin refitting by liberally coating the
contact faces of the hydraulic valve lifters and
the camshaft(s) with molybdenum disulphide
paste.
11Coat the mating faces of the front and
rear bearing caps with sealing compound and
refit the bearing caps in their original positions
as noted during removal.
12Tighten the camshaft bearing cap nuts to
the specified torque in half-turn stages, as
when loosening the nuts. Note that when
refitting the exhaust camshaft, the two smaller
rear bearing cap securing nuts should be
tightened after all the main camshaft bearing
cap nuts have been tightened. Note also that
the two smaller nuts should be tightened to a
lower torque wrench setting than the main
nuts.
13Turn the camshaft until the locating peg
for the camshaft sprocket is uppermost, then
lubricate the lips of a rear camshaft front oil
seal with a little grease, and fit the oil seal,
using a tube or socket of similar diameter with
a washer and the camshaft sprocket bolt.
Screw the camshaft sprocket bolt into the end
of the camshaft to draw the oil seal into
position on its shoulder.
14Repeat the procedure for the remaining
camshaft.
15Refit the distributor with reference to
Chapter 5. Fit a new timing belt and the
camshaft sprockets, then adjust the timing
belt as described in Section 4 or 5, as
applicable.
8Cylinder head -removal and
refitting (engine in vehicle)
4
Note: The engine must be cold when the
cylinder head is removed. Do not remove the
cylinder head from a hot engine. New cylinder
head bolts, a new cylinder head gasket and a
new timing belt must be used on refitting.
The torque settings (as shown in Chapter 2A)
are only applicable to latest specification head
bolts, available from Vauxhall. Earlier type or
alternative make, head bolts may require
different torques. Consult your supplier
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Drain the cooling system, as described in
Chapter 3.3Remove the front section of the exhaust
system, as described in Chapter 4C.
4The cylinder head can be removed
complete with the inlet manifold, or the inlet
manifold can be detached from the cylinder
head before removal, with reference to
Chapter 4B. If no work is to be carried out on
the inlet manifold, it can be unbolted from the
cylinder head and supported to one side out
of the way, thus avoiding the need to
disconnect the relevant hoses, pipes and
wiring.
5If the cylinder head is to be removed
complete with the inlet manifold, disconnect
all relevant hoses, pipes and wiring from the
inlet manifold and associated components,
referring to Chapter 4B, and unbolt the
manifold support bracket from the manifold.
Loosen the alternator mountings with
reference to Chapter 5, then unbolt the upper
alternator mounting from the inlet manifold.
6If the inlet manifold is to be left in the engine
compartment, continue as follows, otherwise
go on to paragraph 17.
7Disconnect the wiring plug from the airflow
meter, and the breather hose from the air box
on the throttle body. Disconnect the air
cleaner trunking and remove the airflow
meter/air box assembly from the throttle
body. Refer to Chapter 4B if necessary.
8Disconnect the end of the throttle cable
from the throttle valve lever, then unbolt the
throttle cable support bracket and remove it
from the inlet manifold.
9Unscrew the two earth lead securing nuts
from the fuel rail (one at each end of the rail)
and disconnect the three earth leads.
10Disconnect the wiring plug from the
throttle position switch.
11Pull up on the wiring harness housing, and
disconnect the wiring plugs from the fuel
injectors by compressing the retaining clips.
Move the wiring harness housing to one side.
12Disconnect the two breather hoses from
the rear of the camshaft cover.
13Loosen the alternator mountings, with
reference to Chapter 5, then unbolt the upper
alternator mounting from the inlet manifold.
14Unbolt the manifold support bracket from
the manifold.15Make a final check to ensure that all
necessary hoses, pipes and wires have been
disconnected, then unscrew the securing nuts
and lift the inlet manifold from the cylinder
head. Ensure that the manifold is properly
supported, taking care not to strain any of the
hoses, pipes and wires, etc., which are still
connected.
16Recover the manifold gasket from the
cylinder head.
