1982 CHEVROLET CAMARO automatic transmission fluid
[x] Cancel search: automatic transmission fluidPage 304 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 304
Never release a depressed clutch pedal
with the bleeder screw open or air will
be drawn into the system.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
UNDERSTANDING AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS
The automatic transmission allows eng ine torque and power to be transmitted
to the rear wheels within a narrow range of engine operating speeds. It will
allow the engine to turn fast enough to produce plenty of power and torque at
very low speeds, while keeping it at a s ensible rpm at high vehicle speeds (and
it does this job without driv er assistance). The transmission uses a light fluid as
the medium for the transmission of power. This fluid also works in the operation
of various hydraulic control circui ts and as a lubricant. Because the
transmission fluid performs all of thes e functions, trouble within the unit can
easily travel from one part to another. For this reason, and because of the
complexity and unusual oper ating principles of the transmission, a very sound
understanding of the basic principles of operation will simplify troubleshooting.
TORQUE CONVERTER
The torque converter replaces the convent ional clutch. It has three functions:
1. It allows the engine to idle with t he vehicle at a standstill, even with the
transmission in gear.
2. It allows the transmission to shi ft from range-to-range smoothly, without
requiring that the driver close the throttle during the shift.
3. It multiplies engine torque to an incr easing extent as vehicle speed drops
and throttle opening is increased. This has the effect of making the
transmission more responsive and redu ces the amount of shifting
required.
The torque converter is a metal case which is shaped like a sphere that
has been flattened on opposite sides. It is bolted to the rear end of the
engine's crankshaft. Generally, the ent ire metal case rotates at engine
speed and serves as the engine's flywheel.
The case contains three sets of bl ades. One set is attached directly to
the case. This set forms the torus or pump. Another set is directly
connected to the output shaft, and forms the turbine. The third set is
mounted on a hub which, in turn, is mounted on a stationary shaft
through a one-way clutch. This third set is known as the stator.
A pump, which is driven by the conv erter hub at engine speed, keeps the
torque converter full of transmission fluid at all times. Fluid flows
continuously through the unit to provide cooling.
Under low speed acceleration, the tor que converter functions as follows:
Page 308 of 875
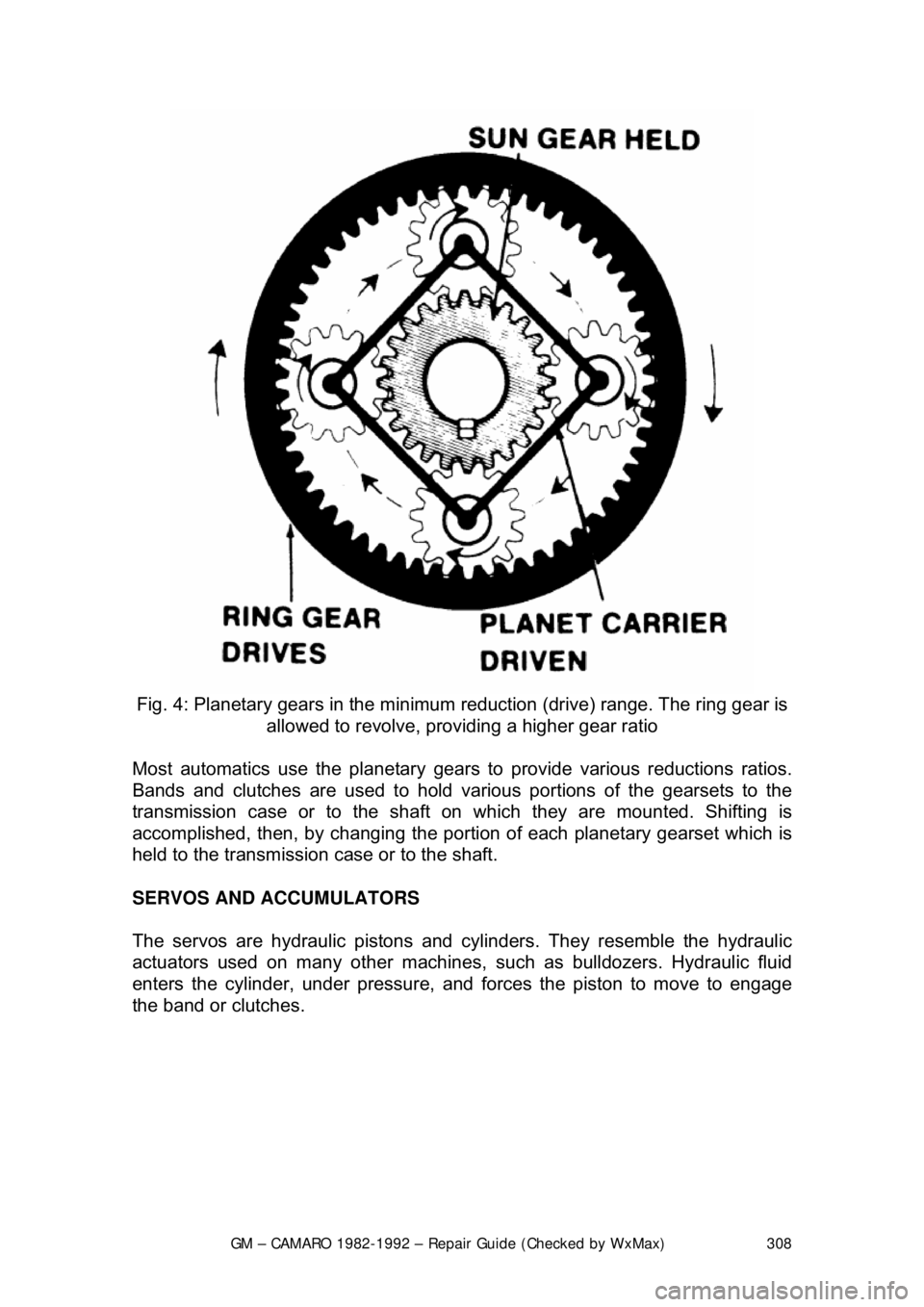
