1985 FORD GRANADA ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 125 of 255
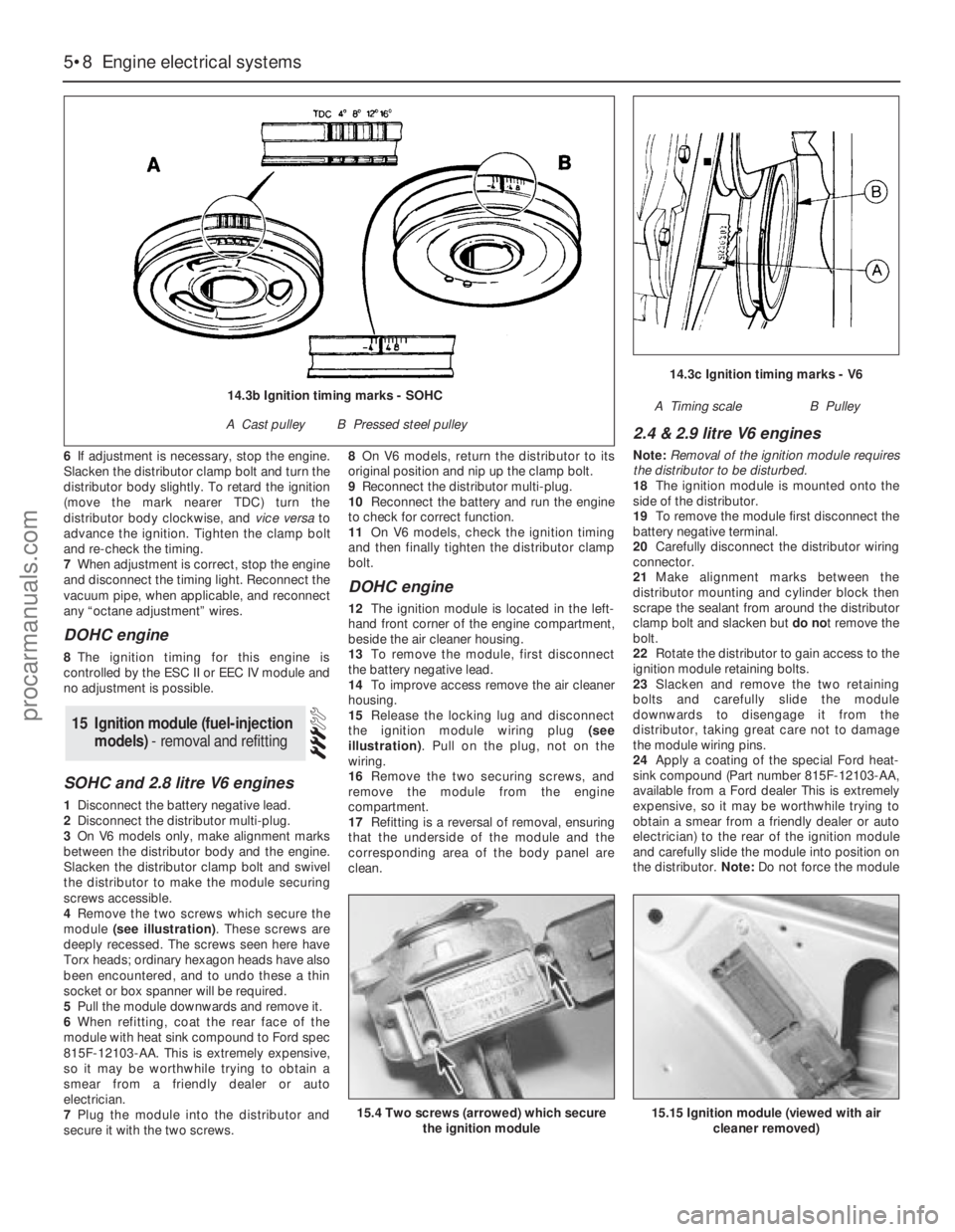
6If adjustment is necessary, stop the engine.
Slacken the distributor clamp bolt and turn the
distributor body slightly. To retard the ignition
(move the mark nearer TDC) turn the
distributor body clockwise, and vice versato
advance the ignition. Tighten the clamp bolt
and re-check the timing.
7When adjustment is correct, stop the engine
and disconnect the timing light. Reconnect the
vacuum pipe, when applicable, and reconnect
any “octane adjustment” wires.
DOHC engine
8The ignition timing for this engine is
controlled by the ESC II or EEC IV module and
no adjustment is possible.
SOHC and 2.8 litre V6 engines
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Disconnect the distributor multi-plug.
3On V6 models only, make alignment marks
between the distributor body and the engine.
Slacken the distributor clamp bolt and swivel
the distributor to make the module securing
screws accessible.
4Remove the two screws which secure the
module (see illustration). These screws are
deeply recessed. The screws seen here have
Torx heads; ordinary hexagon heads have also
been encountered, and to undo these a thin
socket or box spanner will be required.
5Pull the module downwards and remove it.
6When refitting, coat the rear face of the
module with heat sink compound to Ford spec
815F-12103-AA. This is extremely expensive,
so it may be worthwhile trying to obtain a
smear from a friendly dealer or auto
electrician.
7Plug the module into the distributor and
secure it with the two screws.8On V6 models, return the distributor to its
original position and nip up the clamp bolt.
9Reconnect the distributor multi-plug.
10Reconnect the battery and run the engine
to check for correct function.
11On V6 models, check the ignition timing
and then finally tighten the distributor clamp
bolt.