17Remove the timing belt, camshaft
sprockets, and timing belt tensioner and idler
pulleys, as described in Section 4.
18Unscrew the upper and middle studs for
the timing belt outer cover screws. Note that
the upper stud simply unscrews from the
cylinder head, but the middle stud is secured
by a bolt.
19Unscrew the two upper rear timing belt
cover securing bolts from the cylinder head.
20Remove the distributor cap and HT leads
with reference to Chapter 5.
21Disconnect the distributor wiring plug.
22Disconnect the coolant hose from the
left-hand end of the cylinder head.
23Unscrew the bolt securing the crankcase
breather tube bracket to the end of the
cylinder head.
24Disconnect the radiator top hose from the
thermostat housing, and disconnect the
wiring plugs from the temperature gauge
sender and the coolant temperature sensor
(both situated in the thermostat housing).
25Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant hoses, pipes and wires have been
disconnected.
26On X20 XEV models, remove the
camshaft, as described in Section 7.
27Using a Torx socket, and working in the
order shown (see illustrations), loosen all the
cylinder head bolts by a quarter of a turn, then
loosen all the bolts by half a turn, and finally
loosen and remove the bolts. Recover the
washers. Note that the loosening sequence
on X20 XEV differs to other DOHC engines.
28Lift the cylinder head from the cylinder
block. If necessary, tap the cylinder head
gently with a soft-faced mallet to free it from
the block, but do not lever at the mating
faces. Note that the cylinder head is located
on dowels.
DOHC engine procedures 2B•7
8.27B Cylinder head bolt loosening
sequence - (X 20 XEV engines)8.27A Cylinder head bolt loosening
sequence - (20 XEJ and C 20 XE engines)
2B
Page 203 of 525

Torque wrench settings (continued)Nmlbf ft
Big-end bearing cap: *
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3526
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 45º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 15º
Camshaft housing cover to housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Camshaft pulley to camshaft . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4533
Camshaft thrust plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Coolant outlet to thermostat housing:
C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Coolant pump to cylinder block:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C 16 NZ2) (M6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre (M8) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Crankshaft sensor wheel:
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1310
Cylinder head to cylinder block: *
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2):
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 60º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 60º
Stage 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 60º
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 90º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 90º
Stage 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 90º
Drivebelt (ribbed) pulley/timing belt drive to crankshaft: *
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2):
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5541
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 45º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 15º
Drivebelt pulley to timing belt drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
Drivebelt (ribbed) tensioner to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
Drivebelt (ribbed) tensioner to support:
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1813
Engine bracket to cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
Engine bracket to transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
Engine mounting bracket to engine bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
Engine mounting to engine mounting bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6548
Engine mounting to front axle housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4030
Engine mounting to power steering pump support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
Engine mounting to side member . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6548
Exhaust manifold to cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2216
Exhaust pipe to manifold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Flexplate to crankshaft . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6044
Flywheel to crankshaft: *
1.4 and 1.6 litre, (except C16 NZ2):
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3526
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 30º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 15º
C16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6548
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 30º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 15º
Front timing belt cover to rear cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Fuel pump to camshaft housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1813
Guide sleeve, release bearing to transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2216
Heat shield sleeves to cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3022
Inlet manifold to cylinder head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2216
Knock sensor to cylinder block (X16 SZ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1310
Main bearing cap: *
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5037
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 45º
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Angle tighten by 15º
Oil filter to oil pump/cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
2A•6SOHC engine procedures
Page 210 of 525
a)Inlet and exhaust manifolds (where
applicable)
b)Starter motor
c)Rear coolant gallery and hoses
d)Oil pressure switch
e)Oil temperature switch (where applicable)
f)Oil level sensor (where applicable)
g)Knock sensor (where applicable)
h)TDC sensor (where applicable)
i)Distributor components
j)Fuel pump (where applicable)
k)Thermostat/housing (N 16 NZ2, 1.8 and
2.0 litre models)
l)Power steering pump and mounting
bracket (where applicable)
m)Alternator mounting bracket
n)Engine lifting brackets
o)Dipstick/crankcase breather tube
p)Inlet manifold mounting bracket (where
applicable)
13To ensure maximum life, with minimum
trouble, from a rebuilt engine, not only must
everything be correctly assembled, but it must
also be spotlessly clean. All oilways and
coolant passages must be clear, and all
washers must be fitted in their original
positions. Oil all bearings and other moving
surfaces thoroughly with clean engine oil
during assembly.
