1979 DATSUN 210 air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 95 of 548

I
Secondary
slow
air
bleed
2
Secondary
main
air
bleed
3
Secondary
main
nozzle
4
Primary
main
nozzle
5
Primary
main
air
bleed
6
Primary
slow
air
bleed
7
Primary
slow
jet
8
Primary
main
jet
9
Idle
nozzle
10
Primary
throttle
valve
II
Auxiliary
valve
12
Seco
dary
throttle
valve
13
Secondary
main
jet
14
Counterweight
IS
Secondary
slow
jet
EF419A
Fig
EF
24
At
Full
Open
High
Speed
Engine
Fuel
Secondary
slow
system
Step
system
The
construction
of
this
system
corresponds
to
the
idling
and
slow
system
of
the
primary
system
This
system
aims
at
the
power
filling
up
of
the
gap
when
fuel
supply
is
transferred
from
the
primary
system
to
the
secondary
system
The
stepport
is
located
near
the
auxiliary
valve
in
its
fully
closed
state
ANTI
DIESELING
SYSTEM
The
carburetor
is
equipped
with
an
anti
liese1i
lg
solenoid
valye
As
the
ignition
switch
is
turned
off
the
valve
is
brought
into
operation
shutting
off
the
supply
of
fuel
to
the
slow
circuit
The
following
figure
shows
a
see
tional
view
of
this
control
An
ti
dies
eling
solenoid
valve
Ignition
switch
OFF
ON
t
L
li
FLOAT
SYSTEM
There
is
only
one
float
chamber
while
two
carburetor
systems
primary
and
secondary
are
provided
Fuel
fed
from
the
fuel
pump
flows
through
the
filter
and
needle
valve
into
the
float
chamber
A
constant
fuel
level
is
maintained
by
the
float
and
needle
valve
Because
of
the
inner
air
vent
type
float
chamber
ventilation
fuel
con
sumption
is
not
affected
by
dirt
ac
cumulated
in
the
air
cleaner
Ignition
switch
Q
1
T
Battery
niT
EC
3
Fig
EF
25
Anti
dieseling
Solenoid
Valve
The
needle
valve
includes
special
hard
steel
ball
and
wiD
not
wear
for
all
its
considerably
long
use
Besides
the
insertion
of
a
spring
will
prevent
the
flooding
at
rough
road
running
THROTTLE
OPENER
CONTROL
SYSTEM
T
O
C
S
Except
FU
model
The
function
of
the
throttle
opener
is
to
open
the
throttle
valve
of
the
carburetor
slightly
while
the
car
is
in
EF
10
deceleration
During
deceleration
the
manifold
vacuum
rises
and
the
quan
tity
of
mixture
in
the
engine
is
not
suffICient
for
normal
combustion
to
continue
4
consequently
a
great
amount
of
unburned
HC
is
emitted
Carburetors
equipped
with
the
throttle
opener
supply
the
engine
with
an
adequate
charge
of
combustible
mixture
to
maintain
proper
combus
tion
during
deceleration
resulting
in
a
dramatic
reduction
in
HC
emission
The
system
for
the
manual
trans
mission
model
consists
of
servo
dia
phragm
vlicuum
control
valve
throttle
opener
solenoid
valve
spee
l
detecting
switch
and
amplifier
On
the
auto
matic
transmission
model
an
inhibitor
and
inhibitor
relay
are
used
in
place
of
speed
detecting