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 308
Fig. 4: Planetary gears in the minimum reduction (drive) range. The ring gear is
allowed to revolve, providing a higher gear ratio
Most automatics use the pl anetary gears to provide various reductions ratios.
Bands and clutches are used to hold va rious portions of the gearsets to the
transmission case or to the shaft on which they are mounted. Shifting is\
accomplished, then, by c hanging the portion of each planetary gearset which is
held to the transmission case or to the shaft.
SERVOS AND ACCUMULATORS
The servos are hydraulic pistons and cylinders. They resemble the hydrau\
lic
actuators used on many other machines, such as bulldozers. Hydraulic fluid
enters the cylinder, under pressure, and fo rces the piston to move to engage
the band or clutches.
Page 309 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 309
Fig. 5: Servos, operated by pressure, ar e used to apply or release the bands, to
either hold the ring gear or allow it to rotate
The accumulators are used to cushi on the engagement of the servos. The
transmission fluid must pass through the ac cumulator on the way to the servo.
The accumulator housing contains a thin piston which is sprung away from the
discharge passage of the accumulato r. When fluid passes through the
accumulator on the way to the servo, it must move the piston against spring
pressure, and this action smooths out the action of the servo.
HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM
The hydraulic pressure used to operat e the servos comes from the main
transmission oil pump. This fluid is channel ed to the various servos through the
shift valves. There is generally a manual shift valve which is operated by the
transmission selector lever and an automat ic shift valve for each automatic
upshift the transmission provides.
Many new transmissions are electroni cally controlled. On these models,
electrical solenoids are used to better control the hydraulic fluid. Usually, the
solenoids are regulated by an electronic control module.
There are two pressures which affect t he operation of these valves. One is the
governor pressure which is effected by vehicle speed. The other is the
modulator pressure which is effected by intake manifold vacuum or throttle
position. Governor pressure rises wit h an increase in vehicle speed, and
Page 364 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 364
5. Drain the radiator and remove t
he radiator hoses. Disconnect the heater
hoses and the transmission cooler lines.
6. Remove the upper half of the radi ator shroud, if equipped with a manual
transmission. Remove the radiator and fan shroud assembly, if equipped
with an automatic transmission.
