1983 FIAT UNO coolant level
[x] Cancel search: coolant levelPage 179 of 303

removal are in place under the
engine-to-gearbox bolts. Do not allow the
weight of the gearbox to hang on the input
shaft as it is engaged with the clutch friction
disc.
29Refit the starter motor, ensuring that the
wiring harness bracket is in position on the
top bolt.
30Locate the engine/transmission unit at the
front of the car and move it into position under
the engine compartment. Attach the lifting
sling and hoist as during removal.
31Enlist the aid of an assistant to help
steady the combined units as they are raised
into position and to locate the mountings in
the engine compartment.
32Once they are located, tighten the
mountings to the specified torque settings,
then disconnect the lifting hoist and sling.
33The remainder of the refitting and
reconnection procedures are a reversal of the
removal procedure described in Part C. For
further details on reconnecting the
suspension and driveshaft components,
refer to Chapter 7 and Section 13 of this
Chapter.
34Ensure that the exhaust downpipe-to-
manifold connection is clean and renew the
gasket when reconnecting this joint. Use a
smear of exhaust assembly paste on the jointfaces. Use new lockwashers and tighten the
flange nuts securely.
35Ensure that all fuel and coolant
connections are cleanly and securely made.
36Ensure that all wiring connections are
correct and securely made.
37Top up the engine and transmission oil
levels.
38Refill the cooling system.
39Check that all connections are securely
made, then reconnect the battery negative
lead.
Initial start-up after major
overhaul
40Refer to Chapter 1, Section 45.
8 Cooling system
PART A:
999 AND 1108 CC ENGINES
Description
1The operation and function of the cooling
system is essentially as described in Chapter
2 but note the location of the various
components and the routing of the coolant
hoses in Fig. 13.26.
Maintenance
2Topping-up, draining and refilling
procedures are as for 1116 and 1301 cc
engines in Chapter 2, but note that the
coolant capacity is different (see Specifica-
tions).
Thermostat -
removal and refittingÁ
3The thermostat is located on the left-hand
end of the cylinder head, below the
distributor.
4The thermostat cannot be renewed
independently of its housing and if faulty the
complete assembly must be renewed.
5Drain the cooling system.
6Although the thermostat housing can be
removed directly from the cylinder head,
better access is provided if the distributor is
first withdrawn as described in Section 10 of
this Chapter (photo).
7Disconnect the coolant hose from the
thermostat housing and unscrew the housing
flange bolts. Remove the assembly. Note that
it may be necessary to tap it free with a
plastic-faced or wooden mallet if stuck in
place.
8Remove the gasket and clean the mating
surfaces.
9Use a new gasket and bolt the assembly
into position (photo).
10Reconnect the coolant hose, then fill and
bleed the cooling system.
13•54 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Fig. 13.26 Cooling system circuit - 999 and 1108 cc engines (Sec 8A)
1 Coolant pump 2 Thermostat 3 Heater matrix
Fig. 13.27 Cooling system thermostat in open and closed positions - 999 and 1108 cc
engines (Sec 8A)8A.9 Fitting the thermostat housing. Note
the new gasket
8A.6 The thermostat housing (shown with
distributor removal) on the 999 cc engine
Page 180 of 303

Coolant pump -
removal and refitting#
11The coolant pump is located on the
crankshaft pulley end of the engine and is
driven by the timing belt.
12The pump cannot be repaired and must
be regarded as disposable.
13Drain the cooling system.
14Remove the timing belt cover and then set
No. 1 piston to TDC. To achieve this, turn the
crankshaft pulley bolt until the camshaft
sprocket timing mark is aligned with the one
on the cylinder head.
15Release the belt tensioner and slip the
timing belt off the camshaft and coolant pump
sprockets.
16Unbolt and remove the coolant pump and
clean the mounting face of all old gasket
material.
17Apply a continuous bead of RTV silicone
sealant (instant gasket) to the mounting face
of the coolant pump and bolt it into position
(photos).
18Check that the camshaft sprocket and the
crankshaft have not been moved and fit the
timing belt to the camshaft and coolant pump
sprockets. The pump sprocket does not
require setting in any particular position
before connecting the timing belt.