DOHC engine
12The ignition module is located in the left-
hand front corner of the engine compartment,
beside the air cleaner housing.
13To remove the module, first disconnect
the battery negative lead.
14To improve access remove the air cleaner
housing.
15Release the locking lug and disconnect
the ignition module wiring plug (see
illustration). Pull on the plug, not on the
wiring.
16Remove the two securing screws, and
remove the module from the engine
compartment.
17Refitting is a reversal of removal, ensuring
that the underside of the module and the
corresponding area of the body panel are
clean.
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines
Note: Removal of the ignition module requires
the distributor to be disturbed.
18The ignition module is mounted onto the
side of the distributor.
19To remove the module first disconnect the
battery negative terminal.
20Carefully disconnect the distributor wiring
connector.
21Make alignment marks between the
distributor mounting and cylinder block then
scrape the sealant from around the distributor
clamp bolt and slacken but do not remove the
bolt.
22Rotate the distributor to gain access to the
ignition module retaining bolts.
23Slacken and remove the two retaining
bolts and carefully slide the module
downwards to disengage it from the
distributor, taking great care not to damage
the module wiring pins.
24Apply a coating of the special Ford heat-
sink compound (Part number 815F-12103-AA,
available from a Ford dealer This is extremely
expensive, so it may be worthwhile trying to
obtain a smear from a friendly dealer or auto
electrician) to the rear of the ignition module
and carefully slide the module into position on
the distributor. Note: Do not force the module
15Ignition module (fuel-injection
models) - removal and refitting
5•8Engine electrical systems
15.4 Two screws (arrowed) which secure
the ignition module15.15 Ignition module (viewed with air
cleaner removed)
14.3c Ignition timing marks - V6
A Timing scaleB Pulley14.3b Ignition timing marks - SOHC
A Cast pulleyB Pressed steel pulley
procarmanuals.com
Page 131 of 255
Models covered in this Manual have disc
brakes fitted all round. The footbrake operates
hydraulically on all four wheels, and the
handbrake operates mechanically on the rear
wheels. Both footbrake and handbrake are
self-adjusting in use.
Ford’s anti-lock braking system (ABS) is
fitted to all models. The system monitors the
rotational speed of each roadwheel. When a
wheel begins to lock under heavy braking, the
ABS reduces the hydraulic pressure to that
wheel, so preventing it from locking. When this
happens a pulsating effect will be noticed at
the brake pedal. On some road surfaces the
tyres may squeal when braking hard even
though the wheels are not locked.
The main components of the system are the
hydraulic unit, the calipers, pads and discs,
the wheel sensors and the “brain” or control
module. The hydraulic unit contains the
elements of a traditional master cylinder, plus
an electric motor and pump, a pressure
accumulator and control valves. The pump is
the source of pressure for the system and
does away with the need for a vacuum servo.
The hydraulic circuit is split front and rear,
as is normal practice with rear-wheel drive
vehicles. In the event that the hydraulic pump
fails, unassisted braking effort is still available
on the front calipers only.
Warning lights inform the driver of low brake
fluid level, ABS failure and (on some models)
brake pad wear. The low fluid level light
doubles as a “handbrake on” light; if it
illuminates at the same time as the ABS
warning light, it warns of low hydraulic
pressure.
ABS cannot overturn the laws of physics:
stopping distances will inevitably be greater on
loose or slippery surfaces. However, the system
should allow even inexperienced drivers to
retain directional control under panic braking.
From August 1986 the following
modifications were made to the braking
system.
a)The relays differ from earlier versions.b)The hydraulic pump is constructed of iron
rather than alloy.
c)A new pressure warning switch is used.
d)The earlier high pressure rubber hose is
replaced by a steel pipe.
To overcome the problem of excessive rear
brake pad wear, Ford introduced a differential
valve which is screwed into the ABS valve
block.The valve limits the pressure applied to
the rear brake calipers and so reduces brake
pad wear. From 1988 onwards, the valve has
been fitted during production. The differential
valve can also be fitted to earlier models. Refer
to your Ford dealer for further information.
From April 1992 onwards, the models
covered in this Manual were equipped with a
new Teves MK IV anti-lock braking system
instead of the Teves MK II system fitted to the
earlier models.
The Teves MK IV system differs from the
earlier MK II system in the following ways.
a)The source of hydraulic pressure for the
system is a conventional master cylinder
and vacuum servo assembly.
b)A valve block and pump assembly is used
instead of the hydraulic control unit. The
block contains the inlet and outlet
solenoid valves that control the hydraulic
system. There are three pairs of valves,
one for each brake circuit (paragraph c).
c)The hydraulic braking system consists of
three separate circuits; one for each front
brake (which are totally independent of
each other), and a joint circuit which
operates both rear brakes.
d)A G (gravity) switch is incorporated in the
system. This is an inertia type switch and
informs the control module when the
vehicle is decelerating rapidly.
e)A Pedal Travel Sensor (PTS) is fitted to the
vacuum servo unit. The PTS informs the
control module of the position of the brake
pedal when the anti-lock sequence starts
and ensures that a constant pedal height
is maintained during the sequence.
The MK IV system operates as follows.