switch
and
amplifier
on
the
manual
transmission
model
An
altitude
corrector
fitted
to
vacuum
control
valve
serves
to
automatically
regulate
the
operating
pressure
in
the
system
with
variation
of
atmospheric
pressure
T
o
C
S
n
operatIon
At
the
moment
when
the
manifold
vacuum
increases
as
occurs
upon
de
celeration
the
vacuum
control
valve
opens
to
transfer
the
manifold
vacuum
to
the
servo
diaphragm
chamber
and
the
throttle
valve
of
the
carburetor
opens
slightly
Under
this
condition
a
proper
amount
of
fresh
air
is
sucked
into
the
combustion
chamber
As
the
result
complete
combustion
of
fuel
is
as
sisted
by
this
additional
air
and
the
amount
of
H
C
contained
in
exhaust
gases
is
dramatically
reduced
Throttle
Clpener
sol
nold
valve
operation
Manual
transmission
models
The
throttle
opener
solenoid
valve
is
controlled
by
a
speed
detecting
switch
which
is
actuated
by
the
speed
ometer
needle
As
the
car
sp
ed
falls
below
16
km
h
10
MPH
this
switch
is
acti
vated
producing
a
signal
The
signal
is
led
to
the
amplifier
so
that
the
signal
can
be
amplified
to
a
degree
large
enough
to
actuate
the
Page 98 of 548

ELECTRIC
AUTOMATIC
CHOKE
An
electric
heater
warms
a
bi
metal
interconnected
to
the
choke
valve
and
controls
the
position
of
c
oke
valve
and
throttle
valve
in
accordance
with
the
time
elapsed
the
warm
up
condi
tion
of
the
engine
and
the
outside
ambient
temperature
Electric
heater
The
electric
heater
is
made
up
of
a
semiconductor
and
installed
in
the
automatic
choke
cover
in
the
body
2
Bi
metal
Electric
current
flows
through
the
heater
as
the
engine
starts
and
warms
the
bi
metal
The
deflection
of
the
bi
metal
is
transmitted
to
the
choke
valve
through
the
choke
valve
lever
3
Fast
idle
cam
The
fast
idle
cam
determines
the
opening
of
the
throttle
valve
SQ
that
the
proper
amount
of
mixture
cor
responding
to
the
opening
of
the
choke
valve
will
be
obtained
The
opening
of
the
choke
valve
is
de
pendent
upon
the
warm
up
condition
of
the
engine
4
Choke
unloader
When
accelerating
the
engine
during
the
warm
up
period
that
is
before
the
choke
valve
opens
sufficiently
this
unloader
forces
the
choke
valve
open
a
little
so
as
to
obtain
an
adequate
air
fuel
mixture
S
Vacuum
break
diaphragm
After
the
engine
has
been
started
by
cranking
this
diaphragm
forces
the
choke
valve
open
to
the
predetermined
extent
so
as
to
provide
the
proper
air
fuel
ratio
A
two
stage
acting
type
vacuum
diaphragm
is
employed
6
Si
metal
case
index
mark
The
bi
metal
case
index
mark
is
used
for
selling
the
moment
of
the
bi
metal
which
controls
the
air
fuel
mixture
ratio
required
for
starting
Engine
Fuel
r
m
2
3
4
5
6
r
3
1
@
@
Alternator
L
terminal
Automatic
choke
relay
Automatic
