1985 FORD GRANADA fuel pressure
[x] Cancel search: fuel pressurePage 85 of 255
Cooling system
The cooling system is of pressurised type
and includes a front mounted crossflow
radiator, belt-driven water pump, temperature-
sensitive thermo-viscous fan (on DOHC
models, an electrically-operated cooling fan is
fitted, operated by a switch in the thermostat
housing), wax type thermostat, and an
expansion and degas tank.
The radiator matrix is of copper and brass
construction and the end tanks are of plastic.
On automatic transmission models the right-
hand side end tank incorporates the
transmission oil cooler.
The thermostat is located behind the water
outlet elbow at the front of the cylinder head
on OHCmodels, and on the front of the water
pump on V6 models. Its purpose is to ensure
rapid engine warm-up by restricting the flow of
coolant in the engine when cold, and also to
assist in regulating the normal operating
temperature of the engine.
The expansion tank incorporates a pressure
cap which effectively pressurises the cooling
system as the coolant temperature rises,
thereby increasing the boiling point of the
coolant. The tank also has a further degas
function. Any accumulation of air bubbles in
the coolant, in particular in the thermostat
housing and the radiator, is returned to the
tank and released in the air space thus
maintaining the efficiency of the coolant.
On models fitted with the auxiliary warning
system, the expansion tank contains a level
sensor which operates a warning light if the
coolant level falls significantly.
When the engine is started from cold, the
water pump circulates coolant around the
cylinder block, cylinder head(s) and inlet
manifold. The warm coolant passes through
the automatic choke housing (when
applicable) and through the heater matrix
before returning to the engine. As the coolant
expands, the level in the expansion tank rises.
Circulation of coolant through the radiator is
prevented while the thermostat is shut. When
the coolant reaches the predeterminedtemperature the thermostat opens and hot
water passes through the top hose to the top
of the radiator. As the water circulates down
through the radiator, it is cooled by the
passage of air past the radiator when the car is
in forward motion, supplemented by the action
of the thermo-viscous fan when necessary.
Having reached the bottom of the radiator, the
water is now cool and the cycle is repeated.
Circulation of water continues through the
expansion tank, inlet manifold and heater at all
times; the heater temperature control being by
an air flap.
The thermo-viscous fan is controlled by the
temperature of air behind the radiator. When
the air temperature reaches a predetermined
level, a bi-metallic coil commences to open a
valve within the unit and silicon fluid is fed
through a system of vanes. Half of the vanes
are driven directly by the water pump and the
remaining half are connected to the fan blades.
The vanes are arranged so that drive is
transmitted to the fan blades in relation to the
drag or viscosity of the fluid, and this in turn
depends on ambient temperature and engine
speed. The fan is therefore only operated when
required, and compared with direct drive type
fan represents a considerable improvement in
fuel economy, drivebelt wear and fan noise.
Air conditioning
Air conditioning is fitted as standard on
Scorpio models and is optionally available on
some other models. In conjunction with the
heater, the system enables any reasonable air
temperature to be achieved inside the car, it
also reduces the humidity of the incoming air,
aiding demisting even when cooling is not
required.
The refrigeration side of the air conditioning
system functions in a similar way to a
domestic refrigerator. A compressor, belt-
driven from the crankshaft pulley, draws
refrigerant in its gaseous phase from an
evaporator. The compressed refrigerant
passes through a condenser where it loses
heat and enters its liquid phase. After
dehydration the refrigerant returns to the
evaporator where it absorbs heat from air
passing over the evaporator fins. The
refrigerant becomes a gas again and the cycle
is repeated.Various subsidiary controls and sensors
protect the system against excessive
temperature and pressures. Additionally,
engine idle speed is increased when the
system is in use to compensate for the
additional load imposed by the compressor.
Precautions
Antifreeze mixture
Antifreeze mixture is poisonous. Keep it out
of reach of children and pets. Wash splashes
off skin and clothing with plenty of water.
Wash splashes off vehicle paintwork to avoid
discolouration.
Antifreeze/water mixture must be renewed
every two years to preserve its anti-corrosive
properties. In climates where antifreeze
protection is unnecessary, a corrosion
inhibitor may be used instead - consult a Ford
dealer. Never run the engine for long periods
with plain water as coolant. Only use the
specified antifreeze, as inferior brands may not
contain the necessary corrosion inhibitors, or
may break down at high temperatures.
Antifreeze containing methanol is particularly
to be avoided, as the methanol evaporates.
The specified mixture is 45 to 50%
antifreeze and 50 to 55% clean soft water (by
volume). Mix the required quantity in a clean
container.
Air conditioning refrigerant
Although the refrigerant is not itself toxic, in
the presence of a naked flame (or a lighted
cigarette) it forms a highly toxic gas. Liquid
refrigerant spilled on the skin will cause
frostbite. If refrigerant enters the eyes, rinse
them with a dilute solution of boric acid and
seek medical advice immediately.
In view of the above points, and of the need
for specialised equipment for evacuating and
recharging the system, any work which
requires the disconnection of a refrigerant line
must be left to a specialist.
Do not allow refrigerant lines to be exposed
to temperatures above 110°C (230°F) - eg
during welding or paint drying operations and
do not operate the air conditioning system if it
is known to be short of refrigerant, or further
damage may result.
