1986 TOYOTA SUPRA spark plugs
[x] Cancel search: spark plugsPage 392 of 878

COMPRESSION CHECK
HINT: If there is lack of power, excessive oil consumption or
poor fuel economy, measure the compression pressure.
1. WARM UP AND STOP ENGINE
Allow the engine to warm up to normal operating tempera-
ture.
2. 2JZ±GE:
DISCONNECT DISTRIBUTOR CONNECTOR
3. 2JZ±GTE:
DISCONNECT CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR CON-
NECTORS
4. 2JZ±GE:
DISCONNECT HIGH±TENSION CORDS FROM SPARK
PLUGS
(See high±tension cords and cord clamps removal in
Ignition System)
5. 2JZ±GTE:
REMOVE IGNITION COILS ASSEMBLIES
(See ignition coils removal in Ignition System)
6. REMOVE SPARK PLUGS
7. CHECK CYLINDER COMPRESSION
(a) Insert a compression tester into the spark plug hole.
(b) Wh ile cra n kin g th e en g in e , me a su re th e co mp re ssio n
pressure.
HINT: Always use a fully charged battery to obtain engine rev-
olutions of 250 rpm or more.
(c) Repeat steps (a) through (b) for each cylinder.
NOTICE: This measurement must be done in as short a time as
possible.
Standard pressure:
2JZ±GE
1,275 kPa (13.0 kgf/cm
2, 185 psi) or more
2JZ±GTE
1,079 kPa (11.0 kgf/cm
2, 156 psi) or more
Minimum pressure:
2JZ±GE
1,079 kPa (11.0 kgf/cm
2, 156 psi)
2JZ±GTE
883 kPa (9.0 kgf/cm
2, 128 psi)
Difference between each cylinder:
98 kPa (1.0 kgf/cm
2, 14 psi) or less
(d) If the cylinder compression in 1 or more cylinders is low, pour
a small amount of engine oil into the cylinder through the
spark plug hole and repeat steps (a) through (b) for the
cylinder with low compression.
± ENGINEENGINE MECHANICALEG±9
Page 393 of 878

wIf adding oil helps the compression, it is likely that the
piston rings and/or cylinder bore are probably worn or
damaged.
wIf pressure stays low, a valve may be sticking or seating
