1985 FORD GRANADA coolant level
[x] Cancel search: coolant levelPage 22 of 255

Engine
Oil filter type (all models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion C102
Valve clearances (cold):
SOHC:
Inlet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.20 ±0.03 mm (0.008 ±0.001 in)
Exhaust . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.25 ±0.03 mm (0.010 ±0.001 in)
V6:
Inlet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.35 mm (0.014 in)
Exhaust . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.40 mm (0.016 in)
Cooling system
Specific gravity at 45 to 50% antifreeze concentration . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.069 to 1.077
Note:Refer to antifreeze manufacturer for latest recommendations.
Fuel system
Air filter element type:
1.8 litre (carburettor) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion W118
2.0 litre (carburettor) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion W152
2.0 litre and V6 (injection) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion U507
Fuel filter type:
All models (injection) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion L204
Ignition system
Spark plugs:
1.8 and 2.0 litre SOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion RF7YCC or RF7YC
2.0 litre DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion RC7YCC or RC7YC
2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion RN7YCC or RN7YC
2.4 and 2.9 litre V6 without catalytic converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion RC7YCC or RC7YC
2.9 litre V6 with catalytic converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion RS9YCC or RS9YC
Spark plug electrode gap*:
Champion RF7YCC and RN7YCC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.8 mm
Champion RF7YC and RN7YC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.7 mm
Champion RC7YCC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.8 mm
Champion RC7YC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.7 mm
Champion RS9YCC and RS9YC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.0 mm
Ignition HT lead set:
Resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30 k ohms maximum per lead
Type:
1.8 and 2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion LS-09 boxed set
1.8 and 2.0 litre (Male distributor fitting) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Champion LS-10 boxed set
*The spark plug gap quoted is that recommended by Champion for their specified plugs listed above. If spark plugs of any other type are to be
fitted, refer to their manufacturer’s recommendations.
Brakes
Brake pad friction material minimum thickness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.5 mm (0.06 in)
Tyres
Tyre sizes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .175 SR/TR/HR 14, 185/70 HR/TR/VR 14,195/65 HR 15, 205/60
VR 15
Tyre pressures: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .FrontRear
Normal load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.8 bar (26 lbf/in
2)1.8 bar (26 lbf/in2)
Full load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.1 bar (30 lbf/in2)2.9 bar (42 lbf/in2)
Note:Pressures apply only to original-equipment tyres, and may vary if any other make or type is fitted; check with the tyre manufacturer or supplier
for correct pressures if necessary.
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Engine oil drain plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2816 to 21
Engine block coolant drain plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2516 to 18
Spark plugs:
1.8 and 2.0 litre SOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to2815 to 21
2.0 litre DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15 to 2111 to 15
2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30 to 4022 to 30
2.4 and 2.9 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15 to 2111 to 15
Manual gearbox filler/level and drain plugs:
N9 type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23 to 2717 to 20
MT75 type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29 to 4121 to 30
Brake caliper slide bolts:
Front . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Rear . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31 to 3523 to 26
Roadwheel bolts (steel and alloy wheels) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 10052 to 74
1•21
1
Specifications
procarmanuals.com
Page 43 of 255

See Chapter 1, Section 23.
1Make a final check to ensure that everything
has been reconnected to the engine and that no
rags or tools have been left in the engine bay.
2Check that oil and coolant levels are
correct.
3Start the engine. This may take a little longer
than usual as fuel is pumped up to the engine.
4Check that the oil pressure light goes out
when the engine starts.
5Run the engine at a fast tickover and check
for leaks of oil, fuel and coolant. Also check
power steering and transmission fluid cooler
unions, when applicable. Some smoke and
odd smells may be experienced as assembly
lubricant burns off the exhaust manifold and
other components.6Bring the engine to operating temperature.
Check the ignition timing then adjust the idle
speed (if applicable) and mixture.
7Stop the engine and allow it to cool, then re-
check the oil and coolant levels.
8If new bearings, pistons etc have been
fitted, the engine should be run in at reduced
speeds and loads for the first 500 miles (800
km) or so. It is beneficial to change the engine
oil and filter after this mileage.
1When engine performance is down, or if
misfiring occurs which cannot be attributed to
the ignition or fuel system, a compression test
can provide diagnostic clues. If the test is
performed regularly it can give warning of
trouble before any other symptoms become
apparent.
2The engine must be at operating
temperature, the battery must be fully charged
and the spark plugs must be removed. The
services of an assistant will also be required.
3Disable the ignition system by dismantlingthe coil LT feed. Fit the compression tester to
No 1 spark plug hole. (The type of tester which
screws into the spark plug hole is to be
preferred.)
4Have the assistant hold the throttle wide
open and crank the engine on the starter.
Record the highest reading obtained on the
compression tester.