During normal operation the system
functions in the same way as a non-ABS
system would. During this time the three inlet
valves in the valve block are open and theoutlet valves are closed, allowing full hydraulic
pressure present in the master cylinder to act
on the main braking circuit. If the control
module receives a signal from one of the
wheel sensors and senses that a wheel is
about to lock, it closes the relevant inlet valve
in the valve block which then isolates the
brake caliper on the wheel which is about to
lock from the master cylinder, effectively
sealing in the hydraulic pressure. If the speed
of rotation of the wheel continues to decrease
at an abnormal rate, the control module will
then open the relevant outlet valve in the valve
block; this allows the fluid from the relevant
hydraulic circuit to return to the master
cylinder reservoir, releasing pressure on the
brake caliper so that the brake is released. The
pump in the valve block also operates to assist
in the quick release of pressure. Once the
speed of rotation of the wheel returns to an
acceptable rate the pump stops, the outlet
valve closes and the inlet valve is opened,
allowing the hydraulic master cylinder
pressure to return to the caliper which then
reapplies the brake. This cycle can be carried
many times a second. The solenoid valves
connected to the front calipers operate
independently, but the valve connected to the
rear calipers operates both calipers
simultaneously.
The operation of the ABS system is entirely
dependent on electrical signals. To prevent
the system responding to any inaccurate
signals, a built-in safety circuit monitors all
signals received by the control module. If an
inaccurate signal or low battery voltage is
detected, the ABS system is automatically
shut down and the warning lamp on the
instrument cluster is illuminated to inform the
driver that the ABS system is not operational.
Whilst in this state the system functions in the
same way as a non-ABS system would. If a
fault does develop in the ABS system, the car
must be taken to a Ford dealer for fault
diagnosis and repair. The system is equipped
with a diagnostic plug into which a special
diagnostic (STAR) tester can be plugged. This
allows faults to be easily traced.
1General information
10•2Braking system
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Front caliper:
To stub axle carrier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51 to 6138 to 45
Slide bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Rear caliper:
Bracket to carrier plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51 to 6138 to 45
Slide bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31 to 3523 to 26
Hydraulic unit to bulkhead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5130 to 38
Accumulator to pump body . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4526 to 33
Pump mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 to 95 to 7
High pressure hose banjo bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16 to 2412 to 18
Reservoir mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4 to 63 to 4
Wheel sensor fixing bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
Vacuum servo unit retaining nuts (Teves MK IV) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4526 to 33
Master cylinder retaining nuts (Teves MK IV) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Valve block and pump assembly mounting nuts (Teves MK IV) . . . . . . .21 to 2815 to 21
procarmanuals.com
Page 146 of 255

The steering gear is of rack-and-pinion type.
Power assistance is standard on V6 models
and optional on others. The power-assisted
steering gear has a “variable ratio” effect
which increases the steering ratio about the
straight-ahead position: this provides quick
lock-to-lock action without the penalty of
over-responsiveness in open road driving.
The steering wheel is adjustable both up-
and-down and fore-and-aft. Both steering
column and shaft are designed to collapse
under impact. The steering shaft is connected
to the pinion by an intermediate shaft, which
has a universal joint at its upper end and a
flexible coupling at the lower end.
Front suspension is independent, of the
MacPherson strut type, with coil springs and
concentric telescopic shock absorbers. The
struts are attached to the tops of the stub axle
carriers, which are located at their lower ends
by balljoints incorporated in the lower
suspension arms. The lower suspension arms
pivot at their inner ends, where they are
attached to a central crossmember. The anti-
roll bar is attached to the rear of the arms and
serves to control fore-and-aft movement as
well as reducing roll.
Suspension geometry has been designed to
give good steering “feel”, resistance to pulling
caused by uneven braking effort or tyre
deflation, and (in the case of manual steering)
acceptably low steering wheel effort at parking
speeds. Only toe is adjustable in service.
The rear suspension is also independent. It
is of the semi-trailing arm type, with coil
springs and separate telescopic shock
absorbers. An optionally-available ride height
control system keeps the rear suspension
height constant, regardless of vehicle load.
Both front and rear wheel bearings are of a
special taper-roller type and require no
periodic adjustment in service.1Refer to Chapter 1, Section 35, to check the
power steering fluid level.
2If the fluid level falls so low that air enters
the pump, or after component renewal, the
system must be bled as follows.
3Remove the reservoir filler cap. Top-up with
clean fluid to the appropriate “cold” level. It is
important that the fluid is free of air bubbles,
so do not shake the container when topping-
up, and pour the fluid slowly.
4Disconnect the negative LT lead from the
ignition coil. Have an assistant crank the
engine on the starter in two second bursts, at
the same time turning the steering wheel from
lock to lock. Keep the reservoir topped up
whilst this is going on.
5When air bubbles no longer appear in the
fluid, stop the cranking. Reconnect the coil
negative lead and run the engine for a few
seconds, then stop it and check the level
again. Refit the filler cap.
6Run the vehicle for a few miles to warm up
the fluid and expel any remaining air, then stop
the engine and make a final fluid level check.
Manual steering
1Position the steering in the straight-ahead
position, then remove the ignition key so that
the steering is locked.
2Slacken the front wheel nuts. Raise and
support the front of the vehicle and remove
the front wheels.
3Remove the pinch-bolt and nut which
secure the intermediate shaft flexible coupling
to the pinion shaft (see illustration).
4Slacken the track rod end locknuts by half a
turn each (see illustration).
5Remove the split pin from the track rod
balljoint nuts. Unscrew the nuts, break the
balljoint tapers using a separator tool anddisengage the track rod ends from the
steering arms.
6Remove the two bolts which secure the
steering gear to the crossmember. Lift out the
steering gear.
7Mark the positions of the track rod ends on
the track rods, using paint or sticky tape, so
that they can be refitted in approximately the
same positions. Unscrew the track rod ends
and locknuts.
8Commence refitting by screwing on the
locknuts and track rod ends, observing the
previously made position marks when
applicable.