improper, or there may be leakage past the gasket.
8. REINSTALL SPARK PLUGS
9. 2JZ±GE:
RECONNECT HIGH±TENSION CORDS TO SPARK
PLUGS
(See high±tension cords and cord clamps installation in
Ignition System)
10. 2JZ±GTE:
REINSTALL IGNITION COILS ASSEMBLIES
(See ignition coils installation in Ignition System)
11. 2JZ±GE:
RECONNECT DISTRIBUTOR CONNECTOR
12. 2JZ±GTE:
RECONNECT CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR CONNEC-
TORS EG±10
± ENGINEENGINE MECHANICAL
Page 425 of 878
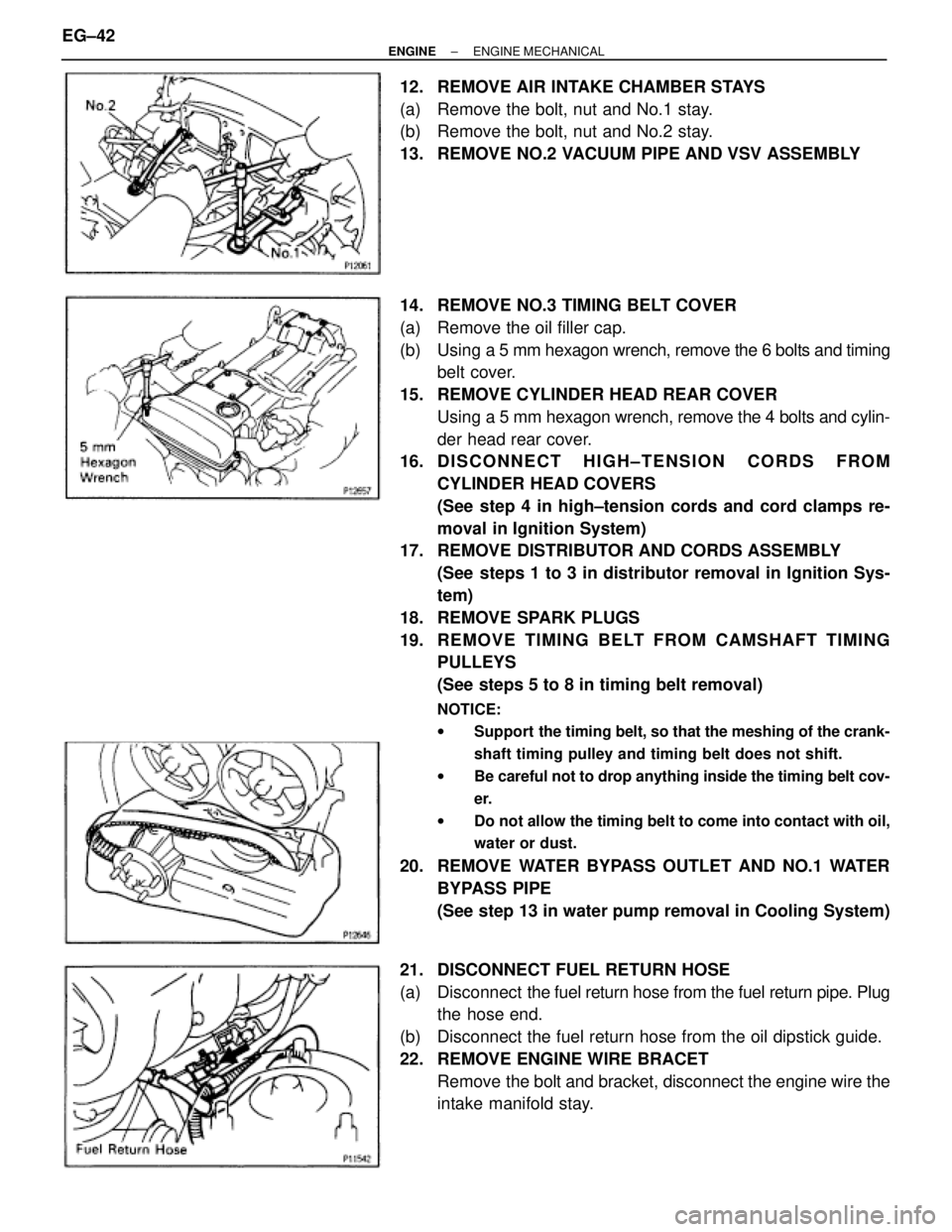
12. REMOVE AIR INTAKE CHAMBER STAYS
(a) Remove the bolt, nut and No.1 stay.
(b) Remove the bolt, nut and No.2 stay.
13. REMOVE NO.2 VACUUM PIPE AND VSV ASSEMBLY
14. REMOVE NO.3 TIMING BELT COVER
(a) Remove the oil filler cap.
(b) Using a 5 mm hexagon wrench, remove the 6 bolts and timing
belt cover.
15. REMOVE CYLINDER HEAD REAR COVER
Using a 5 mm hexagon wrench, remove the 4 bolts and cylin-
der head rear cover.
16. D I S C O N N E C T H I G H ± T E N S I O N C O R D S F R O M
CYLINDER HEAD COVERS
(See step 4 in high±tension cords and cord clamps re-
moval in Ignition System)
17. REMOVE DISTRIBUTOR AND CORDS ASSEMBLY
(See steps 1 to 3 in distributor removal in Ignition Sys-
tem)
18. REMOVE SPARK PLUGS
19. RE MO V E TIMING BE LT FRO M CAMS HAFT TIMING
PULLEYS
(See steps 5 to 8 in timing belt removal)
NOTICE:
wSupport the timing belt, so that the meshing of the crank-
shaft timing pulley and timing belt does not shift.
wBe careful not to drop anything inside the timing belt cov-
er.
wDo not allow the timing belt to come into contact with oil,
water or dust.
20. REMOVE WATER BYPASS OUTLET AND NO.1 WATER
BYPASS PIPE
(See step 13 in water pump removal in Cooling System)
21. DISCONNECT FUEL RETURN HOSE
(a) Disconnect the fuel return hose from the fuel return pipe. Plug
the hose end.
