2013 YAMAHA YZ125LC checking oil
[x] Cancel search: checking oilPage 127 of 168

5-19
FRONT FORK
CHECKING THE BASE VALVE
1. Inspect:
• Base valve "1"
Wear/damage → Replace.
Contamination → Clean.
• O-ring "2"
Wear/damage → Replace.
• Piston metal "3"
Wear/damage → Replace.
• Spring "4"
Damage/fatigue → Replace base
valve.
• Air bleed screw "5"
Wear/damage → Replace.
CHECKING THE COLLAR
1. Inspect:
• Piston metal "1"
Wear/damage → Replace.
CHECKING THE FORK SPRING
1. Measure:
• Fork spring free length "a"
Out of specification → R e p l a c e .
CHECKING THE INNER TUBE
1. Inspect:
• Inner tube surface "a"
Score marks → Repair or replace.
Use #1,000 grit wet sandpaper.
Damaged oil lock piece → Re-
place.
• Inner tube bends
Out of specification → R e p l a c e .
Use the dial gauge "1".
The bending value is shown by one
half of the dial gauge reading.
Do not attempt to straighten a bent
inner tube as this may dangerous-
ly weaken the tube.
CHECKING THE OUTER TUBE
1. Inspect:
• Outer tube "1"
Score marks/wear/damage →
Replace.
CHECKING THE ADJUSTER
1. Inspect:
•Adjuster "1"
• O-ring "2"
Wear/damage → Replace.
ASSEMBLING THE FRONT FORK
1. Wash the all parts in a clean sol-
vent.
2. Stretch the damper assembly ful-
ly.
3. Fill:
• Front fork oil "1"
To damper assembly.
• Be sure to use recommended
fork oil. If other oils are used,
they may have an excessively ad-
verse effect on the front fork per-
formance.
• Never allow foreign materials to
enter the front fork.
4. After filling, pump the damper as-
sembly "1" slowly up and down
(about 200 mm (7.9 in) stroke)
several times to bleed the damper
assembly of air.
Be careful not to excessive full stroke.
A stroke of 200 mm (7.9 in) or more
will cause air to enter. In this case, re-
peat the steps 2 to 4.
5. Measure:
• Oil level (left and right) "a"
Out of specification → A d j u s t .
Fork spring free length
"a":
454 mm (17.9 in)
in)
Inner tube bending limit:
0.2 mm (0.008 in)
Recommended oil:
Suspension oil "S1"
Oil capacity:
199 cm
3 (7.00 Imp oz,
6.73 US oz)
Standard oil level "a":
145–148 mm (5.71–5.83
in)
From top of fully
stretched damper as-
sembly.
Page 134 of 168
5-26
HANDLEBAR
REMOVING THE BRAKE MASTER
CYLINDER
1. Remove:
• Brake master cylinder bracket "1"
• Brake master cylinder "2"
• Do not let the brake master cylin-
der hang on the brake hose.
• Keep the brake master cylinder
cap side horizontal to prevent air
from coming in.
REMOVING THE GRIP
1. Remove:
•Grip "1"
Blow in air between the handlebar or
tube guide and the grip. Then remove
the grip which has become loose.
CHECKING THE HANDLEBAR
1. Inspect:
• Handlebar "1"
Bends/cracks/damage → Re-
place.
Do not attempt to straighten a bent
handlebar as this may dangerous-
ly weaken the handlebar.
ASSEMBLING THE THROTTLE
1. Remove:
• Grip (right) "1"
Apply the adhesive on the tube
guide "2".
• Before applying the adhesive, wipe
off grease or oil on the tube guide
surface "a" with a lacquer thinner.
• Align the mating mark "b" on the
grip (right) with the slot "c" in the
tube guide.
2. Install:
• Grip cap (upper) "1"
• Grip cap (lower) "2"
• Bolt (grip cap) "3"
Temporarily tighten the bolts (grip
cap).
INSTALLING THE HANDLEBAR
1. Install:
• Handlebar lower holder "1"
• Washer "2"
• Nut (handlebar lower holder) "3"
• Install the handlebar lower holder
with its side having the greater dis-
tance "a" from the mounting bolt
center facing forward.
• Apply the lithium soap base grease
on the thread of the handlebar low-
er holders.
• Installing the handlebar lower hold-
er in the reverse direction allows the
front-to-rear offset amount of the
handlebar position to be changed.