1General information and
precautions
3•2Cooling, heating and ventilation systems
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Radiator lower mountings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 126 to 9
Thermostat housing bolts:
SOHC, DOHC and 2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2013 to 15
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 to 105 to 7
Water pump bolts:
SOHC, M8 bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2113 to 16
SOHC, M10 bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4226 to 31
DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2816 to 21
2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 to 137 to 10
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 to 105 to 7
Water pump pulley bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2616 to 19
Water pump/alternator drivebelt tensioner bolt (DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 9752 to 72
Fan-to-viscous clutch bolts:
SOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 106 to 7
V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2313 to 17
Fan shroud bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
Cylinder block drain plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2516 to 18
procarmanuals.com
Page 94 of 255

Chapter 4
Fuel and exhaust systems
Air cleaner and element - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Air cleaner temperature control - description and testing . . . . . . . . .3
Carbon canister - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Carbon canister purge solenoid - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . .45
Exhaust gas oxygen (HEGO) sensor - removal and refitting . . . . . .43
Exhaust manifold(s) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Exhaust system - inspection, repair and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Fuel cut-off inertia switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Fuel filter - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Fuel gauge sender unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Fuel-injection system - depressurisation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Fuel-injection system - idle speed and mixture adjustments . . . . . .31
Fuel-injection system relays - location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Fuel-injectors - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Fuel pressure regulator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Fuel pump - testing, removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Fuel rail temperature switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Fuel tank - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
General information and precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Idle speed control valve - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Inlet manifold - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Mixture adjustment potentiometer - removal and refitting . . . . . . . .38
Pierburg 2V carburettor - dismantling and reassembly . . . . . . . . . .13
Pierburg 2V carburettor - fast idle adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Pierburg 2V carburettor - idle speed and mixture adjustments . . . .11
Pierburg 2V carburettor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12Throttle body - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Throttle cable - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Throttle pedal - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Throttle position sensor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Unleaded fuel - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Vane airflow meter(s) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Vapour separator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Weber 2V carburettor - automatic choke adjustment . . . . . . . . . . .18
Weber 2V carburettor - dismantling and reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Weber 2V carburettor - idle speed and mixture adjustments . . . . .15
Weber 2V carburettor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Weber 2V TLD carburettor - automatic choke unit removal,
refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Weber 2V TLD carburettor - accelerator pump diapragm renewal .25
Weber 2V TLD carburettor - idle speed and mixture adjustments . .19
Weber 2V TLD carburettor - low vacuum enrichment
diaphragm renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Weber 2V TLD carburettor - needle valve and float removal,
refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Weber 2V TLD carburettor - power valve diaphragm renewal . . . . .23
Weber 2V TLD carburettor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Weber 2V TLD carburettor - secondary throttle valve vacuum
diaphragm renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Weber 2V TLD carburettor - throttle kicker removal, refitting
and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
General
System type:
1.8 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Twin choke Pierburg carburettor
2.0 litre carburettor:
SOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Twin choke Weber 2V carburettor
DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Twin choke Weber 2V TLD carburettor
All models with fuel injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Multi-point fuel-injection system controlled by EEC IV engine
management system
Fuel tank capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70 litres (15.4 gallons) approx
Fuel grade*:
Leaded . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97 octane RON (UK 4-star)
Unleaded . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95 octane RON (Premium)
* Models fitted with a catalytic converter must be operated on unleaded fuel at all times. Do notuse leaded fuel as the catalyst will be destroyed.
Idle speed:
1.8 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 ± 20 rpm
2.0 litre carburettor:
SOHC* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 or 875 rpm
DOHC:
Manual gearbox* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 850 ± 25 rpm
Automatic transmission* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 875 ± 25 rpm
2.0 litre fuel-injection:
SOHC* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 or 875 rpm
DOHC* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 875 ± 50 rpm
4•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
4
procarmanuals.com
Page 96 of 255
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•3
4
Weber 2V TLD carburettorPrimarySecondary
Venturi diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23.0 mm25.0 mm
Main jet:
Manual gearbox . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115157
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .112157
Air correction jet:
Manual gearbox . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .175145
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .210145
Emulsion tube:
Manual gearbox . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .F114F3
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .210145
Fast idle speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1800 ±50 rpm
Float level (with gasket) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29.0 ±0.5 mm
Automatic choke vacuum pull-down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5.0 ±0.5 mm
Throttle kicker speed (see text):
Manual gearbox . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2000 ±50 rpm
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2200 ±50 rpm
Fuel-injection system
Make . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Bosch
Fuel pump type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Roller cell, electric
Fuel pump output pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Greater than 5 bar at 12 volts, no flow
System control pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.5 bar
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Inlet manifold:
SOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2113 to 16
DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2415 to 18
V6:
Stage 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4 to 83 to 6
Stage 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 156 to 11
Stage 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15 to 2111 to 16
Stage 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2516 to 18
Stage 5 (after warm-up) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2516 to 18
Exhaust manifold:
OHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2516 to 18
V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25 to 3018 to 22
Plenum chamber to inlet manifold:
2.8 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 to 105 to 7
2.4 & 2.9 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Carburettor bolts (DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 106 to 7
Fuel pump bolts (mechanical pump) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14 to 1810 to 13
Fuel pipe to fuel-injection pressure regulator:
SOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15 to 2011 to 15
2.8 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10 to 127 to 9
Pressure regulator base nut/bolt:
SOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 to 127 to 9
V6:
2.8 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15 to 2011 to 15
2.4 & 2.9 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 to 117 to 8
Fuel rail bolts:
SOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 to 117 to 8
DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2615 to 19
Exhaust downpipe flange nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4026 to 30
Exhaust clamps and U-bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38 to 4528 to 33
Exhaust gas oxygen sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50 to 7037 to 52
Throttle body bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 to 117 to 8
Idle speed control valve bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 to 117 to 8
Fuel filter unions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14 to 2010 to 15
Fuel rail temperature sensor (DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
Fuel rail temperature switch (2.4 & 2.9 litre) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
HEGO sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50 to 7037 to 52
All models are fitted with a rear-mounted fuel
tank. Fuel is conveyed from the tank by a
mechanical or electrical fuel pump, according tomodel and equipment, to the carburettor or fuel-
injection system. The delivery capacity of the
fuel pump exceeds the maximum demands of
the system, so excess fuel is constantly returned
to the tank. This helps to avoid the problems of
vapour locks in the fuel lines.
