1953 JEEP DJ key
[x] Cancel search: keyPage 11 of 376
'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
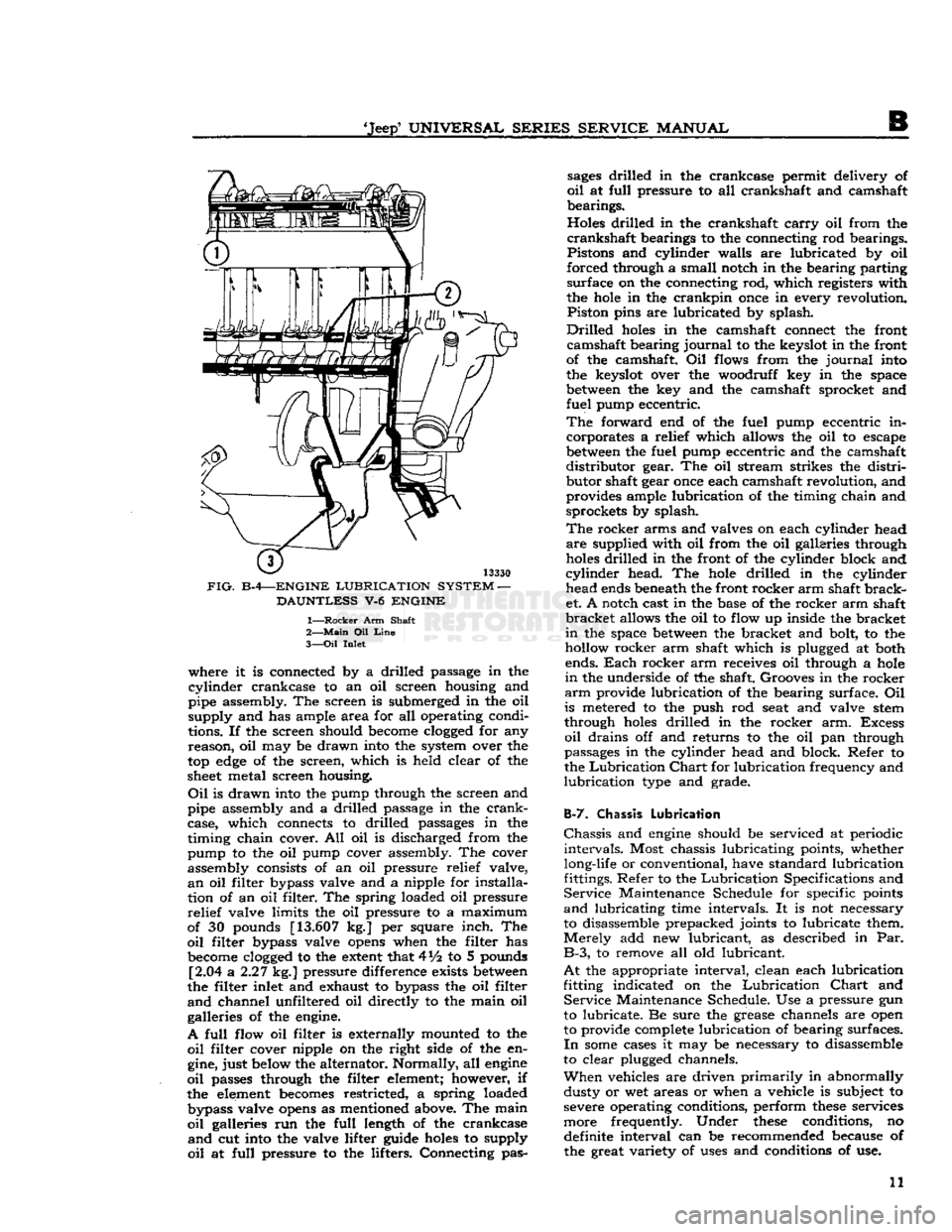
13330
FIG.
B-4—ENGINE
LUBRICATION
SYSTEM
—
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
1—
Rocker
Arm Shaft
2—
Main
Oil
Line
3—
Oil
Inlet where it is connected by a drilled passage in the
cylinder
crankcase to an oil screen housing and
pipe assembly. The screen is submerged in the oil supply and has ample area for all operating condi
tions. If the screen should
become
clogged
for any reason, oil may be drawn into the system over the
top
edge
of the screen, which is held clear of the
sheet
metal screen housing.
Oil
is drawn into the pump through the screen and
pipe assembly and a drilled passage in the
crank
case, which connects to drilled passages in the
timing chain cover. All oil is discharged from the
pump to the oil pump cover assembly. The cover
assembly consists of an oil pressure relief valve,
an
oil filter bypass valve and a nipple for installa
tion of an oil filter. The spring loaded oil pressure
relief
valve limits the oil pressure to a maximum
of 30 pounds [13.607 kg.] per square inch. The
oil
filter bypass valve
opens
when the filter has
become
clogged
to the
extent
that
4V2
to 5 pounds [2.04 a 2.27 kg.] pressure difference exists
between
the filter inlet and exhaust to bypass the oil filter
and
channel unfiltered oil directly to the main oil galleries of the engine.