5Repeat the test on the remaining cylinders,
recording the pressure developed in each.
6Desired pressures are given in the
Specifications. If the pressure in any cylinder
is low, introduce a teaspoonful of clean engine
oil into the spark plug hole and repeat the test.
7If the addition of oil temporarily improves
the compression pressure, this indicates that
bore or piston wear was responsible for the
pressure loss. No improvement suggests that
leaking or burnt valves, or a blown head
gasket, may be to blame.
8A low reading from two adjacent cylinders is
almost certainly due to the head gasket
between them having blown.
9On completion of the test, refit the spark
plugs and reconnect the coil LT feed.
52Compression test -
description and interpretation
51Initial start-up after overhaul
or major repair
50Valve clearances - checking
and adjustment
2A•20SOHCengines
procarmanuals.com
Page 50 of 255

21Working through the starter motor
aperture, unscrew the four torque converter-
to-driveplate nuts. It will be necessary to turn
the crankshaft using a spanner on the
crankshaft pulley bolt in order to gain access
to each nut in turn through the aperture.
22Where applicable, remove the bolt
securing the transmission fluid dipstick tube to
the left-hand side of the cylinder block.
23Unscrew the engine-to-transmission bolts,
noting the locations of the bolts, and the
positions of the earth strap and any wiring
clips attached to the bolts. Recover any shims
fitted between the sump and the transmission
when removing the lower engine-to-
transmission bolts.
24Unscrew the bolt from the engine adapter
plate and, where applicable, pull the blanking
plug from the adapter plate.
25Pull the engine and the transmission apart,
ensuring that the torque converter is held firmly
in place in the transmission housing, otherwise
it could fall out resulting in fluid spillage and
possible damage. It may be necessary to rock
the units slightly to separate them.
1Reverse the procedure described in
paragraphs 1 to 40 ofSection 5, noting the
following points.
2Before attempting to refit the engine, check
that the clutch friction disc is centralised.
3Check that the clutch release arm and
bearing are correctly fitted, and lightly grease
the input shaft splines.
4Check that the engine adapter plate is
correctly positioned on the locating dowels. If
necessary, a cable-tie can be used to
temporarily secure the adapter plate in
position on the cylinder block using one of the
engine-to-gearbox bolt holes.
5If shims were fitted between the sump and
the gearbox, refit them in their original
locations when mating the engine to the
gearbox. If the engine has been overhauled,
where applicable fit the relevant shims as
calculated during engine reassembly .
6Reconnect the clutch cable to the release arm,
ensuring that it is routed as noted during removal.
7Ensure that the roadwheels and the steering
wheel are in the straight-ahead position then
align the marks made on removal and reconnect
the intermediate shaft to the steering gearing.
Tighten the clamp bolt to the specified torque.
8Refit the exhaust downpipe.
9Fill the engine with the correct grade and
quantity of oil.
10Check the throttle cable adjustment. Where
necessary, also adjust the speed control cable
in the same way so that there is only a small
amount of slack present in the cable.
11Reconnect the coolant hoses to the water
pump housing.
12Fill the cooling system .
13Tighten all fixings to the specified torque,
where applicable.1Reverse the procedure described in Section 6,
noting the following points.
2Check that the engine adapter plate is
correctly positioned on the locating dowels. If
necessary, a cable-tie can be used to
temporarily secure the adapter plate in
position on the cylinder block using one of the
engine-to-transmission bolt holes.
3As the torque converter is only loosely
engaged in the transmission, care must be taken
to prevent the torque converter from falling out
forwards. When the torque converter hub is fully
engaged with the fluid pump drivegear in the
transmission, distance A (see illustration 2.20 in
Chapter 7B)must be as specified. Incorrect
installation of the torque converter will result in
damageto the transmission.
4If shims were fitted between the sump and
the transmission, refit them in their original
locations when mating the engine to the
transmission. If the engine has been
overhauled, where applicable fit the relevant
shims as calculated during engine reassembly.
5As the engine is installed, guide the torque
converter studs through the holes in the
driveplate. When the engine is positioned flush
with the engine adapter plate and the
transmission housing, check that the torque
converter is free to move axially a small
amount before refitting and tightening the
engine-to-transmission bolts.
6Do not tighten the torque converter-to-
driveplate nuts until the lower engine-to-
transmission bolts have been fitted and
tightened.
7Ensure that the roadwheels and the steering
wheel are in the straight-ahead position then
align the marks made on removal and
reconnect the intermediate shaft to the
steering gearing. Tighten the clamp bolt to the
specified torque.
8Refit the exhaust downpipe.
9Fill the engine with the correct grade and
quantity of oil.
10Check the throttle cable adjustment. Where
necessary, also adjust the speed control cable
in the same way so that there is only a small
amount of slack present in the cable.
11Reconnect the coolant hoses to the water
pump housing.