Carburettor models have a twin venturidowndraught carburettor of Pierburg
manufacture on 1.8 litre models and Weber on
2.0 litre models. Both makes of carburettor
have an automatic choke.
Fuel-injection, when fitted, is of the Bosch
L-Jetronic type. This system is under the
control of the EEC IV module.
1General information and
precautions
procarmanuals.com
Page 97 of 255

The exhaust system fitted in production is
made of aluminised steel, with stainless steel
used in the endplates and baffles of the rear
silencer. Individual sections of the system are
easily renewed in service.
Emission control for the UK market is
achieved largely by the inherent efficiency of
the fuel, ignition and engine management
systems. A welcome spin-off from such
efficiency is remarkably good fuel economy for
a vehicle of such size and weight.
Precautions
Fuel
Many of the procedures in this Chapter
require the removal of fuel lines and
connections which may result in some fuel
spillage. Residual pressure in fuel-injection
systems will remain in the fuel lines long after
the vehicle was last used, therefore extra care
must be taken when disconnecting a fuel line
hose. Loosen any fuel hose slowly to avoid a
sudden release of pressure which may cause
fuel spray. As an added precaution place a rag
over each union as it is disconnected to catch
any fuel which is forcibly expelled. Before
carrying out any operation on the fuel system
refer to the precautions given in “Safety first!”
at the beginning of this Manual and follow
them implicitly. Petrol is a highly dangerous
and volatile liquid and the precautions
necessary when handling it cannot be
overstressed
Tamperproof adjustment screws
Certain adjustment points in the fuel system
(and elsewhere) are protected by tamperproof
caps, plugs or seals. The purpose of such
tamperproofing is to discourage, and to deter,
adjustment by unqualified operators.
In some EU countries (though not yet in the
UK) it is an offence to drive a vehicle with
missing or broken tamperproof seals. Before
disturbing a tamperproof seal, satisfy yourself
that you will not be breaking local or national
anti-pollution regulations by doing so. Fit a
new seal when adjustment is complete when
this is required by law.
Do not break tamperproof seals on a vehicle
which is still under warranty.
Catalytic converter
The catalytic converter is a reliable and
simple device which needs no maintenance in
itself, but there are some facts of which an
owner should be aware if the converter is to
function properly for the full service life.
a)DO NOT use leaded petrol in a car
equipped with a catalytic converter the
lead will coat the precious metals,
reducing their converting efficiency and
will eventually destroy the converter.
b)Always keep the ignition and fuel systems
well-maintained in accordance with the
manufacturer’s schedule - particularly,
ensure that the air cleaner filter element,
the fuel filter and the spark plugs are
renewed at the correct interval - if the inletair/fuel mixture is allowed to become too
rich due to neglect, the unburned surplus
will enter and burn in the catalytic
converter, overheating the element and
eventually destroying the converter.
c)If the engine develops a misfire, do not
drive the car at all (or at least as little as
possible) until the fault is cured - the
misfire will allow unburned fuel to enter
the converter, which will result in
overheating, as noted above.
d)DO NOT push- or tow-start the car - this
will soak the catalytic converter in
unburned fuel, causing it to overheat when
the engine does start - see b) above.
e)DO NOT switch off the ignition at high
engine speeds - if the ignition is switched
off at anything above idle speed,
unburnedfuel will enter the (very hot)
catalytic converter, with the possible risk
of igniting on the element and damaging
the converter.
f)DO NOT use fuel or engine oil additives -
these may contain substances harmful to
the catalytic converter.
g)DO NOT continue to use the car if the
engine burns oil to the extent of leaving a
visible trail of blue smoke - the unburned
carbon deposits will clog the converter
passages and reduce the efficiency; in
severe cases the element will overheat.
h)Remember that the catalytic converter
operates at very high temperatures -
hence the heat shields on the car’s
underbody and the casing will become hot
enough to ignite combustible materials
which brush against it - DO NOT,
therefore, park the car in dry undergrowth,
over long grass or piles of dead leaves.
i)Remember that the catalytic converter is
FRAGILE, do not strike it with tools during
servicing work, take great care when
working on the exhaust system, ensure
that the converter is well clear of any jacks
or other lifting gear used to raise the car
and do not drive the car over rough
ground, road humps, etc, in such a way as
to “ground” the exhaust system.
j)In some cases, particularly when the car is
new and/or is used for stop/start driving, a
sulphurous smell (like that of rotten eggs)may be noticed from the exhaust. This is
common to many catalytic converter-
equipped cars and seems to be due to the
small amount of sulphur found in some
petrols reacting with hydrogen in the
exhaust to produce hydrogen sulphide
(H
2S) gas; while this gas is toxic, it is not
produced in sufficient amounts to be a
problem. Once the car has covered a few
thousand miles the problem should
disappear - in the meanwhile a change of
driving style or of the brand of petrol used
may effect a solution.
k)The catalytic converter, used on a well-
maintained and well-driven car, should
last for between 50 000 and 100 000 miles
- from this point on, careful checks should
be made at all specified service intervals
of the CO level to ensure that the
converter is still operating efficiently - if
the converter is no longer effective it must
be renewed.
