1953 JEEP DJ key
[x] Cancel search: keyPage 64 of 376

D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
FIG.
D-34—GAUGING
CRANKSHAFT
END
PLAY
FIG.
D-35
—
DRILLING FLYWHEEL
D-84.
Install
Crankshaft Timing
Gear
Install
the woodruff key in the longer of the two keyways on the front end of the crankshaft.
Install
the crankshaft timing gear on the front end of the crankshaft with the timing
mark
facing out, away from the cylinder block. Align the
keyway in the gear with the woodruff key and then
drive
or press the gear
onto
the crankshaft firmly against the thrust washer.
D-85.
Install
Crankshaft
Rear
Bearing Seal
When
installing the crankshaft
rear
bearing seal
around
the crankshaft, apply a thin coat of light cup grease to both halves of the seal except for the
ends which are already treated with sealing com pound. When installing the
rear
main bearing cap
in
the crankcase, place a small amount of plastic- type gasket cement on both sides and face of the
cap to prevent oil leakage. Insert the rubber
packings shown in
Fig. D-3
7
into the
holes
between
the bearing cap and the case. Do not trim
these
packings. The packings are of a predetermined
length that
will
cause them to protrude approxi mately 34* [6 mm.] from the case. When the oil
pan
is installed, it
will
force them tightly into the
holes
and effectively seal any opening
between
the bearing cap and the crankcase.
D-86.
Install
Front
End Plate
Assemble the gasket to the front end plate making
certain
that it is positioned properly down to the
bottom
of the crankcase.
Install
the front end plate
on the cylinder block and tighten in place.
D-87.
Install
Flywheel
Be
sure the crankshaft flange and flywheel mating
surfaces are clean to permit proper flywheel align ment. With the crankshaft in the cylinder block,
FIG.
D-36—
REAMING FLYWHEEL
FIG.
D-37—REAR
BEARING
CAP
PACKING
64
Page 66 of 376

D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
FIG.
D-40—TIMING
GEARS Be
sure
to install a new rubber oil
seal
ring on each
intake
valve stem before installing the retainer
locks.
With
the retainer and spring compressed position a
seal
ring
on the valve stem just above the
lock
recess, then install the locks and release the
spring.
Adjust
the valve tappets to the proper specified
clearance.
Refer to Par. D-108, and specifications
at the end of this section for specifications and
adjustment procedure.
D-91.
Install
Camshaft
Timing
Gear
Turn
the camshaft or crankshaft as necessary so
that the timing marks on the two gears
will
be
together
after the camshaft timing gear is installed.
Refer
to Fig. D-40.
Install
the woodruff key in the key way on the front end of the camshaft.
Start
the large timing gear on the camshaft with the timing
mark
facing out. Do not drive on the camshaft gear, or the camshaft may
dislodge
the plug at the
rear
of the cylinder block causing an oil leak.
Install
the camshaft gear retaining screw and
torque it 30 to 40 lb-ft. [4,1 a 5,5 kg-m.] drawing
the gear
onto
the camshaft in the process. Standard
running
tolerance
between
the timing gears is .000" to .002" [0 a 0,051 mm.] which should be
checked with a
dial
indicator.
D-92.
Install
Timing
Gear
Oil Jet
Install
the timing gear oil jet in the tapped
hole
in
the front of the cylinder block. Position the oil
hole
in the side of the oil jet so that it
will
direct the
oil
stream against the camshaft driven gear just
ahead
of the point of
engagement
with the
crank
shaft drive gear.
D-93.
Install
Oil Pump
The
oil pump is driven from the camshaft by means of a
spiral
(worm) gear. The distributor, in
turn,
is driven by the oil pump by means of a
tongue
on the end of the distributor shaft which
engages
a slot in the end of the oil pump shaft.
Because the
tongue
and the slot are both machined off center, the two shafts can be meshed in only
one position. Since the position of the distributor shaft determines the timing of the engine, and is
controlled by the oil pump shaft, the position of the oil pump shaft with respect to the camshaft is
important.
Turn
the crankshaft to bring
together
the timing
marks
on the crankshaft and camshaft gears. See
Fig.
D-4 0.
Install
the oil pump mounting gasket on
the pump.