(b) Disconnect the fuel return hose from the oil dipstick guide.
22. REMOVE ENGINE WIRE BRACET
Remove the bolt and bracket, disconnect the engine wire the
intake manifold stay. EG±42
± ENGINEENGINE MECHANICAL
Page 432 of 878
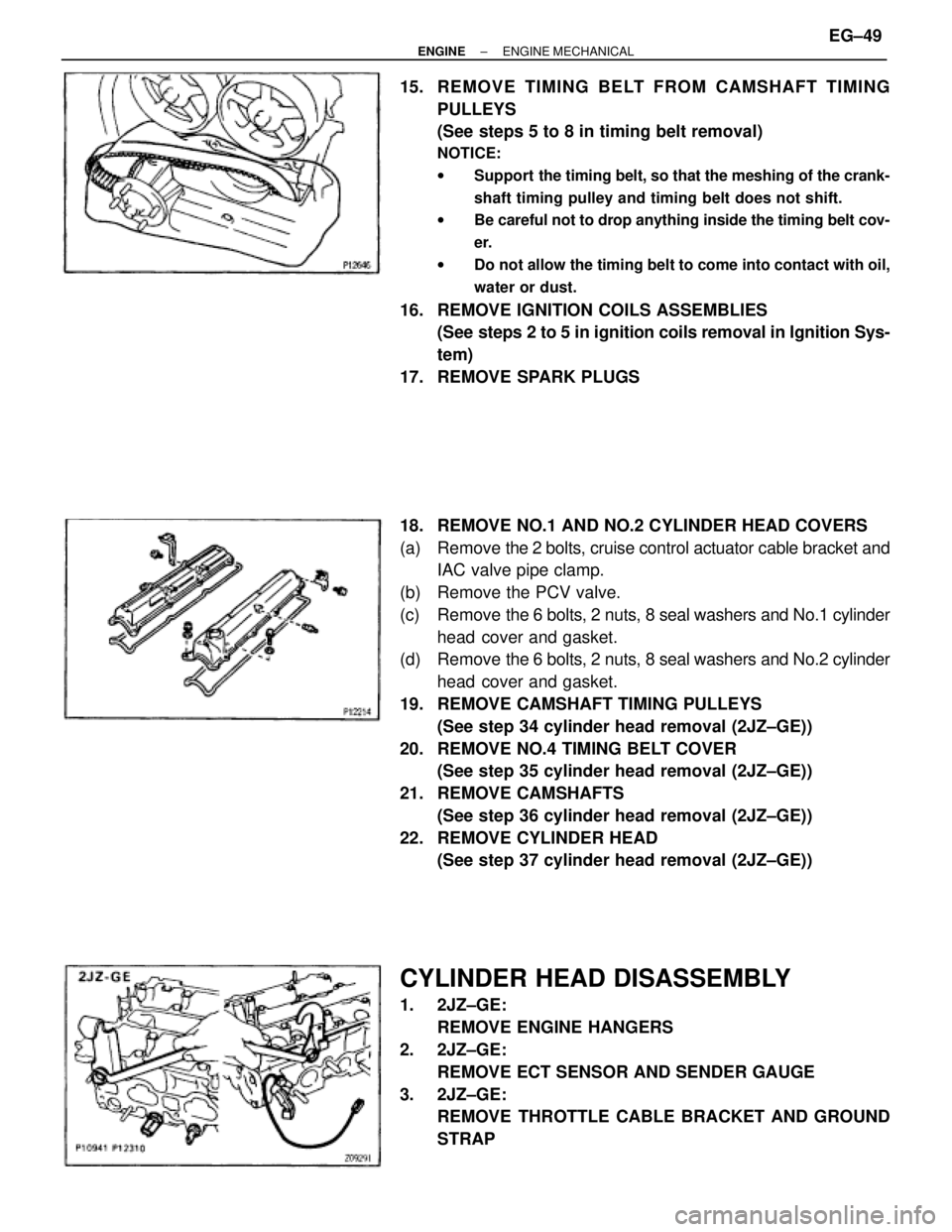
15. REMOVE TIMING BELT FROM CAMSHAFT TIMING
PULLEYS
(See steps 5 to 8 in timing belt removal)
NOTICE:
wSupport the timing belt, so that the meshing of the crank-
shaft timing pulley and timing belt does not shift.
wBe careful not to drop anything inside the timing belt cov-
er.
wDo not allow the timing belt to come into contact with oil,
water or dust.
