1969 FORD MUSTANG service indicator
[x] Cancel search: service indicatorPage 193 of 413

04-01-06
General Axle Service
04-01-06
FLANGE BEARING
CUP RUNOUT
0.000
0.001
0.002
0.003
0.004
0.005
0.006
0.007
0.008
DRIVE SHAFT UNIVERSAL CROSS-SHAFT RUNOUT-INCH
0.000
0.000
0.001
0.002
0.003
0.004
0.005
0.006
0.007
0.008
0.001
0.001
0.0013
0.0022
0.0032
0.0042
0.0051
0.0061
0.0071
0.0081
0.002
0.002
0.0022
0.0027
0.0036
0.0045
0.0053
0.0062
0.0073
0.0082
0.003
0.003
0.0032
0.0037
0.0042
0.005
0.0058
0.0068
0.0075
0.0087
0.004
0.004
0.0042
0.0045
0.005
0.0057
0.0063
0.0072
0.0081
0.009
0.005
0.005
0.0051
0.0053
0.0058
0.0064
0.0071
0.0078
0.0087
0.0094
0.006
0.006
0.0061
0.0062
0.0067
0.0072
0.0078
0.0085
0.0093
0.010
0.007
0.007
0.0071
0.0072
0.0077
0.0081
0.0087
0.0092
0.0099
0.0104
0.008
0.008
0.0081
0.0082
0.0085
0.009
0.0094
0.010
0.0103
0.011
The total (combined) companion flange runout
is
located
in the
square where
the
columns containing
the
flange bearing cup runout
and universal cross shaft runout readings intersect.
FIG. 9—Companion Flange Combined Runout Chart
slightly moving the cross-shaft fore
and aft, then rotate the companion
flange from side-to-side.
8. With the indicator at zero, care-
fully retract the dial stem and rotate
the flange 180 degrees. Rotate the
cross-shaft 180 degrees on the flange
bearing cups to position the exposed
journal under the dial indicator adapt-
er. Rock the cross-shaft fore and aft
and the companion flange side-to-side
to establish the point at which the in-
dicator hand reverses direction. This
will determine the driveshaft universal
cross-shaft run-out. Record this read-
ing (Fig. 8).
9. Repeat steps 5 through 8 at least
three times and average the indicator
readings obtained (Fig. 7).
10.
To determine the total (com-
bined) companion flange runout, it
will be necessary to use the combined
runout chart (Fig. 9). Position a
straight edge at the amount of flange
bearing cup runout indicated on the
left hand column of the chart. Posi-
tion another straight edge vertically at
the amount of driveshaft universal
cross-shaft runout indicated on the top
of the chart. The point at which the
straight edges cross the chart indicates
the combined rear axle flange runout.
For example:
With an indicated 0.003 inch flange
bearing cup runout and an indicated
0.004 inch universal cross-shaft runout
(Fig. 9), the combined companion
flange runout will be 0.005 inch as in-
dicated in the square on the chart
(Fig. 9).
11.
If the reading obtained in Step
10 exceeds specifications, reposition
the companion flange 180 degrees on
the pinion shaft and repeat steps 1
through 10.
12.
If the repeat readings still ex-
ceed specifications, re-position the
flange an additional 90 degrees on the
pinion shaft and check the runout
(Steps 4 through 10).
13.
If the runout is still excessive,
replace the companion flange and
check the runout. If necessary, rotate
the new flange on the pinion shaft
until an acceptable runout is obtained.
If excessive runout is still evident
after replacement of the companion
flange, it will be necessary to replace
the ring and pinion gear, and repeat
the above checks until runout is within
specifications.
14.
Install the driveshaft assembly
(Group 5). Make sure the universal
joint bearing cups are properly posi-
tioned between the companion flange
lugs.
15.
Lower the vehicle. Road test
the vehicle. If drive shaft vibrations
are evident during the road test, re-
move the driveshaft from the compan-
ion flange and rotate it 180 degrees.
Road test the vehicle again.
THUNDERBIRD AND
CONTINENTAL MARK III
1.
Raise the vehicle on a hoist that
supports the rear axle (twin-post
hoist).
2.
Remove the driveshaft assembly
(Group 5).
3.
Check the companion flange for
damage.
4.
To check radial runout, set up
dial indicator as shown in Fig. 10.
5.
Rotate the companion flange
with the dial indicator in place. If the
runout exceeds specifications, remove
the flange and reinstall it 180 degrees
from original position. Follow the
procedure in Part 4-2 for companion
flange installation.
6. If the runout is still excessive, re-
move and reinstall the flange an addi-
tional 90 degrees and recheck runout.
7.
To check lateral (face) runout,
set up the dial indicator as shown in
Fig. 11. Repeat steps 5 and 6.
FLANGE
MOUNT HERE
Too/-4207-C
Too/-6565 USED WITH BRACKET FROM Tool-4201
FIG. 10—Checking Companion Flange Radial Runout—
Thunderbird and Continental Mark III
E1697-Aprocarmanuals.com
Page 194 of 413

04-01-07
General Axle Service
04-01-07
Tool-4201-
C
Tool-6565 USED WITH BRACKET
FROM Too/^*207-C
FLANGE
E1743-A
procedure under Backlash and Differ-
ential Bearing Preload Adjustments.