A
full flow oil filter is externally mounted to the
oil
filter cover nipple on the right side of the en gine, just below the alternator. Normally, all
engine
oil
passes through the filter element; however, if
the element
becomes
restricted, a spring loaded bypass valve
opens
as mentioned above. The main
oil
galleries run the full length of the crankcase
and
cut into the valve lifter guide
holes
to supply
oil
at full pressure to the lifters. Connecting pas
sages
drilled in the crankcase permit delivery of
oil
at full pressure to all crankshaft and camshaft
bearings.
Holes drilled in the crankshaft
carry
oil from the
crankshaft
bearings to the connecting rod bearings.
Pistons and cylinder walls are lubricated by oil
forced through a small notch in the bearing parting
surface on the connecting rod, which registers with
the
hole
in the crankpin
once
in every revolution. Piston pins are lubricated by splash.
Drilled
holes
in the camshaft connect the front camshaft bearing
journal
to the key slot in the front
of the camshaft. Oil flows from the
journal
into
the keyslot over the woodruff key in the space
between
the key and the camshaft sprocket and fuel pump eccentric.
The
forward end of the fuel pump eccentric in corporates a relief which allows the oil to escape
between
the fuel pump eccentric and the camshaft
distributor
gear. The oil stream strikes the distri
butor shaft gear
once
each camshaft revolution, and provides ample lubrication of the timing chain and
sprockets by splash.
The
rocker arms and valves on each cylinder head
are
supplied with oil from the oil galleries through
holes
drilled in the front of the cylinder block and
cylinder
head. The
hole
drilled in the cylinder
head ends beneath the front rocker
arm
shaft brack et. A notch cast in the base of the rocker arm shaft
bracket
allows the oil to flow up inside the bracket
in
the space
between
the bracket and bolt, to the
hollow rocker arm shaft which is plugged at both
ends.
Each
rocker arm receives oil through a
hole
in
the underside of the shaft. Grooves in the rocker
arm
provide lubrication of the bearing surface. Oil
is metered to the push rod seat and valve stem
through
holes
drilled in the rocker arm. Excess
oil
drains off and returns to the oil pan through
passages in the cylinder head and block. Refer to
the
Lubrication
Chart
for lubrication frequency and
lubrication
type and grade.
B-7.
Chassis
Lubrication
Chassis
and
engine
should be serviced at periodic
intervals.
Most chassis lubricating points, whether
long-life or conventional, have standard lubrication
fittings. Refer to the
Lubrication
Specifications and
Service
Maintenance Schedule for specific points
and
lubricating time intervals. It is not necessary
to disassemble prepacked joints to lubricate them.
Merely
add new lubricant, as described in Par.
B-3,
to remove all old lubricant.
At
the appropriate interval, clean each lubrication
fitting indicated on the Lubrication
Chart
and
Service
Maintenance Schedule. Use a pressure gun
to lubricate. Be sure the grease channels are open
to provide complete lubrication of bearing surfaces.
In
some
cases it may be necessary to disassemble
to clear plugged channels.
When
vehicles are driven primarily in abnormally dusty or wet areas or when a vehicle is subject to
severe operating conditions, perform
these
services
more frequently. Under
these
conditions, no definite interval can be recommended because of the great variety of
uses
and conditions of use. 11
Page 17 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
B
Reinstall
the axle shafts, and
refill
the housings to
plug level using the universal joint lubricant
specified in
Lubrication
Specifications.
B-56.
Front
Axle Wheel Bearings
To
lubricate the wheel bearings, it is necessary
to remove, clean, repack, and adjust them. When
front wheel hubs and bearings are removed for
lubrication,
they should be thoroughly washed in a
suitable cleaning solvent. The bearings should be
carefully
dried and then given a thorough cleaning
and
inspection. Use a clean brush to remove all
particles
of old lubricant from bearings and hubs.
After
the bearings are cleaned, inspect them for
pitted races and rollers. Also, check the hub oil
seals.
Note:
Wheel bearing lithium base lubricants are
used at the factory for
initial
fill
of
these
bearings.
When
lithium base and sodium base lubricants are
mixed,
the result is a thinned-out mixture that
can
bleed through seals. It is therefore important
that lubricants with the correct base be used when
lubricating
the wheel bearings.
Should
leaks occur at wheel bearing seals, the leaks
may
be caused by a mixture of two
types
of
lubri
cants.
In such cases, the old lubricant should be
completely removed before new lubricant is added.
Wheel
bearings should be thoroughly cleaned,
lubricated
with lithium base and reinstalled.