16. REMOVE IGNITION COILS ASSEMBLIES
(See steps 2 to 5 in ignition coils removal in Ignition Sys-
tem)
17. REMOVE SPARK PLUGS
18. REMOVE NO.1 AND NO.2 CYLINDER HEAD COVERS
(a) Remove the 2 bolts, cruise control actuator cable bracket and
IAC valve pipe clamp.
(b) Remove the PCV valve.
(c) Remove the 6 bolts, 2 nuts, 8 seal washers and No.1 cylinder
head cover and gasket.
(d) Remove the 6 bolts, 2 nuts, 8 seal washers and No.2 cylinder
head cover and gasket.
19. REMOVE CAMSHAFT TIMING PULLEYS
(See step 34 cylinder head removal (2JZ±GE))
20. REMOVE NO.4 TIMING BELT COVER
(See step 35 cylinder head removal (2JZ±GE))
21. REMOVE CAMSHAFTS
(See step 36 cylinder head removal (2JZ±GE))
22. REMOVE CYLINDER HEAD
(See step 37 cylinder head removal (2JZ±GE))
CYLINDER HEAD DISASSEMBLY
1. 2JZ±GE:
REMOVE ENGINE HANGERS
2. 2JZ±GE:
REMOVE ECT SENSOR AND SENDER GAUGE
3. 2JZ±GE:
REMOVE THROTTLE CABLE BRACKET AND GROUND
STRAP
± ENGINEENGINE MECHANICALEG±49
Page 451 of 878

19. INSTALL WATER BYPASS OUTLET AND NO.1 WATER
BYPASS PIPE
(See step 3 in water pump installation in Cooling System)
20. INSTALL TIMING BELT
(See steps 11 to 17 in timing belt removal)
21. INSTALL SPARK PLUGS
22. INSTALL DISTRIBUTOR AND CORDS ASSEMBLY
(See steps 2, 3 and 5 in distributor installation in Ignition
System)
23. CONNECT HIGH±TENSION CORDS TO CYLINDER HEAD
COVERS
(See step 1 in high±tension cords and cord clamps
installation in Ignition System)
24. INSTALL NO.3 TIMING BELT COVER
25. INSTALL CYLINDER HEAD REAR COVER
26. INSTALL NO.2 VACUUM PIPE AND VSV ASSEMBLY
27. INSTALL AIR INTAKE CHAMBER STAYS
HINT: The No.1 stay is marked with ºFº, and No.2 stay is
marked with ºRº.
(a) Install the No.1 stay with the bolt and nut.
Torque: 18 NVm (185 kgfVcm, 13 ftVlbf)
(a) Install the No.2 stay with the bolt and nut.
Torque: 18 NVm (185 kgfVcm, 13 ftVlbf)
28. I N S TA L L T H R OTTLE BODY AND INTAKE AIR
CONNECTOR ASSEMBLY
(See in injector removal in SFI System)
29. CONNECT EVAP HOSE
30. CONNECT BRAKE BOOSTER VACUUM HOSE
31. INSTALL PS PUMP
(a) Install the pump rear stay with the 2 bolts.
Torque: 39 NVm (400 kgfVcm, 29 ftVlbf)
(b) Install the pump housing with the 2 bolts.
Torque: 58 NVm (590 kgfVcm, 43 ftVlbf)
(c) Connect these hoses:
wAir hose to No.4 timing belt cover
wAir hose to air intake chamber
32. INSTALL EXHAUST MANIFOLDS
(a) Install a new gasket and the exhaust manifold with 4 new
nuts. Install the No.1 and No.2 exhaust manifolds.
Torque: 39 NVm (400 kgfVcm, 29 ftVlbf)
(b) Connect the 2 (main heated) oxygen sensor connectors.