See Chapter 1, Section 38.
1On carburettor models only, the air cleaner
can take in both hot and cold air. Hot air is
obtained from a shroud bolted to the exhaust
manifold.
2A flap valve in the air cleaner spout
determines the mix of hot and cold air. The
valve is operated by a vacuum diaphragm.
Vacuum is obtained from the inlet manifold
and is applied via a heat-sensing valve, which
cuts off the vacuum as the temperature of the
incoming air rises. Thus the air cleaner takes in
only hot air on starting from cold, changing
progressively to cold air as the engine warms
up (see illustrations).
3If the system fails, either the engine will take
a long time to warm up (flap stuck in “cold”
position), or it may run roughly and not
develop full power when warm (flap stuck in
“hot” position). Check it as follows.
3Air cleaner temperature control
- description and testing
2Air cleaner and element -
removal and refitting
4•4Fuel and exhaust systems
3.2b Air cleaner heat sensor3.2a Air cleaner vacuum diaphragm unit
procarmanuals.com
Page 98 of 255
4With the engine cold, disconnect the cold
air inlet trunking from the spout. Look into the
spout and check that the flap valve is covering
the hot air inlet.
5Start the engine and allow it to idle. Check
that the flap moves to cover the cold air inlet. If
the flap does not move, check the diaphragm
and heat sensor as follows.
6Stop the engine. Disconnect the diaphragm
vacuum pipe from the heat sensor. Apply
vacuum to the diaphragm, using a vacuum
head pump or by connecting the pipe directly
to manifold vacuum. If the flap now moves, the
heat sensor or vacuum line was faulty. If the
flap still does not move, the diaphragm is
faulty or the flap is jammed.
7On completion reconnect the vacuum pipe
and the cold air trunking.
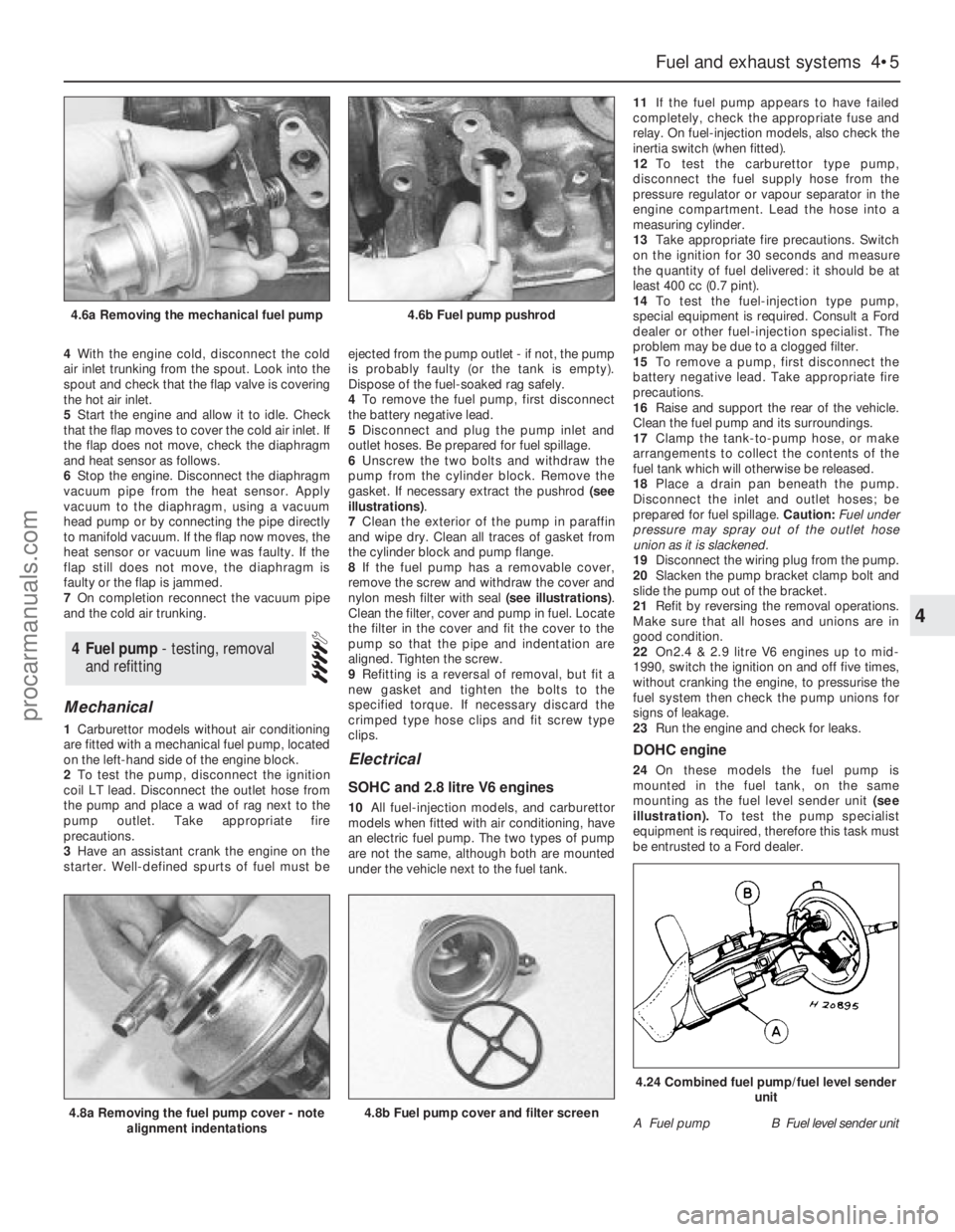
Mechanical
1Carburettor models without air conditioning
are fitted with a mechanical fuel pump, located
on the left-hand side of the engine block.