Repack
the bearing
cones
and rollers with grease
and
reassemble hub in the reverse order of the
disassembly. Test the bearing adjustment as out
lined
in Section Q.
B-57.
Rear
Axle Wheel Bearings
The
Rear
wheel bearings an early models equipped
with
lubrication fittings with a vent opening
through the housings above each fitting should be
lubricated
sparingly, each
2,000
miles
[3.200
km.].
Use
a hand compressor and wheel bearing grease,
forcing
the grease through each lubrication fitting
until
it flows from the vent. Vent should be kept
clear
of obstruction or grease
will
back up into the
brakes.
Do not add grease after it flows from the
vent for it may be forced through the wheel key-
way
onto
the outside of the wheel and possibly
onto
the brake linings.
Rear
wheel bearings that do
not have lubrication fittings should be removed
each
12,000
miles
[19.200
km.] and the bearing
cleaned, inspected and repacked. Refer to proce
dure
in Par. B-56.
Note:
When servicing the Flanged Axle Unit
Bear
ing Assembly, refer to Section N, Par. N-5 for
proper
lubrication procedures.
B-58.
Propeller Shafts
and
Universal Joints
The
propeller shaft slip joints and universals should
be lubricated with a hand compressor grease gun so as to not damage the bearing seals. The units
should be lubricated with a
good
quality grease.
Refer
to the
Lubrication
Chart
for lubrication fre
quency and lubricant type and grade. B-59.
Lights
and
Controls
a.
Check
all interior and exterior lights and light
switches for proper operation, including: parking
lights, headlamps (high beam and low beam),
tail
lights, brake lights, directional lights, and in strument panel lights.
b.
Check
all instrument panel controls and
instru
ments for proper operation.
B-60.
Speedometer Cable
Remove the
speedometer
cable from its housing every
12,000
miles
[19.300
km.].
Clean
it thor
oughly and coat it with a
good
quality light graphite grease.
B-61.
Headlights
Refer
to Section H.
B-62.
Heater Controls
Apply
Lubriplate
130-A to all friction points and
pivot points on the heater controls panel unit as well as the pivot points at the dashpot. Apply
a
few drops of penetrating oil all along the Bowden
cable.
This
oil
will
penetrate into the center wire.
B-63.
Windshield Wiper and
Washer Controls
Lubricate
the friction points and the pivot points
on the windshield wiper transmission and linkage
arms
with a slight amount of
Lubriplate
130-A.
B-64.
Rotate Tires
Refer
to Section Q for the correct method of rotat ing the tires.
B-65.
Body Lube Points
•
Refer to Par. B-66 through B-68.
B-66.
Hood Hinge Pivot Points
Lubricate
the frictional points of the hood hinge
pivot points with a few drops of light-weight
engine
oil.
B-67.
Glove Compartment Door Latch
Sparingly
wipe
Lubriplate
130-A on the
glove
com
partment door latch.
B-68.
Tailgate Hinges
Lubricate
the friction points of the tailgate hinges
with
a few drops of light-weight
engine
oil.
B-69.
LUBRICATION
OF
OPTIONAL EQUIPMENT
B-70.
Pintle Hook
When
lubricating the vehicle, place a few drops of oil on the pintle hook and safety latch pivot pins.
B-7!.
Centrifugal Governor
Check
the oil level in the governor housing at each
vehicle lubrication. Use the same seasonal grade
oil
as is used in the
engine
and change oil at each
engine
oil change. Do not
fill
the housing above
the level indicating plug opening. Keep the vent
in
the filler plug open at all times. 17
Page 33 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
C
FIG.
C-2
7—FAN
BELT
—
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
e. Adjust mixture by turning idle mixture screws
out (counterclockwise) until a loss of engine speed
is indicated; then, slowly
turn
both mixture screws
in
clockwise (leaner) until maximum speed (RPM)
is reached. Continue turning in (clockwise) until a slight drop in speed (RPM) is noted. Make certain
both mixture screws are adjusted equally.
This
will
ensure a "lean as possible" mixture adjustment.
Readjust
idle
stop
screw to idle engine at the
specified
R.P.M.
Note:
This
method of adjusting idle mixture must
be used to keep hydrocarbon and carbon monoxide
emissions to a minimum.
Note:
No fast idle speed adjustment is required.
Fast
idle is controlled by the curb idle speed ad justment screw. If the curb idle speed is correctly set, the fast idle speed
will
be correct.
C-26.
Dash
Pot
Adjustment
Refer
to Section
E, Par.
E-44 for proper carburetor
dash
pot adjustment procedure.
C-27.
Check
Fan
Belt
The
fan belt drives the fan, alternator, and water
pump.
See Fig. C-27.