14Before assembly begins, renew any bolts
or studs with damaged threads.
15Obtain a torque wrench, an angle-torque
gauge, sockets and bits, an oil can, clean
lint-free rag, and a set of engine gaskets and
oil seals, together with a new oil filter.16If they have been removed, new cylinder
head bolts, flywheel bolts, big-end bearing
cap bolts and main bearing cap bolts will also
be required.
17On completion of reassembly, refit the
applicable ancillary components listed in
paragraph 12.
18Follow procedure shown in Section 37.
11Timing belt and sprockets
(without automatic tensioner) -
removal, refitting and adjustment
3
Note: A two-legged puller may be required to
remove the crankshaft sprocket on N 16 NZ2,
1.8 and 2.0 litre models.Some of the later 1.4
and 1.6 litre engines, identifiable by the
squared-off top surfaces of the timing belt
covers, are fitted with spring-loaded auto-matic timing belt tensioners to ensure correct
belt tensioning on assembly.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2On models with power steering, remove the
pump drivebelt, see Chapters 1 and 10.
3Remove the alternator drivebelt, as
described in Chapter 5.
4On C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models,
disconnect the wiring from the temperature
gauge sender.
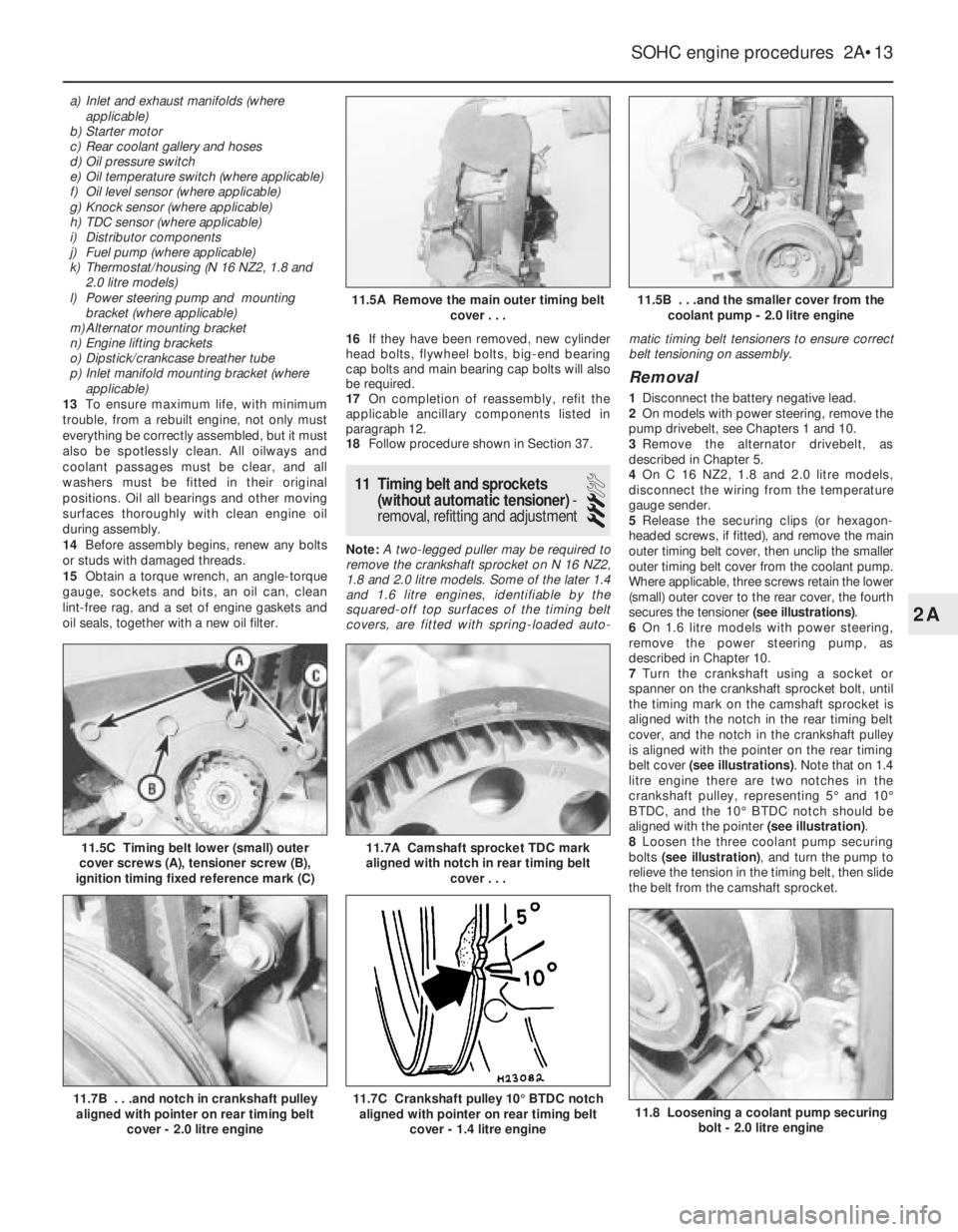
5Release the securing clips (or hexagon-
headed screws, if fitted), and remove the main
outer timing belt cover, then unclip the smaller
outer timing belt cover from the coolant pump.
Where applicable, three screws retain the lower
(small) outer cover to the rear cover, the fourth
secures the tensioner (see illustrations).
6On 1.6 litre models with power steering,
remove the power steering pump, as
described in Chapter 10.
7Turn the crankshaft using a socket or
spanner on the crankshaft sprocket bolt, until