2To test the pump, disconnect the ignition
coil LT lead. Disconnect the outlet hose from
the pump and place a wad of rag next to the
pump outlet. Take appropriate fire
precautions.
3Have an assistant crank the engine on the
starter. Well-defined spurts of fuel must beejected from the pump outlet - if not, the pump
is probably faulty (or the tank is empty).
Dispose of the fuel-soaked rag safely.
4To remove the fuel pump, first disconnect
the battery negative lead.
5Disconnect and plug the pump inlet and
outlet hoses. Be prepared for fuel spillage.
6Unscrew the two bolts and withdraw the
pump from the cylinder block. Remove the
gasket. If necessary extract the pushrod (see
illustrations).
7Clean the exterior of the pump in paraffin
and wipe dry. Clean all traces of gasket from
the cylinder block and pump flange.
8If the fuel pump has a removable cover,
remove the screw and withdraw the cover and
nylon mesh filter with seal (see illustrations).
Clean the filter, cover and pump in fuel. Locate
the filter in the cover and fit the cover to the
pump so that the pipe and indentation are
aligned. Tighten the screw.
9Refitting is a reversal of removal, but fit a
new gasket and tighten the bolts to the
specified torque. If necessary discard the
crimped type hose clips and fit screw type
clips.
Electrical
SOHC and 2.8 litre V6 engines
10All fuel-injection models, and carburettor
models when fitted with air conditioning, have
an electric fuel pump. The two types of pump
are not the same, although both are mounted
under the vehicle next to the fuel tank.11If the fuel pump appears to have failed
completely, check the appropriate fuse and
relay. On fuel-injection models, also check the
inertia switch (when fitted).
12To test the carburettor type pump,
disconnect the fuel supply hose from the
pressure regulator or vapour separator in the
engine compartment. Lead the hose into a
measuring cylinder.
13Take appropriate fire precautions. Switch
on the ignition for 30 seconds and measure
the quantity of fuel delivered: it should be at
least 400 cc (0.7 pint).
14To test the fuel-injection type pump,
special equipment is required. Consult a Ford
dealer or other fuel-injection specialist. The
problem may be due to a clogged filter.
15To remove a pump, first disconnect the
battery negative lead. Take appropriate fire
precautions.
16Raise and support the rear of the vehicle.
Clean the fuel pump and its surroundings.
17Clamp the tank-to-pump hose, or make
arrangements to collect the contents of the
fuel tank which will otherwise be released.
18Place a drain pan beneath the pump.
Disconnect the inlet and outlet hoses; be
prepared for fuel spillage. Caution: Fuel under
pressure may spray out of the outlet hose
union as it is slackened.
19Disconnect the wiring plug from the pump.
20Slacken the pump bracket clamp bolt and
slide the pump out of the bracket.
21Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Make sure that all hoses and unions are in
good condition.
22On2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines up to mid-
1990, switch the ignition on and off five times,
without cranking the engine, to pressurise the
fuel system then check the pump unions for
signs of leakage.
23Run the engine and check for leaks.
DOHC engine
24On these models the fuel pump is
mounted in the fuel tank, on the same
mounting as the fuel level sender unit(see
illustration).To test the pump specialist
equipment is required, therefore this task must
be entrusted to a Ford dealer.
4Fuel pump - testing, removal
and refitting
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•5
4
4.6a Removing the mechanical fuel pump4.6b Fuel pump pushrod
4.8a Removing the fuel pump cover - note