Inspect
the fan belt for serviceability and proper
tension. The tension should be checked with the
Belt
Tension Gauge, W-283. The correct tension on a used belt is 70 to 80 pounds [31,7 a 36,2 kg.]
and
on a new belt 110 to 120 pounds [49,8 a 54,5 kg.]. When preparing for delivery of new car,
the belt strand tension should be 80 to 110 pounds [36,2 a 49,8 kg.]. When installing a new belt, adjust
the strand tension 110 to 120 pounds [49,8 a 54,5 kg.].
Adjust
the fan belt tension by loosening the clamp
bolt on the alternator brace and swinging the alter
nator
away from the engine until proper belt ten
sion is obtained.
Then
tighten the clamp bolt.
Note:
If no
gauge
is available approximate correct
tension is obtained when the thumb pressure mid
way between the pulleys causes the belt to flex
y%
inch
[IV4
cm.].
C-28.
ROAD TEST VEHICLE
After
completing the tune-up, road
test
the vehicle for power and overall performance. Make neces
sary
adjustments.
Note:
Engine run on or "dieseling" is a condition
in
which combustion continues to take place after
the normal ignition
spark
from the distributor has
been shut off by turning off the ignition switch. It is generally caused by excessive engine idle speed
in
combination with retarded ignition timing, en gine heat soak or the use of low octane fuel.
Should
engine dieseling (engine running after igni
tion key is turned off) be experienced on V-6 engine equipped vehicles, installation of Idle Stop
Valve
Kit
Part
No. 991722
will
correct the
difficulty.
33
Page 43 of 376
'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
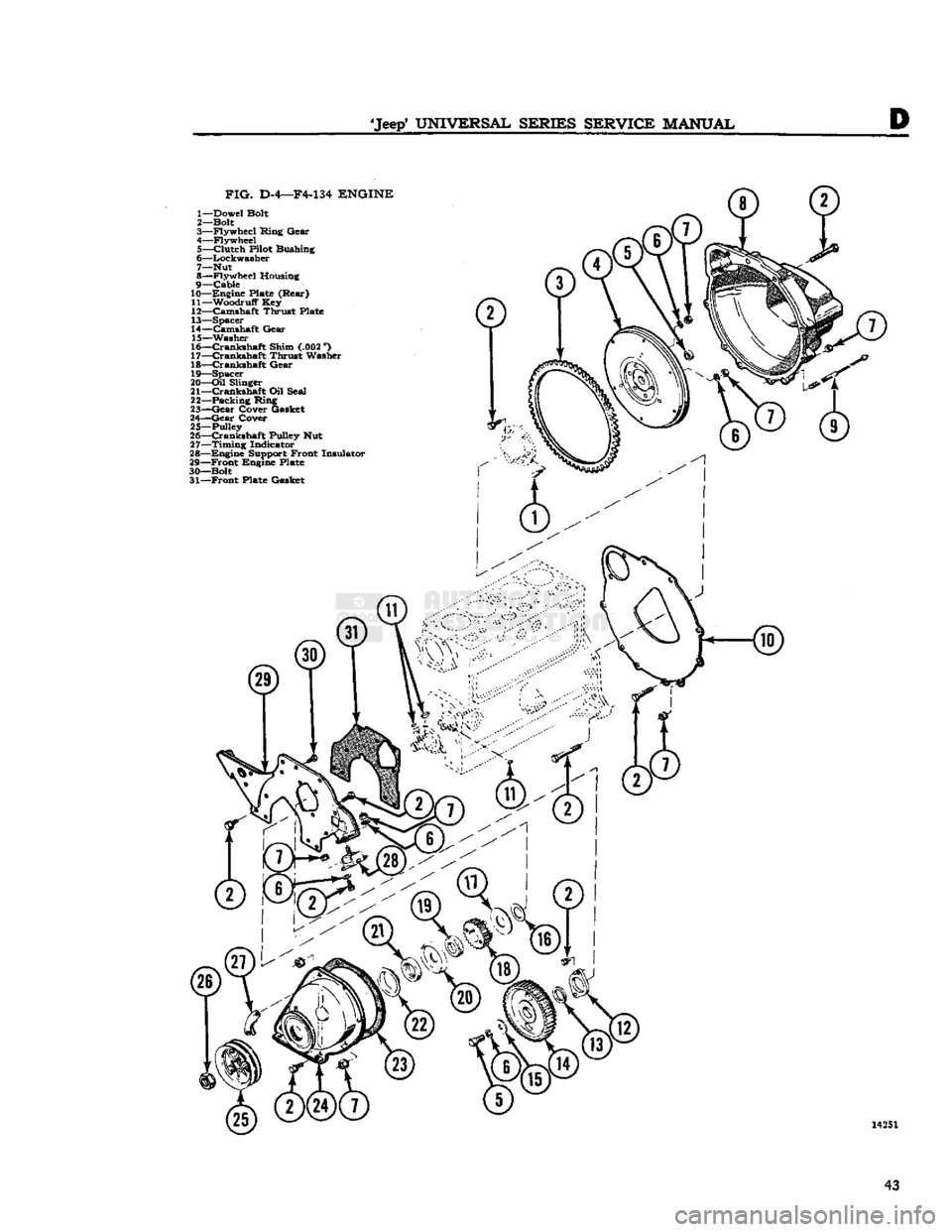
FIG.
