1983 FIAT UNO steering
[x] Cancel search: steeringPage 3 of 303

REPAIRS & OVERHAUL
Engine and Associated Systems
Engine (also see Chapter 13)Page 1•1
Cooling and heating systems (also see Chapter 13)Page2•1
Fuel system (also see Chapter 13)Page 3•1
Ignition system (also see Chapter 13)Page4•1
Transmission
Clutch (also see Chapter 13)Page5•1
Transmission (also see Chapter 13)Page6•1
Driveshafts, hubs, roadwheels and tyres (also see Chapter 13)Page7•1
Brakes
Braking system(also see Chapter 13)Page 8•1
Electrical
Electrical system(also see Chapter 13)Page 9•1
Steering and suspension
SteeringPage 10•1
Suspension (also see Chapter 13)Page 11•1
Bodywork
Bodywork (also see Chapter 13)Page 12•1
Additional information
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models Page 13•1
Wiring DiagramsPage 14•1
REFERENCE
MOT Test Checks PageREF•1
Tools and Working Facilities Page REF•5
General Repair Procedures Page REF•8
Fault FindingPage REF•9
Buying Spare Parts & Vehicle Identification Numbers PageREF•12
Glossary of Technical Terms PageREF•13
IndexPage REF•17
Contents
Page 5 of 303

Safety First!0•5
Working on your car can be dangerous.
This page shows just some of the potential
risks and hazards, with the aim of creating a
safety-conscious attitude.
General hazards
Scalding
• Don’t remove the radiator or expansion
tank cap while the engine is hot.
• Engine oil, automatic transmission fluid or
power steering fluid may also be dangerously
hot if the engine has recently been running.
Burning
• Beware of burns from the exhaust system
and from any part of the engine. Brake discs
and drums can also be extremely hot
immediately after use.
Crushing
• When working under or near
a raised vehicle,
always
supplement the
jack with axle
stands, or use
drive-on
ramps.
Never
venture
under a car which
is only supported by a jack.
• Take care if loosening or tightening high-
torque nuts when the vehicle is on stands.
Initial loosening and final tightening should
be done with the wheels on the ground.
Fire
• Fuel is highly flammable; fuel vapour is
explosive.
• Don’t let fuel spill onto a hot engine.
• Do not smoke or allow naked lights
(including pilot lights) anywhere near a
vehicle being worked on. Also beware of
creating sparks
(electrically or by use of tools).
• Fuel vapour is heavier than air, so don’t
work on the fuel system with the vehicle over
an inspection pit.
• Another cause of fire is an electrical
overload or short-circuit. Take care when
repairing or modifying the vehicle wiring.
• Keep a fire extinguisher handy, of a type
suitable for use on fuel and electrical fires.
Electric shock
• Ignition HT
voltage can be
dangerous,
especially to
people with heart
problems or a
pacemaker. Don’t
work on or near the
ignition system with
the engine running or
the ignition switched on.• Mains voltage is also dangerous. Make
sure that any mains-operated equipment is
correctly earthed. Mains power points should
be protected by a residual current device
(RCD) circuit breaker.
Fume or gas intoxication
• Exhaust fumes are
poisonous; they often
contain carbon
monoxide, which is
rapidly fatal if inhaled.
Never run the
engine in a
confined space
such as a garage
with the doors shut.
• Fuel vapour is also
poisonous, as are the vapours from some
cleaning solvents and paint thinners.
Poisonous or irritant substances
• Avoid skin contact with battery acid and
with any fuel, fluid or lubricant, especially
antifreeze, brake hydraulic fluid and Diesel
fuel. Don’t syphon them by mouth. If such a
substance is swallowed or gets into the eyes,
seek medical advice.
• Prolonged contact with used engine oil can
cause skin cancer. Wear gloves or use a
barrier cream if necessary. Change out of oil-
soaked clothes and do not keep oily rags in
your pocket.
• Air conditioning refrigerant forms a
poisonous gas if exposed to a naked flame
(including a cigarette). It can also cause skin
burns on contact.
Asbestos
• Asbestos dust can cause cancer if inhaled
or swallowed. Asbestos may be found in
gaskets and in brake and clutch linings.
When dealing with such components it is
safest to assume that they contain asbestos.