alignment indentations4.8b Fuel pump cover and filter screenA Fuel pumpB Fuel level sender unit
4.24 Combined fuel pump/fuel level sender
unit
procarmanuals.com
Page 100 of 255
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
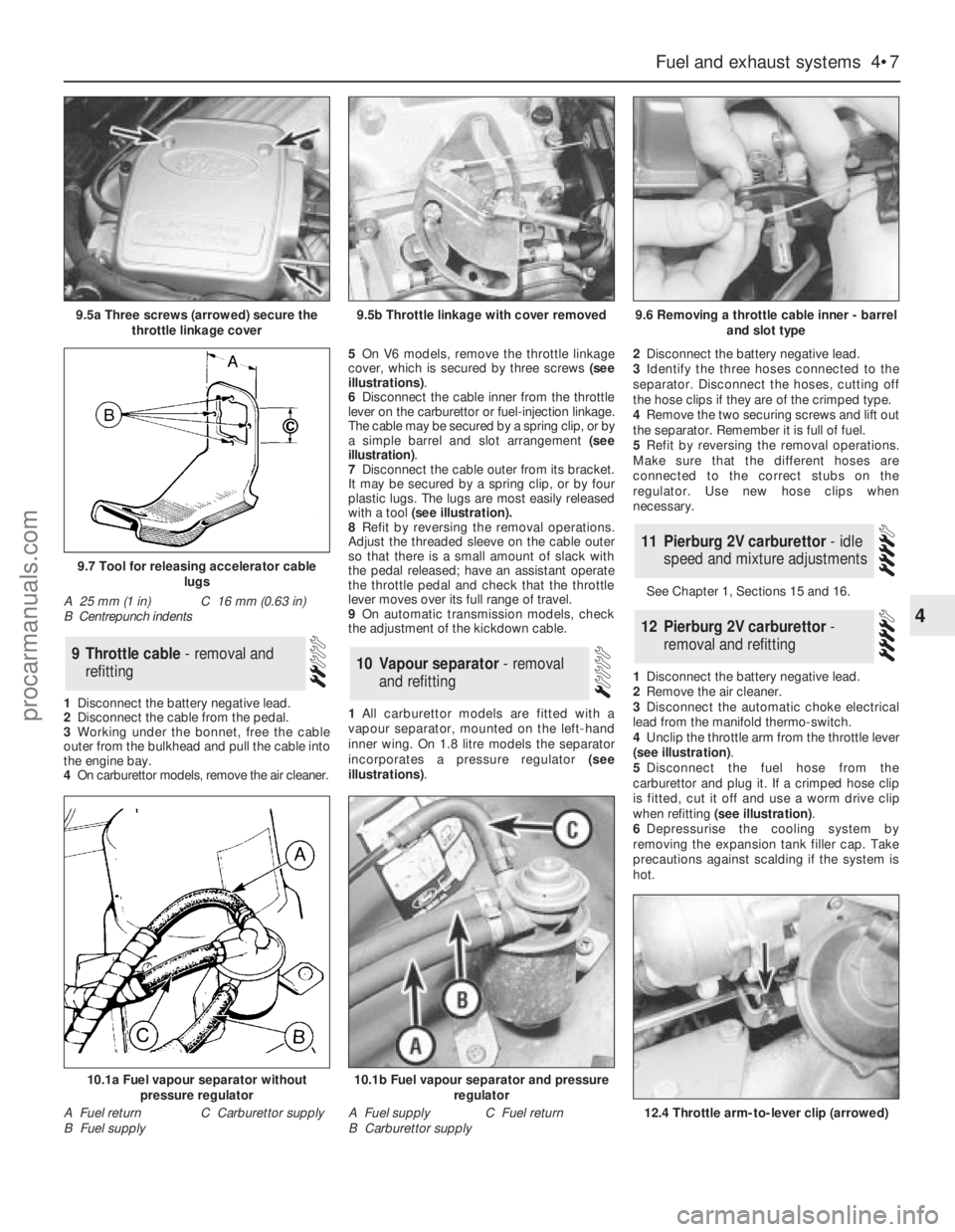
2Disconnect the cable from the pedal.
3Working under the bonnet, free the cable
outer from the bulkhead and pull the cable into
the engine bay.
4On carburettor models, remove the air cleaner.5On V6 models, remove the throttle linkage
cover, which is secured by three screws (see
illustrations).
6Disconnect the cable inner from the throttle
lever on the carburettor or fuel-injection linkage.
The cable may be secured by a spring clip, or by
a simple barrel and slot arrangement (see
illustration).
7Disconnect the cable outer from its bracket.
It may be secured by a spring clip, or by four
plastic lugs. The lugs are most easily released
with a tool (see illustration).
8Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Adjust the threaded sleeve on the cable outer
so that there is a small amount of slack with
the pedal released; have an assistant operate
the throttle pedal and check that the throttle
lever moves over its full range of travel.
9On automatic transmission models, check
the adjustment of the kickdown cable.
1All carburettor models are fitted with a
vapour separator, mounted on the left-hand
inner wing. On 1.8 litre models the separator
incorporates a pressure regulator (see
illustrations).2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Identify the three hoses connected to the
separator. Disconnect the hoses, cutting off
the hose clips if they are of the crimped type.
4Remove the two securing screws and lift out
the separator. Remember it is full of fuel.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Make sure that the different hoses are
connected to the correct stubs on the
regulator. Use new hose clips when
necessary.
See Chapter 1, Sections 15 and 16.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the air cleaner.
3Disconnect the automatic choke electrical
lead from the manifold thermo-switch.
4Unclip the throttle arm from the throttle lever
(see illustration).
5Disconnect the fuel hose from the
carburettor and plug it. If a crimped hose clip
is fitted, cut it off and use a worm drive clip
when refitting (see illustration).
6Depressurise the cooling system by
removing the expansion tank filler cap. Take
precautions against scalding if the system is
hot.
12Pierburg 2V carburettor -
removal and refitting
11Pierburg 2V carburettor - idle
speed and mixture adjustments
10Vapour separator - removal
and refitting9Throttle cable - removal and
refitting
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•7
4
9.5a Three screws (arrowed) secure the
throttle linkage cover9.5b Throttle linkage with cover removed9.6 Removing a throttle cable inner - barrel
and slot type
12.4 Throttle arm-to-lever clip (arrowed)
9.7 Tool for releasing accelerator cable
lugs
A 25 mm (1 in)
B Centrepunch indentsC 16 mm (0.63 in)
10.1a Fuel vapour separator without
pressure regulator
A Fuel return
B Fuel supplyC Carburettor supply
10.1b Fuel vapour separator and pressure
regulator
A Fuel supply
B Carburettor supplyC Fuel return
procarmanuals.com
Page 107 of 255

16Start the engine and note the engine
speed (rpm). The engine speed should
increase above the normal idle speed, and
should be as given in the Specifications.
17If the engine speed is not as specified,
remove the tamperproof plug from the top of
the throttle kicker housing, and turn the
adjustment screw to give the specified speed.
18On completion of adjustment, fit a new
tamperproof cap.
19Disconnect the tubing from the inlet
manifold, and reconnect the throttle kicker
vacuum hose.