With
the wider side of the shaft on top
(nearer
the top of the cylinder block), start the
oil
pump drive shaft into the opening in the left side of the cylinder block with the mounting
holes
in
the body of the pump in alignment with the
holes
in
the cylinder block. Insert a long-blade screw
driver
into the distributor shaft opening in the
opposite
side of the block and
engage
the slot in the oil pump shaft.
Turn
the shaft so that the slot is positioned at what would be roughly the nine-
thirty
position on a clock face. Remove tne screwdriver and, looking down the
distributor
shaft
hole
with a flashlight, observe the position of the slot in the end of the oil pump shaft
to make certain it is properly positioned. Replace the screwdriver and, while turning the screw
driver
clockwise to guide the oil pump drive shaft
gear into
engagement
with the camshaft gear, press
against the oil pump to force it into position. Remove the screwdriver and again observe the
position of the slot. If the installation was properly made, the slot
will
be in a position roughly equiva
lent to eleven o'clock position on a clock face with
the wider side of the shaft
still
on the top. If the
slot is improperly positioned, remove the oil pump
assembly and repeat the operation.
Coat
the threads of the capscrews with gasket
cement and secure the oil pump in place with two
lockwasher-equipped capscrews installed through the body of the oil pump and into the cylinder block
and
one lockwasher-capscrew installed through
the oil pump mounting flange.
D-94.
Install
Timing
Gear
Cover
Apply
a thin coat of gasket paste to the timing
gear cover. Position the gasket on the cover and
carefully
locate the cover on the front of the front mounting plate. Attach the cover and timing
indicator
and tighten the bolts.
D-95.
Install
Pistons and Connecting Rods
Before installing each piston and connecting rod assembly in the cylinder block, generously lubricate
the entire assembly with
engine
oil. Space the ring
gaps
around the piston so that no two
gaps
are
aligned vertically and are not located over the
T-slot
in the piston
skirt.
Insert the assembly in
the correct cylinder with the connecting rod
identifying number toward the camshaft side of
the cylinder block. When installing each assembly, rotate the crankshaft so that the
crankpin
is in
the down position. Fit a piston ring compressor
tightly around the piston rings. Reach up from the
bottom
of the cylinder block and guide the end of
the connecting rod over the crankshaft
journal
as
the piston is tapped down into the cylinder bore
with
hammer handle. 66
Page 67 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
D
Lubricate
the connecting rod bearing surfaces
generously with
engine
oil and install the bearing
cap with the numbered side matched to the num
bered side of the connecting rod. Torque the nuts
evenly 35 to 45 lb-ft. [4,8 a 6,2 kg-m.]. The con
necting rod cap nuts are locked with stamped nuts.
Used
stamped nuts should be discarded and re
placed with new
ones.
These locking stamped nuts
should be installed with the flat face toward the
connecting rod nut.
Turn
the locking nut finger
tight and then 34
turn
more with a wrench. Refer
to Par. D-36 for detailed information on fitting pistons and rings in the cylinder bores.
D-96.
Install
Crankshaft
Pulley
Align
the keyway in the pulley with the woodruff key installed in the crankshaft. Drive the pulley
onto
the crankshaft and secure it in place with
the crankshaft pulley nut. Insert a block of wood
between
one of the counterweights on the
crank
shaft and the side of the cylinder block to prevent the crankshaft from turning, then tighten the nut.
D-97.
Install
Oil Pan
Before installing the oil pan, make a final internal
inspection particularly making certain that the
inside of the cylinder block is clean. Apply a thin
coat of gasket paste on the oil pan. Place the new
oil
pan gasket in position. Set the oil pan in posi
tion on the cylinder block and install the oil pan.
Torque
the attaching
bolts
12 to 15 lb-ft. [1,7 a 2,1
kg-m.].
Install
the oil pan
drain
plug and gasket
and
tighten the plug securely.
D-98.
Install
Cylinder
Head
Make
certain that the entire top of the cylinder
block
assembly, the lower surface of the cylinder
head,
and the cylinder head gasket are clean. Blow
all
dirt
or carbon out of the blind tapped bolt
holes
in
the cylinder block before the cylinder head and gasket are installed. Using aerosol spray sealer
Part
No. 994757, spray a thincoat on both surfaces
of the head gasket, position the new cylinder head gasket with the crimped
edges
of the gasket metal down (See Fig. D-31).
This
gasket position allows a
positive seal along the narrow surfaces of the
cylin
der
head
between
the combustion chambers and
eliminates the possibility of burning combustion
10102
FIG.