the timing mark on the camshaft sprocket is
aligned with the notch in the rear timing belt
cover, and the notch in the crankshaft pulley
is aligned with the pointer on the rear timing
belt cover (see illustrations). Note that on 1.4
litre engine there are two notches in the
crankshaft pulley, representing 5°and 10°
BTDC, and the 10°BTDC notch should be
aligned with the pointer (see illustration).
8Loosen the three coolant pump securing
bolts (see illustration), and turn the pump to
relieve the tension in the timing belt, then slide
the belt from the camshaft sprocket.
SOHC engine procedures 2A•13
11.5C Timing belt lower (small) outer
cover screws (A), tensioner screw (B),
ignition timing fixed reference mark (C)
11.8 Loosening a coolant pump securing
bolt - 2.0 litre engine11.7C Crankshaft pulley 10°BTDC notch
aligned with pointer on rear timing belt
cover - 1.4 litre engine11.7B . . .and notch in crankshaft pulley
aligned with pointer on rear timing belt
cover - 2.0 litre engine
11.7A Camshaft sprocket TDC mark
aligned with notch in rear timing belt
cover . . .
11.5B . . .and the smaller cover from the
coolant pump - 2.0 litre engine11.5A Remove the main outer timing belt
cover . . .
2A
Page 217 of 525

supported to one side out of the way, thus
avoiding the need to disconnect the relevant
hoses, pipes and wiring.
5If the cylinder head is to be removed
complete with the manifolds, disconnect all
relevant hoses, pipes and wiring from the inlet
manifold and associated components,
referring to Chapter 4A or 4B. On carburettor
models, disconnect the hot air hose from the
shroud on the exhaust manifold. Loosen the
alternator mountings, with reference to
Chapter 5, then unbolt the upper alternator
mounting from the inlet manifold.
6If the inlet manifold is to be left in the engine
compartment, continue as follows, otherwise
go on to paragraph 15.
