Page 157 of 2389
AT3737
C1
B2C2
AT3539
SpringFree length
mm (in.)Outer diameter
mm (in.)Color
C
251.0 (2.008)18.0 (0.709)
Red
B
258.5 (2.303)15.2 (0.598)
Orange
C
1
Outer71.2 (2.803)24.4 (0.961)
Blue
Inner43.4 (1.709)17.8 (0.701)
Light green
AT3537
AT3536 AT3538
30. INSTALL ACCUMULATOR PISTONS AND SPRINGS
(a) Install the new O-rings to the pistons.
(b) Install the springs and pistons into the bores.
(c) Place the cover with a new gasket and gradually
tighten the bolts a little a time in sequence.
HINT: Each bolt length (mm, in.) is indicated in the figure.
Torque: 100 kg-cm (7 ft-lb, 10 N-m)
31. PLACE NEW SECOND BRAKE APPLY GASKET
32. INSTALL THROTTLE CABLE AND SOLENOID WIRE
33. INSTALL VALVE BODY TO TRANSAXLE CASE
(a) While holding the cam down with your hand, slip
the cable end into the slot.
(b) Lower the valve body into place.
NOTICE: Do not entangle the solenoid wire.
- AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLEInstallation of Component PartsAT-141
Page 202 of 2389

(e) Tighten the O±ring fittings or the bolted type fittings to
the specified torque.
4. WHEN CONNECTING MANIFOLD GAUGE;
(a) Be sure to connect the charging hose end with a pin
to the compressor charging valve.
(b) The letter ºDº engraved near the compressor service
valve indicates the high pressure side, and ºSº indi-
cates the low pressure side. Pay careful attention
when connecting the hose.
(c) Tighten hose by hand.
(d) To prevent loosening of connected hose, do not apply
drops of compressor oil to the seat of connection.
HINT: After connecting the manifold gauge and the refrig±
erant container (service can), discharge any air in the
hoses.
5. WHEN EVACUATING;
Approx. 15 minutes after removal, check the system for
leaks, then take at least another 15 minutes to make sure
the air is fully removed.
6. WHEN HANDLING REFRIGERANT CONTAINER
(SERVICE CAN);
(a) Must never be heated.
(b) Must be kept below 4
�°C (1 04°F).
(c) If warming service can with hot water, be careful that
the valve on top of the service can is never immersed
in the water, as the water may permeate into the refrig-
erant cycle.
(d) Empty service cans must never be re±used.
7. WHEN A/C IS ON AND REFRIGERANT GAS IS
BEING REPLENISHED;
(a) If there is not enough refrigerant gas in the refrigerant
cycle, oil lubrication becomes insufficient and com-
pressor burnout may occur, so take care to avoid this.
(b) If the valve on the high pressure side is opened, refrig-
erant flows in reverse and causes the service can to
rupture, so only open and close the vlave on the low
pressure side.
(c) If the service can is inverted and refrigerant is inserted
in a liquid state, the liquid is compressed and the com-
pressor brakes down, so the refrigerant must be in-
serted in a g¿¿seous state.
(d) Be careful not to insert too much refrigerant gas, as
this causes trouble such as inadequate cooling, poor
fuel economy, engine overheat, etc.
8. WHEN USING GAS±CYLINDER TYPE LEAK
DETECTION INSTRUMENT;
(a) As a naked flame is used, first make sure that there are
no flammable substances nearby before using it.
(b) Be careful, as poisonous gas is produced when
refrigerant gas comes in contact with heat parts.
± AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEMGenera! InformationAC±3
Page 233 of 2389
INSTALLATION OF COMPRESSOR
(See page AC±25)
1. INSTALL COMPRESSOR WITH FOUR MOUNTING
BOLTS
Torque:
3S±FE engine 280 kg±cm (20 ft±lb, 27 N±m)
2VZ±FE engine 250 kg±cm (18 ft±lb, 25 N±m)
2. INS TALL DRIV E BE LT(S e e ste ps 2 and 3 on pa ge
AC±21)
3. CONNECT TWO HOSES TO COMPRESSOR SERVICE
VALVES
Torque:
Discharge line 250 kg±cm (18 ft±lb, 25 N±m)
Suction line 250 kg±cm (18 ft±lb, 25 N±m)
4. CONNECT CLUTCH LEAD WIRE TO WIRING
HARNESS
5. (2VZ±FE ENGINE MODEL)
PLACE CONDENSER FAN, RADIATOR FAN AND
IGNITOR BRAKET
6. INSTALL BATTERY AND CONNECT NEGATIVE CABLE
TO BATTERY
7. EVACUATE AIR FROM AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM
8. CHARGE AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM WITH
REFRIGERANT AND CHECK FOR GAS LEAKAGE
Specified amount: 600 ± 750 g (1.3 ± 1.7 lb)
± AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEMCompressorAC±31
Page 262 of 2389
2. Planetary Gear Unit
CONSTRUCTION
The planetary gear unit is composed of three sets of planetary gears, three clutches which transmit
power to the planetary gears, and four brakes and three one±way clutches which immobilize the
planetary carrier and planetary sun gear.
± AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLEDescription (A140L and A140E)AT±6
Page 263 of 2389
OPERATION
Power from the engine transmitted to the input shaft via the torque converter is then trans-
mitted to the planetary gears by the operation of the clutch.
By operation of the brake and one±way clutch, either the planetary carrier or the planetary sun
gear are immobilized, altering the speed of revolution of the. planetary gear unit.
Shift change is carried out by altering the combination of clutch and brake operation.
Each clutch and brake operates by hydraulic pressure; gear position is decided according to
the throttle opening angle and vehicle speed, and shift change automatically occurs.
The conditions of operation for each gear position are shown on the following illustrations:
± AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLEDescription (A140L and A140E)AT±7
Page 264 of 2389
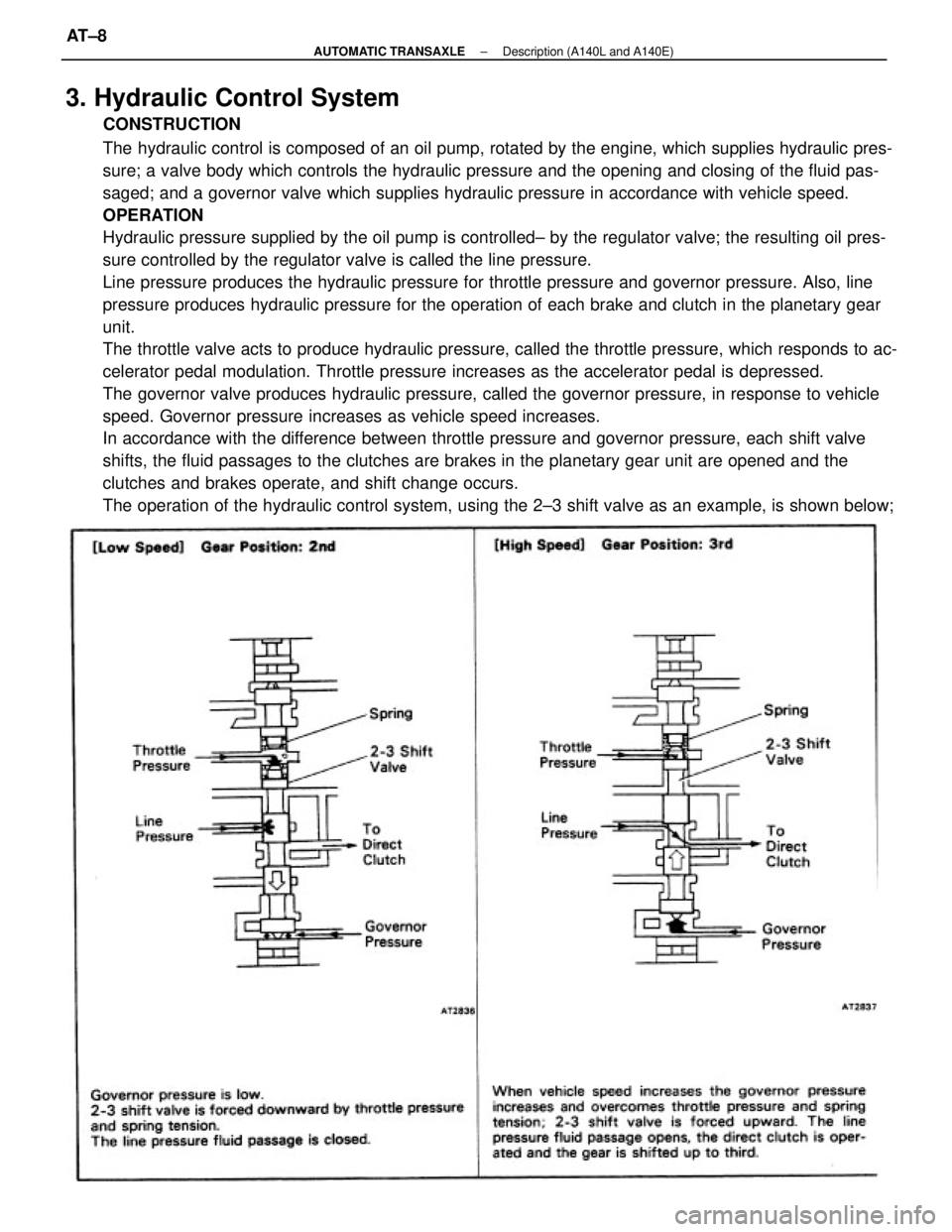
3. Hydraulic Control System
CONSTRUCTION
The hydraulic control is composed of an oil pump, rotated by the engine, which supplies hydraulic pres-
sure; a valve body which controls the hydraulic pressure and the opening and closing of the fluid pas-
saged; and a governor valve which supplies hydraulic pressure in accordance with vehicle speed.
OPERATION
Hydraulic pressure supplied by the oil pump is controlled± by the regulator valve; the resulting oil pres-