D-4—F4-134
ENGINE
1— Dowel Bolt
2— Bolt
3— Flywheel Ring Gear
4— Flywheel 5—
Clutch
Pilot Bushing
6— Lockwasher
7— Nut
8— Flywheel Housing
9—
Cable
10— Engine Plate (Rear)
11— Woodruff Key
12— Camshaft Thrust Plate
13— Spacer
14— Camshaft Gear
15— Washer
16—
Crankshaft
Shim (.002 *)
17—
Crankshaft
Thrust Washer
18—
Crankshaft
Gear
19— Spacer
20—
Oil
Slinger
21—
Crankshaft
Oil Seal
22— Packing Ring
23—
Gear
Cover Gasket
24—
Gear
Cover
25—Pulley
26—
Crankshaft
Pulley Nut
27—
Timing
Indicator
28— Engine Support Front Insulator
29—
Front
Engine Plate
30— Bolt 31—
Front
Plate Gasket 14251
43
Page 44 of 376

D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
Note:
Check
the condition of the rubber O-rings.
Defective O-rings could be the major cause of oil
leakage into cylinders. Always discard and replace
all
O-rings removed as only new O-rings should be installed at reassembly.
D-18.
Ream
Cylinder
Bore Ridges
To
prevent breaking the piston lands, the ridge
at the top of each cylinder bore must be removed
first.
To remove this ridge, use a cylinder ridge
reamer,
as shown in Fig. D-3 following the instruc
tions furnished by the reamer manufacturer. Use
care
not to cut below the top of the upper ring
travel
in the bore. Keep each piston top covered
with
an oil-soaked cloth to prevent cuttings from
falling
into the cylinder.
Note:
This
operation should be performed at this
time before the
engine
is rotated for the sequence
steps
following.
D-19.
Remove Oil Pan
Rotate the
engine
to the upside down position.
Remove the screws and lockwashers that attach
the oil pan to the cylinder block. Remove the oil
pan
and gasket.
Discard
the gasket.
D-20.
Remove Piston and Connecting
Rod
Assemblies
Remove the stamped locking nuts from the lower
end of each connecting rod bearing bolt. Remove
the connecting rod nuts. Remove the bearing cap evenly. Push the connecting rod and piston as
sembly out of the cylinder block with the handle end of a hammer until the piston rings are free from
the cylinder bore. Remove the piston and connecting rod assembly
from
the top of the cylinder block. Reassemble the
connecting rod bearing cap with the bearings in
place in the rod from which it was removed. Rotate
the crankshaft and follow the same procedure until
all
the piston and connecting rod assemblies are
removed.
Pistons and connecting rod assemblies may be removed for repair with the
engine
in the vehicle after draining the cooling system, removing the
oil
pan and the cylinder head, and reaming the ridges as previously described.
D-21.
Remove
Timing
Gear
Cover
Remove the bolts, nuts, and lockwashers, that at
tach
the timing gear cover to the engine. Remove
the cover, timing pointer, and cover gasket.
Dis
card
the gasket. Remove the crankshaft oil seal
from
the timing gear cover and discard the seal. Remove the oil slinger and spacer from the
crank
shaft.
D-22.
Remove
Timing
Gears
Use puller W-172 for pulling both the crankshaft
and
the camshaft gears.
With
the threaded cap-
screws supplied, adapt the puller to the crankshaft
FIG.
D-5—PULLING TIMING GEARS
1—
Puller
W-172 2—
Camshaft
Gear
gear and
pull
the gear.
With
the special hook-type
puller
bolts
that fit behind the camshaft gear
flange,
pull
the camshaft gear. Remove the Wood
ruff
Keys.
D-23.
Remove
Front
End Plate
Remove the screws and lockwashers that attach the
front end plate to the cylinder block. Remove the
front end plate and gasket.
Discard
the gasket.
D-24. Remove
Clutch
Remove four
bolts
and lockwashers diagonally
opposite
that attach the clutch assembly to the
flywheel, leaving two
opposed
bolts
to be
loosened
alternately until the clutch spring pressure is re
lieved.
Then,
support the clutch assembly with
one hand while removing the two remaining bolts.
For
information on disassembly, inspection, repair
and
assembly of the clutch refer to Section I. In
structions for removing the clutch when the
engine
is in the vehicle are also given in Section I.
D-25.
Remove Flywheel
The
flywheel is attached to the crankshaft with two tapered dowel
bolts
and four special bolts.