If the tooth pattern indicates a change
in shim thickness, follow the proce-
dure under Pinion Location.
REMOVABLE CARRIER
TYPE AXLE
The shim location for the removable
carrier type axle is between the pinion
retainer and the carrier (Fig. 13).
When adjusting this type carrier re-
ducing shim thickness will move the
pinion toward the ring gear; increas-
ing shim thickness will move the pi-
nion away from the ring gear (Fig.
13).
FIG. 11—Checking Companion Flange Lateral Runout—
Thunderbird and Continental Mark III
INTEGRAL CARRIER
TYPE AXLE
8. If the runout is still excessive, re-
place the companion flange and check
the runout. If necessary, rotate the
new flange on the pinion shaft until an
acceptable runout is obtained.
If excessive runout is still evident
after replacement of the companion
flange, it will be necessary to replace
the ring and pinion gear, and repeat
the above checks until runout is within
specifications.
9. Install the driveshaft assembly
(Group 5).
PINION LOCATION
ADJUSTMENT
BACKLASH
ADJUSTMENT,
LEFT
ADJUSTING
NUT
E1476-A
FIG. 12—Pinion and Ring Gear
Tooth Contact Adjustment
—
Integral Carrier Type Axles
PINION AND RING GEAR
TOOTH CONTACT
ADJUSTMENT
Two separate adjustments affect pin-
ion and ring gear tooth contact.
They are pinion location and backlash
(Figs.
12 and 13).
Individual differences in matching
the differential housing and the gear
set require the use of shims to locate
the pinion for correct contact with the
ring gear.
When adjusting either type axle,
shim thickness should be increased or
reduced only as indicated by the tooth
pattern check described in the fore-
going Section 1.
If the tooth pattern check indicates
a change in backlash only, follow the
PINION
LOCATION
ADJUSTMENT
SHIMS
LEFT
ADJUSTING
NUT
RIGHT
ADJUSTING
BACKLASH NUT
ADJUSTMENT El 409-A
FIG. 13—Pinion and Ring Gear
Tooth Contact Adjustment—
Removable Carrier Axles
The shim location for the integral
carrier type axle, is between the pi-
nion gear and the pinion rear bearing
cone (Fig. 12). When adjusting this
type axle, increasing shim thickness
moves the pinion toward the ring
gear; reducing shim thickness moves
the pinion away from the ring gear
(Fig. 12).
BACKLASH AND DIFFERENTIAL
BEARING PRELOAD
ADJUSTMENTS (ALL AXLES)
On a Light-Duty (WER) Axle, it is
necessary to remove the rear axle
shafts prior to performing the adjust-
ment procedures. Refer to Rear Axle
Shaft Wheel Bearing and Oil Seal Re-
placement—Light-Duty (WER), Axle,
Part 4-4, Section 2.
To secure a more uniform control
of differential side bearing preload in
service repairs, a dial indicator set-up
such as shown in Fig. 12 is used.
In both types of axle (Fig. 11 and
12),
the ring gear is moved away from
or toward the pinion as described in
the following procedure.
1.
Remove the adjusting nut locks,
loosen the differential bearing cap
bolts,
then torque the bolts to 15 ft-lbs
on integral carrier type axle; 20 ft-lbs
on removable carrier type axles before
making adjustments.
2.
The left adjusting nut is on the
ring gear side of the carrier. The right
nut is on the pinion side. Loosen the
right nut until it is away from the cup.
Tighten the left nut until the ring gear
is just forced into the pinion with
0.000 backlash then rotate the pinion
several revolutions to be sure no bind-
ing is evident. (Recheck the right nutprocarmanuals.com
Page 195 of 413

04-01-08
General Axle Service
04 01-08
Too/-T57L-4067-A
E 1595-A
FIG.
14
—Adjusting Side Bearing Preload—Typical
at this time to be sure that it is still
loose.) Tightening the left nut moves
the ring gear into the pinion to de-
crease backlash, and tightening the
right nut moves the ring gear away.
3.
Install a dial indicator as shown
in Fig. 14.
4.
Tighten the right nut until it first
contacts the bearing cup. Then pre-
load the bearings from 0.008-0.012
inch case spread. Rotate the pinion
gear several revolutions in each direc-
tion while the bearings are loaded, to
seat the bearings in their cups to be
sure no bind is evident. This step is
important.
5. Again loosen the right nut to re-
lease the pre-load. If there is any
backlash between the gears as shown
by the dial indicator,(Fig.l2 or Fig. 10
Part 4-4) tighten the left nut just en-
ough to remove this backlash. At this
time,
make sure that one of the slots
in the left nut is so located that the
lock can be installed without turning
the nut. Carefully, tighten the right
nut until it just contacts the cup.
6. Torque the differential cap bolts
to specification.
On integral carrier type axles, set a
preload of 0.008 to 0.012 inch case
spread for new bearings and 0.003 to
0.005 for the original bearings.
On removable carrier type axles,
the preload is 0.008 to 0.012 inch case
spread for new bearings and 0.005 to
0.008 for the original bearings. As
preload is applied from the right side,
the ring gear is forced away from the
pinion and usually results in the cor-
rect backlash.