D-41—CYLINDER
HEAD
BOLT
TIGHTENING
SEQUENCE
gases
reaching
an
asbestos
portion of the cylinder
head gasket.
Install
the cylinder head bolts. Tighten
the
bolts
with a torque wrench to 60 to 70 lb-ft. 8,3 a 9,7
kg-m.]
in the sequence shown in
Fig.
D-41.
Do not overlook installing the cylinder head bolt
in
the intake
manifold
directly under the
car
buretor
opening.
D-99.
Install
Rocker Arm Assembly
a.
Insert
ball
ends of the intake valve push rods through the cylinder head and cylinder block and
seat them in the cupped head of the intake valve
tappets.
b.
Install
the
rocker-arm
assembly on the 'four
rocker-arm-mounting
studs. Align the rocker arms
so that the
ball
ends of the intake valve tappet
adjusting
screws fit into the cup ends of the push
rods.
c.
Install
the four rocker-arm-attaching nuts.
Thread
each nut down evenly in sequence, one
turn
at a time, until the torque is 30 to 36 lb-ft. [4,1 a 5,0 kg-m.].
d.
Cement a new gasket on the rocker arm cover.
Install
the cover placing an oil seal then a flat
washer
and nut on each cover stud. Cement a new gasket on the exhaust valve cover.
Install
the cover and crankcase ventilation fittings using a
new gasket back of the vent cover and new copper
ring
gaskets under the attaching screw heads.
Torque
the valve tappet cover nuts 7 to 10 lb-ft. [1,0 a 1,4 kg-m.].
D-100.
Install
Distributor and
Spark
Plugs
To
correctly install the distributor, it
will
be neces
sary
to place No. 1 piston in the firing position.
To
locate the firing position of No. 1 piston, first
turn
the
engine
until No. 1 piston is moving up on
the compression stroke as indicated by compression
pressure
being forced through the
spark
plug open
ing.
Turn
the
engine
slowly until the 5° before top
center
mark
on the timing gear cover is in align
ment with the
mark
on the crankshaft pulley. Oil
the distributor housing where it bears on the
cylin
der
block and install the distributor. Mount the
rotor
on distributor shaft and
turn
the shaft until
the rotor points towards No. 1
spark
plug terminal
tower position (when cap is installed, about 5
o'clock) with the contact points just breaking.