choke
cover
P
T
C
heater
Bi
metaJ
spring
Choke
valve
Fig
EF
31
Electric
Automatic
Choke
l
eater
EF045A
l
A
Higher
ambient
temperature
Manifold
vacuum
Clearance
B
B
Lower
ambient
temperature
Clearance
Manifold
vacuum
1
Hi
metal
2
P
T
e
heater
3
Thermostat
cover
4
Vacuum
diaphragm
5
Fast
idle
earn
6
Bi
metal
cover
index
mark
7
Choke
shaft
lever
8
Choke
valve
9
Unloader
tang
10
Throttle
valve
11
Fast
idle
adjusting
screw
EF243
t
Diaphragm
2
Spring
I
3
Spring
11
4
Rod
5
Choke
valve
6
Plate
@
7
Bi
metal
EF884
Fig
EF
32
Electric
Automatic
Choke
EF
13
Page 107 of 548
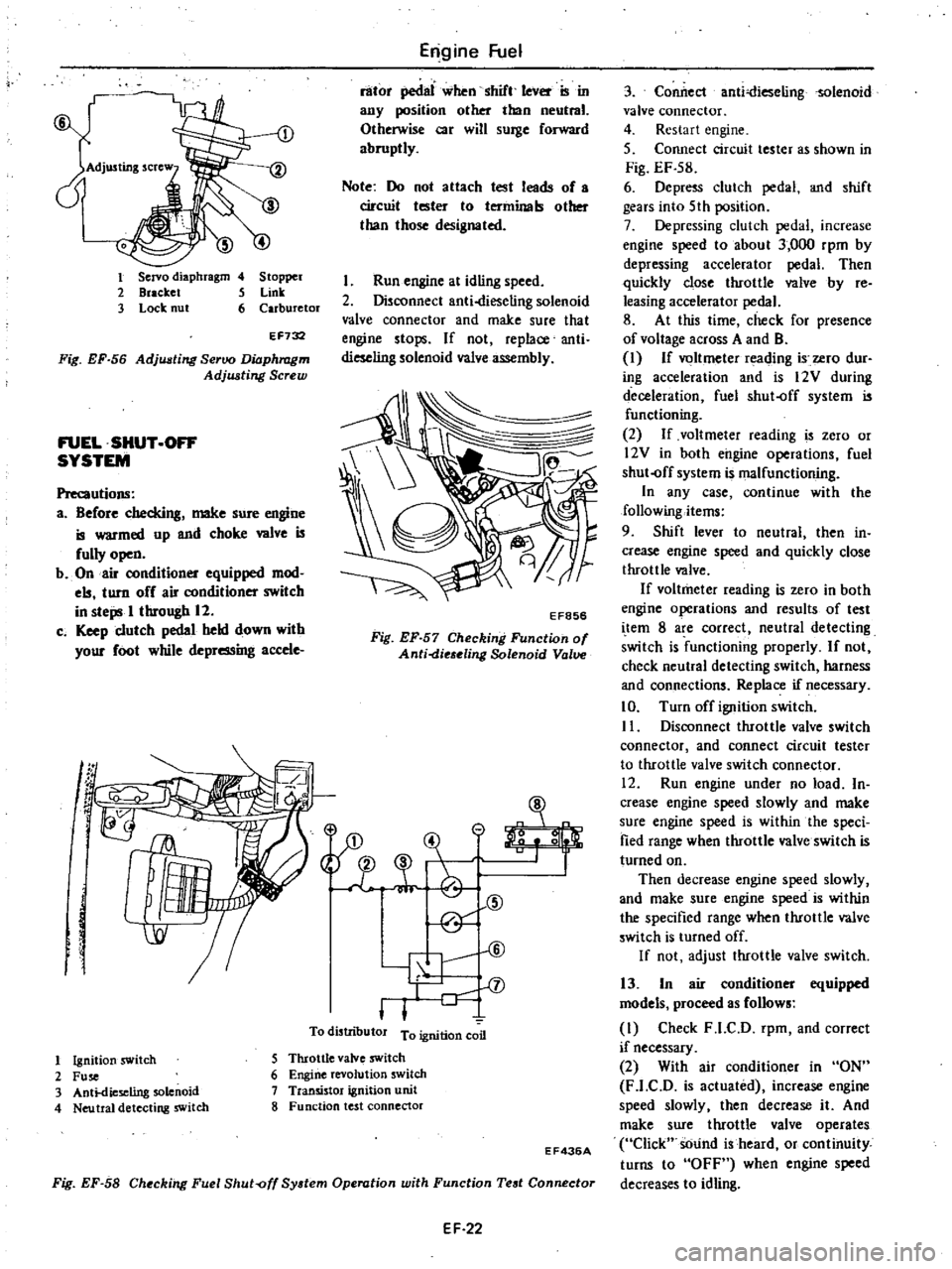
1
Servo
diaphragm
4
Stopper
2
Bracket
5
Link
3
Lock
nut
6
Carburetor
EF732
Fig
EF
56
Adjusting
Seroo
Diaphragm
Adjwting
Screw
FUEL
SHUT
OFF
SYSTEM
Precautions
a
Before
checking
make
sure
engine
is
warmed
up
and
choke
wive
is
fully
open
b
On
air
conditioner
equipped
mod
els
turn
off
air
conditioner
switch
in
steps
I
through
12
c
Keep
clutch
pedal
held
down
with
your
foot
while
depressing
accele
g
f
J
1
Engine
Fuel
rator
pedllI
when
shift
leVer
ISm
any
position
other
than
neutral
Otherwise
car
will
surge
forward
abruptly
Note
Do
not
attach
test
leads
of
a
circuit
tester
to
terminals
other
than
those
designated
Run
engine
at
idling
speed
2
Disconnect
anti
dieseling
solenoid
valve
connector
and
make
sure
that
engine
stops
If
not
replace
anti
dieseling
solenoid
valve
assembly
EF856
Fig
EF
57
Checking
Function
of
Anti
die
eling
Solenoid
Valve
31
A
t
CID
@
V
II
l
To
distributor
T
n
l1on
coon
o
1
Ignition
switch
2
Fuse
3
Anti
dieseling
solenoid
4
Neu
tral
detecting
switch
5
Throttle
valve
swltch
6
Engine
revolution
switch
7
Transistor
ignition
unit
8
Function
test
connector
Fig
EF
58
Checking
Fuel
Shut
off
System
Operation
with
Function
Test
Connector
EF436A
EF
22
3
Conilect
anti
ieselingsolenoid
valve
connector
4
Restart
engine
5
Connect
circuit
tester
as
shown
in
Fig
EF
S8
6
Depress
clutch
pedal
and
shift
gears
into
5th
position
7
Depressing
clutch
pedal
increase
engine
speed
to
about
3
000
rpm
by
depressing
accelerator
pedal
Then
quickly
close
throttle
wIve
by
re
leasing
accelerator
pedal
8
At
this
time
check
for
presence
of
voltage
across
A
and
B
I
If
voltmeter
reading
i
ero
dur
ing
acceleration
and
is
12V
during
deceleration
fuel
shut
off
system
is
functioning
2
If
voltmeter
reading
is
zero
or
l2V
in
both
engine
operations
fuel
shut
off
system
is
malfunctioning
In
any
case
continue
with
the
following
items
9
Shift
lever
to
neutral
then
in
crease
engine
speed
and
quickly
close
throttle
valve
If
voltmeter
reading
is
zero
in
both
engine
operations
and
results
of
test
i
tern
8
are
correct
neutral
detecting
switch
is
functioning
properly
If