Remove
these
attaching parts. Use a pry bar be tween the flywheel and the back of the
engine
and
carefully
loosen
the flywheel from the crankshaft.
If
the flywheel is to be removed with the
engine
in
the vehicle, the transmission and clutch must
first be removed as detailed in Section I.
D-26.
Remove
Crankshaft
Slide
the crankshaft thrust washer and all end-play
adjusting
shims off the front end of the crankshaft.
Pull
the two pieces of
rear
main bearing cap packing out of position
between
the side of the bearing cap
and
the cylinder block.
Note
the marks on the bearing caps and cylinder
block for bearing number and position. 44
Page 53 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
D
satisfactory bearing replacement cannot be made
and
it
will
be necessary to regrind the crankshaft.
Install
the bearing lower
half
and the connecting
rod
cap and draw the cap bolt nuts down equally
and
only slightly tight. Move the connecting rod
endwise, one way or the other, on the crankshaft to be sure the bearing is not tight.
Pull
the nuts tighter, first one then the other, a little at a time,
and
keep trying the fit of the rod on the crankshaft by hand until the recommended torque of 35 to 45 lb-ft. [4,8 a 6,2 kg-m.] is reached. If the
bearings are of the correct size, and have been
properly
lubricated with light
engine
oil before in
stallation,
the connecting rod should be easy to
slide back and forth parallel to the
crankpin.
If
the connecting rod is tight on the crankshaft, a
larger
bearing is required. If there is no binding
or
tightness, it is
still
necessary to check clearance
to guard against too
loose
a fit. The use of "Plasti
gage"
or shim stock of the proper size to measure .001" [0,025 mm.] clearance is recommended for
checking
connecting rod bearing clearances.
This
is the same material recommended for checking
crankshaft
main bearings and the method of check
ing is
similar.
Refer to
Par.
D-45 or D-46. Connect
ing rod bearings are fitted to the same clearance as the main bearings but the torque specified for con
necting rod cap
bolts
is different.
D-50.
Connecting
Rod
Side Play
Check
the connecting rod side play with a feeler
gauge
as shown in Fig. D-l8. The side clearance is .004" to .010"
[0,101
a
0,254
mm.].
D-51.
Camshaft and Bearings
The
camshaft is supported at four points in the
cylinder
block. The front is supported in a re placeable, steel-shell, babbit-lined bearing. The
bearing
is pressed into place The other three bear-
FIG.
D-18—CONNECTING
ROD
SIDE
PLAY
ing surfaces are precision machined in the cylinder
block. The camshaft bearings are pressure
lubri
cated through drilled passages in the crankcase.
End
thrust of the camshaft is taken by a thrust plate bolted to the crankcase. The camshaft is
driven
by a silent helical-cut
tooth
timing gear at
the front of the engine. A worm gear, integral with
the camshaft, drives the oil pump and distributor.
The
fuel pump is actuated by an eccentric forged
onto
the camshaft.
Clean
the camshaft thoroughly in cleaning solvent.
Inspect
all camshaft bearing surfaces to determine
if
they are scored or rough. The cam faces must be
perfectly smooth throughout their contact face
and
must not be scored or worn.
D-52.
Camshaft
Front Bearing Replacement
Use
a suitable driver to remove the camshaft front
bearing
from the cylinder block. To install a new
bearing,
align the oil
hole
in the bearing with the
bored oil
hole
in the cylinder block and drive the
bearing
in until the front end of the bearing is
flush
with the front surface of the cylinder block.
Make
sure the oil
hole
is open and clear. It is not
necessary to line-ream the bearing after installation because bearings for replacement are precision
reamed
to the finished size. Do not stake the
bearing.
D-53-
Camshaft End Play
End
play of the camshaft is determined by running
clearance
between
the
rear
face of the camshaft gear and the thrust plate and is established by the
spacer
thickness. The standard clearance is .004"
to .007"
[0,101
a 0,178 mm.] and can be measured by a
dial
indicator. As a general rule this clearance
will
change but little through wear or when a new gear is installed. To predetermine the correct end
float with the gear, spacer, and thrust plate re
moved, measure the thickness of both the thrust
plate and spacer with a micrometer. The thickness
of the spacer should be approximately .006" [0,152 mm.] greater than that of the thrust plate.
When
this is correct and the parts are assembled
and
drawn tightly
together
by the gear retaining
screw,
the end play should
come
within standard
limits.
D-54.
Timing Gears
and
Cover
The
timing gears are mounted at the front of the
engine. Camshaft drive is through helical-cut
timing gears; a steel gear on the crankshaft and a
pressed fiber gear on the camshaft. The gears are keyed to their respective shafts. The camshaft
driven
gear is secured on the front end of the
camshaft by means of a capscrew and a plain
washer.