Special hazards
Hydrofluoric acid
• This extremely corrosive acid is formed
when certain types of synthetic rubber, found
in some O-rings, oil seals, fuel hoses etc, are
exposed to temperatures above 400
0C. The
rubber changes into a charred or sticky
substance containing the acid. Once formed,
the acid remains dangerous for years. If it
gets onto the skin, it may be necessary to
amputate the limb concerned.
• When dealing with a vehicle which has
suffered a fire, or with components salvaged
from such a vehicle, wear protective gloves
and discard them after use.
The battery
• Batteries contain sulphuric acid, which
attacks clothing, eyes and skin. Take care
when topping-up or carrying the battery.
• The hydrogen gas given off by the battery
is highly explosive. Never cause a spark or
allow a naked light nearby. Be careful when
connecting and disconnecting battery
chargers or jump leads.
Air bags
• Air bags can cause injury if they go off
accidentally. Take care when removing the
steering wheel and/or facia. Special storage
instructions may apply.
Diesel injection equipment
• Diesel injection pumps supply fuel at very
high pressure. Take care when working on
the fuel injectors and fuel pipes.
Warning: Never expose the hands,
face or any other part of the body
to injector spray; the fuel can
penetrate the skin with potentially fatal
results.
Remember...
DO
• Do use eye protection when using power
tools, and when working under the vehicle.
• Do wear gloves or use barrier cream to
protect your hands when necessary.
• Do get someone to check periodically
that all is well when working alone on the
vehicle.
• Do keep loose clothing and long hair well
out of the way of moving mechanical parts.
• Do remove rings, wristwatch etc, before
working on the vehicle – especially the
electrical system.
• Do ensure that any lifting or jacking
equipment has a safe working load rating
adequate for the job.
A few tips
DON’T
• Don’t attempt to lift a heavy component
which may be beyond your capability – get
assistance.
• Don’t rush to finish a job, or take
unverified short cuts.
• Don’t use ill-fitting tools which may slip
and cause injury.
• Don’t leave tools or parts lying around
where someone can trip over them. Mop
up oil and fuel spills at once.
• Don’t allow children or pets to play in or
near a vehicle being worked on.
Page 6 of 303

0•6General dimensions, weights and capacities
Dimensions
Overall length . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3644 mm (143.6 in)
Overall width . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1555 mm (61.3 in)
Height . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1432 mm (56.4 in)
Wheelbase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2362 mm (93.1 in)
Front track . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1340 mm (52.8 in)
Rear track . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1300 mm (51.2 in)
Weights (kerb)
Uno 45:
Three-door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 700 kg (1543 lb)
Five-door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 710 kg (1566 lb)
Uno 55:
Three-door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 730 kg (1610 lb)
Five-door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 740 kg (1632 lb)
Uno 70:
Three-door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 740 kg (1632 lb)
Five-door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 750 kg (1654 lb)
Uno SX:
Three-door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 770 kg (1698 lb)
Five-door . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 780 kg (1720 lb)
Capacities
Fuel tank . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42.0 litre (9.25 gal)
Engine oil (with filter change):
903 cc engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.42 litre (6.0 pint)
1116 and 1301 cc engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.10 Iitre (7.2 pint)
Transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.40 litre (4.2 pint)
Steering box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140.0 cc
Driveshaft CV joints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125.0 cc
Cooling system:
903 cc engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.6 litre (8.1 pint)
1116 cc engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.0 litre (10.6 pint)
1301 cc engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.2 litre (10.9 pint)
For information applicable to later models, see Supplement at end of manual
Page 8 of 303

0•8Roadside Repairs
To avoid repetition, the procedure for
raising the vehicle, in order to carry out work
under it, is not included before each relevant
operation described in this Manual.
It is to be preferred, and it is certainly
recommended, that the vehicle is positioned
over an inspection pit or raised on a lift. Where
these facilities are not available, use ramps or
jack up the vehicle strictly in accordance with
the following guide. Once the vehicle is raised,
supplement the jack with axle stands.
Jacking
The jack supplied with the car should only
be used to change a wheel. Do not use this
jack when overhaul or repair work is being
carried out; employ a hydraulic or screw jack
and supplement it with axle stands.
Jacking points are located under the sills
for use with the jack supplied.To raise the front end with a garage jack,
locate the jack under the transmission lower
mounting, just below and slightly to the rear of
the transmission oil drain plug. Protect the
mounting by placing a block of wood between
the jack head and the mounting.