Move the rotor back and forth slightly until the
driving
lug on the end of the shaft enters the slot cut in the oil pump gear and slide the distributor
assembly down into place. Rotate the distributor body until the contact points are just breaking.
Install
the hold down screw.
Connect
the core
primary
wire to the distributor.
Clean
and adjust the
spark
plugs, setting the elec
trode
gaps
at .030" [0,762 mm.].
Install
the plugs
to prevent any foreign matter entering the com
bustion chambers during the remaining operations.
Torque
the
spark
plugs 25 to 30 lb-ft. [3,5 a 4,6
kg-m.].
Install
spark
plug cables, placing them in the dis
tributor
cap terminal towers starting with No. 1
and
installing in a counter clockwise direction of
the firing order sequence (1-3-4-2). 67
Page 77 of 376
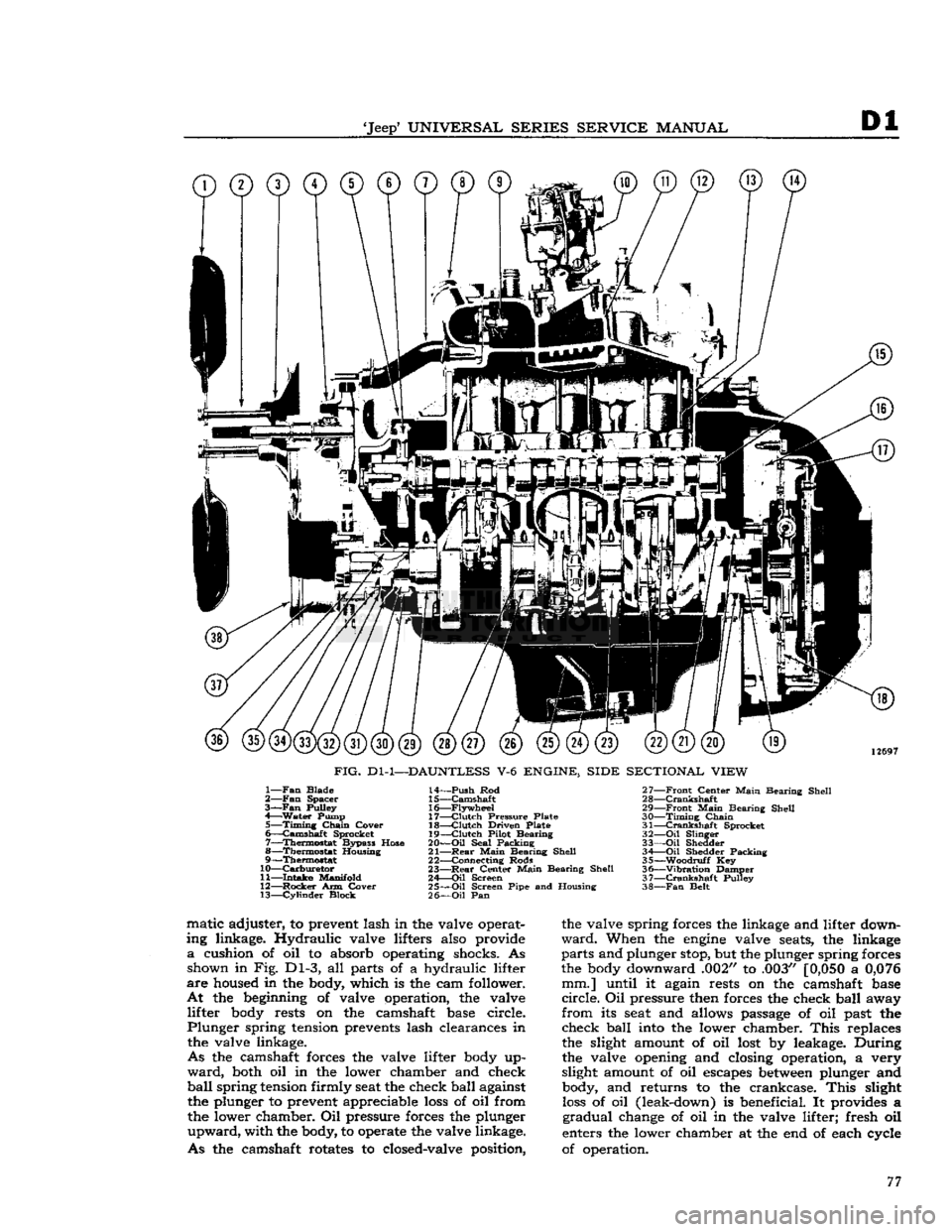
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
©©©©©©©©©
12697
FIG.
Dl-1—DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE, SIDE SECTIONAL VIEW
1—
Fan
Blade
2—
Fan
Spacer
3—Fan
Pulley
4—
Water
Pump 5—
Timing
Chain
Cover
6—
Camshaft
Sprocket
7—
Thermostat
Bypass Hose
8—
Thermostat
Housing
9—
Thermostat
10—
Carburetor
11—
Intake
Manifold
12—
Rocker
Arm Cover 13—
Cylinder
Block 14—
Push
Rod
15—
Camshaft
16—
Flywheel
17—
Clutch
Pressure Plate
18—
Clutch
Driven Plate
19—
Clutch
Pilot Bearing
20—
Oil
Seal Packing
21—
Rear
Main
Bearing Shell
22— Connecting Rods
23—
Rear
Center
Main
Bearing Shell
24—
Oil
Screen
25—
Oil
Screen Pipe and Housing
26—
Oil
Pan 27—
Front
Center
Main
Bearing Shell
28—
Crankshaft
29—
Front
Main
Bearing Shell
30—
Timing
Chain
31—
Crankshaft
Sprocket
32—
Oil
Slinger
33—
Oil
Shedder 34 Oil Shedder Packing
35—
-Woodruff
Key
36—
"Vibration
Damper
37—
Crankshaft
Pulley
38—
Fan
Belt matic adjuster, to prevent lash in the valve operat
ing linkage. Hydraulic valve lifters also provide
a
cushion of oil to absorb operating shocks. As shown in Fig. Dl-3, all parts of a hydraulic lifter
are
housed in the body, which is the cam follower.
At
the beginning of valve operation, the valve lifter body rests on the camshaft base circle.
Plunger
spring tension prevents lash clearances in the valve linkage.