The crankshaft gear is secured on the
front end of the crankshaft by a nut threaded
onto
the front end of the crankshaft holding the
crank
shaft pulley, crankshaft oil slinger, and the
crank
shaft drive gear spacer. The timing gears are
lubricated
through a jet threaded into the
crank
case directly above the gear contact and oil supplied
through a drilled passage from the front main
bearing.
The timing gears are enclosed by the
sealed timing cover. The oil seal in the cover bears 53
Page 57 of 376

'Jeep5
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
D
Driver
W-238 is equipped
with
an
adapter
ring
which
correctly positions the guides. See Fig. D-23. Start a new exhaust valve guide, blunt (nontapered)
end
first,
into
the valve guide bore in the top of the cylinder block. When properly positioned, the
top end of the guide is exactly
1
"
[25,4 mm.] below
the level of the top of the block as shown in Fig.
D-24.
Start
a new intake valve guide, tapered end
first, into position from the
bottom
of the cylinder
head.
When properly positioned, the end of the
guide is just flush with the end of the valve guide
bore in the cylinder head as shown in Fig. D-24.
Run
a reamer (Tool
C-3 8)
through the new
guides
after they have been correctly positioned.
D-62. Tappets
and
Cover
The
valve tappets are lubricated through oil troughs cast in the crankcase. The troughs are
filled by oil sprayed from the connecting rod ends
and
passages are drilled through the tappet
guides
to
carry
the oil to the tappets. A
groove
around the center of the tappet shank carries the oil up and down the guide.
Check
the threads and fit of the exhaust valve ad
justing
screw in the exhaust valve tappets. The fit of a screw should be such that a wrench is required to
turn
it into or out of the tappet as
these
are of
the self-locking type. Replace the worn part, either
the screw or the tappet, or both, if there is
loose
ness
between
the parts.
D-63.
Crankshaft Rear Bearing Seal
Oil
leakage through the
rear
main bearing is pre vented by a metal supported neoprene lip type
seal
which can readily be installed without remov
ing the crankshaft.
Should
trouble be experienced with oil leaking
from
the
rear
main bearing there are several points
which
should be checked.
a.
Be sure that the identifying paint daub on the
bearing
cap is the same as that appearing on the
center bearing web.
b.
The bearing to crankshaft clearance must not
exceed .0029"
[0,0736
mm.].
c.
Place sealer on the faces of the
rear
bearing cap
from
the
rear
oil
groove
to the oil seal grooves.
d-
Be sure the rubber oil seals extend about 34" [6 mm.] below the
bottom
face of the cap.
e.
Be sure the oil pan gasket is not leaking.
f.
Check
to be sure the oil leak is not at the cam
shaft
rear
bearing expansion plug or from the
crankcase.
D-64.
Floating Oil
Intake •
Refer to Fig. D-25 and D-26.
The
floating oil intake is attached to the
bottom
of the crankcase with two screws. The float and
screen causes it to ride, raise and lower with the
amount of oil in the pan.
This
prevents water or
dirt,
which
may have accumulated in the
bottom
of the oil pan, from circulating through the
engine
because the oil is drawn horizontally from the top
surface.
Whenever removed, the float, screen, and
tube should be cleaned thoroughly to remove any
accumulation
of
dirt.
Also clean the oil pan.
Fluctuating
oil pressure can usually be traced to
an
air leak
between
the oil float support and the
crankcase.
Be
sure the float support flange is flat.
Clean
both
the flange and the crankcase surfaces thoroughly
before installing a new gasket. Be sure the retaining
screws are tight.
D-65. Oil
Pump
The
oil pump is located externally on the left side
of the engine. In operation oil is drawn from the
crankcase
through the floating oil intake then passes through a drilled passage in the crankcase
to the pump from which it is forced through
drilled
passages to the crankshaft and camshaft
bearings. When it is necessary to remove an oil
pump,
first remove the distributor cover and
note
the position of the distributor rotor so that the pump may be reinstalled without disturbing the
ignition timing. To install the pump without dis
turbing
the timing, the pump gear must be cor
rectly
meshed with the camshaft driving gear to
allow
engagement
of the key on the distributor shaft with the pump shaft slot, without changing the position of the distributor rotor. Distributor
can
be installed only in one position as the slot and
driving
key are machined off-center.
The
oil pump consists of an inner and outer rotor
within
the pump body. An oil relief valve is mounted in the pump body which controls the oil
pressure.
To disassemble the pump, Fig. D-27, first remove the gear which is retained by straight
pin.
It
will
be necessary to file off one end of the
pin
before driving it out with a small drift. By re
moving the cover the outer rotor and the inner
rotor
and shaft may be removed through the cover opening.
Failure
of the pump to operate at
full
efficiency may usually be traced to excessive
end float of the rotors or excessive clearance be tween the rotors. The clearance
between
the outer
rotor
and the pump body should also be checked.