not
check
neutral
detecting
switch
harness
and
connections
Replace
if
necessary
10
Turn
off
ignition
switch
II
Disconnect
throttle
valve
switch
connector
and
connect
circuit
tester
to
throttle
valve
switch
connector
12
Run
engine
under
no
load
In
crease
engine
speed
slowly
and
make
sure
engine
speed
is
within
the
speci
fied
range
when
throttle
valve
switch
is
turned
on
Then
decrease
engine
speed
slowly
and
make
sure
engine
speed
is
within
the
specified
range
when
throttle
valve
switch
is
turned
off
If
not
adjust
throttle
valve
switch
13
In
air
conditioner
equipped
models
proceed
as
follows
I
Check
F
l
C
D
rpm
and
correct
if
necessary
2
With
air
conditioner
in
ON
F
l
C
D
is
actuated
increase
engine
speed
slowly
then
decrease
it
And
make
sure
throttle
valve
operates
Click
sOund
is
heard
or
continuity
turns
to
OFF
when
engine
speed
decreases
to
idling
Page 108 of 548

If
not
adjust
throttle
valve
switch
Fig
EF
59
Adjusting
Throttle
Valve
Switch
Eng
ine
Fuel
If
throttle
valve
switch
cannot
be
adjusted
to
specification
replace
Engine
operation
Throttle
valve
switch
continuity
Engine
speed
rpm
When
engine
speed
increases
OFF
ON
1
150
t200
When
engine
speed
decreases
ON
OFF
I
000
t
200
Inspecting
engine
revolution
switch
Note
Before
checking
the
engine
revolution
switch
make
sure
the
functions
of
other
components
are
correct
in
accordance
with
the
items
described
above
Disconnect
throttle
valve
switch
connector
2
Connect
circuit
tester
3
Run
engine
at
idling
speed
4
Depress
clutch
pedal
and
shift
gear
into
5th
position
5
Depressing
clutch
pedal
increase
engine
speed
slowly
Make
sure
engine
speed
is
within
the
specified
range
when
voltmeter
goes
from
OV
to
l2V
Then
decrease
engine
speed
slowly
and
make
sure
engine
speed
is
within
the
specified
range
when
voltmeter
goes
from
12V
to
OV
EF
23
MAJOR
SERVICE
OPERATION
The
perfectly
adjusted
carburetor
deliver
the
proper
fuel
and
air
ratios
at
aD
speeds
for
the
particular
engine
for
which
it
was
designed
By
com
pletely
disassembling
at
re
ular
inter
vals
which
will
allow
cleaning
of
all
parts
and
passages
the
carburetor
can
be
maintained
in
its
original
condition
and
will
continue
to
deliver
the
proper
ratios
To
maintain
accurate
carburetion
of
passages
and
discharge
holes
ex
treme
care
must
be
taken
in
cleaning
Use
only
carburetor
solvent
and
compressed
air
to
clean
all
passages
and
discharge
holes
Never
use
wire
or
other
pointed
instrument
to
clean
or
carburetor
calibration
will
be
affected
REMOVAL
Remove
carburetor
from
engine
taking
sufficient
care
to
the
following
Precautions
a
When
disconnecting
fuel
lines
do
not
spill
fuel
from
fuel
pipe
b
When
removing
carburetor
do
not
drop
any
nut