7.
Measure the backlash on several
teeth around the ring gear. If the
measurements vary more than 0.003
inch (both integral and removable car-
rier) there is excessive runout in the
gears or their mountings, which must
be corrected to obtain a satisfactory
unit. If the backlash is out of specifi-
cation, loosen one adjusting nut and
tighten the oposite nut an equal a-
mount to move the ring gear away
from or toward the pinion. When
moving the adjusting nuts, the final
movement should always be made in a
tightening direction. For example, if
the left nut had to be loosened one
notch, loosen the nut two notches,
then tighten it one. This insures that
the nut is contacting the bearing cup,
and that the cup cannot shift after
being put in service. After all such ad-
justments, check to be sure that the
case spread remains as specified for
the new or original bearings used.
8. Again check the tooth contact
pattern. If the pattern is still incor-
rect, a change in pinion location (shim
thickness) is indicated.
PINION LOCATION
Removable Carrier Type Axle
1.
Remove the attaching bolts and
the pinion and bearing retainer assem-
bly from the carrier.
2.
Measure the original shim thick-
ness with a micrometer. Increase or
decrease the shim thickness as indicat-
ed by the tooth pattern check des-
cribed in Section 1.
3.
Replace the pinion retainer O-
ring (Fig. 39, Part 4-2). Coat the O-
ring with axle lubricant before install-
ing. Do not roll the O-ring into the
groove. Snap it into position.
4.
Being careful not to pinch the
O-ring, install the pinion and bearing
retainer assembly in the carrier with
the corrected shim pack.
Before installing the pinion and
bearing retainer assembly, determine
which type of gear set is being used.
The non-hunting and pantial non-
hunting types can be identified by the
paint timing marks on the gear teeth
(Fig. 51, Part 4-2). Part 4-5 can also
be referred to for identification.
If the gear set is of the non-hunting
or partial non-hunting type clean the
teeth on both the pinion and drive
gear so that the timing marks are vis-
ible.
Rotate the differential case and
ring gear assembly in the carrier until
the marked teeth on the ring gear are
opposite the pinion entry hole. Place
the assembly in the carrier so that the
marked tooth on the pinion indexes
between the marked teeth on the ring
gear (Fig. 51, Part 4-2).
In almost every case of improper
assembly (gear assembled out of time)
the noise level and probability of fai-
lure will be higher than they would be
with properly assembled gears.
When installing the hunting type
gear set (no timing marks), assemble
the pinion and retainer assembly into
the carrier without regard to the
matching on any particular gear teeth.
5.
Install the retainer-to-carrier
mounting bolts and torque to specifi-
cations.
6. Adjust the backlash between the
ring gear and pinion as outlined in the
foregoing procedures.
7.
Make a tooth pattern check. If
the pattern is still unsatisfactory, re-
peat this procedure changing the shim
thickness each time until a satisfactory
tooth pattern is obtained.
Integral Carrier Type Axle
1.
Remove the differential case and
the drive pinion from the carrier cast-
ing, and then remove the pinion bear-
ings as described under Removal of
Differential Case and Drive Pinion in
Section 4.
2.
Measure the original shim thick-
ness with a micrometer. Increase or
decrease the shim thickness as indicat-
ed by the tooth pattern check des-
cribed in the foregoing Section 1 and
shown in Fig. 4.
3.
Install the corrected shim pack
and the bearings on the pinion, and
then install the pinion and the differ-
ential case in the carrier casting as
outlined under Installation of Drive
Pinion and Differential Case in Sec-
tion 4 of Part 4-3.
4.
Adjust the backlash between the
ring gear and pinion as outlined in the
foregoing procedure.
5.