As
the camshaft forces the valve lifter body up
ward,
both oil in the lower chamber and check
ball
spring
tension firmly seat the check ball against the plunger to prevent appreciable
loss
of oil from
the lower chamber. Oil pressure forces the plunger
upward,
with the body, to operate the valve linkage.
As
the camshaft rotates to closed-valve position, the valve spring forces the linkage and lifter down
ward.
When the
engine
valve seats, the linkage
parts
and plunger stop, but the plunger spring forces
the body downward .002" to .003"
[0,050
a
0,076
mm.] until it again rests on the camshaft base
circle.
Oil pressure then forces the check ball away
from
its seat and allows passage of oil past the check ball into the lower chamber.
This
replaces
the slight amount of oil lost by leakage. During
the valve opening and closing operation, a very
slight amount of oil escapes
between
plunger and body, and returns to the crankcase.
This
slight
loss
of oil (leak-down) is beneficial. It provides a
gradual
change of oil in the valve lifter; fresh oil
enters the lower chamber at the end of each cycle
of operation. 77
Page 82 of 376

Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
d.
Use two large screwdrivers to alternately pry
forward the camshaft sprocket and
then
the crank
shaft sprocket, until the camshaft sprocket is pried
from the camshaft. Remove the camshaft sprocket, sprocket key, and timing chain from the
engine;
then
pry the crankshaft sprocket from the crankshaft.
Dl-23.
Remove Rocker Arm Cover
Refer to Fig. Dl-8.
Remove
positive
crankcase ventilator valve from right rocker arm cover. Remove four screws which attach each rocker arm cover to cylinder head.
Remove each rocker arm cover and
gasket
from cylinder head. 14198
FIG.
Dl-6—ENGINE
CRANKCASE
PARTS
1— Connecting Rod Assy.
2— —Piston Pin
3—
Piston and Pin Assy.
4—
Ring
Set 5— Connecting Rod
Bolt
and Nut
6— Connecting Rod Bearing
7— Damper Spring
8— Damper
Bolt
9—
Timing
Chain Damper (Right)
10—
Cylinder
Block
11— Camshaft
12—
Woodruff
Key
13— Camshaft Bearing (No. 1 Front) 14— Camshaft Bearing (No. 2)
15— Camshaft Bearing (No. 3) 16—
Camshaft
Bearing (No. 4
Rear)
31-
17—
Camshaft
Plug
(Rear)
32-18—
Flywheel
33-
19—
Ring
Gear
34-
20— Crankshaft Bearing Set 35-
21—
Main
Bearing Oil Seal
(Rear)
36-
2 2—Crankshaft 3 7-
23—
Main
Bearing Packing Oil Seal
(Rear)
28-
24— Bearing Cap
Bolt
39-
25— Woodruff Key 40-
26—
Timing
Chain Damper
(Left)
41-
27— Damper Bolt 42- 28—
Timing
Chain
43-
29—
Camshaft
Sprocket 44-
30— Crankshaft Sprocket
—Crankshaft
Slinger
—Crankshaft
Shedder
—Crankshaft
Packing (Front)
—Timing
Gear
Cover Gasket
—Timing
Gear
Cover
—Vibration
Damper
-Bolt
-Washer
-Bolt
—Dowel Pin
-Camshaft
Thrust
Retainer and Bolt
—Washer
-Distributor
Drive
Gear
—Fuel
Pump Eccentric
82
Page 83 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
14028
j
FIG.
D1-7—TIMING
CHAIN
AND
SPROCKET ALIGNMENT 1—
Camshaft Sprocket
2—
Crankshaft
3—Timing
Chain
Timing
Marks
Dl-24.
Remove
Cylinder
Head Assembly
a.
Unscrew, but do not remove, three
bolts
(Fig.
Dl-8)
which attach rocker
arm
assembly to cylinder
head.
Remove rocker arm assembly, with bolts,
from
cylinder head. See Section F2 for
engines
equipped with exhaust emission control.
b. Remove
eight
cylinder head bolts, cylinder head,
and
gasket from cylinder block.
Dl-25.
Remove Push Rod and Valve
Lifter
Refer
to Fig. Dl-8. Remove push rods and valve lifters from the
cylin
der
block.
Mark,
or otherwise identify, each valve
lifter
according to its cylinder and valve position.
Note:
If valve lifters are not to be serviced, cover
valve lifters and camshaft with a clean cloth to
protect them from dirt
Dl-26.
Remove Camshaft
Refer
to Fig. Dl-6.