9Bring the rack to the straight-ahead
position. Do this by counting the number of
turns of the pinion needed to go from lock to
lock, then applying half that number of turns
from full lock on one side.
10Offer the steering gear to the vehicle,
engaging the flexible coupling and loosely
fitting the securing bolts. Note that the master
spline on the pinion shaft mates with the
corresponding groove in the flexible coupling.
11Tighten the two steering gear-to-
crossmember bolts to the specified Stage 1
torque. Slacken the bolts and retighten to the
Stage 2 torque. Finally tighten the bolts
through the angle specified for Stage 3.
12Make sure that the flexible coupling and
pinion shaft are properly engaged, then fit the
pinch-bolt and nut. Tighten the pinch-bolt to
the specified torque.
3Steering gear - removal and
refitting
2Power steering fluid - level
check and bleeding1General information
Steering and suspension 11•3
11
3.3 Master spline and groove on pinion
shaft and coupling
Torque wrench settings (continued)Nmlbf ft
Rear suspension
Driveshaft stub axle nut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .250 to 290180 to 210
Final drive mounting to floor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Final drive mounting to rear cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40 to 5030 to 37
Guide plate-to-floor bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5130 to 38
Guide plate insulator bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69 to 8851 to 65
Lower arm to crossmember . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80 to 9559 to 70
Brake anchor plate to lower arm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52 to 6438 to 47
Anti-roll bar bracket bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Shock absorber mountings:
Top . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73 to 9754 to 72
Bottom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68 to 9250 to 68
Rear hub bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80 to 10059 to 74
Wheels
Wheel nuts (steel or alloy wheels) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 10052 to 74
procarmanuals.com
Page 155 of 255

7Unbolt the guide plate from the body on the
side concerned.
8Carefully lower the jack until the spring is no
longer under tension. Remove the spring and
the rubber buffer.
9Refit by reversing the removal operations,
tightening all fastenings to the specified torque
when known.
Note: Ford tool No 15-014, or locally made
equivalent, will be required for this job.
1Raise and support the rear of the vehicle.
2Flatten the lockwasher which secures the
guide plate centre bolt. Remove the centre
bolt and the two bolts which hold the guide
plate to the floor; remove the guide plate.
3Wedge a piece of wood between the
crossmember and the floor.
4Draw the insulator out with the special tool
(see illustration).
5Smear the new insulator with glycerine or
liquid soap, then press it in as follows.
6Use the special tool spindle or other long
M12 bolt. Screw a nut up to the bolt head,
then fit a plain washer and the insulator onto
the bolt. Pass the bolt through the hole in the
crossmember and screw it into the floor, then
press the insulator home by winding the nut
and washer up the bolt.
7Remove the installation tool and the wood.
8Refit the guide plate, tightening the bolts to
the specified torque. Secure the centre bolt
with the lockwasher.
9Lower the vehicle.
1Remove the rear hub.
2Disconnect both rear brake flexible hoses
from the brake pipes. Free the brake pipes
from the brackets on the lower arms.
3Unclip the handbrake cable from the lower
arm.
4Remove the rear spring.
5Remove the lower arm-to-crossmember
bolts. Withdraw the lower arm.6Renew the rubber bushes if wished, using
lengths of tube or sockets and a vice, or large
nuts and bolts. Lubricate the new bushes with
glycerine or liquid soap.
7Refit by reversing the removal operations,
tightening the lower arm-to-crossmember
bolts with the weight of the vehicle back on its
wheels. Bleed the brake hydraulic system on
completion.
1Raise and support the rear of the vehicle.
2Separate the anti-roll bar from the link rods
on each side by prising them free (see
illustration).
3Unbolt the two anti-roll bar brackets.
Remove the bar, brackets and bushes (see
illustration).
4Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Tighten the bracket bolts to the specified
torque.
1Working inside the vehicle, remove the
luggage area side trim to gain access to the
shock absorber top mounting.
2Raise and support the rear of the vehicle.
Raise a jack under the rear suspension lower
arm to take the load off the shock absorber.3On models with ride height control,
disconnect the air line from the shock
absorber.
4Unbolt the shock absorber top mounting
(see illustration).
5Unbolt the shock absorber lower mounting
(see illustration). Pull the shock absorber out
of the lower mounting bracket and remove it.
6Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Tighten the shock absorber mountings to the
specified torque. On models with ride height
control, use new O-rings on the air line union.
The ride height control system is an optional
extra, designed to keep the rear suspension
height constant regardless of vehicle load.
This is obviously useful if heavy loads are often
carried, or if the vehicle is used for towing.
The main components of the system are a
height sensor, a compressor and two special
rear shock absorbers. The compressor
supplies air to the shock absorbers, so
“pumping up” the rear suspension, when so
commanded by the height sensor. Other
components include the connecting pipes,
electrical wiring and a compressor relay. The
relay is mounted behind the glovebox.
Variations in vehicle height are not
recognised by the system for approximately
20 seconds, in order to prevent responses to
temporary changes such as those induced by
32Ride height control system -
general information
31Rear shock absorber -
removal and refitting
30Rear anti-roll bar - removal
and refitting
29Rear suspension lower arm -
removal and refitting
28Rear crossmember insulator
- removal and refitting
11•12Steering and suspension
28.4 Drawing out an insulator with the
special tool
31.4 Undoing a rear shock absorber top
mounting31.5 Undoing a rear shock absorber lower
mounting
30.2 Rear anti-roll bar link rod30.3 A rear anti-roll bar bracket - bolt
arrowed
procarmanuals.com
Page 159 of 255

important also to keep watch on those parts of
the vehicle not immediately visible, for
instance the underside, inside all the wheel
arches, and the lower part of the engine
compartment.