Make a tooth pattern check. If
the pattern is still unsatisfactory, re-
peat this procedure changing the shim
thickness each time until a satisfactory
tooth pattern is obtained.procarmanuals.com
Page 196 of 413
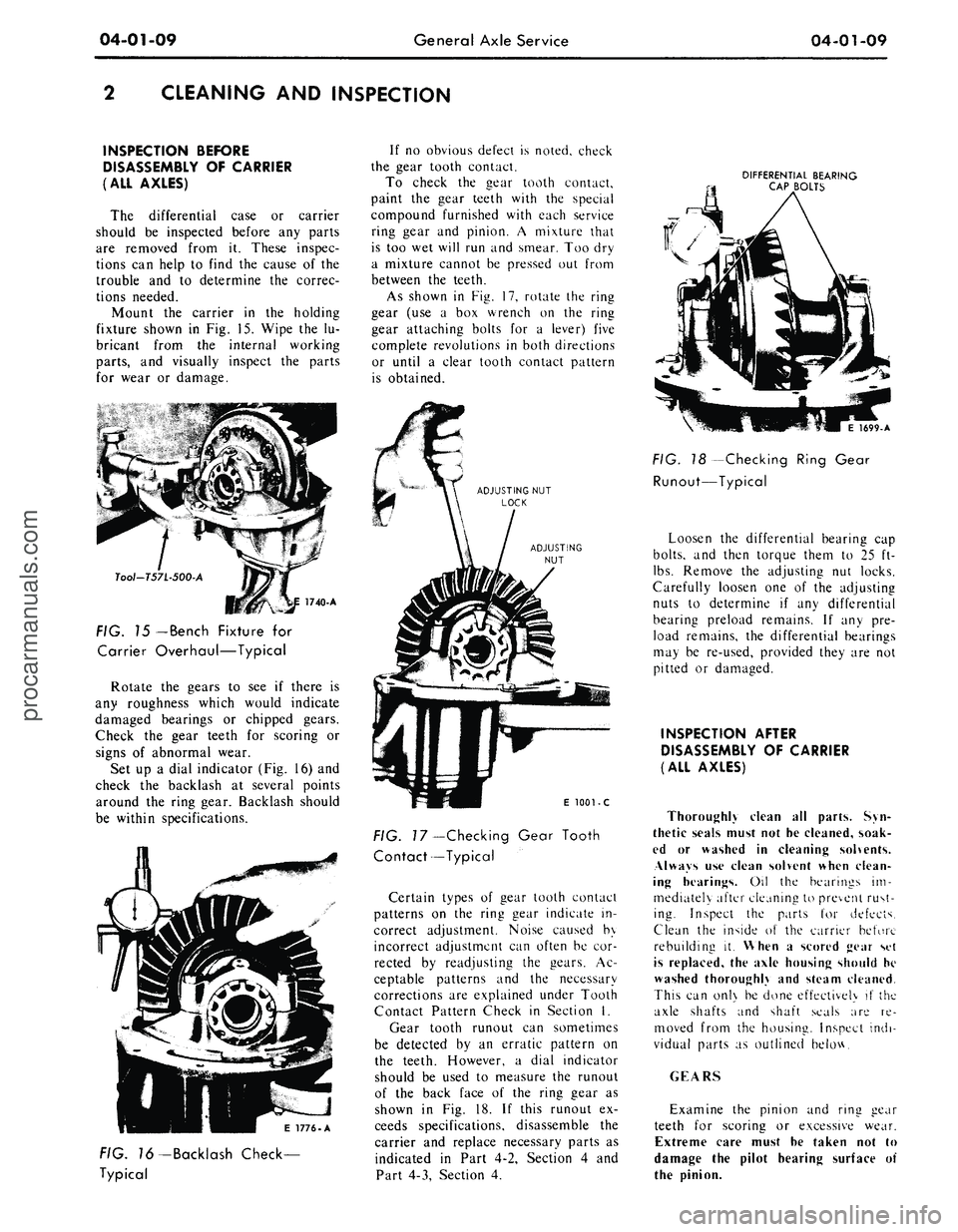
04-01-09
General Axle Service
04-01-09
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
INSPECTION BEFORE
DISASSEMBLY OF CARRIER
(ALL AXLES)
The differential case or carrier
should be inspected before any parts
are removed from it. These inspec-
tions can help to find the cause of the
trouble and to determine the correc-
tions needed.
Mount the carrier in the holding
fixture shown in Fig. 15. Wipe the lu-
bricant from the internal working
parts,
and visually inspect the parts
for wear or damage.
Tool-T57L-500-A
FIG. 15
— Bench
Fixture for
Carrier Overhaul—Typical
Rotate the gears to see if there is
any roughness which would indicate
damaged bearings or chipped gears.
Check the gear teeth for scoring or
signs of abnormal wear.
Set up a dial indicator (Fig. 16) and
check the backlash at several points
around the ring gear. Backlash should
be within specifications.
If no obvious defect is noted, check
the gear tooth contact.
To check the gear tooth contact,
paint the gear teeth with the special
compound furnished with each service
ring gear and pinion. A mixture that
is too wet will run and smear. Too dry
a mixture cannot be pressed out from
between the teeth.
As shown in Fig. 17, rotate the ring
gear (use a box wrench on the ring
gear attaching bolts for a lever) five
complete revolutions in both directions
or until a clear tooth contact pattern
is obtained.
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING
CAP BOLTS
E 1776-A
FIG. 76-Backlash Check-
Typical
E
1001 - C
FIG.
7
7—Checking Gear Tooth
Contact—Typical
Certain types of gear tooth contact
patterns on the ring gear indicate in-
correct adjustment. Noise caused by
incorrect adjustment can often be cor-
rected by readjusting the gears. Ac-
ceptable patterns and the necessary
corrections are explained under Tooth
Contact Pattern Check in Section I.
Gear tooth runout can sometimes
be detected by an erratic pattern on
the teeth. However, a dial indicator
should be used to measure the runout
of the back face of the ring gear as
shown in Fig. 18. If this runout ex-
ceeds specifications, disassemble the
carrier and replace necessary parts as
indicated in Part 4-2, Section 4 and
Part 4-3, Section 4.
1699-A
FIG. 18 -Checking Ring Gear
Runout—Typical
Loosen the differential bearing cap
bolts,
and then torque them to 25 ft-
lbs.
Remove the adjusting nut locks.
Carefully loosen one of the adjusting
nuts to determine if any differential
bearing preload remains. If any pre-
load remains, the differential bearings
may be re-used, provided they are not
pitted or damaged.
INSPECTION AFTER
DISASSEMBLY OF CARRIER
(ALL AXLES)
Thoroughly clean all parts. Syn-
thetic seals must not he cleaned, soak-
ed or washed in cleaning solvents.