Carefully
withdraw camshaft forward from bear
ing bores; avoid marring the bearing surfaces. Re
move
camshaft from cylinder block.
Dl-27.
Remove Flywheel Housing and
Clutch
a.
If flywheel housing and clutch was not pre
viously removed, remove six mounting
bolts
and
flywheel housing from cylinder block.
b.
Mark
clutch cover and flywheel to assure that
clutch
will
be installed in identical position when
engine
is assembled.
c. Remove six attaching screws and clutch assem
bly from flywheel.
D1-28. Remove Flywheel
Refer
to Fig. Dl-6.
Remove six attaching
bolts
and flywheel from
engine
crankshaft.
Dl-29.
Remove Oil Pan
Refer
to Fig. Dl-5.
To
gain access to oil pan mounting bolts, invert
the
engine.
Remove mounting bolts, oil pan, and gasket from
engine
cylinder block.
Dl-30.
Remove Oil Pump Intake Pipe and Screen
Refer
to Fig. Dl-5.
Remove two attaching screws, and oil pump intake
pipe and screen assembly from
engine
cylinder block.
Dl-31.
Remove Piston and
Connecting
Rod Assembly
a.
Examine the cylinder bores. If bores are worn
so that shoulder or ridges exist at the top of piston
ring
travel, remove the ridges with a ridge reamer.
FIG.
Dl-8-
-CYLINDER HEAD,
AND COVER
ROCKER
ARM
1—
—Right
Rocker
Arm
Cover
2—
Rocker
Arm
Cover
Bolt
3—
Gasket
4—
Bolt
5—
Baffle
6—
Left
Rocker
Arm
Cover
7—
Rocker
Arm Shaft
8—Plug
9—
Rocker
Arm Spring
10—
Cylinder
Head
11—
Head
Gasket
12—
Push
Rod
13—
Valve
Lifter
14—
Intake
Valve
15—
Exhaust
Valve
16—
Dowel
Pin
17—
Valve
Spring 18—
Valve
Spring Cap
19—
Valve
Spring Cap Key
20—
Cotter
Pin
21—
Rocker
Arm Shaft End Washer
22—
Rocker
Arm Shaft Spring
23—
Rocker
Arm
24—
Rocker
Arm Shaft
Bracket
25—
Bolt
83
Page 100 of 376

Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
14262
FIG.
D1-38—TIMING
CHAIN,
TIMING
GEARS
AND
COVER
1—
Crankshaft
Pulley
2—
Crankshaft
Pulley Bolt
3—
Washer
4—
Vibration
Damper 5—
Timing
Gear
Cover
6—
Gasket
7—
Dowel
Pin
g—Woodruff Key
9—Timing
Chain
Damper (Right) 10—
Damper
Bolt
11—
Camshaft
Sprocket
12—
Fuel
Pump
Eccentric
13—
Distributor
Camshaft
Gear
14—
Washer
15—
Special
Bolt 16—
-Thrust
Spring
17—
Thrust
Button 18—
Oil
Shedder
(Crankshaft)
19—
-Crankshaft
Packing
(Front)
20—
-Crankshaft
Slinger •
21—
Crankshaft
Sprocket
22—
Timing
Chain
23—
Damper
Bolt .
2
A
Timing
Chain
Damper
(Left)
25
Spring
D1-84.
Install Timing Chain
and
Sprocket
a.
Turn
crankshaft so that No. 1 piston is at top
center.
b.
Temporarily install sprocket key and camshaft
sprocket on camshaft.
Turn
camshaft so that index
mark
of sprocket is downward. Remove key and sprocket from camshaft.
c.
Assemble timing chain and sprockets.
Install
keys, sprocket, and chain assembly on the camshaft
and
crankshaft so that index marks of both sprockets are aligned as shown in
Fig.
Dl-39.
Note:
It
will
be necessary to hold spring-loaded
timing chain damper out of the way while installing
timing chain and sprocket assembly.
d.
Install
front oil slinger on crankshaft with in
side diameter against sprocket (concave side to
ward
front of engine).
e.
Install
fuel pump eccentric on camshaft and key
with
oil
groove
of eccentric forward. See
Fig.
Dl-40.
f.
Install
distributor drive gear on camshaft. Secure gear and eccentric to camshaft with retaining
washer and bolt. Torque
bolt
40 to 55 lb-ft. [5,53
a
7,6 kg-m.].
