2016 NISSAN NOTE light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 1901 of 3641

HOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMSGI-13
< HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M B
GI
N
O P
4Wire color • This shows a code for the color of the wire.
B = Black
W = White
R = Red
G = Green
L = Blue
Y = Yellow
LG = Light Green
BG = Beige
BR = Brown LA = Lavender
OR or O = Orange
P = Pink
PU or V (Violet) = Purple
GY or GR = Gray
SB = Sky Blue
CH = Dark Brown
DG = Dark Green
• When the wire color is striped, the base color is given first, followed by the stripe color as shown below:
Example: L/W = Blue with White Stripe
5 Connector • This means the connector information.
• This unit-side is described by the connector symbols.
Number
Item Description
Revision: August 2015 2016 Versa Note
cardiagn.com
Page 1904 of 3641
GI-16
< HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL >
ABBREVIATIONS
I
K
L
M
N
HOCHeated oxidation catalyst
HPCM Hybrid power train control module
ABBREVIATION DESCRIPTION
I/M Inspection and maintenance
IA Intake air
IAC Idle air control
IAT Intake air temperature
IBA Intelligent brake assist
IC Ignition control
ICC Intelligent cruise control
ICM Ignition control module
IPDM E/R Intelligent power distribution module engine room ISC Idle speed control
ISS Input shaft speed
ITS Information technology suite
ABBREVIATION DESCRIPTION
KS Knock sensor
ABBREVIATION DESCRIPTION
LBC Li-ion battery controller
LCD Liquid crystal display
LCU Local control unit
LDP Lane departure prevention
LDW Lane departure warning
LED Light emitting diode
LH Left-hand
LHD Left-hand drive
LIN Local interconnect network
ABBREVIATION DESCRIPTION
M/T Manual transaxle/transmission
MAF Mass airflow
MAP Manifold absolute pressure
MDU Multi display unit
MI Malfunction indicator
MIL Malfunction indicator lamp
MOD Moving object detection
ABBREVIATION DESCRIPTION
NOX Nitrogen oxides
ABBREVIATION
DESCRIPTION
Revision: August 2015 2016 Versa Note
cardiagn.com
Page 1930 of 3641
GI-42
< BASIC INSPECTION >
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
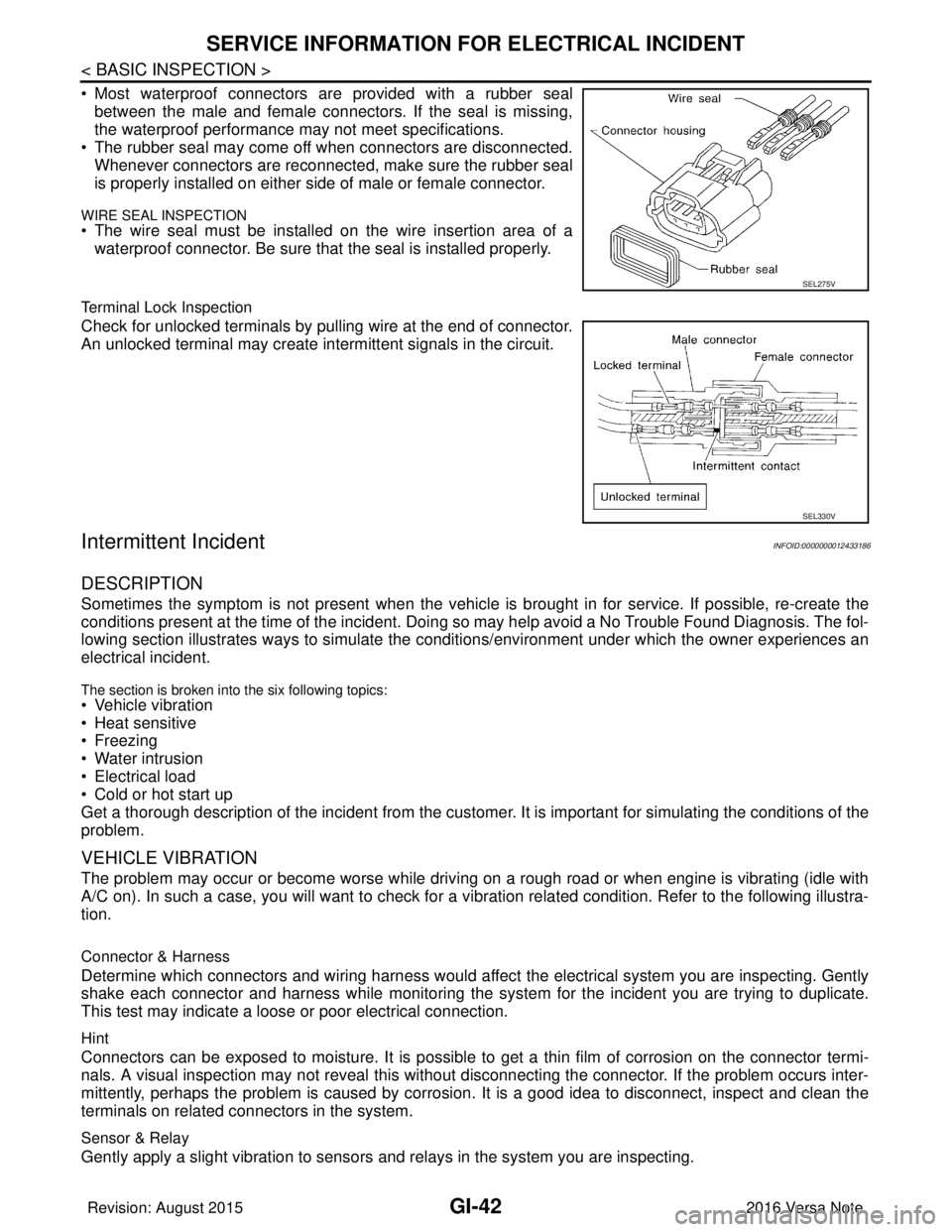
• Most waterproof connectors are provided with a rubber sealbetween the male and female connectors. If the seal is missing,