12Fill the cooling system.
13Tighten all fixings to the specified torque,
where applicable.
1Reverse the procedure described in Section 7,
noting the following points.
2Before attempting to reconnect the engine
to the gearbox, check that the clutch friction
disc is centralised.
3Check that the clutch release arm andbearing are correctly fitted, and lightly grease
the input shaft splines.
4Check that the engine adapter plate is
correctly positioned on the locating dowels. If
necessary, a cable-tie can be used to
temporarily secure the adapter plate in
position on the cylinder block using one of the
engine-to-gearbox bolt holes.
5If shims were fitted between the sump and
the gearbox, refit them in their original
locations when mating the engine to the
gearbox. If the engine has been overhauled,
where applicable fit the relevant shims as
calculated during engine reassembly.
6Ensure that the roadwheels and the steering
wheel are in the straight-ahead position then
align the marks made on removal and
reconnect the intermediate shaft to the
steering gearing. Tighten the clamp bolt to the
specified torque.
7Reconnect the clutch cable to the release
arm, ensuring that it is routed as noted during
removal.
8Refit the propeller shaft.
9Refit the exhaust system.
10Fill the engine with the correct grade and
quantity of oil.
11Check the throttle cable adjustment. Where
necessary, also adjust the speed control cable
in the same way so that there is only a small
amount of slack present in the cable.
12Reconnect the coolant hoses to the water
pump housing.
13Fill the cooling system.
14Check and if necessary top-up the
gearbox oil level.
15Tighten all fixings to the specified torque,
where applicable.
1Reverse the procedure described in Section 8,
noting the following points.
2Check that the engine adapter plate is
correctly positioned on the locating dowels. If
necessary, a cable-tie can be used to
temporarily secure the adapter plate in
position on the cylinder block using one of the
engine-to-transmission bolt holes.
3As the torque converter is only loosely
engaged in the transmission, care must be taken
to prevent the torque converter from falling out
forwards. When the torque converter hub is fully
engaged with the fluid pump drivegear in the
transmission, distance A (see illustration 2.20 in
Chapter 7B)must be as specified. Incorrect
installation of the torque converter will result in
damage to the transmission.
4If shims were fitted between the sump and
the transmission, refit them in their original
locations when mating the engine to the
transmission. If the engine has been
overhauled, where applicable fit the relevant
shims as calculated during engine reassembly.
5As the engine and transmission are mated
12Engine/automatic
transmission assembly -
reconnection and refitting
11Engine/manual gearbox
assembly - reconnection and
refitting
10Engine - refitting (automatic
transmission in vehicle)
9Engine - refitting (manual
gearbox in vehicle)
DOHCengine 2B•7
2B
procarmanuals.com
Page 51 of 255
together, guide the torque converter studs
through the holes in the driveplate. When the
engine is positioned flush with the engine
adapter plate and the transmission housing,
check that the torque converter is free to move
axially a small amount before refitting and
tightening the engine-to-transmission bolts.
6Do not tighten the torque converter-to-
driveplate nuts until the lower engine-to-
transmission bolts have been fitted and
tightened.
7Ensure that the roadwheels and the steering
wheel are in the straight-ahead position then
align the marks made on removal and
reconnect the intermediate shaft to the
steering gearing. Tighten the clamp bolt to the
specified torque.
8Reconnect the selector rod and adjust as
described in Chapter 7, PartB.
9Refit the propeller shaft.
10Refit the exhaust system.
11Fill the engine with the correct grade and
quantity of oil.
12Check the throttle cable adjustment. Where
necessary, also adjust the speed control cable
in the same way so that there is only a small
amount of slack present in the cable.
13Reconnect the coolant hoses to the water
pump housing.
14Fill the cooling system.
15Check and if necessary top-up the
transmission fluid level.
16Tighten all fixings to the specified torque,
where applicable.
Proceed as described in Part A, Section 23
of this Chapter but note that on certain
models, it may be necessary to unbolt the
engine mounting brackets from the cylinder
block to allow sufficient clearance to remove
the mountings.
1Refer to Part A, Section 8 of this Chapter,
paragraphs 1 to 8 inclusive.
2A selection of splined and Torx sockets will
be required to remove many of the bolts when
dismantling the engine.
3Before dismantling the main engine
components, the following externally mounted
ancillary components can be removed.
a)Inlet manifold (and carburettor, where
applicable).
b)Exhaust manifold.
c)Alternator.
d)Water pump, and thermostat.
e)Water pump/alternator drivebelt tensioner.
f)Distributor cap, HT leads and spark plugs.
g)Oil pressure warning lamp switch.
h)Crankshaft speed/position sensor.
i)Oil filter.
j)Dipstick.
k)Engine mounting brackets (if not already
done).
l)Crankcase ventilation pipe and hoses.m)Clutch.
n)Alternator mounting bracket.
o)Air conditioning compressor mounting
bracket (where applicable).
p)Engine lifting brackets.