19Tension the belt as described in Sec-
tion 5B of this Chapter.
20Fit the timing belt cover.
21After allowing one hour for the gasket
material to cure, refill and bleed the cooling
system.
PART B:
1301 CC TURBO IE ENGINE
Description
1The cooling system on this model has flow
and return connections to the turbocharger,
and is an essential means of cooling the
turbocharger.
2The radiator cooling fan is of two-speed
type, being controlled by a two-stage
thermostatic switch screwed into the radiator
side tank.
3According to the coolant temperature level,
the fan speed is regulated to provide the most
effective cooling.
4The remote cooling system expansion tank
is mounted in the left-hand rear corner of the
engine compartment (photo).
PART C:
1372 CC IE AND 1372 CC
TURBO IE ENGINES
Description
1The cooling system layout and components
for the 1372 cc engines is shown in
Figs. 13.29 and 13.30.
2The system on each engine operates in
essentially the same manner as that
described for the other models in Chapter 2,
but the location of components and the
coolant hose routings differ according to
model. The cooling system expansion tank
location differs according to model, being
either located on the side of the radiator ormounted separately on the side of the inner
wing panel.
3On Turbo models, the cooling system also
assists in cooling the turbocharger.
Maintenance
4The maintenance procedures are
essentially the same as those described for
the other models in Chapter 2.
Cooling system - draining,
flushing and refillingÁ
Warning: Wait until the engine is
cold before starting this
procedure. Do not allow
antifreeze to come into contact
with your skin or painted surfaces of the
vehicle. Rinse off spills immediately with
plenty of water. Never leave antifreeze
lying around in an open container or in a
puddle in the driveway or on the garage
floor. Children and pets are attracted by its
sweet smell. Antifreeze is fatal if ingested.
5Disconnect the battery negative lead.
6Working inside the vehicle, turn the heater
temperature control knob fully to the right,
which will fully open the heater coolant valve.
7With the expansion tank cap removed,
place a suitable container beneath the
radiator bottom hose.
8Loosen the clip and ease the bottom hose
away from the radiator outlet (photo). Allow
the coolant to drain into the container.
9Reposition the container under the front of
the cylinder block, and unscrew the cylinder
block drain plug (photo). Allow the coolant to
drain into the container.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•55
8A.17B Tightening the coolant pump bolts8A.17A Fitting the coolant pump to the
999 cc engineFig. 13.28 Sectional view of the coolant
pump on the 999 and 1108 cc engines
(Sec 8A)
8C.9 Cylinder block drain plug8C.8 Bottom hose connection to the
radiator8B.4 Topping up the expansion tank with
antifreeze on the 1301 cc engine
13
Page 182 of 303

10Apply suitable sealant to the threads of
the drain plug, then refit and tighten the plug.
11Dispose of the drained coolant safely, or
keep it in a covered container if it is to be
re-used.
12If required, the system can be flushed
through as described in Section 2 of Chap-
ter 2.
13Before attempting to refill the cooling
system, make sure that all hoses have been
reconnected, that the hoses and clips are in
good condition, and that the clips are tight.
Also ensure that the cylinder block drain plug
has been refitted and tightened. Note that an
antifreeze mixture must be used all year round
to prevent corrosion of the engine
components - refer to Section 3, Chapter 2.
14Open the bleed screw in the top of the
expansion tank (photo).
15Remove the expansion tank cap, and fill
the system by slowly pouring the coolant into
the expansion tank to prevent air locks from
forming.
16Top up the coolant until liquid free from air
bubbles emerges from the radiator bleed
screw orifice, then close the bleed screw.
17Continue topping up until the coolant
reaches the Maximum mark on the expansion
tank.
18Start the engine and run it until it reaches
normal operating temperature, then stop the
engine and allow it to cool. Normal operating
temperature is reached when the cooling fancuts into operation. Feel the radiator top hose
to ensure that it is hot. If cool, it indicates an
air lock in the system.
19Check for leaks, particularly around
disturbed components. Check the coolant
level in the expansion tank, and top up if
necessary. Note that the system must be cold
before an accurate level is indicated. There is
a risk of scalding if the expansion tank cap is
removed whilst the system is hot.