7Disconnect the air cleaner trunking from the
air box on the carburettor or throttle body, or
directly from the throttle body (as applicable),
and disconnect the camshaft cover breather
hose that runs to the carburettor or throttle
body (as applicable), (see illustration).
8On C 16 NZ2, 1.8 and 2.0 litre models,
disconnect the smaller coolant hose from the
top of the thermostat housing.
9On 1.6 litre models (except C 16 NZ2),
disconnect the breather hose (which runs
from the camshaft cover to the inlet manifold)
at the camshaft cover.
10On fuel injection models, unbolt the two
wiring harnesses earth leads from the
camshaft housing (see illustration).
11On 1.4 and 1.6 litre models (except C 16
NZ2), disconnect the stub hose that connects
the crankcase breather tube to the rear of thecamshaft housing (see illustration).
12Loosen the alternator mountings, referring
to Chapter 5, then unbolt the upper alternator
mounting from the inlet manifold.
13Make a final check to ensure that all
necessary hoses, pipes and wires have been
disconnected, then unscrew the securing
nuts, noting the location of the engine lifting
bracket, and lift the inlet manifold from the
cylinder head. Ensure that the manifold is
properly supported, taking care not to strain
any of the hoses, pipes and wires, etc., which
are still connected.
14Recover the manifold gasket from the
cylinder head.
15If desired, remove the exhaust manifold,
with reference to Chapter 4C.
16Remove the timing belt and the camshaft
sprocket, as described in Section 11.
17Unscrew the two upper rear timing belt
cover securing bolts from the camshaft
housing.
18Disconnect the HT leads from the spark
plugs and the coil, labelling them if necessary
to aid refitting, and remove the distributor
cap, referring to Chapter 5. Where applicable,
disconnect the distributor wiring plug.
19If not already done, disconnect the stub
hose that connects the crankcase breather
tube to the camshaft housing. If applicable
unscrew the bolt securing the crankcase
breather tube bracket to the end of the
cylinder head (see illustrations).
20Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
thermostat housing.21On carburettor models, disconnect the fuel
hoses from the fuel pump. Be prepared for fuel
spillage, and plug the open ends of the hoses,
to prevent further fuel loss and dirt ingress.
22Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant hoses, pipes and wires, etc., have
been disconnected.
23Working from the outside inwards in a
spiral pattern as shown (see illustration),
loosen all the cylinder head bolts by a quarter
of a turn. Then loosen all the bolts by half a
turn, and finally loosen and remove the bolts.
Recover the washers.
24Lift the camshaft housing from the
cylinder head (see illustration). If necessary,
tap the housing gently with a soft-faced mallet
to free it from the cylinder head, but do not
lever at the mating faces. Note that the
camshaft housing is located on dowels.
25Lift the rocker arms and their thrust pads
from the cylinder head, keeping them in order
so that they can be refitted in their original
positions (see illustrations).
26Lift the hydraulic valve lifters from the
cylinder head, and place them upright in an oil
bath until they are to be refitted (see
illustration). Ensure that the depth of oil is
sufficient to fully cover the valve lifters, and
keep the lifters in order, so that they can be
refitted in their original positions.
27Lift the cylinder head from the cylinder
block (see illustration). If necessary, tap the
cylinder head gently with a soft-faced mallet
to free it from the block, but do not lever at the
mating faces. Note that the cylinder head is
located on dowels.
2A•20SOHC engine procedures
20.7 Disconnecting a camshaft cover
breather hose -
2.0 litre engine20.11 Disconnecting the crankcase
breather tube stub hose -
1.6 litre engine
20.23 Cylinder head bolt loosening
sequence - SOHC engines20.19B Unbolting the crankcase breather
tube bracket from the cylinder head -
2.0 litre model20.19A Disconnecting the crankcase
breather tube stub hose -
2.0 litre engine
20.10 Unbolting the fuel injection wiring
harness earth leads from the camshaft
housing - 2.0 litre engine