the waterproof performance may not meet specifications.
• The rubber seal may come off when connectors are disconnected. Whenever connectors are reconnected, make sure the rubber seal
is properly installed on either side of male or female connector.
WIRE SEAL INSPECTION
• The wire seal must be installed on the wire insertion area of awaterproof connector. Be sure that the seal is installed properly.
Terminal Lock Inspection
Check for unlocked terminals by pulling wire at the end of connector.
An unlocked terminal may create intermittent signals in the circuit.
Intermittent IncidentINFOID:0000000012433186
DESCRIPTION
Sometimes the symptom is not present when the vehicle is brought in for service. If possible, re-create the
conditions present at the time of the incident. Doi ng so may help avoid a No Trouble Found Diagnosis. The fol-
lowing section illustrates ways to simulate the condi tions/environment under which the owner experiences an
electrical incident.
The section is broken into the six following topics:
• Vehicle vibration
• Heat sensitive
• Freezing
• Water intrusion
• Electrical load
• Cold or hot start up
Get a thorough description of the incident from the customer. It is important for simulating the conditions of the
problem.
VEHICLE VIBRATION
The problem may occur or become worse while driving on a rough road or when engine is vibrating (idle with
A/C on). In such a case, you will want to check for a vi bration related condition. Refer to the following illustra-
tion.
Connector & Harness
Determine which connectors and wiring harness would affect the electrical system you are inspecting. Gently
shake each connector and harness while monitoring the sy stem for the incident you are trying to duplicate.
This test may indicate a loose or poor electrical connection.
Hint
Connectors can be exposed to moisture. It is possible to get a thin film of corrosion on the connector termi-
nals. A visual inspection may not reveal this without disconnecting the connector. If the problem occurs inter-
mittently, perhaps the problem is caused by corrosion. It is a good idea to disconnect, inspect and clean the
terminals on related connectors in the system.