Radiator (and cooling fan)
- removal and refitting Á
20Disconnect the battery negative lead.
21Detach the wiring connectors from the
cooling fan and the fan switch located in the
radiator (photos).
22If preferred, the cooling fan unit can be
removed separately from the radiator, by
undoing the attachment bolts and carefully
withdrawing the unit upwards from the
vehicle. Take care not to damage the radiator
core as it is lifted clear (photo).
23Drain the cooling system as described
earlier in this part of the Section, but note that
it will not be necessary to remove the cylinder
block drain plug.
24Undo the retaining screws and remove
the front grille panel.
25Loosen off the retaining clips and detach
the upper coolant hose and the expansion
hose from the radiator.26Note their direction of fitting, then prise
free the radiator retaining clips. Carefully lift
the radiator from the car.
27Refitting is a reversal of the removal
procedure. Ensure that as the radiator is
lowered into position, it engages in the two
rubber location grommets.
28With the radiator (and cooling fan) refitted,
top up the cooling system as described earlier
in this Section (photo).
Thermostat -
removal and refitting Á
Note: A new thermostat cover gasket must be
used on refitting.
29Drain the cooling system as described
earlier in this Section, but note that there is no
need to drain the cylinder block.
30Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
thermostat cover (situated at the gearbox end
of the cylinder head).
31Unscrew the two thermostat cover
securing bolts, noting that the left-hand bolt
may also secure the HT lead bracket, and
remove the thermostat/cover assembly.
Recover the gasket (photo).
32If faulty, the thermostat must be renewed
complete with the housing as an assembly.
33If desired the thermostat can be tested as
described in Chapter 2.
34Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•57
8C.21B Cooling fan switch wiring
connector8C.21A Cooling fan and wiring connector8C.14 Bleed screw location on top of the
expansion tank (arrowed)
8C.31 Thermostat unit removal on the
1372 cc ie engine (distributor removed for
clarity)8C.28 Topping up the radiator coolant level
on the 1372 cc ie engine. Note orientation
of radiator retaining clip (arrowed)8C.22 Cooling fan to radiator securing bolt
13
Page 187 of 303
PART B:
CARBURETTOR MODELS
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF) -