(c) Except California:
Install the manifold heat insulator with the 4 nuts. EG±68
± ENGINEENGINE MECHANICAL
Page 453 of 878
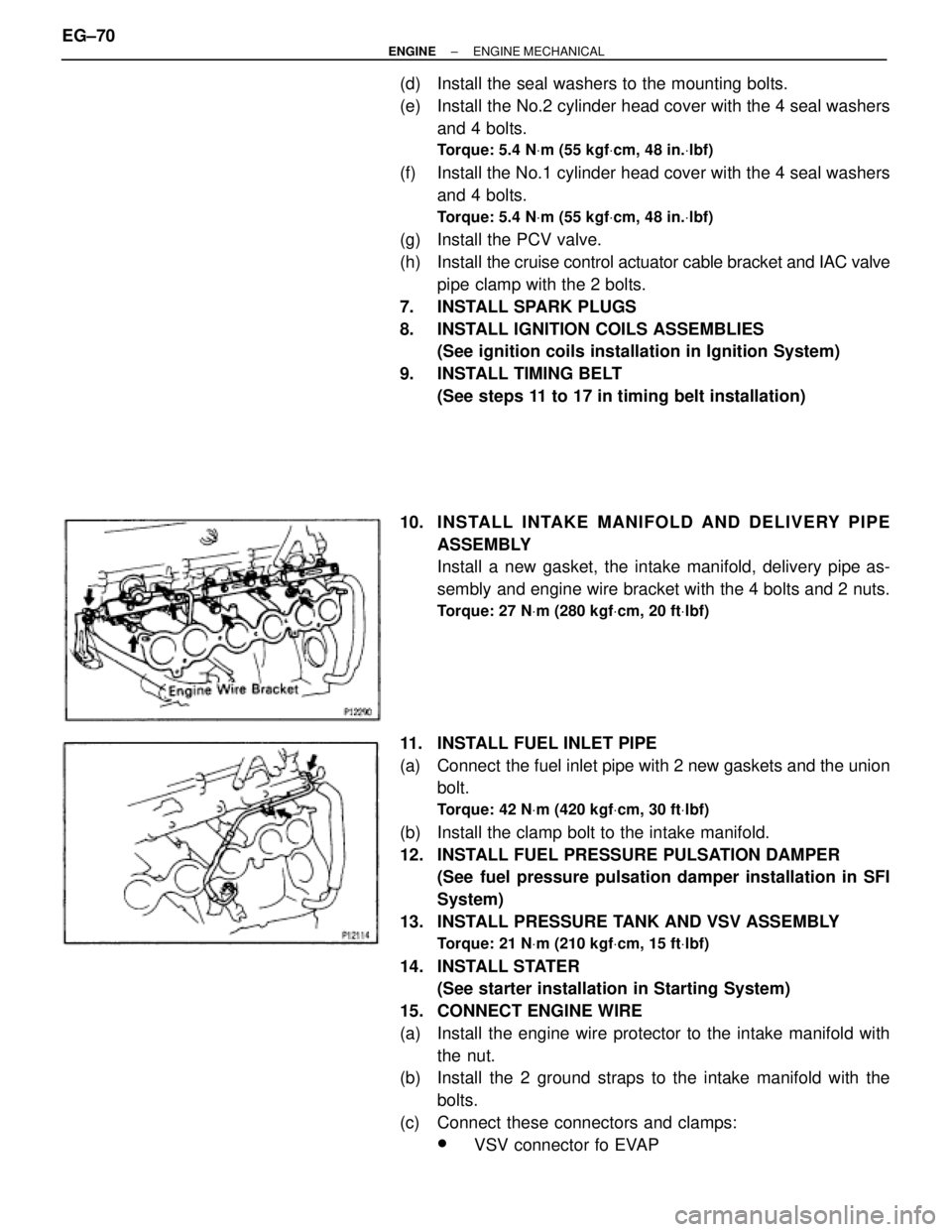
(d) Install the seal washers to the mounting bolts.
(e) Install the No.2 cylinder head cover with the 4 seal washers
and 4 bolts.
Torque: 5.4 NVm (55 kgfVcm, 48 in.Vlbf)
(f) Install the No.1 cylinder head cover with the 4 seal washers
and 4 bolts.