Sensor & Relay
Gently apply a slight vibration to sensors and relays in the system you are inspecting.
SEL275V
SEL330V
Revision: August 2015 2016 Versa Note
cardiagn.com
Page 1935 of 3641
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENTGI-47
< BASIC INSPECTION >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M B
GI
N
O P
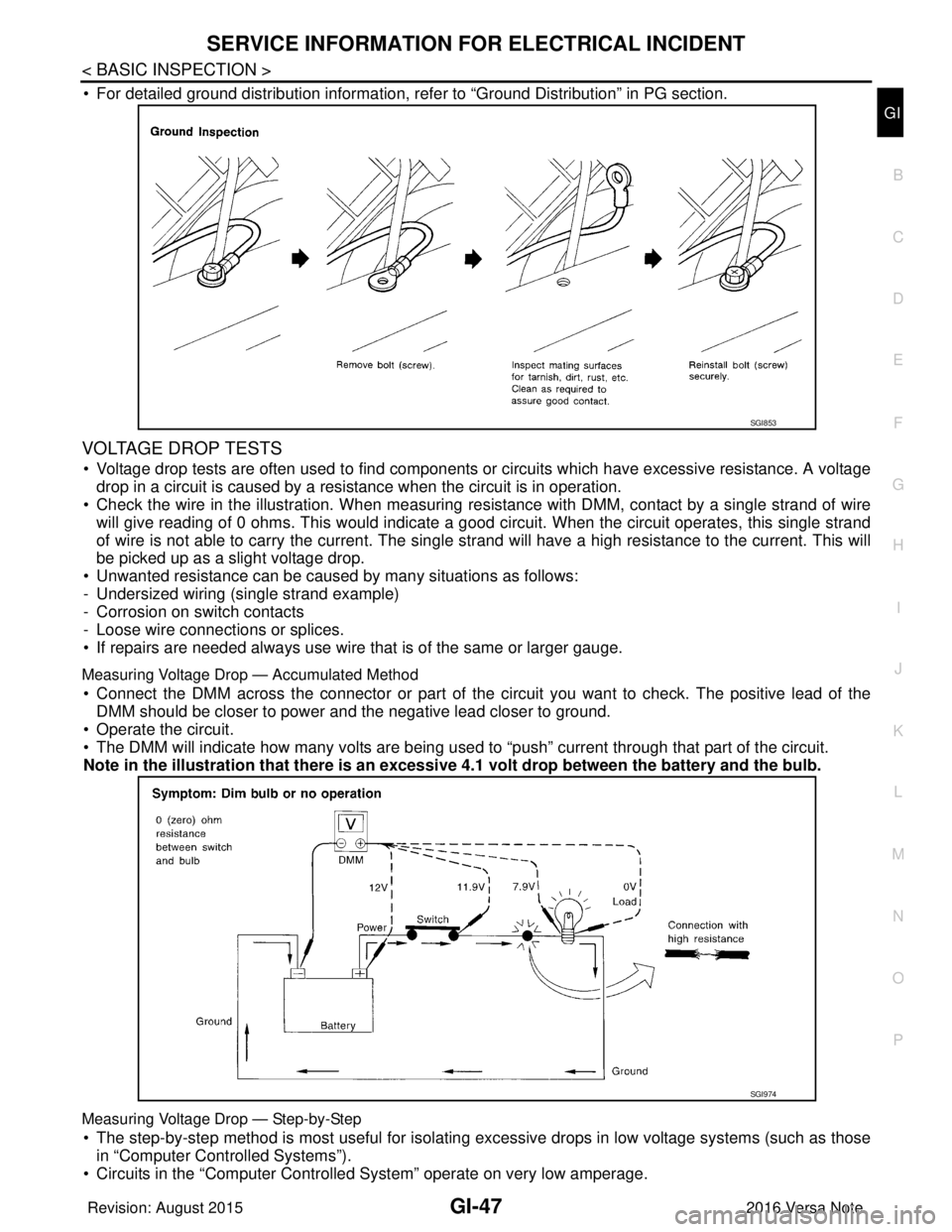
• For detailed ground distribution information, refer to “Ground Distribution” in PG section.