The basic maintenance routine for the
bodywork is washing - preferably with a lot of
water, from a hose. This will remove all the
loose solids which may have stuck to the
vehicle. It is important to flush these off in
such a way as to prevent grit from scratching
the finish. The wheel arches and underframe
need washing in the same way, to remove any
accumulated mud, which will retain moisture
and tend to encourage rust. Paradoxically
enough, the best time to clean the underframe
and wheel arches is in wet weather, when the
mud is thoroughly wet and soft. In very wet
weather, the underframe is usually cleaned of
large accumulations automatically, and this is
a good time for inspection.
Periodically, except on vehicles with a wax-
based underbody protective coating, it is a
good idea to have the whole of the underframe
of the vehicle steam-cleaned, engine
compartment included, so that a thorough
inspection can be carried out to see what
minor repairs and renovations are necessary.
Steam-cleaning is available at many garages,
and is necessary for the removal of the
accumulation of oily grime, which sometimes
is allowed to become thick in certain areas. If
steam-cleaning facilities are not available,
there are some excellent grease solvents
available which can be brush-applied; the dirt
can then be simply hosed off. Note that these
methods should not be used on vehicles with
wax-based underbody protective coating, or
the coating will be removed. Such vehicles
should be inspected annually, preferably just
prior to Winter, when the underbody should be
washed down, and any damage to the wax
coating repaired. Ideally, a completely fresh
coat should be applied. It would also be worth
considering the use of such wax-based
protection for injection into door panels, sills,
box sections, etc, as an additional safeguard
against rust damage, where such protection is
not provided by the vehicle manufacturer.
After washing paintwork, wipe off with a
chamois leather to give an unspotted clear
finish. A coat of clear protective wax polish will
give added protection against chemical
pollutants in the air. If the paintwork sheen has
dulled or oxidised, use a cleaner/polisher
combination to restore the brilliance of the
shine. This requires a little effort, but such
dulling is usually caused because regular
washing has been neglected. Care needs to
be taken with metallic paintwork, as special
non-abrasive cleaner/polisher is required to
avoid damage to the finish. Always check that
the door and ventilator opening drain holes
and pipes are completely clear, so that water
can be drained out. Brightwork should be
treated in the same way as paintwork.
Windscreens and windows can be kept clear
of the smeary film which often appears, by theuse of proprietary glass cleaner. Never use
any form of wax or other body or chromium
polish on glass.
Mats and carpets should be brushed or
vacuum-cleaned regularly, to keep them free
of grit. If they are badly stained, remove them
from the vehicle for scrubbing or sponging,
and make quite sure they are dry before
refitting. Seats and interior trim panels can be
kept clean by wiping with a damp cloth. If they
do become stained (which can be more
apparent on light-coloured upholstery), use a
little liquid detergent and a soft nail brush to
scour the grime out of the grain of the material.
Do not forget to keep the headlining clean in
the same way as the upholstery. When using
liquid cleaners inside the vehicle, do not over-
wet the surfaces being cleaned. Excessive
damp could get into the seams and padded
interior, causing stains, offensive odours or
even rot. If the inside of the vehicle gets wet
accidentally, it is worthwhile taking some
trouble to dry it out properly, particularly
where carpets are involved. Do not leave oil or
electric heaters inside the vehicle for this
purpose.
Repairs of minor scratches in
bodywork
If the scratch is very superficial, and does
not penetrate to the metal of the bodywork,
repair is very simple. Lightly rub the area of the
scratch with a paintwork renovator, or a very
fine cutting paste, to remove loose paint from
the scratch, and to clear the surrounding
bodywork of wax polish. Rinse the area with
clean water.
Apply touch-up paint to the scratch using a
fine paint brush; continue to apply fine layers
of paint until the surface of the paint in the
scratch is level with the surrounding
paintwork. Allow the new paint at least two
weeks to harden, then blend it into the
surrounding paintwork by rubbing the scratch
area with a paintwork renovator or a very fine
cutting paste. Finally, apply wax polish.
Where the scratch has penetrated right
through to the metal of the bodywork, causing
the metal to rust, a different repair technique is
required. Remove any loose rust from the
bottom of the scratch with a penknife, then
apply rust-inhibiting paint to prevent the
formation of rust in the future. Using a rubber
or nylon applicator, fill the scratch with
bodystopper paste. If required, this paste can
be mixed with cellulose thinners to provide a
very thin paste which is ideal for filling narrow
scratches. Before the stopper-paste in the
scratch hardens, wrap a piece of smoothcotton rag around the top of a finger. Dip the
finger in cellulose thinners, and quickly sweep
it across the surface of the stopper-paste in
the scratch; this will ensure that the surface of
the stopper-paste is slightly hollowed. The
scratch can now be painted over as described
earlier in this Section.
Repairs of dents in bodywork
When deep denting of the vehicle’s
bodywork has taken place, the first task is to
pull the dent out, until the affected bodywork
almost attains its original shape. There is little
point in trying to restore the original shape
completely, as the metal in the damaged area
will have stretched on impact, and cannot be
reshaped fully to its original contour. It is
better to bring the level of the dent up to a
point which is about 3 mm below the level of
the surrounding bodywork. In cases where the
dent is very shallow anyway, it is not worth
trying to pull it out at all. If the underside of the
dent is accessible, it can be hammered out
gently from behind, using a mallet with a
wooden or plastic head. Whilst doing this,
hold a suitable block of wood firmly against
the outside of the panel, to absorb the impact
from the hammer blows and thus prevent a
large area of the bodywork from being “belled-
out”.