20Refit the plastic shield and the air cleaner.
On 2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 models especially,
residual pressure will remain in the fuel lines
long after the vehicle was last used therefore
the fuel system must be depressurised before
any hose is disconnected; the system is
depressurised via the vent valve on the fuel
rail, noting that it may be necessary to depress
the valve several times before the pressure is
fully released. As an added precaution place a
rag over the valve as it is depressed to catch
any fuel which is forcibly expelled. Before
carrying out any operation on the fuel system
refer to the precautions given in Safety first! at
the beginning of this Manual and follow them
implicitly. Petrol is a highly dangerous and
volatile liquid and the precautions necessary
when handling it cannot be overstressed.
Access to the relays is obtained by
removing the facia top cover (crash pad).
The relays are located on the passenger
side(see illustration). Also see Chapter 13,
Section 16.
See Chapter 1, Section 41.
SOHC and 2.8 litre V6 engines
1Idle speed is controlled by the EEC IV
module and no direct adjustment is possible.
2Idle mixture adjustment should not be
necessary on a routine basis. After component
renewal or a similar circumstance it may be
checked and adjusted as follows.
3The engine must be at operating temperature.
The valve clearances must be correct, the air
cleaner element must be clean and the ignition
system must be in good condition.
4Connect an exhaust gas analyser (CO
meter) and a tachometer (rev. counter) to the
engine as instructed by their makers.
5Run the engine at 3000 rpm for 15 seconds,
then allow it to idle. Repeat the procedure
every 60 seconds until adjustment is
complete.
6With the engine idling after the 3000 rpm
burst, record the CO level when the reading
has stabilised. The desired value is given in the
Specifications.
7If adjustment is necessary, remove the
tamperproof plug from the mixture adjusting
screw on the underside of the vane airflow
meter (see illustration).
8On V6 models, note that adjustment should
first be carried out on the front airflow meter.The rear meter should only be adjusted if the
range of adjustment on the front meter is
insufficient.
9Turn the mixture adjusting screw with a
hexagon key until the CO level is correct (see
illustration).
10Stop the engine and disconnect the test
gear.
11Fit a new tamperproof plug if required.
DOHC engine
Note: Before carrying out any adjustments
ensure that the ignition timing and spark plug
gaps are as specified. To carry out the
adjustments, an accurate tachometer and an
exhaust gas analyser (CO meter) will be
required.
12Idle speed is controlled by the EEC IV
module, and manual adjustment is not possible,
although the “base” idle speed can be adjusted
by a Ford dealer using special equipment.
13On models with a catalytic converter, the
mixture is controlled by the EEC IV module,
and no manual adjustment is possible.
14On models without a catalytic converter,
the idle mixture can be adjusted as follows.
15Run the engine until it is at normal
operating temperature.
16Stop the engine and connect a tachometer
and an exhaust gas analyser in accordance
with the manufacturer’s instructions.
17Start the engine and run it at 3000 rpm
for 15 seconds, ensuring that all electrical
loads (headlamps, heater blower, etc) are
switched off, then allow the engine to idle, and
check the CO content. Note that the reading
will initially rise, then fall and finally stabilise.
18If adjustment is necessary, remove the
cover from the mixture adjustment
potentiometer (located on the right-hand side
of the engine compartment, behind the MAP
sensor), and turn the screw to give the
specified CO content (see illustration).
19If adjustment does not produce a change
in reading, the potentiometer may be at the
extreme of the adjustment range. To centralise
the potentiometer, turn the adjustment screw