VOLTAGE DROP TESTS
• Voltage drop tests are often used to find components or circuits which have excessive resistance. A voltage drop in a circuit is caused by a resistance when the circuit is in operation.
• Check the wire in the illustration. When measuring re sistance with DMM, contact by a single strand of wire
will give reading of 0 ohms. This would indicate a good circuit. When the circuit operates, this single strand
of wire is not able to carry the current. The single strand will have a high resistance to the current. This will
be picked up as a slight voltage drop.
• Unwanted resistance can be caused by many situations as follows:
- Undersized wiring (single strand example)
- Corrosion on switch contacts
- Loose wire connections or splices.
• If repairs are needed always use wire that is of the same or larger gauge.
Measuring Voltage Drop — Accumulated Method
• Connect the DMM across the connector or part of the ci rcuit you want to check. The positive lead of the
DMM should be closer to power and the negative lead closer to ground.
• Operate the circuit.
• The DMM will indicate how many volts are being used to “push” current through that part of the circuit.
Note in the illustration that there is an excessi ve 4.1 volt drop between the battery and the bulb.
Measuring Voltage Drop — Step-by-Step
• The step-by-step method is most useful for isolating excessive drops in low voltage systems (such as those
in “Computer Controlled Systems”).
• Circuits in the “Computer Controll ed System” operate on very low amperage.
SGI853
SGI974
Revision: August 2015 2016 Versa Note
cardiagn.com
Page 1936 of 3641
GI-48
< BASIC INSPECTION >
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
• The (Computer Controlled) system operations can be adversely affected by any variation in resistance in the
system. Such resistance variation may be caused by poor connection, improper installation, improper wire
gauge or corrosion.