Note: A puller will be required to remove the
crankshaft pulley. A new crankshaft pulley bolt,
a new timing chain tensioner plunger
assembly, new upper and lower timing chain
cover gaskets and a new camshaft cover
gasket and reinforcing sleeve sealing rings
must be used on refitting.
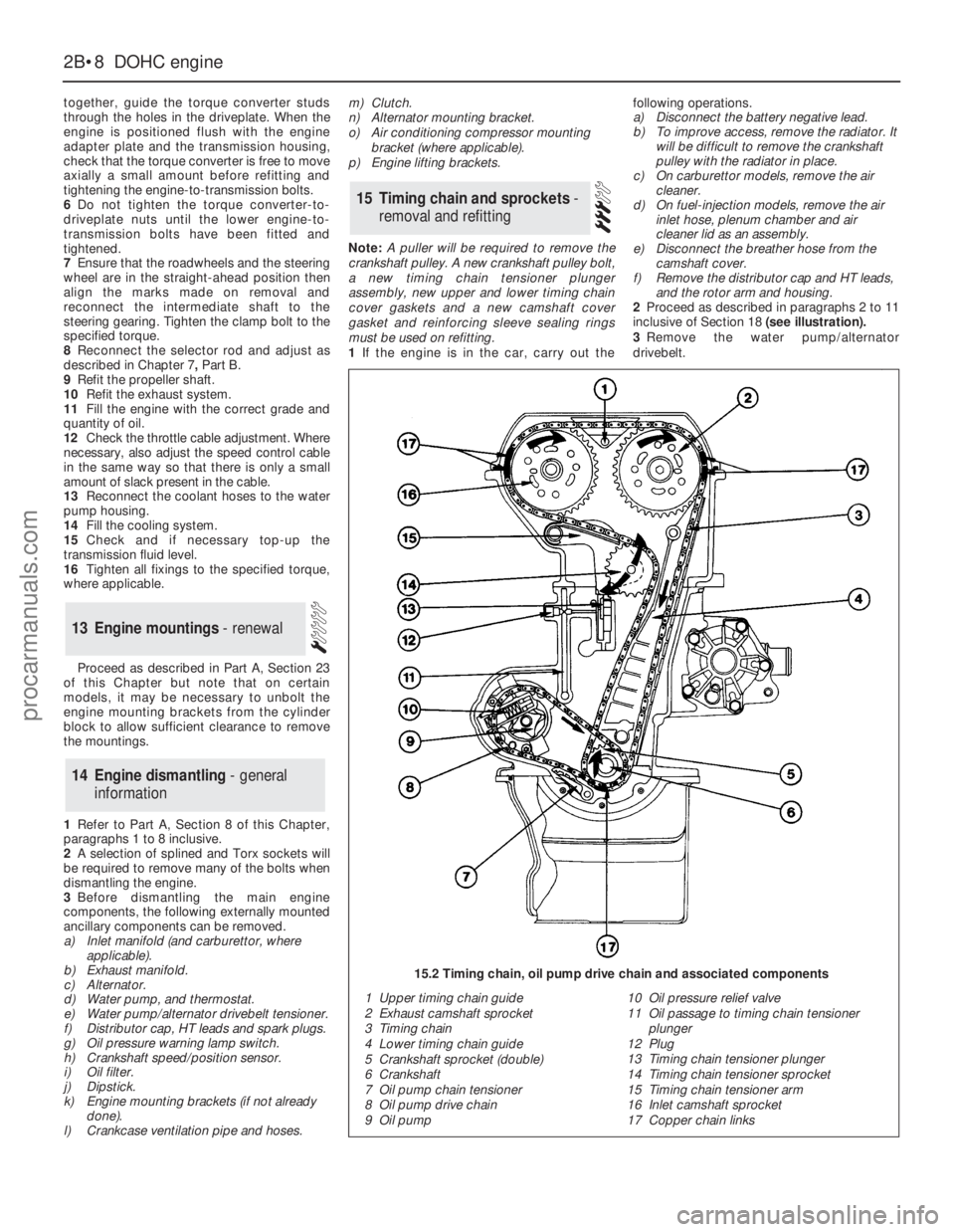
1If the engine is in the car, carry out thefollowing operations.
a)Disconnect the battery negative lead.
b)To improve access, remove the radiator. It
will be difficult to remove the crankshaft
pulley with the radiator in place.
c)On carburettor models, remove the air
cleaner.
d)On fuel-injection models, remove the air
inlet hose, plenum chamber and air
cleaner lid as an assembly.
e)Disconnect the breather hose from the
camshaft cover.
f)Remove the distributor cap and HT leads,
and the rotor arm and housing.
2Proceed as described in paragraphs 2 to 11
inclusive of Section 18 (see illustration).