7. Disconnect the throttle linkage, includi ng the cruise control detent cable.
8. Remove the air conditioning compressor and lay aside.
Do not disconnect the air conditioning lines.
9. Disconnect the power steering pump and drain the fluid into a suitable
container. Remove the vacuum brake booster line.
10. Remove the distributor cap and spark plug wires.
11. Disconnect the engine electrical connection at the bulkhead connection
and disconnect any necessary vacuum hoses.
12. Working inside the vehicle, re move the right-hand hush panel and
disconnect the ECM harness at the EC M. Raise and safely support the
vehicle. Remove the right fenderwell splash shield and feed the harness
through the fenderwell.
13. Disconnect the exhaust pipes at the exhaust manifolds and remove
exhaust system from the vehicle.
14. Remove the flywheel cover and remo ve the converter bolts, if equipped
with automatic transmission.
15. Disconnect the transmission an d starter wire connections.
16. Remove the bellhousing and t he motor mount through-bolts.
17. Disconnect the clutch fork return spring, if equipped with a manual
transmission. Lower the vehicle.
18. Relieve the fuel system pressu re. Disconnect the fuel lines.
19. Support the transmission with a suit able jack. Attach an engine lifting
device.
20. Remove the engine assembly.
To install: 21. Position the engine assembly in the vehicle.
22. Attach the motor mount to engine br ackets and lower the engine in place.
Remove the engine lifting device and the transmission jack.
23. Raise and support the vehicle safely.
24. Install the motor mount through-bolts and tighten the nuts to specification. Install t he bellhousing bolts and tight en to 35 ft. lbs. (47
Nm).
25. On vehicles with automatic transmissi on, install the converter to flywheel
attaching bolts to 46 ft. lbs. (63 Nm).
26. Install the flywheel splash shield and tighten to 89 inch lbs. (10 Nm).
Install the clutch return spring, if equipped with manual transmission.
27. Connect the starter wires and the fuel lines.
28. Install the exhaust system.
29. Lower the vehicle.
30. Install the power steering pump and the air conditioning compressor.
Page 716 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 716
INJECTOR REPLACEMENT
Use care in removing injectors to prev
ent damage to the electrical connector
pins on top of the injector, the fuel injector fuel filter and nozzle. The fuel injector
is serviced as a complete assembly on ly and should never be immersed in any
type of cleaner.
SINGLE INJECTOR UNITS 1. Relieve the fuel system pressure.
2. Remove the air cleaner.
3. Detach the injector connector by squeezing the two tabs together and
pulling straight up.
4. Remove the screws securing the fuel meter cover. Note the location of
any short screws for correct placement during reassembly.
CAUTION - DO NOT remove the four screws se curing the pressure regulator to
the fuel meter cover. The fuel pressure regulator includes a large spring under
heavy tension which could cause personal injury if released.
5. With the old fuel meter gasket in place to prevent damage to the casting,
use a prytool and fulcrum to pry the inje ctor carefully until it is free from
the fuel meter body.
6. Remove the injector.
7. Remove the large O-ring and steel back-up washer at the top of the
injector cavity in the fuel meter body.
8. Remove the small O-ring located at the bottom of the injector cavity.
To Install: 9. Lubricate the new, small O-ring with automatic transmission fluid; then,
push the new O-ring on the nozzle end of the injector up against the
injector fuel filter.
10. Install the steel backup washer in the recess of the fuel meter body.
Lubricate the new large O-ring with automatic transmission fluid, then
install the O-ring directly above t he backup washer, pressing the O-ring
down into the cavity recess. The O-ri ng is properly installed when it is
flush with the casting surface.
WARNING - Do not attempt to reverse this procedure and install the backup
washer and O-ring after the injector is located in the cavity. To do so will
prevent proper seating of the O-ring in th e cavity recess which could result in a
fuel leak and possible fire.
11. Install the injector by using a pushing/twisting mo tion to center the nozzle
O-ring in the bottom of the injector cavity and aligning the raised lug on
the injector base with the notch cast into the fuel meter body. Push down
on the injector making sure it is fully seated in the cavity. Injector
installation is correct when the lug is seated in the notch and the
electrical terminals are parallel to the throttle shaft.