Always use clean solvent when clean-
ing hearings. Oil the bearings im-
mediately after cleaning to prevent rust-
ing. Inspect the parts for defects.
Clean the inside of the carrier before
rebuilding it. When a scored gear set
is replaced, the axle housing should he
washed thoroughly and steam cleaned.
This can onl\ be done effectively if the
axle shafts and shaft seals are re-
moved from the housing. Inspect indi-
vidual parts as outlined below.
GEARS
Examine the pinion and ring gear
teeth for scoring or excessive wear.
Extreme care must he taken not to
damage the pilot hearing surface of
the pinion.procarmanuals.com
Page 215 of 413

04-02-18
Rear Axle — Removable Carrier Type
04-02-18
E 1195-C
FIG. 41—Removing
or
Installing
Pinion
and
Retainer Assembly
10.
Hold
the
flange with
the
tool
shown
in Fig. 22
(Ford)
or Fig. 23
(Mercury),
and
torque
the
pinion shaft
nut
to 175
ft-lbs.
Do not
exceed
175
ft-Ibs
at
this time.
11.
Check
the
pinion bearing
pre-
load
as
shown
in Fig. 42.
Correct
pre-load will
be
obtained when
the
torque required
to
rotate
the
pinion
in
the retainer
is as
specified
in
Part
4-3.
If
the
torque required
to
rotate
the pin-
ion
is
less than specified, tighten
the
pinion shaft
nut a
little
at a
time until
Inch-Pound
Torque Wrench
E1899A
FIG. 42—Checking Pinion Bearing
Preload
the proper preload
is
established.
Do
not overtighten
the nut. If
excessive
preload
is
obtained
as a
result
of
over-
tightening, replace
the
collapsible
bearing spacer.
Do
not
back
off the
pinion shaft
nut
to establish pinion bearing preload.
If
the torque
on the
pinion shaft
nut is
less than
175
ft-lbs after bearing
pre-
load
is
established,
a new
collapsible
spacer must
be
used.
SOLID PINION BEARING
SPACER INSTALLATION
The spacer
is
serviced
in 20
sizes
listed
in
Part
4-5. The
manner
of sel-
ecting
the
size spacer required
for ob-
taining correct preload
is
included
in
the following assembly procedure.
1.
Install
the
drive pinion rear bear-
ing cone
and
roller assembly
on the
pinion shaft
as
shown
in
Figs.
38 or
39.
2.
Select
a new
solid spacer
of a
larger size (0.485 inch thick),
and
slide
it over
the
pinion shaft against
the
rear bearing.
The pinion bearing preload
can be
accurately measured only when
the
pinion shaft
nut is
torqued
to 180-
220 ft-lbs.
If a
spacer smaller than
re-
quired
was
used,
the
specified
180-
220 ft-lbs torque would damage
the
bearings.
For
this reason,
the
largest
spacer should
be
tried first. Then,
if
the bearings
are too
loose,
the
size
of
the spacer
can be
decreased until
the
correct preload
is
obtained.
3.
Position
the
bearing retainer
and
cup assembly
on the
pinion shaft
and
install
the
front bearing cone
and rol-
ler. Press
the
front bearing cone
and
roller assembly into position,
as
shown
in Fig. 38.
4.
Mount
the
retainer
in a
holding
fixture
as
shown
in Fig. 23, and
place
the slinger over
the
pinion shaft
and
against
the
front bearing.
5.
Install
the
U-joint flange with
the tool shown
in Fig. 46.
6. Hold
the
flange with
the
tool
shown
in Fig. 23 or 24, and
install
the
old pinion shaft
nut.
Using
a
ft-lb
tor-
que wrench, torque
the nut to
180-220
ft-lbs.
While tightening
the nut,
rotate
the bearing retainer
to
determine
the
existance
of any
bearing preload
which will
be
indicated
by a
slight
drag
in the
rotation
of the
retainer.
DETERMINING SPACER
SIZE FROM
PRELOAD READING
1.
If
bearing drag indicates
a pre-
load condition exists, apply
an
in-lb
torque wrench
to the
pinion
nut as
shown
in Fig. 42 and
read
the
torque
required
to
turn
the
shaft. Effort
should
be
12-1/2
to
32-1/2 in-lbs.
2.
If
preload
is the
correct valve,
proceed with assembly procedure
given
in
Final Assembly
of
Pinion
and
Retainer, which follows.
2.
If
preload exists,
but is
below
specification, select
the
correct spacer
from
Fig. 43 and
install, completing
assembly
as
shown
in
Final Assembly
of Pinion
and
Retainer.
DETERMINING SPACER
SIZE FROM
END
PLAY READING
1.
If no
perceptible preload
is
felt
when rotating
the
pinion shaft, install
a dial indicator
as
shown
in Fig. 44,
so that
the
indicator point
is
resting
on
the end of the
pinion gear shaft
(companion flange
end).
2.
Use
both hands
to
squeeze
the
pinion shaft
and the
bearing retainer
together
(Fig. 45).
Record
the
endplay
reading shown
on the
dial indicator.
3.