• Do not tighten the nuts yet.
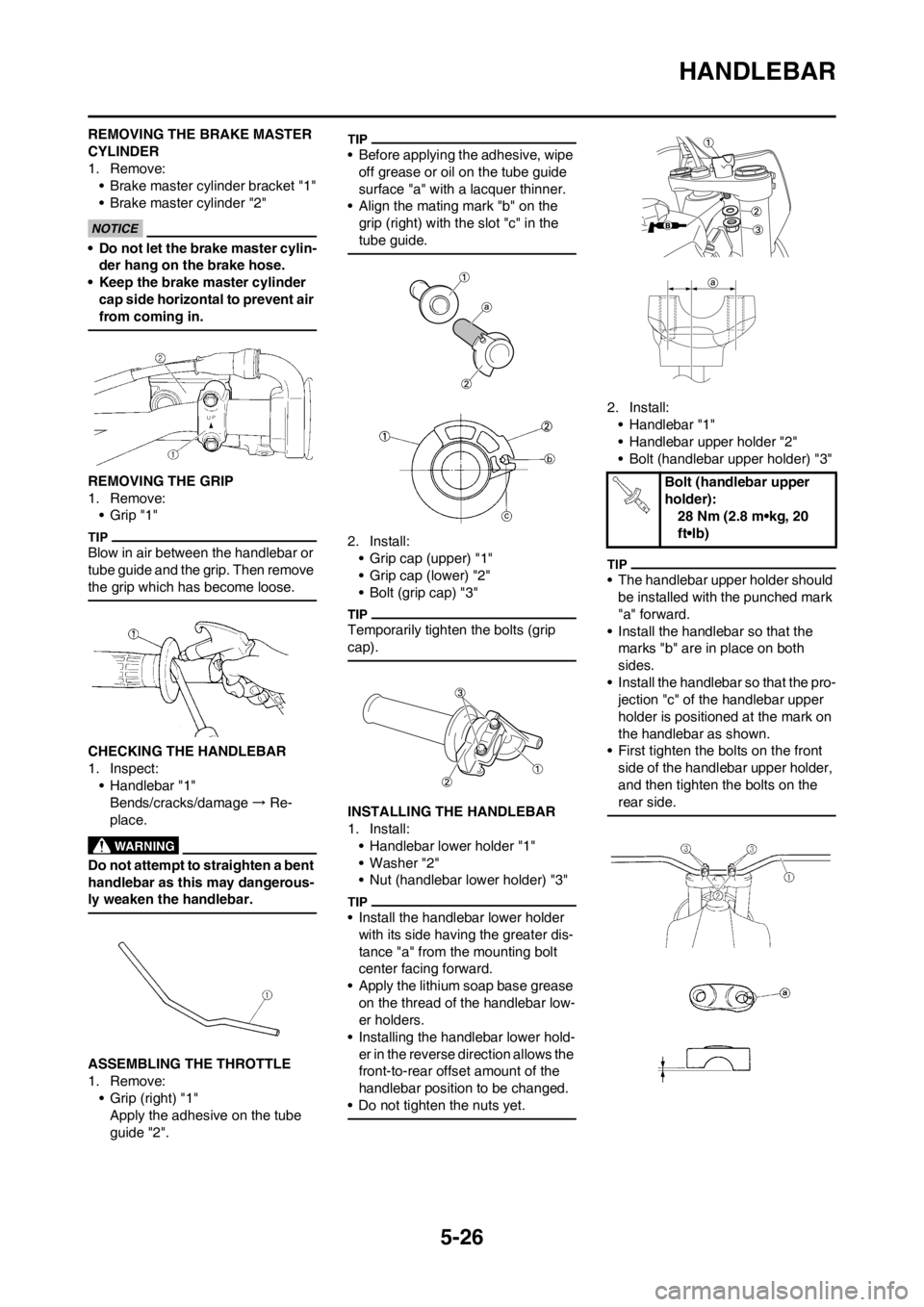
2. Install:
• Handlebar "1"
• Handlebar upper holder "2"
• Bolt (handlebar upper holder) "3"
• The handlebar upper holder should
be installed with the punched mark
"a" forward.
• Install the handlebar so that the
marks "b" are in place on both
sides.
• Install the handlebar so that the pro-
jection "c" of the handlebar upper
holder is positioned at the mark on
the handlebar as shown.