3Remove the water pump/alternator
drivebelt.
15Timing chain and sprockets -
removal and refitting
14Engine dismantling - general
information
13Engine mountings - renewal
2B•8DOHCengine
1 Upper timing chain guide
2 Exhaust camshaft sprocket
3 Timing chain
4 Lower timing chain guide
5 Crankshaft sprocket (double)
6 Crankshaft
7 Oil pump chain tensioner
8 Oil pump drive chain
9 Oil pump10 Oil pressure relief valve
11 Oil passage to timing chain tensioner
plunger
12 Plug
13 Timing chain tensioner plunger
14 Timing chain tensioner sprocket
15 Timing chain tensioner arm
16 Inlet camshaft sprocket
17 Copper chain links
15.2 Timing chain, oil pump drive chain and associated components
procarmanuals.com
Page 85 of 255
Cooling system
The cooling system is of pressurised type
and includes a front mounted crossflow
radiator, belt-driven water pump, temperature-
sensitive thermo-viscous fan (on DOHC
models, an electrically-operated cooling fan is
fitted, operated by a switch in the thermostat
housing), wax type thermostat, and an
expansion and degas tank.
The radiator matrix is of copper and brass
construction and the end tanks are of plastic.
On automatic transmission models the right-
hand side end tank incorporates the
transmission oil cooler.
The thermostat is located behind the water
outlet elbow at the front of the cylinder head
on OHCmodels, and on the front of the water
pump on V6 models. Its purpose is to ensure
rapid engine warm-up by restricting the flow of
coolant in the engine when cold, and also to
assist in regulating the normal operating
temperature of the engine.
The expansion tank incorporates a pressure
cap which effectively pressurises the cooling
system as the coolant temperature rises,
thereby increasing the boiling point of the
coolant. The tank also has a further degas
function. Any accumulation of air bubbles in
the coolant, in particular in the thermostat
housing and the radiator, is returned to the
tank and released in the air space thus
maintaining the efficiency of the coolant.
On models fitted with the auxiliary warning
system, the expansion tank contains a level
sensor which operates a warning light if the
coolant level falls significantly.
When the engine is started from cold, the
water pump circulates coolant around the
cylinder block, cylinder head(s) and inlet
manifold. The warm coolant passes through
the automatic choke housing (when
applicable) and through the heater matrix
before returning to the engine. As the coolant
expands, the level in the expansion tank rises.
Circulation of coolant through the radiator is
prevented while the thermostat is shut. When
the coolant reaches the predeterminedtemperature the thermostat opens and hot
water passes through the top hose to the top
of the radiator. As the water circulates down
through the radiator, it is cooled by the
passage of air past the radiator when the car is
in forward motion, supplemented by the action
of the thermo-viscous fan when necessary.
Having reached the bottom of the radiator, the
water is now cool and the cycle is repeated.
Circulation of water continues through the
expansion tank, inlet manifold and heater at all
times; the heater temperature control being by
an air flap.
The thermo-viscous fan is controlled by the
temperature of air behind the radiator. When
the air temperature reaches a predetermined
level, a bi-metallic coil commences to open a
valve within the unit and silicon fluid is fed
through a system of vanes. Half of the vanes
are driven directly by the water pump and the
remaining half are connected to the fan blades.
The vanes are arranged so that drive is
transmitted to the fan blades in relation to the
drag or viscosity of the fluid, and this in turn
depends on ambient temperature and engine
speed. The fan is therefore only operated when
required, and compared with direct drive type
fan represents a considerable improvement in
fuel economy, drivebelt wear and fan noise.
Air conditioning
Air conditioning is fitted as standard on
Scorpio models and is optionally available on
some other models. In conjunction with the
heater, the system enables any reasonable air
temperature to be achieved inside the car, it
also reduces the humidity of the incoming air,
aiding demisting even when cooling is not
required.
The refrigeration side of the air conditioning
system functions in a similar way to a
domestic refrigerator. A compressor, belt-
driven from the crankshaft pulley, draws
refrigerant in its gaseous phase from an
evaporator. The compressed refrigerant
passes through a condenser where it loses
heat and enters its liquid phase. After
dehydration the refrigerant returns to the
evaporator where it absorbs heat from air
passing over the evaporator fins. The
refrigerant becomes a gas again and the cycle
is repeated.Various subsidiary controls and sensors
protect the system against excessive
temperature and pressures. Additionally,
engine idle speed is increased when the
system is in use to compensate for the
additional load imposed by the compressor.
Precautions
Antifreeze mixture
Antifreeze mixture is poisonous. Keep it out
of reach of children and pets. Wash splashes
off skin and clothing with plenty of water.
Wash splashes off vehicle paintwork to avoid
discolouration.