description
Warning: Refer to the beginning
of this Section before starting
any work.
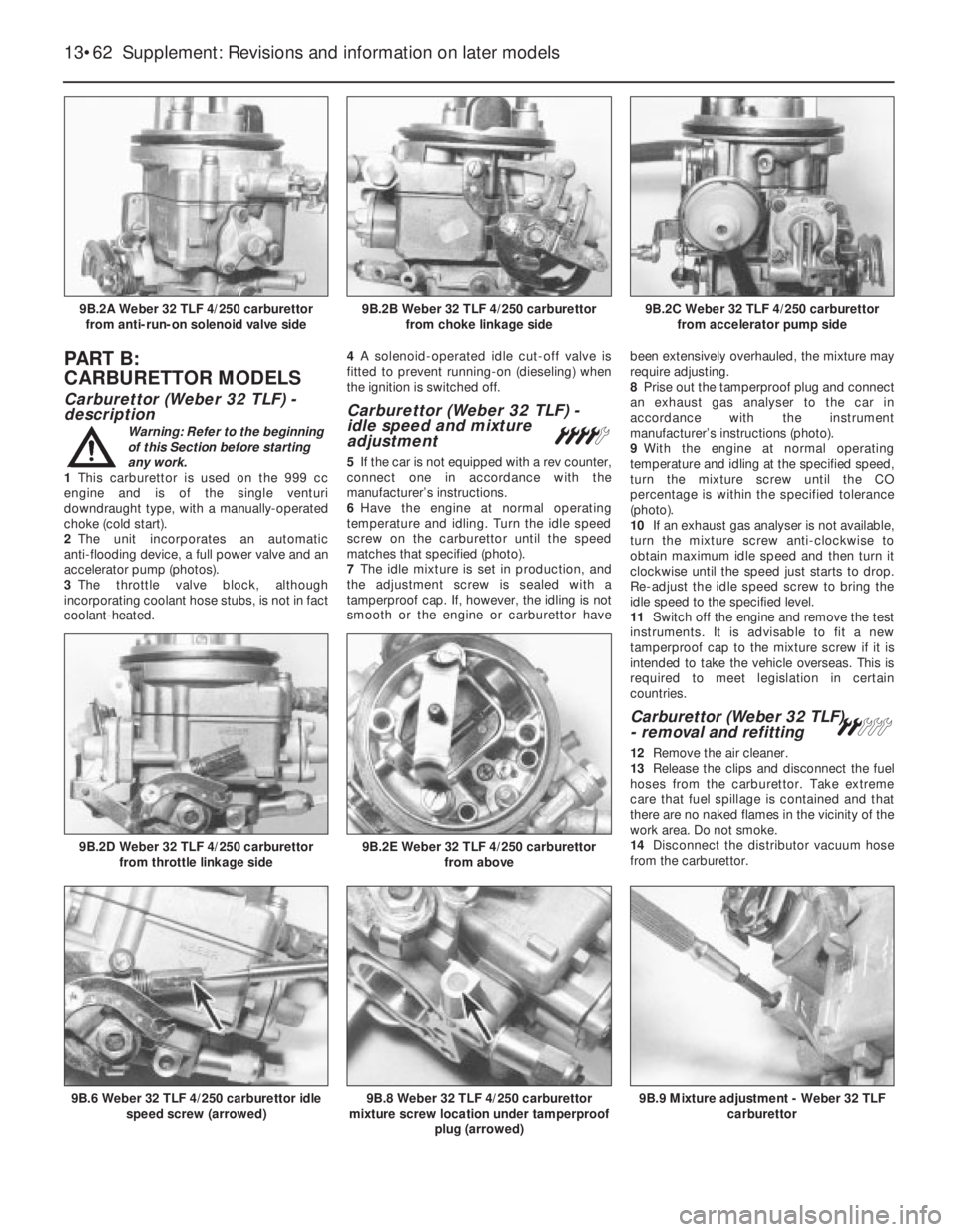
1This carburettor is used on the 999 cc
engine and is of the single venturi
downdraught type, with a manually-operated
choke (cold start).
2The unit incorporates an automatic
anti-flooding device, a full power valve and an
accelerator pump (photos).
3The throttle valve block, although
incorporating coolant hose stubs, is not in fact
coolant-heated.4A solenoid-operated idle cut-off valve is
fitted to prevent running-on (dieseling) when
the ignition is switched off.
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF) -
idle speed and mixture
adjustment
¢
5If the car is not equipped with a rev counter,
connect one in accordance with the
manufacturer’s instructions.
6Have the engine at normal operating
temperature and idling. Turn the idle speed
screw on the carburettor until the speed
matches that specified (photo).
7The idle mixture is set in production, and
the adjustment screw is sealed with a
tamperproof cap. If, however, the idling is not
smooth or the engine or carburettor havebeen extensively overhauled, the mixture may
require adjusting.
8Prise out the tamperproof plug and connect
an exhaust gas analyser to the car in
accordance with the instrument
manufacturer’s instructions (photo).
9With the engine at normal operating
temperature and idling at the specified speed,
turn the mixture screw until the CO
percentage is within the specified tolerance
(photo).
10If an exhaust gas analyser is not available,
turn the mixture screw anti-clockwise to
obtain maximum idle speed and then turn it
clockwise until the speed just starts to drop.
Re-adjust the idle speed screw to bring the
idle speed to the specified level.
11Switch off the engine and remove the test
instruments. It is advisable to fit a new
tamperproof cap to the mixture screw if it is
intended to take the vehicle overseas. This is
required to meet legislation in certain
countries.
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF)
- removal and refitting ª
12Remove the air cleaner.
13Release the clips and disconnect the fuel
hoses from the carburettor. Take extreme
care that fuel spillage is contained and that
there are no naked flames in the vicinity of the
work area. Do not smoke.
14Disconnect the distributor vacuum hose
from the carburettor.
