1982 CHEVROLET CAMARO sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 573 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 573
7. Install the retaining bracket.
8. Connect the negative battery cable.
ELECTRONIC ENGINE CONTROLS
COMPUTER COMMAND CO NTROL (CCC) SYSTEM
The Computer Command Control (CCC) Sy stem is an electronically controlled
exhaust emission system that can m onitor and control a large number of
interrelated emission cont rol systems. It can monitor various engine/vehicle
operating conditions and then use this in formation to control multiple engine
related systems. The CCC syst em is thereby making constant adjustments to
maintain optimum vehicle performance und er all normal driving conditions while
at the same time allowing the catalyti c converter to effectively control the
emissions of HC, CO and NO
x.
OPERATION
The Electronic Control Module (ECM) is required to maintain the exhaust
emissions at acceptable le vels. The module is a sma ll, solid state computer
which receives signals from many source s and sensors; it uses these data to
make judgements about operating conditions and then control output signals to
the fuel and emission systems to ma tch the current requirements.
Inputs are received from m any sources to form a complete picture of engine
operating conditions. Some inputs are simp ly Yes or No messages, such as that
from the Park/Neutral switch; the vehicle is either in gear or in Park/Neutral;
there are no other choices. Other data is sent in quantitative input, such as
engine rpm or coolant temperature. T he ECM is pre-programmed to recognize
acceptable ranges or combinations of si gnals and control the outputs to control
emissions while providing good driv eability and economy. The ECM also
monitors some output circuits, making sure that the components function as
commanded. For proper engine oper ation, it is essential that all input and output
components function properly and comm unicate properly with the ECM.
Since the control module is programmed to recognize the presence and value
of electrical inputs, it will also note the lack of a signal or a radical change in
values. It will, for example, react to the loss of signal from the vehicle speed
sensor or note that engine coolant temperature has risen beyond acceptable
(programmed) limits. Once a fault is recognized, a numeric code is assigned
and held in memory. The SERVICE ENGIN E SOON Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL), will illuminate to advise the operator that the system has detected a fault.
More than one code may be stored. Although not every engine uses every
code, possible codes range from 12-999. Additionally, the same code may carry
different meanings relative to each engine or engine family. For example, on the
3.3L (VIN N) engine, code 46 indicates a fault found in the power steering
pressure switch circuit. The same code on the 5.7L (VIN F) engine indicates a
fault in the VATS anti-theft system.
Page 575 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 575
Fig. 2: Electronic Control Module (ECM)
LEARNING ABILITY
The ECM can compensate for minor variations within the fuel system through
the block learn and fuel in tegrator systems. The fuel integrator monitors the
oxygen sensor output voltage, adding or subtracting fuel to drive the mixture
rich or lean as needed to reach the ideal air fuel ratio of 14.7:1. The integrator
values may be read with a scan tool; the display will range from 0-255 and
should center on 128 if the oxygen sens or is indicating a 14.7:1 mixture.
Fig. 3: Among other features, a scan tool combines many standard testers into
a single device for quick and accurate diagnosis
Page 577 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 577
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP
The primary function of the MIL is to adv
ise the operator and the technician that
a fault is detected, and, in most cases, a code is stored. Under normal
conditions, the malfunction indicator la mp will illuminate when the ignition is
turned ON. Once the engine is started and running, the ECM will perform a
system check and extinguish the lamp if no fault is found.
Additionally, the lamp can be used to retrieve stored codes after the system is
placed in the Diagnostic Mode. Codes ar e transmitted as a series of flashes
with short or long pauses. When the syst em is placed in the Field Service
Mode, the dash lamp will indicate open loop or closed loop function to the
technician.
INTERMITTENTS
If a fault occurs intermittently, such as a loose connector pin breaking contact
as the vehicle hits a bump, the ECM will note the fault as it occurs and energize
the dash warning lamp. If the problem se lf-corrects, as with the terminal pin
again making contact, the dash lamp will extinguish after 10 seconds but\
a code
will remain stored in the ECM memory.
When an unexpected code appe ars during diagnostics, it may have been set
during an intermittent failure that self-c orrected; the codes are still useful in
diagnosis and should not be discounted.
OXYGEN SENSOR
OPERATION
An oxygen sensor is used on all models. The sensor protrudes into the exhaust
stream and monitors the oxygen content of the exhaust gases. The difference
between the oxygen content of the exhaust gases and that of the outside air
generates a voltage si gnal to the ECM. The ECM monitors this voltage and,
depending upon the value of the signal rece ived, issues a command to adjust
for a rich or a lean condition.