Install
camshaft thrust retainer as
sembly
onto
camshaft retaining bolt. Refer to
items
16 and 17 Fig. Dl-38.
Dl-85.
Install Crankshaft Front
Oil
Seal
From
rear
of timing chain cover, coil new packing
around
crankshaft opening at cover so that
ends
100
Page 125 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
E
is generally caused by excessive
engine
idle speed
in
combination with retarded ignition timing,
engine
heat soak or the use cf low octane fuel.
Should
engine
dieseling
(engine
running after ignition key is turned off) be experienced on V-6
engine
equipped vehicles, installation of Idle Stop
Valve
Kit
Part
No.
991722
will
correct the
difficulty.
E-43.
Fast
Idle Adjustment
No fast idle speed adjustment is required.
Fast
idle is controlled by the curb idle speed adjustment
screw.
If curb idle speed is correctly set and the choke rod is properly adjusted, fast idle speed
will
be correct;
E-44.
Dash Pot Adjustment —
F4
and V-6 Engine
•
Refer to
Figs.
E-27 and E-28. Before adjusting the dash pot, the
engine
idle speed
and
mixture should be correctly adjusted.
With
the
engine
idling at normal operating temperature,
adjust
the dash pot as follows:
The
dash pot adjustment is made with the throttle
set at curb idle (not fast idle). Loosen dash pot lock
nut and
turn
the dash pot assembly until dash pot
plunger contacts the throttle lever without the plunger being depressed.
Then
turn
the dash pot
assembly 2turns against the throttle lever, de pressing the dash pot plunger. Tighten the lock nut
securely. As a final check, open carburetor and
allow throttle to snap closed. Time dash pot delay ing action from the point where the throttle lever
hits the dash pot to the point where the lever
stops
moving. The dash pot should delay or cushion
closing action for two seconds by saying, "One
thousand and one, one thousand and two."
14204
FIG.
E-27—DASH
POT
ADJUSTMENT—V6
ENGINE
1—
Throttle
Lever
3—Dash Pot
2—
Plunger
4—Lock
Nut
E-45.
FUEL
PUMP
(DOUBLE-ACTION)
—
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
•
Early
Models
The
double-action fuel pump consists of a metal
body, a rubber diaphragm, rocker arm, valves,
FIG.
E-28—DASH
POT
ADJUSTMENT—F4
ENGINE
1—
Throttle
Lever
3—Dash Pot
2—
Plunger
4—Lock
Nut springs, gaskets, and a glass sediment bowl complete
with
strainer.
The
metal pump body provides
a
work
ing housing for the diaphragm, lever, valves, and springs. The fuel pump is mounted on the left side
of the
engine
and is actuated by an eccentric on the
camshaft. An air
dome
is cast into the metal cover
to relieve the carburetor
needle
valve and the fuel
pump diaphragm of excessive pressure when the
carburetor
needle
valve is closed.
Tracing
pump operation from the beginning, the
camshaft eccentric forces the diaphragm up, over
coming spring pressure.
This
action creates a
partial
vacuum
in the pump chamber.
Fuel
from the main
tank
is forced into the low-pressure pump chamber
through the open disc valve. Incoming fuel supplies
the force necessary to open the valve, which is
a
one-way check valve. As the
engine
camshaft continues to rotate, spring pressure forces the
diaphragm
downward as the pump rocker arm
follows the camshaft eccentric to its low
spot.
The
downward action of the diaphragm
closes
the intake valve and forces fuel to the carburetor
reservoir
through the pump
outlet
valve. Both intake and
outlet
valves are one-way check valves
opened and closed by fuel flow. No mechanical components are required in the control of valve
operation.
Fuel
is delivered to the carburetor only when the float
needle
is off its seat. When the fuel level in the carburetor bowl is high enough for the float to
force the
needle
against its seat, pressure backs up
to the fuel pump air
dome
and causes the diaphragm
to
stop
pumping. In this position, the pump is said
to be balanced because the pressure in the pump- to-carburetor line equals that of the diaphragm
spring.
In this way, fuel from the pump to the
carburetor
is always under pressure. The carburetor
uses
fuel, causing the float to drop and
pull
the
carburetor
needle
valve off its seat. Pressure in the pump immediately drops as fuel is delivered to the
carburetor
reservoir. Almost instantaneously the
diaphragm
again starts operating to pump more 125