To raise the rear of the car, the jack should
be placed under the spare wheel housing as
far to the rear as possible. Place a wooden
bearer between the jack head and the
housing.
Towing
When being towed, use the left-hand front
towing eye.
When towing another vehicle, use the rear
towing eye adjacent to the exhaust tailpipe.
When being towed, remember that the
brake pedal will require heavier pressure due
to lack of servo assistance. Always turn theignition key to MAR to retain the steering in
the unlocked position.
Wheel changing
With the car on firm level ground, apply the
handbrake fully. Remove the hub cap or
wheel trim, if fitted.
Release, but do not remove, the bolts.
Chock the front and rear of the opposite
roadwheel and then raise the car using the sill
jack supplied with the car if it is being done at
the roadside. Alternatively use a workshop
jack supplemented with axle stands.
Remove the wheel bolts, change the wheel
and screw in the bolts finger tight. It is
recommended that the bolt threads are
smeared with multi-purpose grease. Lower
the car, remove the jack and tighten the wheel
bolts to the specified torque. Refit any wheel
trim that was removed.
Spare wheel and jack stowage
Front tow hook Rear tow hook
Jacking, towing and wheel changing
Page 9 of 303

Roadside Repairs0•9
Puddles on the garage floor or drive, or
obvious wetness under the bonnet or
underneath the car, suggest a leak that needs
investigating. It can sometimes be difficult to
decide where the leak is coming from,
especially if the engine bay is very dirty
already. Leaking oil or fluid can also be blown
rearwards by the passage of air under the car,
giving a false impression of where the
problem lies.Warning: Most automotive oils
and fluids are poisonous. Wash
them off skin, and change out of
contaminated clothing, without
delay.
Identifying leaks
The smell of a fluid leaking
from the car may provide a
clue to what’s leaking. Some
fluids are distinctively
coloured. It may help to clean the car and
to park it over some clean paper as an
aid to locating the source of the leak.
Remember that some leaks may only
occur while the engine is running.
Sump oil Gearbox oil
Brake fluid
Power steering fluid
Oil from filter
Antifreeze
Engine oil may leak from the drain plug......or from the base of the oil filter.
Leaking antifreeze often leaves a crystalline
deposit like this.Gearbox oil can leak from the seals at the
inboard ends of the driveshafts.
A leak occurring at a wheel is almost
certainly brake fluid.Power steering fluid may leak from the pipe
connectors on the steering rack.
Page 10 of 303

0•10Routine maintenance
Maintenance is essential for ensuring safety and desirable for the
purpose of getting the best in terms of performance and economy
from the car. Over the years the need for periodic lubrication has been
greatly reduced if not totally eliminated. This has unfortunately tended
to lead some owners to think that because no such action is required
the items either no longer exist or will last forever. This is certainly not