Torque: 5.4 NVm (55 kgfVcm, 48 in.Vlbf)
(g) Install the PCV valve.
(h) Install the cruise control actuator cable bracket and IAC valve
pipe clamp with the 2 bolts.
7. INSTALL SPARK PLUGS
8. INSTALL IGNITION COILS ASSEMBLIES
(See ignition coils installation in Ignition System)
9. INSTALL TIMING BELT
(See steps 11 to 17 in timing belt installation)
10. INS TALL INTAKE MANIFO LD AND DE LIV E RY PIP E
ASSEMBLY
Install a new gasket, the intake manifold, delivery pipe as-
sembly and engine wire bracket with the 4 bolts and 2 nuts.
Torque: 27 NVm (280 kgfVcm, 20 ftVlbf)
11. INSTALL FUEL INLET PIPE
(a) Connect the fuel inlet pipe with 2 new gaskets and the union
bolt.
Torque: 42 NVm (420 kgfVcm, 30 ftVlbf)
(b) Install the clamp bolt to the intake manifold.
12. INSTALL FUEL PRESSURE PULSATION DAMPER
(See fuel pressure pulsation damper installation in SFI
System)
13. INSTALL PRESSURE TANK AND VSV ASSEMBLY
Torque: 21 NVm (210 kgfVcm, 15 ftVlbf)
14. INSTALL STATER
(See starter installation in Starting System)
15. CONNECT ENGINE WIRE
(a) Install the engine wire protector to the intake manifold with
the nut.
(b) Install the 2 ground straps to the intake manifold with the
bolts.
(c) Connect these connectors and clamps:
wVSV connector fo EVAP EG±70
± ENGINEENGINE MECHANICAL
Page 618 of 878
METER, ANALOG
Current flow activates a magnetic
coil which causes a needle to
move, thereby providing a relative
display against a background
calibration. LED (LIGHT EMITTING DIODE)
Upon current flow, these diodes
emit light without producing the
heat of a comparable light. IGNITION COIL
Converts low±voltage DC current
into high±voltage ignition current
for firing the spark plugs. 1. SINGLE
FILAMENT
GROUND
The point at which wiring attaches
to the Body, thereby providing a
return path for an electrical circuit;
without a ground, current cannot
flow.Current flow causes a headlight
filament to heat up and emit light.
A headlight may have either a
single (1) filament or a double (2)
filament. BATTERY
Stores chemical energy and
converts it into electrical energy.
Provides DC current for the auto's
various electrical circuits.
CAPACITOR (Condenser)
A small holding unit for temporary
storage of electrical voltage.
CIRCUIT BREAKER
Basically a reusable fuse, a circuit
breaker will heat and open if too
much current flows through it. Some
units automatically reset when cool,
others must be manually reset.
DIODE
A semiconductor which allows
current flow in only one direction.
DIODE, ZENER
A diode which allows current flow
in one direction but blocks reverse
flow only up to a specific voltage.
Above that potential, it passes the
excess voltage. This acts as a
simple voltage regulator.
FUSE
A thin metal strip which burns
through when too much current
flows through it, thereby stopping
current flow and protecting a
circuit from damage.
FUSIBLE LINK
A heavy±gauge wire placed in
high amperage circuits which
burns through on overloads,
thereby protecting the circuit.
The numbers indicate the cross±
section surface area of the wires.HORN
An electric device which sounds a
loud audible signal.
LIGHT
Current flow through a filament
causes the filament to heat up
and emit light.
METER, DIGITAL
Current flow activates one or
many LED's, LCD's, or fluorescent
displays, which provide a relative
or digital display.
MOTOR
A power unit which converts
electrical energy into mechanical
energy, especially rotary motion. CIGARETTE LIGHTER
An electric resistance heating
element.
DISTRIBUTOR, IIA
Channels high±voltage current
from the ignition coil to the
individual spark plugs.2. DOUBLE
FILAMENT HEADLIGHTS
FUEL
(for High Current Fuse or
Fusible Link.)
(for Medium Current Fuse)
M
16
GLOSSARY OF TERMS AND SYMBOLS