Page 782 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 782
10. Refill the engine with the correct amount
of fresh oil. Please refer to the
Capacities chart at the end of this section.
11. Check the oil level on the dipstick. It is normal for the level to be a bit
above the full mark. Start the engine and allow it to idle for a few
minutes.
CAUTION - Do not run the engi ne above idle speed until it has built up oil
pressure, as indicated w hen the oil light goes out
12. Shut off the engine and allow the oil to flow back to the crankcase for a
minute, then recheck the oil level. C heck around the filter and drain plug
for any leaks, and correct as necessary.
MANUAL TRANSMISSIONS
FLUID RECOMMENDATIONS
• 1982-85 4-speed manual transmissi ons - SAE 80W/90 GL-5 gear
lubricant
• 1986-87 4-speed manual transmission - Dexron®®II automatic
transmission fluid
• 1982-84 5-speed manual transmissions - use SAE 80W/90 GL-5 gear
lubricant (SAE 80W GL-5 in Canada)
• 1985-92 5-speed manual transmissi ons - Dexron®II automatic
transmission fluid
LEVEL CHECK
The oil in the manual tr ansmission should be check ed every 12 months or
15,000 miles.
1. Raise the car and support on jackstands as close to level as possible. \
2. Remove the filler plug from the side of the transmission housing.
3. If lubricant begins to trickle out of the hole, there is enough and you need
not go any further. Otherwise, carefully insert your finger (watch out for
sharp threads) and check to see if the oil is up to the edge of the hol\
e.
4. If not, add oil through the hole until the level is at the edge of the hole.
Most lubricants come in a plasti c squeeze bottle with a nozzle; making
additions simple.
5. Install and tighten the filler plug.
DRAIN AND REFILL
The fluid in the manual transmission do es not require changing. If you do
choose to change the transmission fluid, the fluid can be drained out through
the lower drain plug hole on the side of the transmission. Fill the transmission
with the recommended lubricant to the bottom of the filler plug hole and install
the filler plug.
Page 783 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 783
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
FLUID RECOMMENDATIONS
Use only Dexron®II Automati
c Transmission Fluid.
LEVEL CHECK
Fig. 1: Read automatic transmission flui d level on dipstick and add, as required
Check the automatic transmission fluid le vel at each oil change. Driving with too
much or too little transmission fluid ca n damage the transmission. The dipstick
can be found in the rear of the engine compartment. The fluid level should be
checked only when the transmission is at normal operating temperature. If your
Camaro has been driven at highway speeds fo r a long time, in city traffic in hot
weather, or pulling a trailer, wait for about 30 minutes for the fluid to cool down
so a correct reading can be read.
1. Park the car on a level surface, with the parking brake on. Start the
engine and let it idle for about 15 minutes. Move the transmission
through all the gears and then back to P.
2. Remove the dipstick and carefully touch the wet end of the dipstick to see if the fluid is cool, warm, or ho t. Wipe it clean and then reinsert it
firmly. Be sure that it has been pushed all the way in. Remove the
dipstick again and check the fluid leve l while holding it horizontally.
a. If fluid is cool (room temper ature), the level should be about
1/8-3/8
in. (3-10mm) below the ADD mark.
Page 784 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 784
b. If fluid is warm, the le
vel should be close to the ADD mark, either
above or below.
c. If fluid is too hot to touc h, the level should be at the FULL mark.
3. If the fluid level is low, add Dexr on®II automatic transmission fluid (ATF)
through the dipstick tube. This is eas ily done with the aid of a funnel.
Check the level often as you are f illing the transmission. Be extremely
careful not to overfill it. Overfilling will cause slippage, seal damage and
overheating. Approximately 1 pint (0.473L) of ATF will raise the fluid level
from one notch/line to the other.
If the fluid on the dipstick appears discolored (brown or black), or smells burnt,
serious transmission troubles, probably due to overheating, should be
suspected. The transmission should be inspected by a qualified technician to
locate the cause of the burnt fluid.
DRAIN AND REFILL
Please refer to the "PAN AND FILTER SERVICE" procedure listed in this
section.