No attempt should ever be made to meas ure the voltage output of the sensor.
The current drain of any conventional vo ltmeter would be such that it would
permanently damage the sensor.
Page 578 of 875
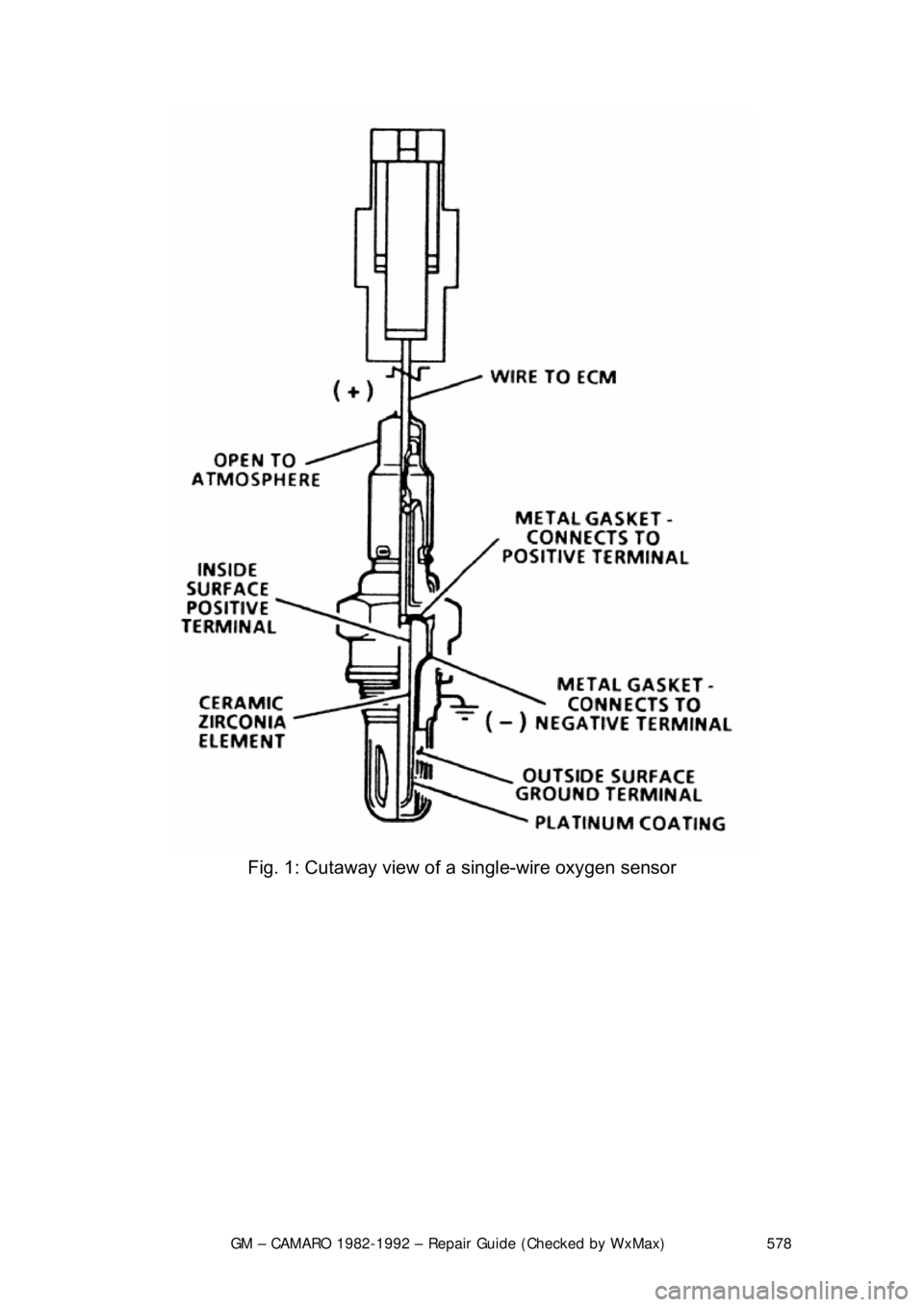
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 578
Fig. 1: Cutaway view of a single-wire oxygen sensor
Page 579 of 875
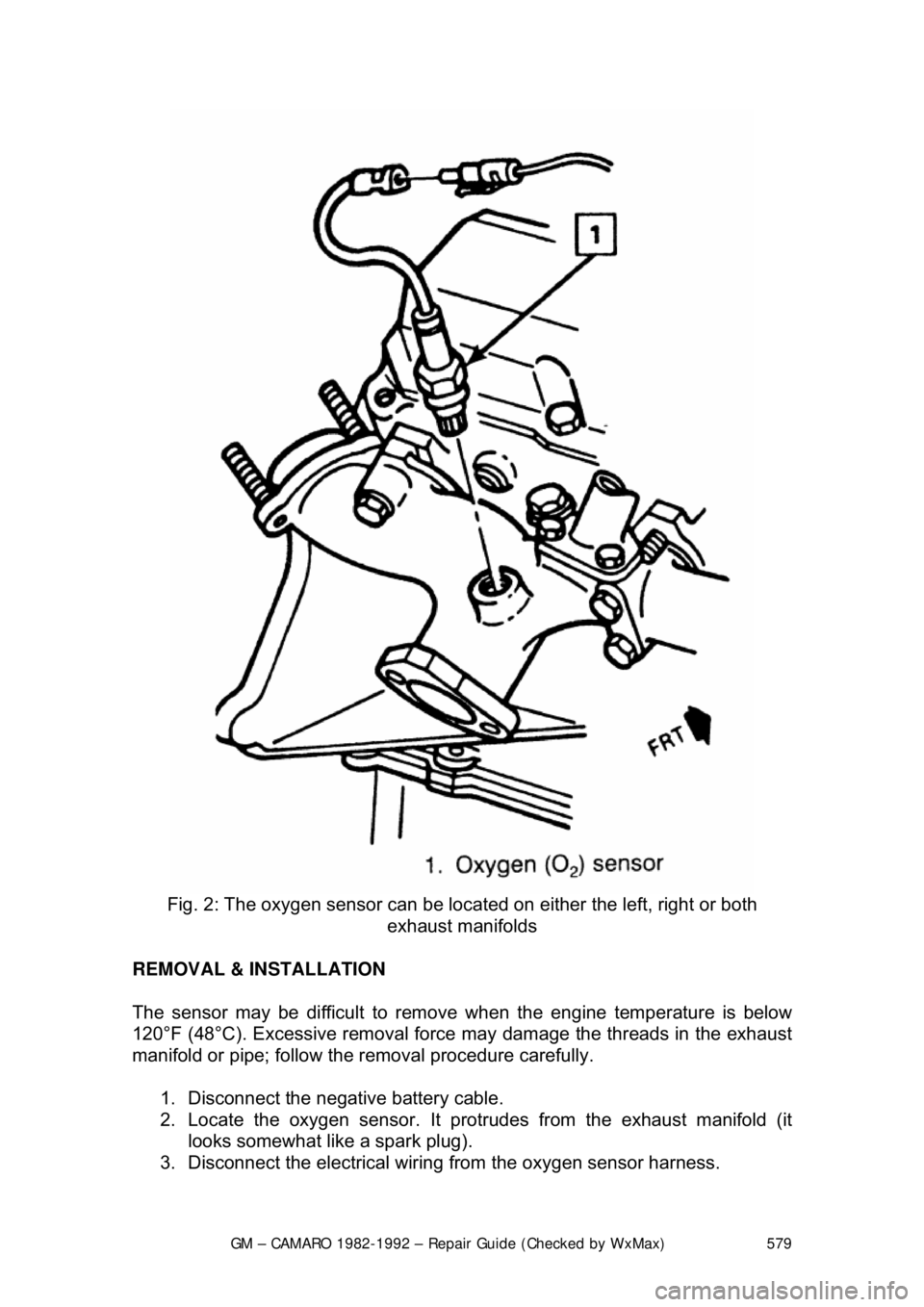
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 579
Fig. 2: The oxygen sensor can be locat ed on either the left, right or both
exhaust manifolds
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
The sensor may be difficult to remove when the engine temperature is below
120°F (48°C). Excessive removal force may damage the threads in the exhaust
manifold or pipe; follow the removal procedure carefully.
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Locate the oxygen sensor. It protr udes from the exhaust manifold (it
looks somewhat like a spark plug).
3. Disconnect the electrical wiring from the oxygen sensor harness.
Page 580 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 580
4. Spray a commercial solvent onto the sensor threads and allow it to soak
in for at least five minutes.