Should the dent be in a section of the
bodywork which has a double skin, or some
other factor making it inaccessible from
behind, a different technique is called for. Drill
several small holes through the metal inside
the area - particularly in the deeper section.
Then screw long self-tapping screws into the
holes, just sufficiently for them to gain a good
purchase in the metal. Now the dent can be
pulled out by pulling on the protruding heads
of the screws with a pair of pliers.
The next stage of the repair is the removal
of the paint from the damaged area, and from
an inch or so of the surrounding “sound”
bodywork. This is accomplished most easily
by using a wire brush or abrasive pad on a
power drill, although it can be done just as
effectively by hand, using sheets of abrasive
paper. To complete the preparation for filling,
score the surface of the bare metal with a
screwdriver or the tang of a file, or
alternatively, drill small holes in the affected
area. This will provide a really good “key” for
the filler paste.
To complete the repair, see the Section on
filling and respraying.
Repairs of rust holes or gashes in
bodywork
Remove all paint from the affected area, and
from an inch or so of the surrounding “sound”
bodywork, using an abrasive pad or a wire
brush on a power drill. If these are not
available, a few sheets of abrasive paper will
do the job most effectively. With the paint
removed, you will be able to judge the severity
of the corrosion, and therefore decide whether
to renew the whole panel (if this is possible) or
4Minor body damage - repair
3Maintenance - upholstery and
carpets
12•2Bodywork and fittings
procarmanuals.com
Page 160 of 255

to repair the affected area. New body panels
are not as expensive as most people think,
and it is often quicker and more satisfactory to
fit a new panel than to attempt to repair large
areas of corrosion.
Remove all fittings from the affected area,
except those which will act as a guide to the
original shape of the damaged bodywork (eg
headlight shells etc). Then, using tin snips or a
hacksaw blade, remove all loose metal and
any other metal badly affected by corrosion.
Hammer the edges of the hole inwards, in
order to create a slight depression for the filler
paste.
Wire-brush the affected area to remove the
powdery rust from the
surface of the remaining metal. Paint the
affected area with rust-inhibiting paint, if the
back of the rusted area is accessible, treat this
also.
Before filling can take place, it will be
necessary to block the hole in some way. This
can be achieved by the use of aluminium or
plastic mesh, or aluminium tape.
Aluminium or plastic mesh, or glass-fibre
matting, is probably the best material to use
for a large hole. Cut a piece to the
approximate size and shape of the hole to be
filled, then position it in the hole so that its
edges are below the level of the surrounding
bodywork. It can be retained in position by
several blobs of filler paste around its
periphery.
Aluminium tape should be used for small or
very narrow holes. Pull a piece off the roll, trim
it to the approximate size and shape required,
then pull off the backing paper (if used) and
stick the tape over the hole; it can be
overlapped if the thickness of one piece is
insufficient. Burnish down the edges of the
tape with the handle of a screwdriver or
similar, to ensure that the tape is securely
attached to the metal underneath.
Bodywork repairs - filling and
respraying
Before using this Section, see the Sections
on dent, deep scratch, rust holes and gash
repairs.
Many types of bodyfiller are available, but
generally speaking, those proprietary kits
which contain a tin of filler paste and a tube of
resin hardener are best for this type of repair.
A wide, flexible plastic or nylon applicator will
be found invaluable for imparting a smooth
and well-contoured finish to the surface of the
filler.
Mix up a little filler on a clean piece of card
or board - measure the hardener carefully
(follow the maker’s instructions on the pack),
otherwise the filler will set too rapidly or too
slowly. Using the applicator, apply the filler
paste to the prepared area; draw the
applicator across the surface of the filler to
achieve the correct contour and to level the
surface. As soon as a contour that
approximates to the correct one is achieved,
stop working the paste - if you carry on too
long, the paste will become sticky and begin
to “pick-up” on the applicator. Continue to
add thin layers of filler paste at 20-minuteintervals, until the level of the filler is just proud
of the surrounding bodywork.
Once the filler has hardened, the excess can
be removed using a metal plane or file. From
then on, progressively-finer grades of abrasive
paper should be used, starting with a 40-
grade production paper, and finishing with a
400-grade wet-and-dry paper. Always wrap
the abrasive paper around a flat rubber, cork,
or wooden block - otherwise the surface of the
filler will not be completely flat. During the
smoothing of the filler surface, the wet-and-
dry paper should be periodically rinsed in
water. This will ensure that a very smooth
finish is imparted to the filler at the final stage.
At this stage, the “dent” should be
surrounded by a ring of bare metal, which in
turn should be encircled by the finely
“feathered” edge of the good paintwork. Rinse
the repair area with clean water, until all of the
dust produced by the rubbing-down operation
has gone.
Spray the whole area with a light coat of
primer - this will show up any imperfections in
the surface of the filler. Repair these
imperfections with fresh filler paste or
bodystopper, and once more smooth the
surface with abrasive paper. Repeat this
spray-and-repair procedure until you are
satisfied that the surface of the filler, and the
feathered edge of the paintwork, are perfect.
Clean the repair area with clean water, and
allow to dry fully.