Antifreeze/water mixture must be renewed
every two years to preserve its anti-corrosive
properties. In climates where antifreeze
protection is unnecessary, a corrosion
inhibitor may be used instead - consult a Ford
dealer. Never run the engine for long periods
with plain water as coolant. Only use the
specified antifreeze, as inferior brands may not
contain the necessary corrosion inhibitors, or
may break down at high temperatures.
Antifreeze containing methanol is particularly
to be avoided, as the methanol evaporates.
The specified mixture is 45 to 50%
antifreeze and 50 to 55% clean soft water (by
volume). Mix the required quantity in a clean
container.
Air conditioning refrigerant
Although the refrigerant is not itself toxic, in
the presence of a naked flame (or a lighted
cigarette) it forms a highly toxic gas. Liquid
refrigerant spilled on the skin will cause
frostbite. If refrigerant enters the eyes, rinse
them with a dilute solution of boric acid and
seek medical advice immediately.
In view of the above points, and of the need
for specialised equipment for evacuating and
recharging the system, any work which
requires the disconnection of a refrigerant line
must be left to a specialist.
Do not allow refrigerant lines to be exposed
to temperatures above 110°C (230°F) - eg
during welding or paint drying operations and
do not operate the air conditioning system if it
is known to be short of refrigerant, or further
damage may result.
1General information and
precautions
3•2Cooling, heating and ventilation systems
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Radiator lower mountings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 126 to 9
Thermostat housing bolts:
SOHC, DOHC and 2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2013 to 15
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 to 105 to 7
Water pump bolts:
SOHC, M8 bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2113 to 16
SOHC, M10 bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4226 to 31
DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2816 to 21
2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 to 137 to 10
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 to 105 to 7
Water pump pulley bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2616 to 19
Water pump/alternator drivebelt tensioner bolt (DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 9752 to 72
Fan-to-viscous clutch bolts:
SOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 106 to 7
V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2313 to 17
Fan shroud bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
Cylinder block drain plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2516 to 18
procarmanuals.com
Page 90 of 255

See Chapter 1, Section 21.
1On 2.0 litre DOHC engines only, remove the
water pump/alternator drivebelt as described
in the previous Section.
2Loosen the alternator lower mounting
through-bolt, then remove the alternator upper
mounting bolt, and swing the alternator away
from the engine.
3Unscrew the central securing bolt, and
withdraw the drivebelt tensioner assembly.
4Commence refitting by positioning the
tensioner on the cylinder block, ensuring that
the lug on the rear of the tensioner bracket
engages with the corresponding hole in the
cylinder block (see illustration). Tighten the
securing bolt.
5Swing the alternator into position to align
the upper mounting bolt hole with the
corresponding hole in the drivebelt tensioner
assembly, then refit and tighten the upper
mounting bolt, then the lower throughbolt.
6Check the full length of the drivebelt for cracks
and deterioration and renew if necessary.
7Fit the drivebelt using a reversal of the
removal procedure, and release the tensioner
to tension the drivebelt.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Depressurize the cooling system by
unscrewing the expansion tank cap. Take
precautions against scalding if the system
is hot.
3Slacken the hose clips on all the hoses
which are connected to the tank. Pull off and
plug those hoses which are above the
waterline.4Remove the two screws which secure the
tank. Tilt the tank so that the coolant lies away
from the outlets, then disconnect and plug the
remaining hose.
5Disconnect the coolant level sensor, when
fitted, and remove the tank.
6Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Top-up the cooling system on completion.
1The temperature gauge sender is located
towards the front of the engine. On SOHC
models it is just below the inlet manifold (see
illustration); on V6 models it is just below the
top hose connection on the front of the left-
hand cylinder head, and on DOHC models it is
located at the front of the inlet manifold (see
illustration).
2Slacken the expansion tank cap to release
pressure in the cooling system, taking
precautions against scalding if the system
is hot.Tighten the cap again to minimise
coolant loss.
3Disconnect the wiring from the sender unit.
Unscrew and remove it, being prepared for
some coolant spillage.
4Smear sealant on the sender unit threads
before refitting, then insert and tighten it.
Reconnect the wiring.
5Top-up the cooling system if necessary,
then run the engine and check the operation of
the temperature gauge.The cooling fan switch is located in the end
of the thermostat housing.
Removal and refitting of the switch is as
described for the temperature gauge sender in
the previous Section.
Models before April 1992
Front
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the instrument cluster (Chapter 13).
3Remove the facia top (Chapter 12).
4Unclip the two control cables from the
control levers (see illustration).
5On air conditioned models, disconnect the
hoses from the vacuum switch.
6Remove the four screws which secure the
heater control assembly. Withdraw the
assembly from the facia.
7When refitting, secure the control assembly
with the four screws. Reconnect the vacuum
switch (when applicable) and the control
cables. Adjust the control cables if necessary
by altering the positions of the cable clips.