• The step by step voltage drop test can identify a component or wire with too much resistance.
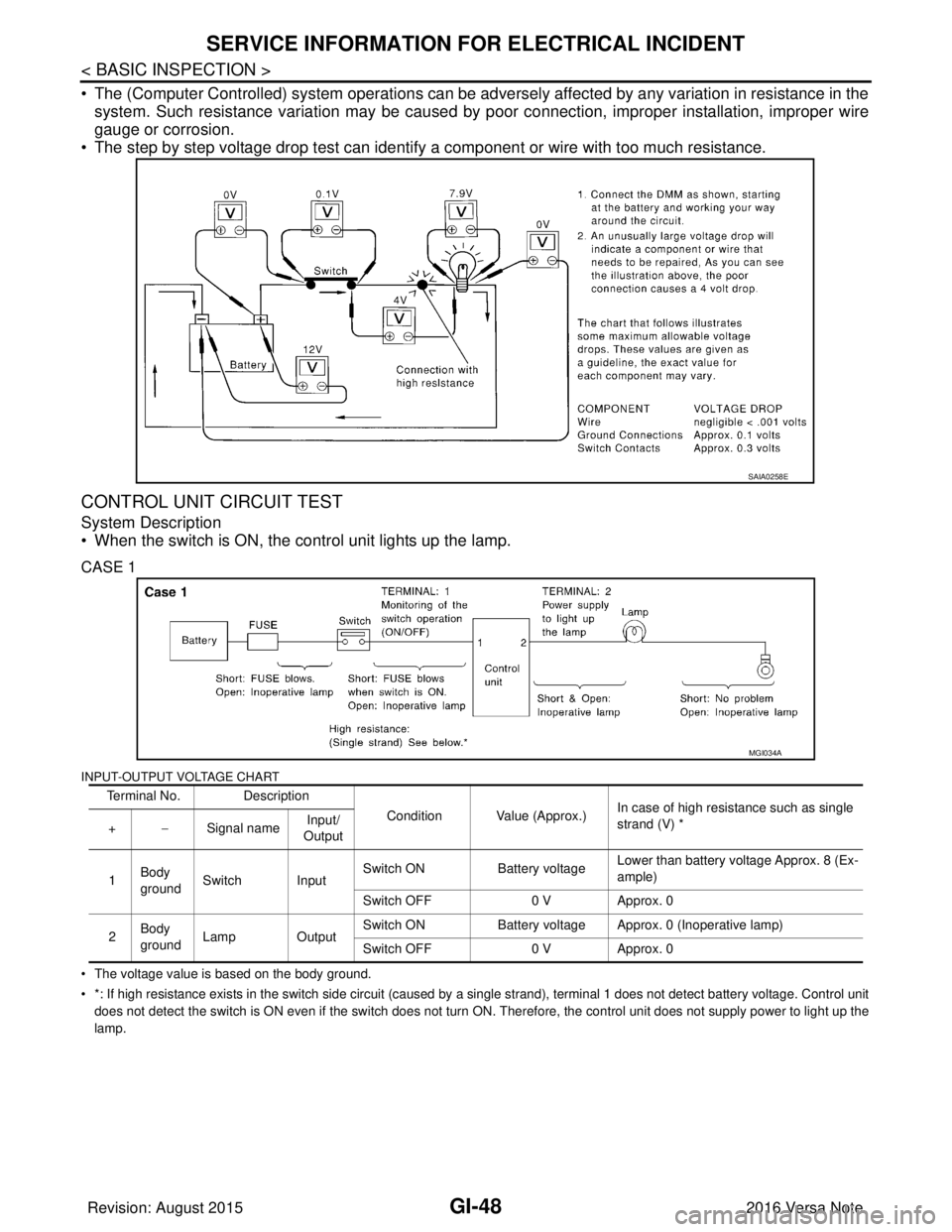
CONTROL UNIT CIRCUIT TEST
System Description
• When the switch is ON, the control unit lights up the lamp.
CASE 1
INPUT-OUTPUT VOLTAGE CHART
• The voltage value is based on the body ground.
• *: If high resistance exists in the switch side circuit (caused by a single strand), terminal 1 does not detect battery voltag e. Control unit
does not detect the switch is ON even if the switch does not turn ON. Therefore, the control unit does not supply power to ligh t up the
lamp.
SAIA0258E
Terminal No. Description
Condition Value (Approx.)In case of high resistance such as single
strand (V) *
+ −Signal name Input/
Output
1 Body
ground Switch Input Switch ON
Battery voltageLower than battery voltage Approx. 8 (Ex-
ample)
Switch OFF 0 V Approx. 0
2 Body
ground
Lamp Output Switch ON
Battery voltage Approx. 0 (Inoperative lamp)
Switch OFF 0 V Approx. 0
MGI034A
Revision: August 2015 2016 Versa Note
cardiagn.com
Page 1945 of 3641
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSESGW-5
< SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
L
M A
B
GW
N
O P
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
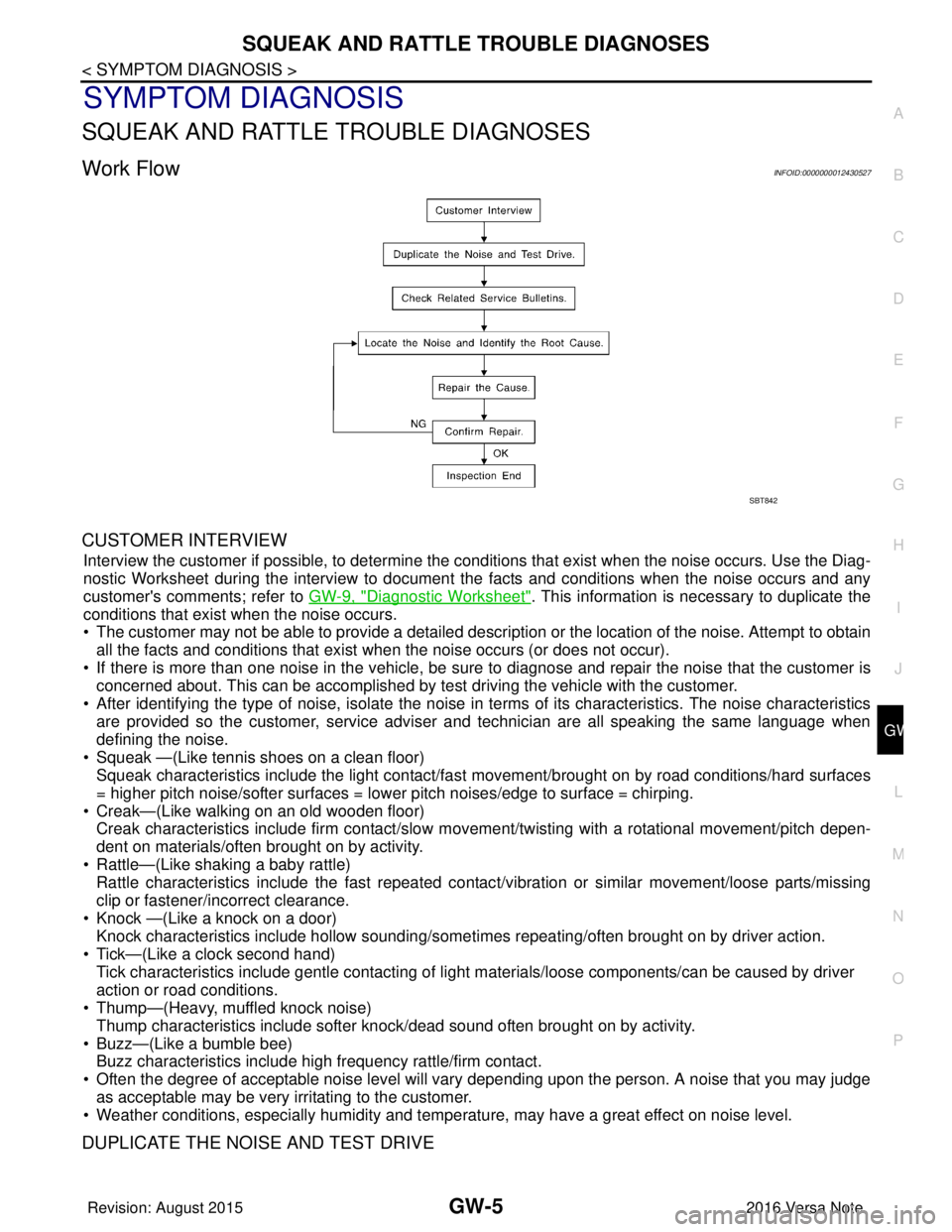
Work FlowINFOID:0000000012430527
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interv iew to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to GW-9, "
Diagnostic Worksheet". This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
• The customer may not be able to provide a detailed descr iption or the location of the noise. Attempt to obtain
all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
• If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer is
concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
• After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
• Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor) Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard surfaces
= higher pitch noise/softer surfaces = lower pitch noises/edge to surface = chirping.
• Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor) Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow mo vement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch depen-
dent on materials/often brought on by activity.
• Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle) Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contac t/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
• Knock —(Like a knock on a door) Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/someti mes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
• Tick—(Like a clock second hand) Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of li ght materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
• Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer k nock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
• Buzz—(Like a bumble bee) Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
• Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
• Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE
SBT842
Revision: August 2015 2016 Versa Note
cardiagn.com
Page 1947 of 3641

SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSESGW-7
< SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
L
M A
B
GW
N
O P
INSTRUMENT PANEL
Most incidents are caused by contact and movement between:
1. Cluster lid A and the instrument panel
2. Acrylic lens and combination meter housing
3. Instrument panel to front pillar finisher
4. Instrument panel to windshield
5. Instrument panel pins
6. Wiring harnesses behind the combination meter
7. A/C defroster duct and duct joint
These incidents can usually be located by tapping or moving the components to duplicate the noise or by
pressing on the components while driving to stop the noi se. Most of these incidents can be repaired by apply-
ing felt cloth tape or silicone spray (in hard to reach areas). Urethane pads can be used to insulate wiring har-
ness.