the case; it is essential to carry out regular visual examinations as
comprehensively as possible in order to spot any possible defects at
an early stage before they develop into major and expensive repairs.
For information applicable to later models, see Supplement.
Every 250 miles (400 km), weekly,
or before a long journey
m mCheck engine oil level
m mCheck brake reservoir fluid level
m mCheck tyre pressures
m mCheck operation of all lights and horn
m mTop up washer fluid reservoirs, adding a screen
wash, and check operation of washers and wipers
m mCheck coolant level
m mCheck battery electrolyte level
Every 6000 miles (10 000 km)
or six months, whichever comes first
m mRenew engine oil and filter (Chapter 1, Section 2)
m mCheck drivebelt tension (Chapter 2, Section 8)
m mCheck carburettor idle speed and mixture
adjustments (Chapter 3)
m mCheck contact points and dwell angle (mechanical
breaker distributors) (Chapter 4, Section 3)
m mCheck tyre tread wear (Chapter 7, Section 7)
m mCheck disc pads for wear (Chapter 8, Section 3)
Every 36 000 miles (60 000 km)
or three years, whichever comes first
m mRenew the timing belt - 1116 and 1299/1301 cc
(Chapter 1, Section 28)
m mCheck exhaust system for corrosion (Chapter 3,
Section 19)
m mRenew contact breaker points and adjust dwell
angle (mechanical breaker distributors) (Chapter 4,
Section 3)
m mCheck and adjust ignition timing (Chapter 4,
Section 4)
m mRenew spark plugs (Chapter 4, Section 11)
m mCheck clutch adjustment (Chapter 5, Section 2)
m mCheck transmission oil level (Chapter 6, Section 2)
m mCheck driveshaft and steering rack gaiters for splits
(Chapters 7 and 10)
m mCheck rear brake shoe linings for wear (Chapter 8,
Section 4)
m mCheck handbrake travel (Chapter 8, Section 16)
m mCheck headlamp beam alignment (Chapter 9,
Section 17)
m mCheck balljoints for wear (Chapter 10, Section 2)
m mCheck front wheel alignment (Chapter 10, Section 8)
m mCheck suspension bushes for wear (Chapter 11,
Section 2)
m mCheck seat belts for fraying (Chapter 12, Section 23)
m mLubricate controls, hinges and locks
Every 24 000 miles (40 000 km)
or two years, whichever comes first
m mRenew coolant anti-freeze mixture (Chapter 2,
Section 3)
m mRenew transmission oil (Chapter 6, Section 2)
m mRenew brake hydraulic fluid (Chapter 8, Section 12)
m mCheck for underbody corrosion and clean out door
and sill drain holes (Chapter 12, Section 2)
Every 12 000 miles (20 000 km) or
12 months, whichever comes first
m mCheck and adjust valve clearances (Chapter 1,
Sections 5 and 26)
m mRenew air cleaner element (Chapter 3, Section 2)
Page 13 of 303

Lubricants and Fluids0•13
Component or system Lubricant type/specification
1 EngineMultigrade engine oil, viscosity SAE 15W/40, meeting API-SG or CCMC
G2/G3 specification (or equivalent multigrade engine oil with viscosity
rating suitable for ambient temperature in which vehicle is operated -
see owner’s handbook)
2 Transmission:
1372 cc Turbo ie model FIAT ZC 80/S gear oil
All other models FIAT ZC 90 gear oil