The repair area is now ready for final
spraying. Paint spraying must be carried out in
a warm, dry, windless and dust-free
atmosphere. This condition can be created
artificially if you have access to a large indoor
working area, but if you are forced to work in
the open, you will have to pick your day very
carefully. If you are working indoors, dousing
the floor in the work area with water will help
to settle the dust which would otherwise be in
the atmosphere. If the repair area is confined
to one body panel, mask off the surrounding
panels; this will help to minimise the effects of
a slight mis-match in paint colours. Bodywork
fittings (eg chrome strips, door handles etc)
will also need to be masked off. Use genuine
masking tape, and several thicknesses of
newspaper, for the masking operations.
Before commencing to spray, agitate the
aerosol can thoroughly, then spray a test area
(an old tin, or similar) until the technique is
mastered. Cover the repair area with a thick
coat of primer; the thickness should be built
up using several thin layers of paint, rather
than one thick one. Using 400-grade wet-and-
dry paper, rub down the surface of the primer
until it is really smooth. While doing this, the
work area should be thoroughly doused with
water, and the wet-and-dry paper periodically
rinsed in water. Allow to dry before spraying
on more paint.
Spray on the top coat, again building up thethickness by using several thin layers of paint.
Start spraying at one edge of the repair area,
and then, using a side-to-side motion, work
until the whole repair area and about 2 inches
of the surrounding original paintwork is
covered. Remove all masking material 10 to 15
minutes after spraying on the final coat of
paint.
Allow the new paint at least two weeks to
harden, then, using a paintwork renovator, or a
very fine cutting paste, blend the edges of the
paint into the existing paintwork. Finally, apply
wax polish.
Plastic components
With the use of more and more plastic body
components by the vehicle manufacturers (eg
bumpers. spoilers, and in some cases major
body panels), rectification of more serious
damage to such items has become a matter of
either entrusting repair work to a specialist in
this field, or renewing complete components.
Repair of such damage by the DIY owner is
not really feasible, owing to the cost of the
equipment and materials required for effecting
such repairs. The basic technique involves
making a groove along the line of the crack in
the plastic, using a rotary burr in a power drill.
The damaged part is then welded back
together, using a hot-air gun to heat up and
fuse a plastic filler rod into the groove. Any
excess plastic is then removed, and the area
rubbed down to a smooth finish. It is important
that a filler rod of the correct plastic is used, as
body components can be made of a variety of
different types (eg polycarbonate, ABS,
polypropylene).
Damage of a less serious nature (abrasions,
minor cracks etc) can be repaired by the DIY
owner using a two-part epoxy filler repair
material. Once mixed in equal proportions, this
is used in similar fashion to the bodywork filler
used on metal panels. The filler is usually
cured in twenty to thirty minutes, ready for
sanding and painting.
If the owner is renewing a complete
component himself, or if he has repaired it with
epoxy filler, he will be left with the problem of
finding a suitable paint for finishing which is
compatible with the type of plastic used. At
one time, the use of a universal paint was not
possible, owing to the complex range of
plastics encountered in body component
applications. Standard paints, generally
speaking, will not bond to plastic or rubber
satisfactorily. However, it is now possible to
obtain a plastic body parts finishing kit which
consists of a pre-primer treatment, a primer
and coloured top coat. Full instructions are
normally supplied with a kit, but basically, the
method of use is to first apply the pre-primer
to the component concerned, and allow it to
dry for up to 30 minutes. Then the primer is
applied, and left to dry for about an hour
before finally applying the special-coloured
top coat. The result is a correctly-coloured
component, where the paint will flex with the
plastic or rubber, a property that standard
paint does not normally posses.
Bodywork and fittings 12•3
12
If bodystopper is used, it can be
mixed with cellulose thinners,
to form a thin paste which is
ideal for filling small holes.
procarmanuals.com
Page 175 of 255

weatherstrips and remove the trim. Also
remove the webbing guide, which is secured
by two screws.
5Unbolt the lower anchor and the retractor,
again noting the position of any washers or
spacers. Remove the retractor and webbing
(see illustration).
6The seat belt buckle is secured to the seat
frame by two Torx screws(see illustration).
There is no need to renew the buckle just
because the retractor and webbing are being
renewed. If it is wished to remove the buckle,
first remove the seat.
7Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Tighten all anchorages to the specified torque,
and make sure that the belt is not twisted.1This Section describes the removal and
refitting of factory or dealer-installed rear seat
belts. A rear belt kit can be purchased from a
Ford dealer and should be found to
correspond with the items shown here. If a
proprietary kit is purchased, make sure it is
suitable for the vehicle in question and follow
the manufacturer’s instructions.
2Fold the rear seat cushion forwards.
3Feed the buckle webbing through the slits in
the carpet. Remove the buckle securing bolt,
remove the pins from the buckle elastic straps
and remove the buckles.
4Remove the lower anchor bolts, then fold
the seat backrests forwards. Fold back the
luggage area carpet and remove the backrest
hinges.
5Remove the seat back striker pins (low
series) or adjuster mechanism cover (high
series) (see illustration).
6Prise the webbing guides from each side
cushion.
7Remove the side cushions. Each one is
retained by a single nut and washer located
near the loudspeaker (see illustration). With
the nut and washer removed, the cushion is
then released by prising open the metal tags
which secure its bottom wire. Pull the bottom
of the cushion forwards and upwards to free it
from the retractor.
8The retractor can now be unbolted and thewebbing withdrawn through the side cushions.
9Commence refitting by fitting the retractor.
First fit the rear bolt and tighten it by a few
turns only, so that the retractor is still free to
move. Push the retractor rearwards and then
downwards so that it takes up its fitted
positions, then fit the front bolt. Tighten both
bolts to the specified torque.