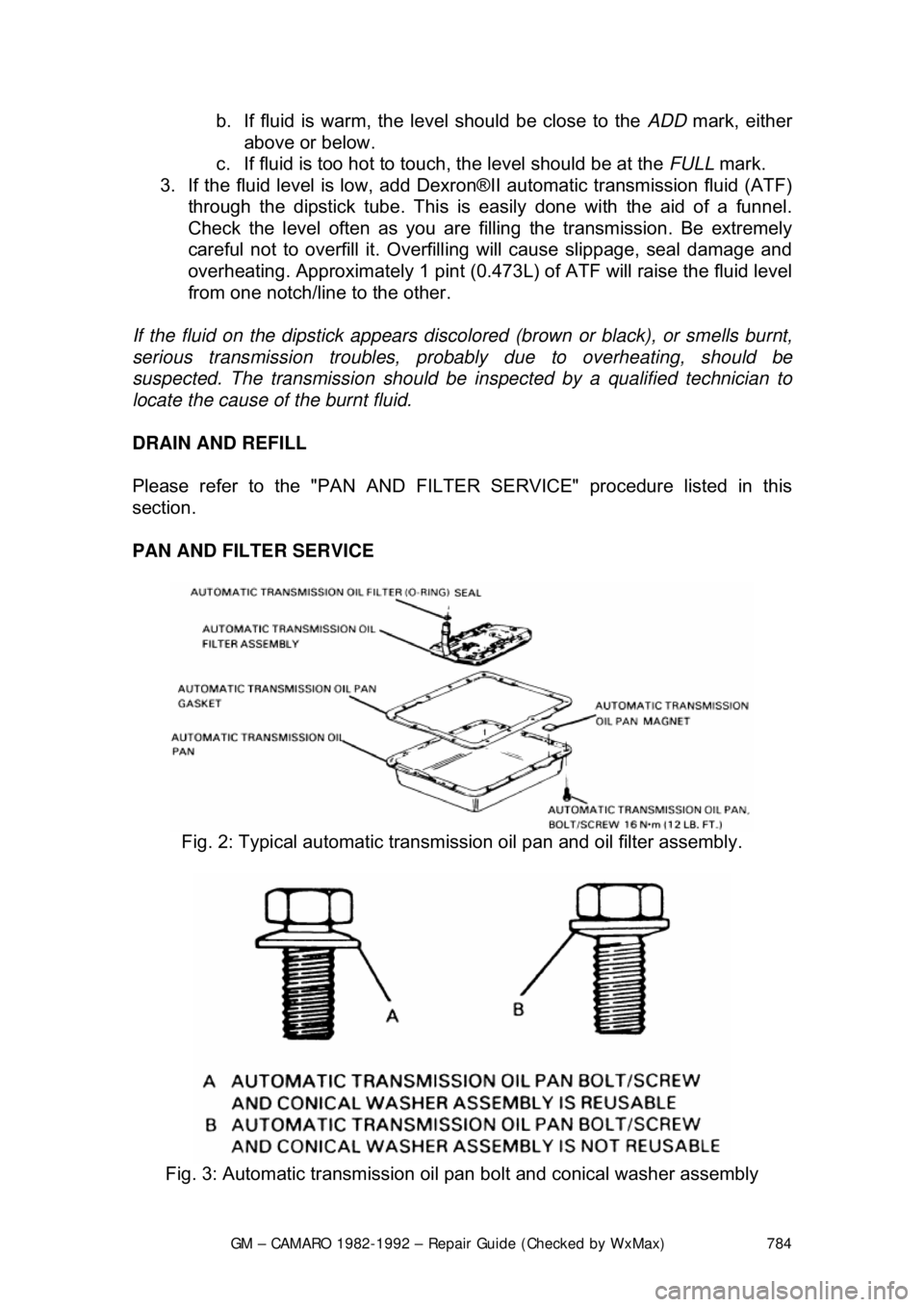
PAN AND FILTER SERVICE
Fig. 2: Typical automatic transmiss ion oil pan and oil filter assembly.
Fig. 3: Automatic transmission oil pan bolt and conical washer assembly