13•62 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
9B.9 Mixture adjustment - Weber 32 TLF
carburettor9B.8 Weber 32 TLF 4/250 carburettor
mixture screw location under tamperproof
plug (arrowed)9B.6 Weber 32 TLF 4/250 carburettor idle
speed screw (arrowed)
9B.2E Weber 32 TLF 4/250 carburettor
from above9B.2D Weber 32 TLF 4/250 carburettor
from throttle linkage side
9B.2C Weber 32 TLF 4/250 carburettor
from accelerator pump side9B.2B Weber 32 TLF 4/250 carburettor
from choke linkage side9B.2A Weber 32 TLF 4/250 carburettor
from anti-run-on solenoid valve side
Page 191 of 303

adjustments described in this sub-Section,
however, will require removal of the
carburettor.
39Disconnect the short, curved diaphragm
hose from the top cover.
40Extract the top cover screws, lift the cover
from the carburettor body, and rotate it in
order to release the cranked choke control
rod from its key hole (photo). Mop out the fuel
and clean the jets.
41Check the jet sizes and other components
against those listed in the Specifications, in
case a previous owner has substituted
incorrect components (photo).
42Overhaul procedures are generally as
given in Chapter 3, Section 14 for the Weber
30/32 DMTR, but use the Specifications listed
in this Chapter. Additional overhaul
procedures are given here.
Fuel inlet needle valve
43If a high float level causing flooding of the
carburettor has been evident, first check that
the inlet valve housing is tight, and its washer
is sealing satisfactorily. A leak here will cause
fuel to bypass the inlet valve.
44If the needle valve is to be renewed,
remove it in the following way.
45Access to the fuel inlet needle valve is
obtained by carefully tapping out the float arm
pivot pin. Take care, the pivot pin pillars are
very brittle (photo).
46Unscrew the fuel inlet valve body and
remove the valve and washer.47When refitting the new valve, always use a
new sealing washer.
Float stroke (travel) - see Fig. 3.10
48The float stroke should be between 42.5
and 43.5 mm when measured from the top
cover gasket. Adjust if necessary by bending
the tab on the end of the arm.
Accelerator pump
49Adjustment of the accelerator pump is
very rarely required, but if performance is
suspect, carry out the following operations.
50Fill the carburettor float chamber and then
operate the throttle valve plate lever several
times to prime the pump.
51Position a test tube under the accelerator
pump jet and give ten full strokes of the
throttle lever, pausing between each stroke to
allow fuel to finish dripping.
52The total volume of fuel collected should
be as specified. Adjust the nut on the pump
control if necessary to increase or decrease
the volume of fuel ejected.
General
53When the stage is reached where the
valve plate spindle bushes have worn, then
the carburettor should be renewed complete.
54When reassembling the carburettor, use
new gaskets which can be obtained in a repair
pack.
Carburettor (Weber 32 ICEV
61/250 and DMTE 30/32,
DMTE 30/150) - general
55These carburettor types are fitted to later
models according to engine type. They are
similar in structure and operation to their
equivalents described in Chapter 3. Reference
can therefore be made to that Chapter for the
description and any operations concerning
them, but refer to Section 2 of this Chapter for
their specifications.
Carburettor (Solex
C 30/32-CIC 8) - description
56This carburettor is fitted as an alternative
to the Weber unit on 1116 cc models
produced for certain markets. The removal,
refitting and overhaul procedures are
essentially the same as described earlier for
the Weber carburettors.
PART C:
BOSCH LE2-JETRONIC
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM
Description
Warning: Refer to the beginning
of this Section before starting
any work.
1The Bosch LE2-Jetronic fuel injection
system, fitted to the 1301 cc Turbo ie model,
is an electronically controlled multi-point
injection (MPi) system.
2The fuel injectors are fed at constant
pressure in relation to inlet manifold vacuum
pressure.
3The system electronic control unit (ECU)
actuates the injectors for variable duration,
and so supplies the precise volume of fuel
required for any given engine speed and load
condition.
4The ECU also monitors the air induction, air
temperature, coolant temperature and throttle
opening as additional parameters to compute
the required opening of the fuel injectors,
giving maximum power with fuel economy.