Disassemble
the
pinion shaft
and
retainer
and
install
the
correct spacer
as shown
in Fig. 43.
4.
Proceed with assembly
of the pin-
ion shaft
and
retainer
as
directed
in
Final Assembly
of
Pinion
and
Retain-
er.
FINAL ASSEMBLY
OF
PINION
AND
RETAINER
1.
Install
the
drive pinion rear bear-
ing cone
and
roller assembly
on the
AS
END
PLAY
READS
(10/1000 inch)
USE THIS
SPACER
0
0.481
1
0.480
2
0.479
3
0.478
4
0.476
If there
is no end
play
and
preload
on the
bearings
IF PRELOAD READS
(in-lbs.)
USE THIS SPACER
2-11
0.482
12-20
0.483
5
0.476
6
0.474
7
0.474
8
0.472
9
0.472
10
0.470
11
0.470
12
0.468
13
0.468
14
0.466
15
0.465
exists:
21-30
0.484
31-45
0.485
FIG. 43— Solid Spacer Selectionprocarmanuals.com
Page 238 of 413
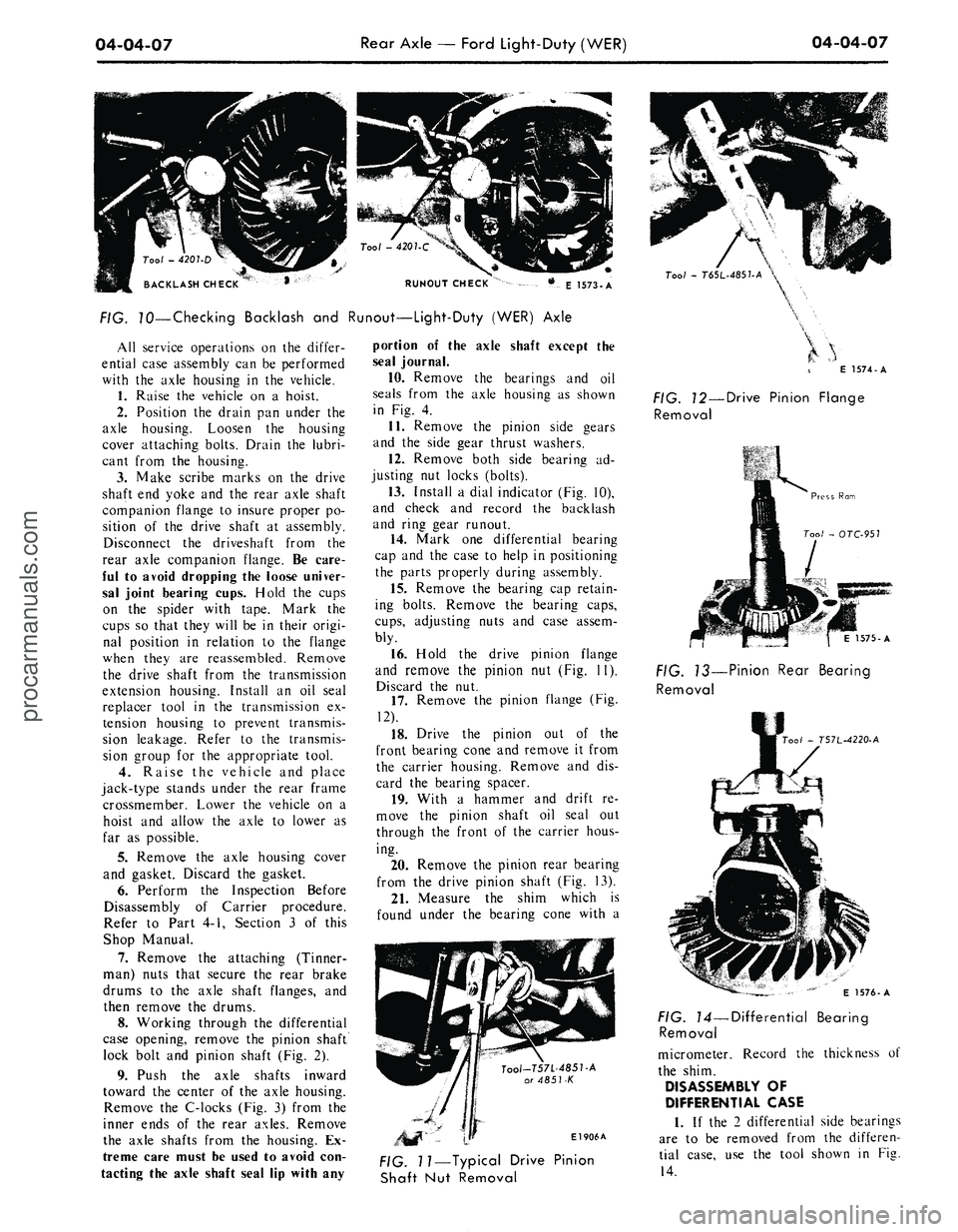
04-04-07
Rear Axle — Ford Light-Duty (WER)
04-04-07
RUNOUT CHECK
E 1573-A
FIG. 70—Checking Backlash and Runout—Light-Duty (WER) Axle
All service operations on the differ-
ential case assembly can be performed
with the axle housing in the vehicle.