CAUTION:
Do not use silicone spray to isolate a squeak or ra ttle. If you saturate the area with silicone, you will
not be able to recheck the repair.
CENTER CONSOLE
Components to pay attention to include:
1. Shift selector assembly cover to finisher
2. A/C control unit and cluster lid C
3. Wiring harnesses behind audio and A/C control unit
The instrument panel repair and isolation pr ocedures also apply to the center console.
DOORS
Pay attention to the:
1. Finisher and inner panel making a slapping noise
2. Inside handle escutcheon to door finisher
3. Wiring harnesses tapping
4. Door striker out of alignment causing a popping noise on starts and stops
Tapping or moving the components or pressing on them while driving to duplicate the conditions can isolate
many of these incidents. You can usually insulate the ar eas with felt cloth tape or insulator foam blocks from
the NISSAN Squeak and Rattle Kit (J-50397) to repair the noise.
TRUNK
Trunk noises are often caused by a loose jack or loose items put into the trunk by the owner.
In addition look for:
1. Trunk lid bumpers out of adjustment
2. Trunk lid striker out of adjustment
3. The trunk lid torsion bars knocking together
4. A loose license plate or bracket
Most of these incidents can be repaired by adjusting, se curing or insulating the item(s) or component(s) caus-
ing the noise.
SUNROOF/HEADLINING
Noises in the sunroof/headlining area can often be traced to one of the following:
1. Sunroof lid, rail, linkage or seals making a rattle or light knocking noise
2. Sun visor shaft shaking in the holder
3. Front or rear windshield touching headlining and squeaking
Again, pressing on the components to stop the noise while duplicating the conditions can isolate most of these
incidents. Repairs usually consist of insulating with felt cloth tape.
OVERHEAD CONSOLE (FRONT AND REAR)
Overhead console noises are often caused by the cons ole panel clips not being engaged correctly. Most of
these incidents are repaired by pushing up on the c onsole at the clip locations until the clips engage.