sure controlled by the regulator valve is called the line pressure.
Line pressure produces the hydraulic pressure for throttle pressure and governor pressure. Also, line
pressure produces hydraulic pressure for the operation of each brake and clutch in the planetary gear
unit.
The throttle valve acts to produce hydraulic pressure, called the throttle pressure, which responds to ac-
celerator pedal modulation. Throttle pressure increases as the accelerator pedal is depressed.
The governor valve produces hydraulic pressure, called the governor pressure, in response to vehicle
speed. Governor pressure increases as vehicle speed increases.
In accordance with the difference between throttle pressure and governor pressure, each shift valve
shifts, the fluid passages to the clutches are brakes in the planetary gear unit are opened and the
clutches and brakes operate, and shift change occurs.
The operation of the hydraulic control system, using the 2±3 shift valve as an example, is shown below;
± AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLEDescription (A140L and A140E)AT±8
Page 266 of 2389

2. Electronic Control System
COMPONENTS
The electronic control system for controlling the shift timing and the operation of the lock±up clutch
is composed of the following three parts:
(a) Sensors: These sense the vehicle speed and throttle position and send this data to the ECT ECU
in the form of electronic signals.
(b) ECT ECU: This determines the shift and lock±up timing based upon the signals from the. sensors.
(e) Actuators: Solenoid valves divert hydraulic pressure from one circuit of the hydraulic control unit
to another, thus controlling shifting and lock±up timing.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
NO. 1 AND NO. 2
BRAKE LIGHT SWITCH
O/D MAIN SWITCH
THROTTLE POSITION
SENSOR
CRUISE CONTROL
COMPUTER PATTERN SELECT
SWITCH
NEUTRAL START
SWITCH
LOCK±UP SOLE±
NOID VALVE NO. 2 SOLENOID
VA LV E NO. 1 SOLENOID
VA LV E
Control of shift
tinning
Self±diagnostic
systemControl of lock±up
timing
WATER TEMP.
SENSORO/D OFF INDI±
CATOR LIGHT Back±up system
ECT ECU
ENGINE
ECU
ACTUATOR
SENSOR ACTUATOR
± AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLEDescription (A140L and A140E)AT±10
Page 269 of 2389
Operating Mechanism for Each Gear (A140L A140E)
1. CLUTCH BRAKE AND ONE±WAY CLUTCH
'Down±shift only ± no up±shift `Down±shift only ± no up±shift
Shift lever
position Shift lever
positionGear position
Gear Position
Parking Parking
Reverse
A140L
Reverse
A140E
Neutral Neutral
2nd2nd
3rdO/D
O/D2nd
2nd2nd
1 st
2nd1 st
1 st3rd
1 st1 st
3rd
± AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLETroubleshooting (Operating Mechanism ± for Each Gear)
(A140L and A140E)AT±14