1.
Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
2.
Position the drain pan under the
axle housing. Loosen the housing
cover attaching bolts. Drain the lubri-
cant from the housing.
3.
Make scribe marks on the drive
shaft end yoke and the rear axle shaft
companion flange to insure proper po-
sition of the drive shaft at assembly.
Disconnect the driveshaft from the
rear axle companion flange. Be care-
ful to avoid dropping the loose univer-
sal joint bearing cups. Hold the cups
on the spider with tape. Mark the
cups so that they will be in their origi-
nal position in relation to the flange
when they are reassembled. Remove
the drive shaft from the transmission
extension housing. Install an oil seal
replacer tool in the transmission ex-
tension housing to prevent transmis-
sion leakage. Refer to the transmis-
sion group for the appropriate tool.
4.
Raise the vehicle and place
jack-type stands under the rear frame
crossmember. Lower the vehicle on a
hoist and allow the axle to lower as
far as possible.
5.
Remove the axle housing cover
and gasket. Discard the gasket.
6. Perform the Inspection Before
Disassembly of Carrier procedure.
Refer to Part 4-1, Section 3 of this
Shop Manual.
7.
Remove the attaching (Tinner-
man) nuts that secure the rear brake
drums to the axle shaft flanges, and
then remove the drums.
8. Working through the differential
case opening, remove the pinion shaft
lock bolt and pinion shaft (Fig. 2).
9. Push the axle shafts inward
toward the center of the axle housing.
Remove the C-locks (Fig. 3) from the
inner ends of the rear axles. Remove
the axle shafts from the housing. Ex-
treme care must be used to avoid con-
tacting the axle shaft seal lip with any
portion of the axle shaft except the
seal journal.
10.
Remove the bearings and oil
seals from the axle housing as shown
in Fig. 4.
11.
Remove the pinion side gears
and the side gear thrust washers.
12.
Remove both side bearing ad-
justing nut locks (bolts).
13.
Install a dial indicator (Fig. 10),
and check and record the backlash
and ring gear runout.
14.
Mark one differential bearing
cap and the case to help in positioning
the parts properly during assembly.
15.
Remove the bearing cap retain-
ing bolts. Remove the bearing caps,
cups,
adjusting nuts and case assem-
bly.
16.
Hold the drive pinion flange
and remove the pinion nut (Fig. 11).
Discard the nut.
17.
Remove the pinion flange (Fig.
12).
18.
Drive the pinion out of the
front bearing cone and remove it from
the carrier housing. Remove and dis-
card the bearing spacer.
19.
With a hammer and drift re-
move the pinion shaft oil seal out
through the front of the carrier hous-
ing.
20.
Remove the pinion rear bearing
from the drive pinion shaft (Fig. 13).
21.
Measure the shim which is
found under the bearing cone with a
Tool-T57L-485T-A
or 4851-K
El 906A
Tool
-
T6SL-485UA
\
E 1574-A
FIG. 12—Drive Pinion Flange
Removal
1575-A
FIG. 13—Pinion Rear Bearing
Removal
00/
- T57L-4220-A
FIG. 11—Typical Drive Pinion
Shaft Nut Removal
E 1576-A
FIG. 14—Differential Bearing
Removal
micrometer. Record the thickness of
the shim.
DISASSEMBLY OF
DIFFERENTIAL CASE
1.
If the 2 differential side bearings
are to be removed from the differen-
tial case, use the tool shown in Fig.
14.procarmanuals.com
Page 248 of 413

05-01-01
05-01-01
Clutch
GROUP
5
PART
5-1
PAGE
Drive Shaft 05-01-01
PART
5-2
General Clutch Service 05-02-01
PART
5-3
Clutch
PART
5-4
Specifications
PAGE
05-03-01
05-04-01
PART
5-1
Drive Shaft
COMPONENT INDEX
DESCRIPTION
DRIVE SHAFT ANGLE CHECK
DRIVE SHAFT BALANCE CHECK
DRIVE SHAFT BALANCING
(Single Universal Joint)
DRIVE SHAFT DISASSEMBLY
AND
OVERHAUL
Single Universal Joint — Ford Design
Double Cardan Joint — Dana Design
Double Cardan Joint — Saginaw Design
DRIVE SHAFT REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
DRIVE SHAFT RUNOUT CHECK
MODEL APPLICATION
All
Models
01-01
01-01
01-01
01-02
01-01
Ford
01-04
01-04
N/A
N/A
Mercury
01-04
01-04
N/A
N/A
Meteor
01-04
01-04
N/A
N/A
Cougar
01-04
01-04
N/A
N/A
Fairlane
01-04
01-04
N/A
N/A
Falcon
01-04
01-04
N/A
N/A
Montego
01-04
01-04
N/A
N/A
Mustang
01-04
01-04
N/A
N/A
Lincoln-
Continental
N/A
N/A
01-04
N/A
Thunderbird
N/A
N/A
N/A
01-05
Continental-
Mark
III
N/A
N/A
N/A
01-05
A page number indicates that the item
is for the
vehicle listed
at the
head
of
the column.
N/A indicates that
the
item
is not
applicable
to the
vehicle listed.