20 turns clockwise followed by 10 turns anti-
clockwise, then repeat the adjustment
procedure.
31Fuel-injection system - idle
speed and mixture adjustment
30Fuel filter - renewal
29Fuel-injection system relays -
location
28Fuel-injection system -
depressurisation
4•14Fuel and exhaust systems
31.18 Remove the cover from the mixture
adjustment potentiometer31.9 Idle mixture adjustment - fuel-injection
models
29.2 Fuel injection system relays - 2.4 and
2.9 litre V6 engines
A Power relayB Fuel pump relay
31.7 Tamperproof plug (arrowed) covering
mixture adjusting screw
Airflow meter is inverted for photo
procarmanuals.com
Page 109 of 255
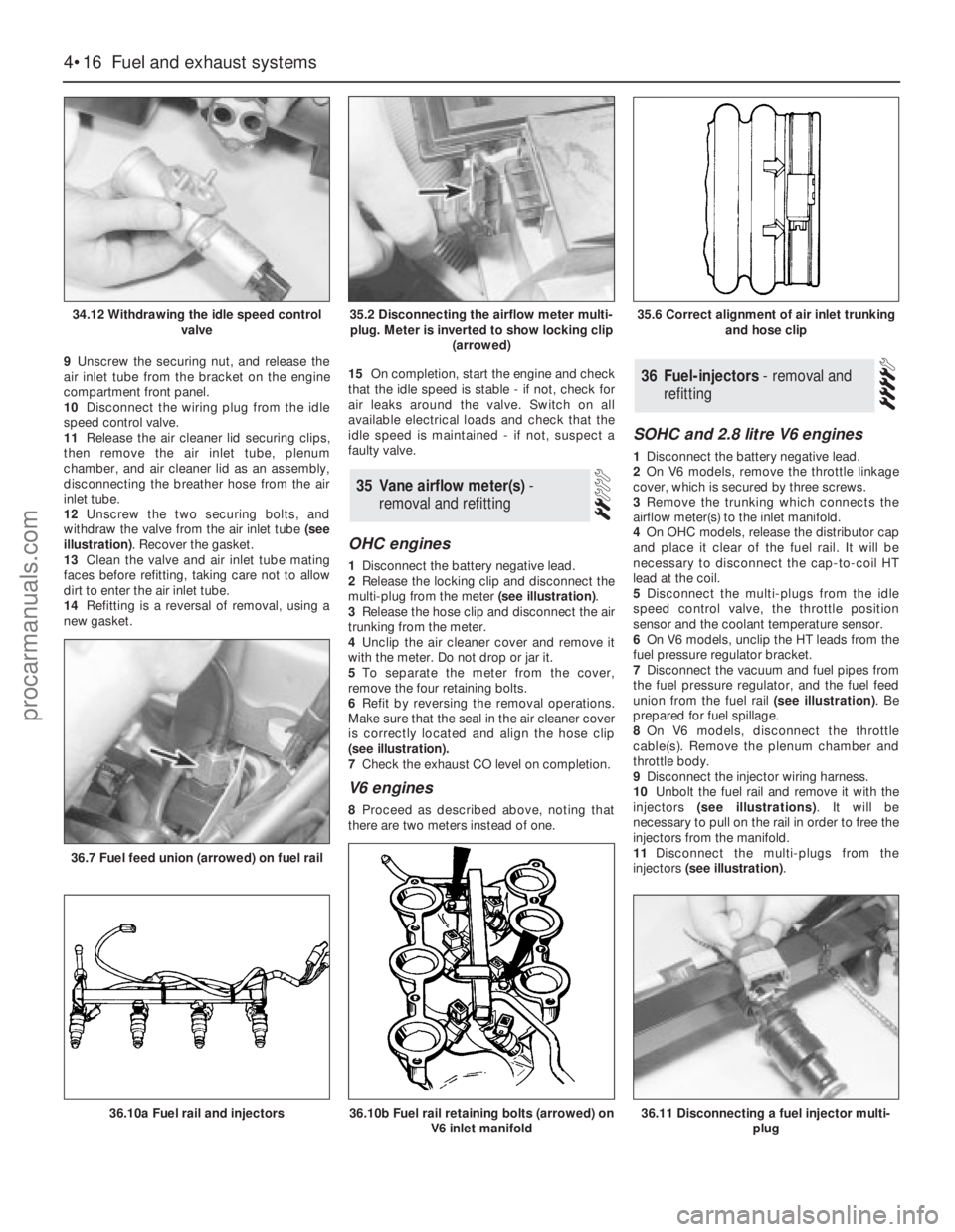
9Unscrew the securing nut, and release the
air inlet tube from the bracket on the engine
compartment front panel.
10Disconnect the wiring plug from the idle
speed control valve.
11Release the air cleaner lid securing clips,
then remove the air inlet tube, plenum
chamber, and air cleaner lid as an assembly,
disconnecting the breather hose from the air
inlet tube.
12Unscrew the two securing bolts, and
withdraw the valve from the air inlet tube (see
illustration). Recover the gasket.
13Clean the valve and air inlet tube mating
faces before refitting, taking care not to allow
dirt to enter the air inlet tube.
14Refitting is a reversal of removal, using a
new gasket.15On completion, start the engine and check
that the idle speed is stable - if not, check for
air leaks around the valve. Switch on all
available electrical loads and check that the
idle speed is maintained - if not, suspect a
faulty valve.
OHC engines
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Release the locking clip and disconnect the
multi-plug from the meter (see illustration).
3Release the hose clip and disconnect the air
trunking from the meter.
4Unclip the air cleaner cover and remove it
with the meter. Do not drop or jar it.
5To separate the meter from the cover,
remove the four retaining bolts.
6Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Make sure that the seal in the air cleaner cover
is correctly located and align the hose clip
(seeillustration).
7Check the exhaust CO level on completion.
V6 engines
8Proceed as described above, noting that
there are two meters instead of one.
SOHC and 2.8 litre V6 engines
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2On V6 models, remove the throttle linkage
cover, which is secured by three screws.
3Remove the trunking which connects the
airflow meter(s) to the inlet manifold.
4On OHCmodels, release the distributor cap
and place it clear of the fuel rail. It will be
necessary to disconnect the cap-to-coil HT
lead at the coil.
5Disconnect the multi-plugs from the idle
speed control valve, the throttle position
sensor and the coolant temperature sensor.
6On V6 models, unclip the HT leads from the
fuel pressure regulator bracket.
7Disconnect the vacuum and fuel pipes from
the fuel pressure regulator, and the fuel feed
union from the fuel rail (see illustration). Be
prepared for fuel spillage.
8On V6 models, disconnect the throttle
cable(s). Remove the plenum chamber and
throttle body.
9Disconnect the injector wiring harness.
10Unbolt the fuel rail and remove it with the
injectors (see illustrations). It will be
necessary to pull on the rail in order to free the
injectors from the manifold.
11Disconnect the multi-plugs from the
injectors (see illustration).
36Fuel-injectors - removal and
refitting
35Vane airflow meter(s) -
removal and refitting
4•16Fuel and exhaust systems
34.12 Withdrawing the idle speed control
valve
36.7 Fuel feed union (arrowed) on fuel rail
36.10a Fuel rail and injectors36.10b Fuel rail retaining bolts (arrowed) on
V6 inlet manifold36.11 Disconnecting a fuel injector multi-
plug
35.2 Disconnecting the airflow meter multi-
plug. Meter is inverted to show locking clip
(arrowed)35.6 Correct alignment of air inlet trunking
and hose clip
procarmanuals.com