or
bolt
into
intake
manifold
c
Be
careful
not
to
bend
or
scr
tch
any
part
d
Link
system
of
carburetor
differ
between
models
for
U
S
A
and
Canada
For
details
see
Figure
EF
60
which
is
based
on
Canadian
models
Page 114 of 548

CLEANING
AND
INSPECTION
Dirt
gum
water
or
carbon
con
tamination
in
or
on
exterior
moving
parts
of
a
carburetor
are
often
respon
sible
for
unsatisfactory
performance
For
this
reason
efficient
carhuretion
depends
upon
careful
cleaning
and
inspection
while
servicing
Blow
all
passages
and
castings
with
compressed
air
and
blow
off
all
parts
until
dry
Note
Do
not
pass
drills
or
wires
through
calibrated
jets
or
passages
as
this
may
enlarge
orifice
and
seriously
affect
carburetor
calibra
tion
2
Check
all
parts
for
wear
If
wear
is
noted
damaged
parts
must
be
re
placed
Note
especially
the
following
I
Check
float
needle
and
seat
for
wear
If
wear
is
noted
assembly
must
be
replaced
2
Check
throttle
and
choke
shaft
bores
in
throttle
chamber
and
choke
chamber
for
wear
or
out
of
roundness
3
Inspect
idle
adjusting
needle
for
hurrs
or
ridges
Such
a
condition
re
quires
replacement
Engine
Fuel
3
Inspect
gaskets
to
see
if
they
appear
hard
or
brittle
or
if
edges
are
torn
or
distorted
If
any
such
condi
tion
is
noted
they
must
be
replaced
4
Check
filter
screen
for
dirt
or
lint
Clean
and
if
screen
is
distorted
or
remains
plugged
replace
5
Check
linkage
for
operating
condition
6
Inspect
operation
of
accelerating
pump
Pour
fuel
into
float
chamber
and
make
throttle
lever
operate
Check
condition
of
fuel
injection
from
the
accelerating
nome
7
Push
connecting
rod
of
dia
phragm
chamber
and
block
passage
of
vacuum
with
finger
When
connecting
rod
becomes
free
check
for
leakage
of
air
or
damage
to
diaphragm
Jets
Carburetor
performance
depend
on
jets
and
air
bleeds
That
is
why
these
components
must
be
fabricated
with
utmost
care
To
clean
them
use
cleaning
solvent
and
blow
air
on
them
Larger
inner
nwnbers
stamped
on
the
EF
29
jets
indicate
larger
diameters
Ac
cordingIy
main
and
slow
jets
with
larger
numbers
provide
richer
mixture
the
smaller
numbers
the
leaner
mix
ture
Conversely
the
main
and
slow
air
bleeds
through
which
air
to
passes
make
the
fuel
leaner
if
they
bear
larger
numbers
the
smaller
numbers
the
richer
fuel
Assembly
To
assemble
reverse
the
disassem
bly
procedure
taking
care
to
the
following
I
Thoroughly
wash
all
the
parts
before
assembling
2
Inspect
gaskets
to
see
if
they
appear
hard
or
brittle
or
if
edges
are
torn
or
distorted
If
any
of
such
undesirable
condi
tions
is
noted
they
must
be
replaced
3
Install
jet
and
air
bleed
having
the
Same
size
number
as
that
of
original
one
4
After
reassembling
carburetor
check
each
rotating