In addition look for:
Revision: August 2015 2016 Versa Note
cardiagn.com
Page 1962 of 3641
GW-22
< REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION >
FRONT DOOR GLASS AND REGULATOR
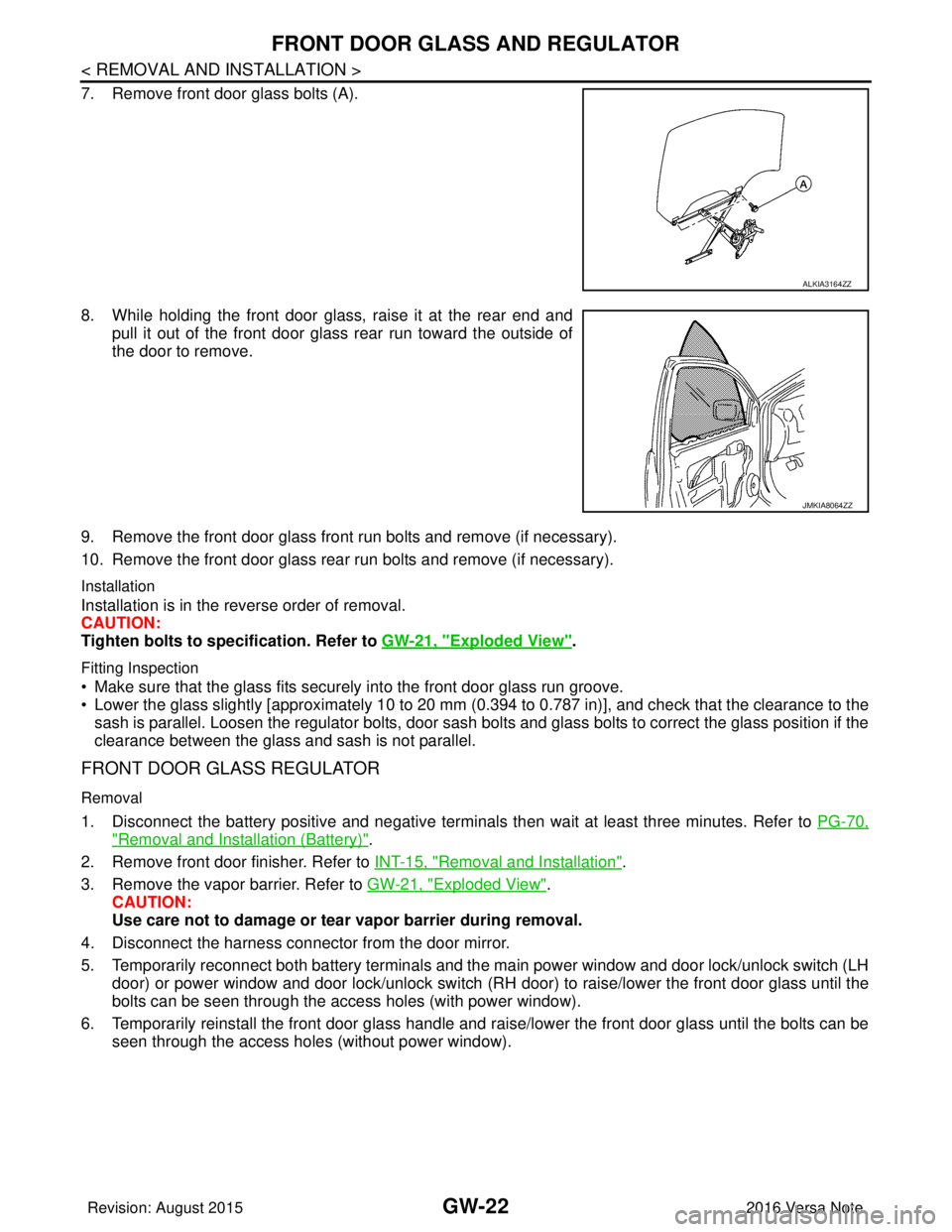
7. Remove front door glass bolts (A).
8. While holding the front door glass, raise it at the rear end andpull it out of the front door glass rear run toward the outside of
the door to remove.
9. Remove the front door glass front run bolts and remove (if necessary).
10. Remove the front door glass rear run bolts and remove (if necessary).
Installation
Installation is in the reverse order of removal.
CAUTION:
Tighten bolts to specification. Refer to GW-21, "
Exploded View".
Fitting Inspection
• Make sure that the glass fits securely into the front door glass run groove.
• Lower the glass slightly [approximately 10 to 20 mm (0.394 to 0.787 in)], and check that the clearance to the
sash is parallel. Loosen the regulator bolts, door sash bolts and glass bolts to correct the glass position if the
clearance between the glass and sash is not parallel.
FRONT DOOR GLASS REGULATOR
Removal
1. Disconnect the battery positive and negative terminal s then wait at least three minutes. Refer to PG-70,
"Removal and Installation (Battery)".
2. Remove front door finisher. Refer to INT-15, "
Removal and Installation".
3. Remove the vapor barrier. Refer to GW-21, "
Exploded View".
CAUTION:
Use care not to damage or tear vapor barrier during removal.
4. Disconnect the harness connector from the door mirror.
5. Temporarily reconnect both battery terminals and the main power window and door lock/unlock switch (LH door) or power window and door lock/unlock switch (RH door) to raise/lower the front door glass until the
bolts can be seen through the access holes (with power window).
6. Temporarily reinstall the front door glass handle and raise/lower the front door glass until the bolts can be seen through the access holes (without power window).
ALKIA3164ZZ
JMKIA8064ZZ
Revision: August 2015 2016 Versa Note
cardiagn.com