Fuel supply system
5The fuel supply system consists of an
electric pump and primary filter, located
adjacent to the fuel tank. A fuel pressure peak
damper is located next to the pump (photo).
6Fuel is then pumped through a filter to the
fuel rail and injectors. The injectors are of the
13•66 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
9C.5 Electric fuel pump/filter/pressure
damper assembly location on a 1301 cc
Turbo ie model
9B.41 Jets on the Weber 30/32 DMTE
carburettor (top cover removed)
9B.45 Float pivot arrangement and needle
valve on the Weber 30/32 DMTE
carburettor
9B.40 Unscrewing a top cover screw from
the Weber 30/32 DMTE carburettor9B.37F Unscrewing a carburettor fixing nut
Page 193 of 303

Idle speed and mixture
adjustment¢
29Before carrying out any adjustments, the
engine must be at operating temperature, the
fan having cut in at second speed and then
switched off.
30Release the locknut and turn the main idle
speed screw in the throttle valve housing until
the engine idles at the specified speed. This
should be all that is necessary to obtain the
correct idle speed, as the throttle valve plate
base setting is set during production.
However, if wear has taken place, or incorrect
adjustment has been carried out previously,
proceed in the following way.
31Disconnect the intake duct from the
throttle valve housing. Release the locknut on
the base (small) adjusting screw, and turn thescrew until there is a clearance between the
lower edge of the throttle valve plate and the
throat wall of between 0.05 and 0.1 mm
(photos).
32With the engine still at operating
temperature, start the engine, and having
released the locknut, turn the main (large) idle
speed screw fully clockwise to close the
bypass passage.
33Now turn the base (small) screw until the
engine idles at between 700 and 800 rpm.
Tighten the locknut.
34Finally, turn the main (large) adjusting
screw to give an idle speed of between 800
and 900 rpm.
35It is unlikely that the mixture will require
alteration, but if it does, connect an exhaust
gas analyser to the car in accordance with the
equipment manufacturer’s instructions.
36With the engine at operating temperature,
prise out the tamperproof cap, and turn the
mixture screw, which is located in the airflow
meter, until the CO level is as given in the
Specifications. Turning the screw clockwise
richens the mixture, turning it anti-clockwise
weakens the mixture. Use a close-fitting Allen
key for the adjustment (photo).
Fuel injection system -
electrical testsª
37When carrying out checks to trace a fault
in the system, an ohmmeter should be used
for the following tests.
38Disconnect the multipin connector from
the ECU, and also the one from the system
control relay, and apply the probes of the
ohmmeter in accordance with the following
sequence to check for continuity in thecables. The component wiring plug will of
course be disconnected for the test.
ECU connector Component connector
plug terminal plug terminal
1 1 of ignition coil
2 2 of throttle position
switch
3 3 of throttle position
switch
4 50 of ignition switch
5 Earth
5 5 of airflow meter
7 7 of airflow meter
8 8 of airflow meter
9 9 of airflow meter
9 9 of throttle position
switch
9 18 of supplementary air
valve
9 87 main relay socket
10 10 of coolant temperature
sensor
12 Injector terminals
13 Earth
System control Component connector
relay connector plug terminal
plug terminal
1 1 of ignition coil
15 15 of ignition switch
30 Battery positive
31 Earth
50 50 of ignition switch
87 Injector terminals
87 18 of throttle position
switch
87 9 of ECU multipin socket
87b Fuel pump (fused)
13•68 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Fig. 13.42 ECU and component connector plug terminals - 1301 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 9C)
For colour code see main wiring diagrams
9C.31C Checking throttle valve plate
opening with a feeler blade
9C.36 Using an Allen key to adjust the
mixture (CO level)
9C.31B Idle speed base setting screw (1)
and main adjustment screw (2)9C.31A Disconnecting the throttle valve
housing intake duct9C.27B Removing the air cleaner element
Page 198 of 303

PART D:
BOSCH MONO-JETRONIC
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM
Warning: Refer to the beginning
of this Section before starting
any work.