Match
the rotors
together
with one
lobe
of the inner
rotor
pushed as far as possible into the notch of the outer rotor. Measure the clearance
between
the
lobes
of the rotors as shown in
Fig.
D-28.
This
clear ance should be .010"
[0,254
mm.] or less.
If
more, replace both rotors. Measure the clearance
between
the outer rotor and the pump body as
shown in Fig. D-29. Should this clearance exceed .012" [0,305 mm.] the fault is probably in the
pump body and it should be replaced. End float
of the rotors is controlled by the thickness of the cover gasket which is made of special material that
can
be only slightly compressed. Never use other
than
a standard factory gasket.
Check
the cover
to be sure the inner surface is not rough or scored
and
that it is flat within .001" [0,025 mm.]
tested
with
feeler
gauges,
Fig. D-30. Measure thickness of
the rotors which must be within .001" [0,025 mm.]
of each other. Assemble the rotors in the pump body and install the cover without the gasket.
When
the cover screws are tightened to normal
tension, there should be interference
between
the
rotors and the cover making it impossible to
turn
the pump shaft by hand. Remove the cover and re- 57
Page 63 of 376
![JEEP DJ 1953 Service Manual
Jeep
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
D
is .004" to .007"
[0,102
a 0,178 mm.] as measured
by a dial indicator. Should a check
show
too little
end play, place a shim of suitable thickness
JEEP DJ 1953 Service Manual
Jeep
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
D
is .004" to .007"
[0,102
a 0,178 mm.] as measured
by a dial indicator. Should a check
show
too little
end play, place a shim of suitable thickness](/manual-img/16/57041/w960_57041-62.png)
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
D
is .004" to .007"
[0,102
a 0,178 mm.] as measured
by a dial indicator. Should a check
show
too little
end play, place a shim of suitable thickness
between
the camshaft shoulder and the spacer. Too much
end play may be corrected by removing shims or
dressing off the spacer a slight amount. See Fig. D-33.
D-82. Install Crankshaft and Bearings
Fit
the three upper main bearings
into
their
respective
locations
in the cylinder block. Fit the
three lower main bearings
into
their respective
bearing caps.
NOTE:
It is
possible
to incorrectly install the front main bearing. The bearing is properly installed in
the cap with the narrower of the two radial oil
grooves
toward the front
edge
of the cap. If this
bearing is not properly installed, the oil
grooves
in
the two halves of the bearing will not match at the
parting line and premature failure of the bearing
will
result.
Lubricate
all bearing surfaces
generously
with
clean, light
engine
oil. Place the crankshaft in
position
in the cylinder block and install the main
bearing caps. Torque the
bolts
65 to 75 lb-ft.
[9,0 a 10,4 kg-m.] rotating the crankshaft after
each bearing cap is
tightened
D-83. Check Crankshaft End-Play
End
play of the crankshaft is set by the running
clearance
between
the crankshaft thrust washer
and the front
face
of the front main bearing. The
standard end play is .004" to .006"
[0,102
a 0,152
mm.] which is controlled by .002"
[0,051
mm.]
shims placed
between
the thrust washer and the
shoulder on the crankshaft. Check the end play
with a dial indicator as shown in
Fig.
D-34. If clear ance is incorrect, adjustment is made by adding or
removing shims.
Install
the thrust washer with the
beveled
inner
edge
toward the front bearing.
10668
FIG.
D-33—VALVES, CAMSHAFT,
AND
TIMING GEARS
1— Nut
2—
Left
Rocker Arm
3—
Rocker
Arm Shaft Spring
4—
Rocker
Shaft
Lock
Screw 5—
Rocker
Shaft
6— Nut 7—
Right
Rocker Arm
8—
Rocker
Arm Shaft Bracket
9—
Intake
Valve Tappet Adjusting Screw
10—
Intake
Valve Upper Retainer
Lock
11—
Oil
Seal
12—
Intake
Valve Spring Upper Retainer 13—
Intake
Valve Spring
14—
Intake
Valve Push Rod 15—
Intake
Valve
16—
Intake
Valve Tappet
17—
Camshaft
18—
Camshaft
Front Bearing
19—
Camshaft
Thrust Plate Spacer
20—
Camshaft
Thrust Plate
21— Bolt and Lockwasher
22— Bolt 13—Lockwasher
24—Camshaft
Gear
Washer 25—
Crankshaft
Gear
26—
Camshaft
Gear
27— Woodruff Key No. 9
28—
Exhaust
Valve Tappet
29— Tappet Adjusting Screw
30—
Spring
Retainer
Lock
31— Roto Cap Assembly
32—
Exhaust
Valve Spring
33—
Exhaust
Valve
34—
Rocker
Shaft Support Stud
35—
Washer
36—
Rocker
Arm Cover Stud 63