10The remainder of refitting is a reversal of
the removal procedure. Tighten the belt and
buckle anchor bolts to the specified torque.
Cushion
1Fold the seat cushion forwards and remove
the hinge retaining screws (see illustration).
To remove the hinges as well, unbolt the
hinges from the body instead.
2When refitting, just nip up the hinge screws
or bolts and check the fit of the cushions.
Tighten the screws or bolts fully when
satisfied.
Backrests
3Fold the backrests forward and peel back
the carpet to expose the hinges (see
illustration).
4Remove the hinge screws, free the seat belt
webbing clips (when applicable) and remove
the backrests.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
49Rear seat components -
removal and refitting
48Rear seats belts - removal
and refitting
12•18Bodywork and fittings
47.1 Front seat belt adjustable top anchor
47.6 Front seat belt buckle secured by two
Torx screws (arrowed)
48.5 Removing a seat back striker pin49.1 Rear seat hinge-to-cushion screws48.7 Removing a side cushion nut
47.3 Removing the weatherstrip from the
B-pillar47.5 Seat belt retractor mechanism -
securing the bolt arrowed
procarmanuals.com
Page 181 of 255

the circuit between the relevant connector and
the battery is problem-free.
13Continue to check the remainder of the
circuit in the same fashion.
14When a point is reached at which no
voltage is present, the problem must lie
between that point and the previous test point
with voltage. Most problems can be traced to
a broken, corroded or loose connection.
Finding a short-circuit
15To check for a short-circuit, first disconnect
the load(s) from the circuit (loads are the
components which draw current from a circuit,
such as bulbs, motors, heating elements, etc).
16Remove the relevant fuse from the circuit,
and connect a circuit tester or voltmeter to the
fuse connections.
17Switch on the circuit, bearing in mind that
some circuits are live only when the ignition
switch is moved to a particular position.
18If voltage is present (indicated either by
the tester bulb lighting or a voltmeter reading),
this means that there is a short-circuit.
19If no voltage is present, but the fuse still
blows with the load(s) connected, this
indicates an internal fault in the load(s).
Finding an earth fault
20The battery negative terminal is connected
to “earth” - the metal of the engine/transmission
and the car body - and most systems are wired
so that they only receive a positive feed, the
current returning via the metal of the car body.
This means that the component mounting andthe body form part of that circuit. Loose or
corroded mountings can therefore cause a range
of electrical faults, ranging from total failure of a
circuit, to a puzzling partial fault. In particular,
lights may shine dimly (especially when another
circuit sharing the same earth is in operation),
motors (eg wiper motors or the radiator cooling
fan motor) may run slowly, and the operation of
one circuit may have an apparently-unrelated
effect on another. Note that on many vehicles,
earth straps are used between certain
components, such as the engine/transmission
and the body, usually where there is no metal-to-
metal contact between components, due to
flexible rubber mountings, etc.
21To check whether a component is properly
earthed, disconnect the battery, and connect
one lead of an ohmmeter to a known good
earth point. Connect the other lead to the wire
or earth connection being tested. The
resistance reading should be zero; if not,
check the connection as follows.
22If an earth connection is thought to be
faulty, dismantle the connection, and clean
back to bare metal both the bodyshell and the
wire terminal, or the component’s earth
connection mating surface. Be careful to
remove all traces of dirt and corrosion, then
use a knife to trim away any paint, so that a
clean metal-to-metal joint is made. On
reassembly, tighten the joint fasteners
securely; if a wire terminal is being refitted, use
serrated washers between the terminal and
the bodyshell, to ensure a clean and secure
connection. When the connection is remade,
prevent the onset of corrosion in the future byapplying a coat of petroleum jelly or silicone-
based grease, or by spraying on (at regular
intervals) a proprietary ignition sealer, or a
water-dispersant lubricant.
Headlight
1Open and prop the bonnet. Remove the
cover from the rear of the headlight unit by
twisting it anti-clockwise.
2Disconnect the wiring plug from the
headlight bulb. Release the spring clip by
squeezing its legs together and move it clear
of the bulb (see illustration).
3Remove the headlight bulb (see
illustration). Caution: If the lights have just
been in use, the bulb may be extremely hot.
4When handling the new bulb, use a tissue or
clean cloth to avoid touching the glass with
the fingers. If the glass is accidentally touched,
wipe it clean using methylated spirit. Moisture
and grease from the skin can cause
blackening and rapid failure of the new bulb.
5Fit the new bulb, making sure that the legs
and cut-outs in the bulb base and the reflector
match up. Secure with the spring clip.
6Reconnect the wiring plug. Check the
headlight for correct operation, then refit and
secure the rear cover.
Front parking light (sidelight)
7Gain access as for the headlight bulb, then
pull the parking light bulbholder from the
headlight reflector.
8Extract the wedge base bulb from the
holder (see illustration). Fit the new bulb, refit
the bulbholder and check for correct
operation.
Auxiliary driving light (when fitted)
9From above the auxiliary light unit, release
the cover spring clip and remove the cover
(see illustration).
10Release the spring clip from the bulb.
Withdraw the bulb and unplug its wiring
connector (see illustration). Caution: If the
lights have just been in use, the bulb may be
extremely hot.
11Do not touch the glass of the new bulb
with the fingers.
3Exterior lights - bulb renewal
13•4Body electrical system
3.2 Squeeze the spring clip legs (arrowed)
to remove the headlight bulb3.3 Removing a headlight bulb
3.8 Removing the front parking light bulb
from the holder3.9 Auxiliary driving light cover3.10 Removing the auxiliary driving light
bulb
procarmanuals.com