5. Carefully remove the sensor wit h a special oxygen sensor socket.
To install: 6. First coat the new sensor's th reads with GM anti-seize compound No.
5613695 or the equivalent. This is not a conventional anti-seize paste.
The use of a regular compound may el ectrically insulate the sensor,
rendering it inoperative. Y ou must coat the threads with an electrically
conductive anti-seize compound. Installati on torque is 30 ft. lbs. (41 Nm).
Do not overtighten.
7. Reconnect the electric al wiring. Be careful not to damage the electrical
pigtail. Check the sensor boot fo r proper fit and installation.
8. Reconnect the negative battery cable.
COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
OPERATION
Most engine functions are affected by the coolant temperature. Determining
whether the engine is hot or cold is largely dependent on the temperature of the
coolant. An accurate temperature signal to the ECM is supplied by the coolant
temperature sensor. The coolant temperatur e sensor is a thermistor mounted in
the engine coolant stream. A thermistor is an electrical device that varies its
resistance in relation to changes in temperature. Low coolant temperature
produces a high resistance and high coolant temperature produces low
resistance. The ECM supplies a signal of 5 volts to the coolant temperature
sensor through a resistor in the ECM and measures the voltage. The voltage
will be high when the engine is cold and low when the engine is hot.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Drain the cooling system to an appropr iate and clean container for reuse.
3. Disconnect the electrical wiring fr om the coolant temperature sensor.
4. Remove the coolant temperature sensor.
To install: 5. Install the coolant temperature sensor.
6. Connect the electrical wiring.
7. Fill the cooling system.
8. Connect the negative battery cable.
9. Start the engine and check for leaks.
Page 581 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 581
Fig. 1: Coolant temperature sensor. The in take air temperature sensor is similar
in appearance
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) VALVE
OPERATION
Engine idle speeds are controlled by the ECM through the IAC valve mounted
on the throttle body. The ECM sends volt age pulses to the IAC motor windings
causing the IAC motor shaft and pintle to move IN or OUT a given distance
(number of steps) for each pulse (called counts). The movement of the pintle
controls the airflow around the throttle plat e, which in turn, controls engine idle
speed. IAC valve pintle position counts ca n be observed using a scan tool. Zero
counts correspond to a fully closed passage, while 140 counts or more
corresponds to full flow.
Idle speed can be categorized in 2 ways : actual (controlled) idle speed and
minimum idle speed. Contro lled idle speed is obtained by the ECM positioning
the IAC valve pintle. Resulting idle speed is determined by total air fl\
ow
(IAC/passage + PCV + throttle valve + ca librated vacuum leaks). Controlled idle
speed is specified at normal operating c onditions, which consists of engine
coolant at normal operating temper ature, air conditioning compressor OFF,
manual transmission in neutral or automatic transmission in D.
Minimum idle air speed is set at t he factory with a stop screw. This setting
allows a certain amount of air to bypas s the throttle valves regardless of IAC
valve pintle positioning. A co mbination of this air flow and IAC pintle positioning
allows the ECM to control engine idle speed. During normal engine idle
operation, the IAC valve pintle is positioned a calibrated number of steps
(counts) from the seat. No adjustment is required during routine maintenance.
Tampering with the minimum idle speed adjustment may result in premature
failure of the IAC valve or imprope rly controlled engine idle operation.
Page 585 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 585
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR
OPERATION
The MAP sensor measures the changes in
intake manifold pressure, which
result from engine load/ speed changes and converts this information to a
voltage output. The MAP sensor reading is the opposite of a vacuum gauge
reading: when manifold pressu re is high, MAP sensor value is high and vacuum
is low. A MAP sensor will produce a low output on engine coast-down with a
closed throttle while a wide open throttle will produce a high output. The high
output is produced because the pressure inside the manifold is the same as
outside the manifold, so 100 percent of t he outside air pressure is measured.
The MAP sensor is also used to meas ure barometric pressure under certain
conditions, which allows the ECM to autom atically adjust for different altitudes.
The MAP sensor changes the 5 volt signal supplied by the ECM, which reads
the change and uses the information to cont rol fuel delivery and ignition timing.
Fig. 1: MAP sensor
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the vacuum connection.
3. Release the electrical wiring lo cking tab and disconnect the connector.
4. Remove the bolts or release the MAP sensor locking tabs and remove
the sensor.
To install: 5. Install the bolts or snap sensor onto the bracket.