8When satisfied with the operation of the
cables, refit the other disturbed components.
Rear
9Remove the centre console (Chapter 12).
10Unclip the control cables and remove the
control unit.
11Refit in the reverse order to removal.
Models from April 1992
12Undo the two instrument panel surround
retaining screws, then carefully release the
retaining clips and remove the surround from
the facia.
13Pull off the three knobs from the heater
and ventilation controls to gain access to the
two hidden central vent panel retaining
screws. Slacken and remove the four panel
retaining screws and partially withdraw the
17Heater controls - removal and
refitting
16Cooling fan switch - removal
and refitting
15Temperature gauge sender -
removal and refitting
14Expansion tank - removal and
refitting
13Water pump/alternator
drivebelt tensioner - removal
and refitting
12Water pump/alternator
drivebelt(s) - inspection,
renewal and adjustment
Cooling, heating and ventilation systems 3•7
3
13.4 On refitting, ensure the drivebelt
tensioner lug (A) engages with hole in the
mounting bracket (B)15.1a Temperature gauge sender (manifold
removed)15.1b Temperature gauge sender unit
location (arrowed)
17.4 Heater control cable clip (arrowed)
viewed through windscreen
procarmanuals.com
Page 91 of 255

panel. Disconnect the wiring connectors from
the heated window switches and fuel
computer (where fitted) and remove the panel
from the car.
14Undo the two retaining screws then
manoeuvre the control panel out of the facia
and disconnect the wiring connector (see
illustration).
15Unclip the central fan switch from the
panel then, using a small flat-bladed
screwdriver, bend back the retaining tabs and
remove the cover from the panel base plate
(see illustration).
16Cut the cable retaining clips then release
the cables from the toothed guides and
remove the base plate.
17Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure securing the cables to the base
plate using new retaining clips.
Models before April 1992
Front
1Remove the heater controls as described in
the previous Section.
2Remove the centre console as described in
Chapter 12. Also remove the console bracket
and the gear lever inner gaiter.
3Unclip the under-dash trim on both sides.
Remove the glovebox lid.
4Remove the radio (Chapter 13).
5Remove the ABS and (when applicable) the
EEC IV modules (Chapters 10 and 13).
6Remove the remaining lower trim on the
passenger side to expose the heater casing.
7Remove the two securing screws and
release the cables from the heater.
8When refitting, place the air distribution and
temperature control valve levers in their
uppermost positions, then connect the cables.
9The remainder of refitting is a reversal of the
removal procedure.
Rear
10Remove the centre console (Chapter 12).
11Remove the front seat on the side
concerned. Also remove the rear seat cushion. 12Remove the front seat belt lower anchor bolt.
13Remove the front scuff plate, which is
secured by three screws. Remove the front
screw from the rear scuff plate.
14Roll back the front carpet from the scuff
plates to expose the heater cable. Release the
cable from its ties and disconnect it from the
control unit and the nozzle (see illustration).
15Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Models from April 1992
16Remove the facia undercovers, the right-
hand lower facia panel and the glovebox .
17Undo the two retaining nuts, then release
the retaining clips and remove the trim panel
from the glovebox aperture.
18Remove the heater control panel.
19Slacken and remove the control cable
retaining screws then release the retaining
clips (one screw and one clip for each cable).
Detach the cables from the heater assembly
and withdraw them from the facia whilst noting
the correct routing (see illustration).
20Refitting is a reverse of the removal
procedure noting the following points.
a)Ensure that the cables are correctly routed
prior to connecting them to the heater
housing.
b)Prior to refitting the glovebox aperture trim
panel, check that the panel controls
function correctly and that the cables
move the relevant operating lever
smoothly from the fully open to the fully
closed position without any trace of undue
friction.
Models before April 1992
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Depressurise the cooling system by
slackening the expansion tank cap. Take
precautions against scalding if the system is
hot.3Disconnect the two heater hoses from the
stubs on the bulkhead. Be prepared for some
coolant spillage: catch the coolant in a clean
container if it is fit for re-use. Plug the hoses,
or tie them up with their open ends raised.
4Expel as much coolant as possible from the
heater matrix by blowing through it.
5Remove the matrix connector plate and
gasket from the bulkhead.
6Working inside the vehicle, remove the
centre console and other trim as described for
access to the heater control cables .
7Remove the instrument cluster surround,
which is secured by four screws. Also pull out
the heater louvre panel.
8Remove the facia panel top, which is
secured by five screws and four clips.
9Detach the air trunking from the heater
casing. Release the trunking from the
bulkhead when necessary.
10Remove the two nuts which secure the
heater unit. Pull the unit into the vehicle until
the pipe stubs are clear of the bulkhead, then
remove it sideways. Be prepared for coolant
spillage.
11Check the condition of the foam gasket on
the bulkhead and renew it if necessary.
12Refit by reversing the removal operations.