3 Cooling systemEthylene glycol based antifreeze
4 Brake and clutch hydraulic system(s)Hydraulic fluid to DOT 3 or 4, or SAE J1703C
5 Driveshaft CV joints and steering rackLithium based molybdenum disulphide
General greasingMulti-purpose lithium based grease
Page 28 of 303
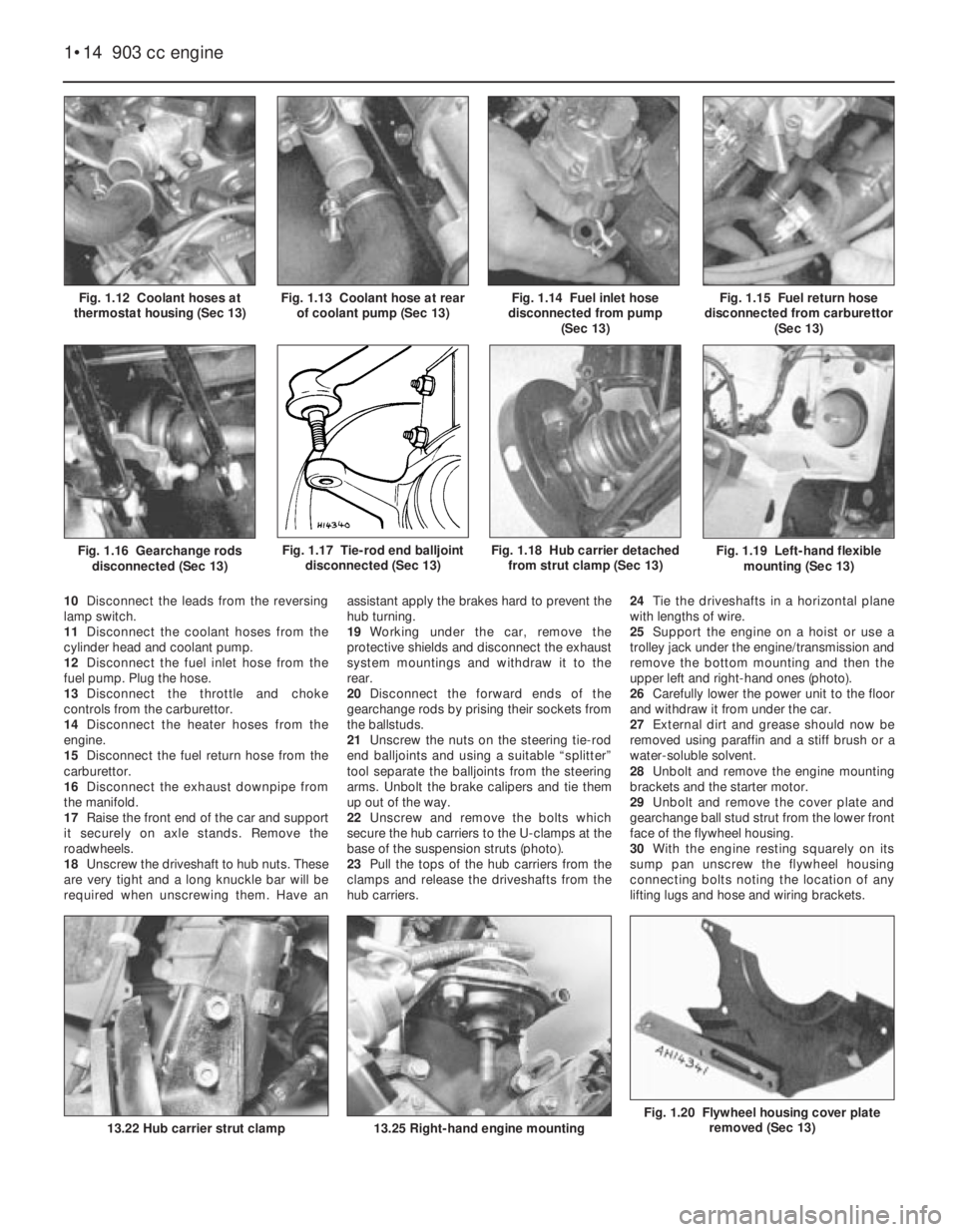
Fig. 1.20 Flywheel housing cover plate
removed (Sec 13)
Fig. 1.19 Left-hand flexible
mounting (Sec 13)
10Disconnect the leads from the reversing
lamp switch.
11Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
cylinder head and coolant pump.
12Disconnect the fuel inlet hose from the
fuel pump. Plug the hose.
13Disconnect the throttle and choke
controls from the carburettor.
14Disconnect the heater hoses from the
engine.
15Disconnect the fuel return hose from the
carburettor.
16Disconnect the exhaust downpipe from
the manifold.
17Raise the front end of the car and support
it securely on axle stands. Remove the
roadwheels.
18Unscrew the driveshaft to hub nuts. These
are very tight and a long knuckle bar will be
required when unscrewing them. Have anassistant apply the brakes hard to prevent the
hub turning.
19Working under the car, remove the
protective shields and disconnect the exhaust
system mountings and withdraw it to the
rear.
20Disconnect the forward ends of the
gearchange rods by prising their sockets from
the ballstuds.
21Unscrew the nuts on the steering tie-rod
end balljoints and using a suitable “splitter”
tool separate the balljoints from the steering
arms. Unbolt the brake calipers and tie them
up out of the way.
22Unscrew and remove the bolts which
secure the hub carriers to the U-clamps at the
base of the suspension struts (photo).
23Pull the tops of the hub carriers from the
clamps and release the driveshafts from the
hub carriers.24Tie the driveshafts in a horizontal plane
with lengths of wire.
25Support the engine on a hoist or use a
trolley jack under the engine/transmission and
remove the bottom mounting and then the
upper left and right-hand ones (photo).
26Carefully lower the power unit to the floor
and withdraw it from under the car.
27External dirt and grease should now be
removed using paraffin and a stiff brush or a
water-soluble solvent.
28Unbolt and remove the engine mounting
brackets and the starter motor.
29Unbolt and remove the cover plate and
gearchange ball stud strut from the lower front
face of the flywheel housing.
30With the engine resting squarely on its
sump pan unscrew the flywheel housing
connecting bolts noting the location of any
lifting lugs and hose and wiring brackets.
1•14 903 cc engine
13.25 Right-hand engine mounting
Fig. 1.18 Hub carrier detached
from strut clamp (Sec 13)
13.22 Hub carrier strut clamp
Fig. 1.17 Tie-rod end balljoint
disconnected (Sec 13)Fig. 1.16 Gearchange rods
disconnected (Sec 13)
Fig. 1.15 Fuel return hose
disconnected from carburettor
(Sec 13)Fig. 1.14 Fuel inlet hose
disconnected from pump
(Sec 13)Fig. 1.13 Coolant hose at rear
of coolant pump (Sec 13)Fig. 1.12 Coolant hoses at
thermostat housing (Sec 13)