Description
1The Bosch Mono-Jetronic fuel injection
system fitted to the 1372 cc ie engine and
later 999/1108 ‘FIRE’ models is an electroni-
cally-controlled single point injection (SPi)
system. The SPi system is a compromise
between a conventional carburettor fuel
supply system and a multi-point fuel injection
(MPi) system.
2Compared with a conventional carburettor,
the SPi unit is a relatively simple device. Fuel
is pumped to the SPi unit and then injected
into the inlet system by a single solenoid valve
(fuel injector), mounted centrally on top of the
unit. The injector is energised by an electrical
signal sent from the electronic control unit
(ECU), at which point the injector pintle is
lifted from its seat and atomised fuel is
delivered into the inlet manifold under
pressure. The electrical signals take two forms
of current; a high current to open the injector
and a low current to hold it open for the
duration required. At idle speed the injector
is pulsed at every other intake stroke rather
than with every stroke as during normal
operation.
3The air-to-fuel mixture ratio is regulated by
values obtained from the ignition coil (engine
speed), engine coolant temperature sensor,
throttle position switch, and the Lambda
sensor in the exhaust system. No adjustments
to the fuel mixture are possible.
4The throttle position switch enables the
ECU to compute both throttle position and its
rate of change. Extra fuel can then be
provided for acceleration when the throttle is
suddenly opened. Throttle position
information, together with the idle tracking
switch, provide the ECU with the closed
throttle position information.
5The 1372 cc ie system layout and principal
components are shown in Figs. 13.44 and13.45. Note that the Digiplex 2 electronic
ignition, is not fitted to FIRE models
(999/1108 cc).
6The fuel system pump is immersed in the
fuel tank and forms a combined unit with the
fuel level sender unit. A cartridge type in-line
fuel filter is fitted to the fuel line, and is located
in the engine compartment.
7The fuel pressure in the system is
controlled by a mechanical diaphragmregulator in the injection unit turret. High
pressure in the system causes the diaphragm
to operate and excess fuel is returned to the
fuel tank.
8The air intake temperature and volume is
regulated to ensure the correct mixture ratio
under all operating conditions. The
temperature of the air passing through the
injection unit is measured by a sensor which
transmits such information to the ECU for the
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•73
9C.101 Fuel tank anti-blow-back
compartment (arrowed)9C.99D Throttle cable balljoint retaining
spring clip (arrowed)9C.99C Throttle cable nipple (arrowed) in
throttle linkage cut-out
Fig. 13.44 Bosch Mono-Jetronic fuel injection system components and layout on the
1372 cc ie engine (Sec 9D)
1 Fuel pump relay
2 Injection system relay
3 Fuel pump fuse
4 Ignition coil
5 Digiplex 2 ECU
6 Battery
7 Idle speed check actuator
8 Injector connector9 Fuel pressure regulator
10 Injector
11 Throttle position switch
12 Ignition switch
13 Coolant temperature
sensor
14 Engine speed and TDC
sensor15 Secondary fuel filter
16 Fuel supply pipe
17 Fuel return pipe
18 Diagnostic socket
19 Fuel injection ECU
20 Fuel pump/level sender
unit13
Page 203 of 303

c) If the engine develops a misfire, do not
drive the car at all (or at least as little as
possible) until the fault is cured - the
misfire will allow unburned fuel to enter
the converter, which will result in its
overheating, as noted above.
d) DO NOT push- or tow-start the car - this
will soak the catalytic converter in
unburned fuel, causing it to overheat
when the engine does start - see b)
above.
e) DO NOT switch off the ignition at high
engine speeds - if the ignition is switched
off at anything above idle speed,
unburned fuel will enter the (very hot)
catalytic converter, with the possible risk
of its igniting on the element and
damaging the converter.
f) DO NOT use fuel or engine oil additives -
these may contain substances harmful to
the catalytic converter.
g) DO NOT continue to use the car if the
engine burns oil to the extent of leaving a
visible trail of blue smoke - the unburned
carbon deposits will clog the converter
passages and reduce its efficiency; in
severe cases the element will overheat.
h) Remember that the catalytic converter
operates at very high temperatures and
the casing will become hot enough to
ignite combustible materials which brush
against it. DO NOT, therefore, park the car
in dry undergrowth, over long grass or
piles of dead leaves.