13Top-up the cooling system on completion,
and check the level again after the engine has
been run.
Models from April 1992
14Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
15Drain the cooling system.
19Heater assembly - removal
and refitting
18Heater control cables -
removal and refitting
3•8Cooling, heating and ventilation systems
17.14 Heater control panel retaining screws
(arrowed)
18.19 Heater control cable retaining screw
and clip (arrowed)
17.15 Exploded view of the heater control
panel
A Control cable retaining clips
B Cover
C Fan switch
D Base plate18.14 Rear heater control cable at nozzle
procarmanuals.com
Page 92 of 255

16Locate the heater matrix feed and return
hoses on the engine compartment bulkhead.
Slacken the retaining clips and disconnect
both hoses from the matrix unions. Be
prepared for some coolant spillage. Plug the
matrix unions to prevent residual coolant
being spilt as the assembly is removed.
17Slacken and remove the two retaining
screws then remove the matrix cover plate
and gasket from the bulkhead; discard the
gasket as a new one should be used on
refitting.
18Remove the facia panel.
19Release the facia wiring loom from the
bulkhead to gain access to the demister
nozzle fasteners (see illustration).
20Remove the retaining nut and screw then
detach each windscreen demister nozzle from
the heater assembly. Undo the two retaining
nuts and detach the centre face level nozzle
from the heater.
21Slacken and remove the two retaining nuts
then detach the right-hand face level nozzle
from the heater and remove it from the vehicle.
Repeat the procedure for the left-hand nozzle.
22To detach each rear footwell nozzle from
the heater unit, remove the pin from the nozzle
retaining clip whilst supporting the outer part
of the retaining clip from the rear (see
illustration). Note: If the rear of the clip is not
supported when the pin is removed it will drop
down into the nozzle. To retrieve the clip will
require the removal of the vent which first
requires the front seat to be removed and
carpet lifted.
23Disconnect the wiring connector from the
heater control panel.
24Undo the two nuts securing the heater
assembly to the bulkhead then carefully
manoeuvre the assembly out of the vehicle
whilst being prepared for the possibility of
coolant spillage from the matrix unions.
25Refitting is a reverse of the removal
procedure noting the following points.
a)Tighten all retaining nuts and screws
securely and ensure that all nozzles are
securely connected to the heater
assembly so that there are no air gaps or
leaks.b)Check the operation of all heater cables
before refitting the facia, ensuring that the
relevant component moves smoothly from
the fully open to the fully closed position.
c)Ensure that the heater hoses are correctly
reconnected and are securely held by the
retaining clips.
d)Use a new gasket when refitting the matrix
cover plate.
e)Refill the cooling system.
1Remove the heater assembly as described
in the previous Section.
2Remove the two screws which secure the
heater matrix. Withdraw the matrix.
3If the matrix is leaking it is best to obtain a
new or reconditioned unit; home repairs are
seldom successful.4To dismantle, release the clips which secure
the casing halves together by using a
screwdriver. Carefully prise the halves apart
and separate them.
5Remove the flap valves and operating levers
from the casing halves, noting how they are
fitted for reference when reassembling.
6Flush the matrix with clean water to remove
any debris.
7Reassembly is a reversal of dismantling.
Additional clips may be needed to secure the
casing halves once they have been separated.
1Drain the cooling system.
2Noting the correct fitted positions, slacken
the retaining clips and disconnect the coolant
hoses from the valve.
3Disconnect the vacuum pipe from the top of
the valve then unclip the valve and remove it
from the retaining bracket.
4Refitting is a reverse of the removal
procedure ensuring that the coolant hoses are
reconnected to their original unions on the
valve and are securely held in position with the
retaining clips.
1Only those items which can be renewed
without discharging the system are described
here. Other items must be dealt with by a Ford
dealer or air conditioning specialist (see
illustration).
Compressor drivebelt
2Disconnect the battery earth lead.
3On OHC engines, remove the radiator
cooling fan.
4Slacken the compressor strap and pivot
bolts (see illustration),move the compressor
22Air conditioning system -
component renewal
21Heater coolant valve -
removal and refitting
20Heater matrix - dismantling
and reassembly
Cooling, heating and ventilation systems 3•9
3
19.19 Release the facia wiring loom from
the bulkhead to gain access to the
demister nozzle retaining nut and screw
(arrowed)19.22 Detach the rear footwell nozzles from
the heater assembly
If the heater matrix is blocked
it can sometimes be cleared
by reverse-flushing using a
garden hose and a proprietary
radiator cleaning product if necessary.
22.1 Air conditioning system
component locations
1 De-ice thermostat
2 Evaporator
3 Expansion valve
4 Compressor
5 Compressor clutch
6 Pressure switch
7 Sight glass
8 Dehydrator
9 Cooling fan
10 Condenser
procarmanuals.com