DRIVE SHAFT TESTS
DRIVE LINE BALANCE CHECK
If detailed parts
of the
drive shaft
are replaced
and
shaft vibration
is en-
countered after installation, disconnect
the shaft
at the
slip yoke. Rotate
the
slip yoke
180
degrees; then, reconnect
the shaft
to the
slip yoke.
If the
vibra-
tion persists, disconnect
the
shaft
at
the rear axle companion flange.
Ro-
tate
the
companion flange
180
degrees
and reconnect
the
shaft
to the
flange.
DRIVE LINE ANGLE CHECK
Vibration
or
"shudder" which
is no-
ticeable either
on
fast acceleration
or
when coasting, using
the
engine
for a
brake,
may be
caused
by the
rear axle
housing being loose
on the
rear
springs
or by
improper pinion angle.
Refer
to
Group
3,
Part
2 for
pinion
angle checking procedures.
If the
rear
axle U-bolts (Fairlane, Montego,
Mustang, Cougar, Falcon models
only)
are
loose, torque
the
nuts
to
specification.
DRIVE SHAFT RUNOUT CHECK
Using
a
dial indicator, check
the
runout
at
each
end and in the
middle
of
the
driveshaft.
The
rear check
should
be
made
on the
small tube
sec-
tion
of the
shaft between
the
balance
weights
and the
yoke welds. Drive-
shaft runout should
not
exceed 0.035
inch
at any one
point.
DESCRIPTION
The drive shaft
is the
means
of
transferring power from
the
engine,
through
the
transmission,
to the dif-
ferential
in the
rear axle,
and
then
to
the rear wheels.
The
drive shaft incor-
porates
two
universal joints
and a
slip
yoke
(Fig. 1) or two
double cardan
universal joints,
one at
each
end of the
shaft (Figs.
2 and 3).
Each double
procarmanuals.com
Page 255 of 413

05-02-01
General Clutch Service
05-02-01
PART
5-2
General Clutch Service
COMPONENT INDEX
MODEL APPLICATION
3
a>
1
o>
il
•U
i
!-
II
CLUTCH DISC
Cleaning and Inspection
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
N/A
N/A
N/A
CHECKING FLYWHEEL HOUSING
ALIGNMENT
02-01
02-01
02-01
02-01
02-01
02-01
02-01
02-01
N/A
N/A
N/A
CORRECTING FLYWHEEL HOUSING
ALIGNMENT
02-03
02-03
02-03
02-03
02-03
02-03
02-03
02-03
N/A
N/A
N/A
PILOT BUSHING
Cleaning and Inspection
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
N/A
N/A
N/A
PRESSURE PLATE AND COVER
Cleaning and Inspection
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
N/A
N/A
N/A
RELEASE BEARING
Cleaning and Inspection
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
02-04
N/A
N/A
N/A
A page number indicates that the item is for the vehicle listed at the head of the column.
N/A indicates that the item is not applicable to the vehicle listed.
l
FLYWHEEL HOUSING ALIGNMENT
Alignment of the flywheel housing
bore and rear face with the engine
should be checked as a possible cause
of any of the following troubles- ex-
cessive transmission gear wear, ..ans-
mission jumping out of gear, especial-
ly third gear, drive line vibration, ex-
cessive pilot bushing wear, noisy re-
lease bearing, or excessive clutch spin
time.
INSPECTION
1. With the clutch release bearing
removed, install the indicator pilot
tool shown in Fig. 1.
2.
Clean the faces of the flywheel
housing bolt bosses, and remove all
burrs, nicks, and paint from the
mounting face of the housing.
3.
Install the dial indicator on the
pilot and adjust the holder so the but-
ton will contact a circumference just
inside of the transmission mounting
holes.
4.
Push the flywheel forward to re-
move crankshaft end play. Set the dial
indicator face to read zero.
5.
Remove the spark plugs to alle-
viate compression.
6. Pull the engine crankshaft
through one revolution. The crank-
shaft must be held in the forward po-
sition while rotating it.
7. Note the indicator reading and
mark the maximum point of runout
on the face of the housing (Fig. 1).
8. Position the dial indicator to
check bore alignment (Fig. 1). The
bore must be clean and free of burrs,
nicks and paint.
9. Pull the crankshaft through one
revolution. Note the indicator reading
and mark the maximum point of run-
out on the face of the housing as
shown in Fig. 1.
10.
Remove the dial indicator from
the crankshaft and the housing.
11.
Select the Dia-L-lgner pilot
(Fig. 2) which will fit snugly in the
bore of the flywheel housing.
12.
Press the pilot into place on the
locator on the back of the dial.
13.
Position the Dia-L-lgner on the
face of the housing (Fig. 3) with the
pilot in the bore.
14.
Rotate the face runout arrow to
the positive face runout mark on the
housing.
15.
Without moving the face runout
arrow, rotate arrow A until it is at the
negative bore reading.
16.
Slide arrow A to register the
amount of bore runout on the .010-
line of the white scale. Use the
scale No. to coincide with the pilot
being used.
17.
Rotate arrow B until it points
CHECKING
FACE
RUN OUT
CHECKING
BORE
RUN OUT
C
1783-
A
FIG.
1—Flywheel
Housing Alignment Checkprocarmanuals.com