portion
or
sliding
portion
for
smooth
operation
Page 115 of 548

Engine
fuel
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
In
the
following
table
the
symp
toms
and
causes
of
carburetor
troubles
and
remedies
for
them
are
listed
to
facilitate
quick
repairs
There
are
various
causes
of
engine
malfunctions
It
sometimes
happens
that
a
carburetor
which
has
no
fault
appears
to
have
some
problems
when
Condition
Probable
cause
Overflow
Dirt
accumulated
on
needle
valve
Fuel
pump
pressure
too
high
Needle
valve
improperly
seated
Excessive
fuel
consumption
Fuel
overflow
Slow
jet
too
large
on
each
main
jet
Main
air
bleed
clogged
Choke
valve
does
not
open
fully
Outlet
valve
seat
of
accelerator
pump
improper
Unked
opening
of
secondary
throttle
valve
opens
ioo
early
Power
shortage
Mainjels
clogged
Every
throttle
valve
Joes
not
open
fully
Idling
adjustment
incorrect
Fuel
filter
clo
ll
ed
Vacuum
jet
clogged
Air
cleaner
clogged
Diaphragm
damaged
Power
valve
operating
improperly
Improper
idling
Slow
jet
clogged
Every
throttle
valve
does
not
close
Secondary
throttle
valve
operating
im
properly
Throttle
valve
shafts
wom
Packing
between
manifold
carburetor
faulty
Manifold
carburetor
tightening
improper
Fuel
overflow
T
O
C
S
adjustment
incorrect
Vacuum
control
solenoid
damaged
Stuck
dash
pot
EF
30
acfuaJIy
theelectric
syslem
i
at
fatilt
Therefore
whenever
the
engine
is
mal
functioning
the
electrical
system
should
be
checked
fust
before
adjust
ing
carburetor
Corrective
action
Clean
needle
valve
Repair
pump
Replace
See
above
item
Replace
Clean
Adjust
Lap
Adjust
Clean
Adjust
Repair
Repair
Clean
Clean
Replace
Adjust
Clean
Adjust
Overhaul
and
clean
Replace
Replace
packing
Correct
tightening
See
the
first
item
Adjust
Replace
Replace
Page 125 of 548

Emission
Control
System
CRANKCASE
EMISSION
CONTROL
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
This
system
returns
blow
by
gas
to
both
the
intake
manifold
and
carbure
tor
aitdeaner
The
positive
crankcase
ventilation
P
C
v
valve
is
provided
to
conduct
crankcase
blow
by
gas
to
the
intake
manifold
During
partial
throttle
operation
of
the
engine
the
intake
manifold
sucks
the
blow
by
gas
through
the
P
C
V
valve
Normally
the
capacity
of
the
valve
is
sufficient
to
handle
any
blow
by
and
a
small
amount
of
ventilating
air
L
J
J
o
I
Fresh
air
Blow
by
gas
The
ventilating
air
is
then
drawn
from
the
dust
side
of
the
carburetor
air
cleaner
through
the
tube
connect
ing
carburetor
air
cle
er
to
rocker
cover
into
the
crankcase
Under
full
throttle
condition
the
manifold
vacuum
is
insufficient
to
draw
the
blow
by
flow
through
the
valve
and
its
flow
goes
through
the
tube
connection
in
the
reverse
direc
tion
On
cars
with