i) Remember that the catalytic converter is
FRAGILE - do not strike it with tools
during servicing work, take great care
when working on the exhaust system,
ensure that the converter is well clear of
any jacks or other lifting gear used to raise
the car and do not drive the car over
rough ground road humps, etc., in such a
way as to ground the exhaust system.
j) In some cases, particularly when the car is
new and/or is used for stop/start driving, a
sulphurous smell (like that of rotten eggs)
may be noticed from the exhaust. This is
common to many catalytic
converter-equipped cars and seems to be
due to the small amount of sulphur found
in some petrols reacting with hydrogen in
the exhaust to produce hydrogen sulphide
(H
2S) gas; while this gas is toxic, it is not
produced in sufficient amounts to be a
problem. Once the car has covered a few
thousand miles the problem should
disappear - in the meanwhile a change of
driving style or of the brand of petrol used
may effect a solution.
k) The catalytic converter, used on a
well-maintained and well driven car,
should last for at least 50 000 miles
(80 000 km) or five years - from this point
on, careful checks should be made at all
specified service intervals on the CO level
to ensure that the converter is still
operating efficiently - if the converter is no
longer effective it must be renewed.
Fuel evaporation control system
- general
76As mentioned earlier, fuel evaporation is
contained within the system. In high outdoor
temperatures, when the vehicle is parked for a
period of time, the fuel in the tank evaporates,
building up pressure. When the pressure builds
up to a predetermined level a vent valve opens
to allow the vapours to pass on to and absorbed
by a carbon filter. However, if extreme pressure
or vacuum should build up, a two way safety
valve opens to allow external venting.
77If the safety valve needs replacing, note
that it must be fitted correctly. The black end
should be connected to the fuel tank and the
blue to the carbon filter.
78The vapours in the carbon filter are
flushed by warm air passing through the filter
on to a ECU controlled vapour cut-off
solenoid.
79The cut-off solenoid is closed when
starting the engine and opens to allow
vapours to be drawn into the inlet manifold,
through a second solenoid. If the cut-off
solenoid needs replacing ensure that the
black arrow on the casing is pointing towards
the inlet manifold.
80The second solenoid, known as an Elbi
solenoid, is closed when the engine is turned
off, thus preventing engine run-on. The side
facing connection is for the inlet manifold
pipe.
PART E:
BOSCH L3.1/2 JETRONIC
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEMS
Warning: Refer to the beginning
of this Section before starting
any work.
Description
1A Bosch L3.1 (or L3.2, as fitted from 1992)
Jetronic fuel injection system is fitted to the
1372 cc Turbo ie engine. The system circuit
and main component locations are shown in
Figs. 13.48 and 13.49.
2The L3.1/2 Jetronic system is a multi-point
fuel injection (MPi) system. It operates in a
similar manner to that of the LE2-Jetronic
system fitted to the 1301 cc Turbo ie engine
described in Part C of this Section. The L3.1/2
system is more sophisticated and has the
ability to provide reasonably efficient engine
operation when system sensors malfunction.
As with the LE2 system, the fuel and air
supply mixture circuits are regulated in
accordance with the electronic control unit
(ECU), but on the L3.1/2 system the control
unit is attached to the upper part of the
airflow meter.
3The ECU analyses the information passed
to it from the system sensors. These signals
are then processed and the air/fuel mixture is
constantly adjusted as required to provide the
13•78 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Fig. 13.48 Bosch L3.1 Jetronic fuel injection system - 1372 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 9E)
1 ECU
1A Diagnostic socket
2 Injection system relay and
fuel pump relay
3 Ignition switch
4 Battery
5 Fuel tank
6 Fuel pump
6A Primary fuel filter7 Coolant temperature
sensor
8 Intake air cooling radiator
(intercooler)
9 Air cleaner
10 Supplementary air valve
11 Throttle position switch
11A Throttle housing
12 Airflow meter12A Intake air temperature
sensor
13 Fuel pressure regulator
14 Fuel rail (to injectors)
15 Secondary fuel filter
16 Injectors
17 Injector cooling fan
18 Thermostatic switch (to
engage injector cooling fan)