an
excessively
high
blow
by
some
of
the
flow
will
go
through
the
tube
connection
to
car
buretor
air
cleaner
under
all
condi
tions
r
IiI
e
1
LJ
1
Seal
type
oil
level
gauge
2
DafOe
plate
3
Flame
arrester
4
Filter
5
P
C
V
valve
6
Steel
net
1
Baffle
plate
EC871
Fig
EC
5
Crankcase
Emis
ion
Control
Sy
tem
EC
6
INSPECTION
p
C
V
VALVE
AND
FILTER
With
ei
gine
runnirig
at
idle
remove
the
ventilator
hose
from
P
C
V
valve
if
the
valve
is
working
a
hissing
noise
wiD
be
heard
as
air
passes
through
the
valve
and
a
strong
vacuum
should
be
felt
irnniediately
when
a
fmger
is
placed
over
valve
inlet
EC139A
Fig
EC
6
Checking
PC
V
Vo
ve
VENTILATION
HOSE
I
Check
hoses
and
hose
connec
tions
for
ieaks
2
oisconn
ct
all
hoses
and
clean
with
compressed
air
If
any
hose
cannot
be
free
of
obstructions
replace
Ensure
that
flame
arrester
is
surly
inserted
in
hose
between
air
cleaner
and
rocker
rover
ET277
Fig
EC
7
Checking
Ventilation
Hose
Page 127 of 548

Emission
Control
System
EARLY
FUEL
EVAPORATIVE
E
FE
SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
@
jl
D
W
o
0
0
UL
@
1
Intake
manifold
9
Screw
2
Stove
gasket
10
Thermostat
spring
3
Mar
fold
stove
11
Heat
control
valve
4
Heat
shield
plate
12
Control
valve
shaft
5
Snap
ring
13
Exhaust
manifold
6
Countczwcight
14
Cap
7
Key
15
Bushing
8
Stopper
pin
16
Coil
spring
The
early
fuel
evaporative
system
is
provided
with
a
chamber
above
a
manifold
stove
mounted
between
the
intake
and
exhaust
manifolds
During
engine
warming
up
air
fuel
mixture
in
the
carburetor
is
heated
in
the
cham
ber
by
exhaust
gas
This
reuslts
in
improved
evaporation
of
atomized
fuel
droplets
in
the
mixture
and
in
smaller
content
of
hydrocarbons
HC
in
the
exhaust
gas
especially
in
cold
weather
operation
OPERATION
The
counterweight
rotates
counter
clockwise
and
stops
at
the
stopper
pin
mounted
on
the
exhaust
manifold
while
the
engine
temperature
is
low
With
this
condition
the
heat
control
valve
is
in
the
fully
closed
position
obstructing
the
flow
of
exhaust
gas
As
engine
temperature
goes
up
and
the
ambient
temperature
becomes
high
enough
to
actuate
the
thermostat
spring
the
counterweight
begins
to
j
@
l
7
1
1
5
If
@
I
Exhaust
gas
flows
valve
dosed
valve
opened
EC247
Fig
EC
8
Early
Fuel
Eaaporatiae
E
F
E
System
rotate
clockwise
and
again
comes
into
contact
with
the
stopper
pin
With
this
condition
the
heat
control
valve
is
in
the
full
open
position
and
exhaust
gas
passes
through
the
exhaust
manifold
without
heating
the
manifold
stove
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
1
Snap
ring
2
Lock
bolt
3
Key
4
Counterweight
5
Thermosta
t
spring
6
Coil
spring
7
Heat
controlvalve
EC913
8
Valve
shaft
Fig
EC
9
KF
E
Sy
tem
Component
EC
8