• First tighten the bolts on the front
side of the handlebar upper holder,
and then tighten the bolts on the
rear side.
Bolt (handlebar upper
holder):
28 Nm (2.8 m•kg, 20
ft•lb)
Page 143 of 168

5-35
SWINGARM
HANDLING NOTE
Support the machine securely so
there is no danger of it falling over.
REMOVING THE CAP
1. Remove:
• Left cap "1"
Remove with a slotted-head screw-
driver inserted under the mark "a" on
the left cap.
REMOVING THE BEARING
1. Remove:
• Bearing "1"
Remove the bearing by pressing its
outer race.
CHECKING THE SWINGARM
1. Inspect:
• Bearing "1"
• Bushing "2"
Free play exists/unsmooth revolu-
tion/rust → Replace bearing and
bushing as a set.
2. Inspect:
• Oil seal "3"
Damage →Replace.
CHECKING THE RELAY ARM
1. Inspect:
• Bearing "1"
•Collar "2"
Free play exists/unsmooth revolu-
tion/rust → Replace bearing and
collar as a set. 2. Inspect:
• Oil seal "3"
Damage → Replace.
CHECKING THE CONNECTING
ROD
1. Inspect:
•Bearing "1"
• Collar "2"
Free play exists/unsmooth revolu-
tion/rust →Replace bearing and
collar as a set.
2. Inspect:
• Oil seal "3"
Damage →Replace.
INSTALLING THE BEARING AND
OIL SEAL
1. Install:
•Bearing "1"
• Oil seal "2"
To swingarm.
• Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the bearing when install-
ing.
• Install the bearing by pressing it on
the side having the manufacture's
marks or numbers.
• First install the outer and then the
inner bearings to a specified depth
from inside.
2. Install:
• Bearing "1"
• Washer "2"
• Oil seal "3"
To relay arm.
• Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the bearing when install-
ing.
• Install the bearing by pressing it on
the side having the manufacture's
marks or numbers.
• Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the washer.
3. Install:
• Bearing "1"
• Oil seal "2"
To connecting rod.
• Apply the molybdenum disulfide
grease on the bearing when install-
ing.
• Install the bearing by pressing it on
the side having the manufacture's
marks or numbers.
Installed depth of bear-
ing:
Outer "a": 0 mm (0 in)
Inner "b": 6.5 mm (0.26
in)
Installed depth of bear-
ing "a":
0 mm (0 in)
Installed depth of bear-
ing "a":
0 mm (0 in)
Page 148 of 168
5-40
REAR SHOCK ABSORBER
HANDLING NOTE
• Support the machine securely so
there is no danger of it falling
over.
• This rear shock absorber is pro-
vided with a separate type tank
filled with high-pressure nitro-
gen gas. To prevent the danger
of explosion, read and under-
stand the following information
before handling the shock ab-
sorber. The manufacturer can
not be held responsible for prop-
erty damage or personal injury
that may result from improper
handling.
• Never tamper or attempt to dis-
assemble the cylinder or the
tank.
• Never throw the rear shock ab-
sorber into an open flame or
other high heat. The rear shock
absorber may explode as a re-
sult of nitrogen gas expansion.
• Be careful not to damage any
part of the gas tank. A damaged
gas tank will impair the damp-
ing performance or cause a
malfunction.
• Take care not to scratch the
contact surface of the piston
rod with the cylinder; or oil
could leak out.
• Never attempt to remove the
plug at the bottom of the nitro-
gen gas tank. It is very danger-
ous to remove the plug.
• When scrapping the rear shock
absorber, follow the instruc-
tions on disposal.
NOTES ON DISPOSAL (YAMAHA
DEALERS ONLY)
Before disposing the rear shock ab-
sorber, be sure to extract the nitrogen
gas from valve "1". Wear eye protec-
tion to prevent eye damage from es-
caping gas and/or metal chips.
To dispose of a damaged or worn-
out rear shock absorber, take the
unit to your Yamaha dealer for this
disposal procedure.
REMOVING THE BEARING
1. Remove:
• Stopper ring (upper bearing) "1"
Press in the bearing while pressing its
outer race and remove the stopper
ring.
2. Remove:
• Upper bearing "1"
Remove the bearing by pressing its
outer race.
3. Remove:
• Lower bearing "1"
Remove the bearing by pressing its
outer race.
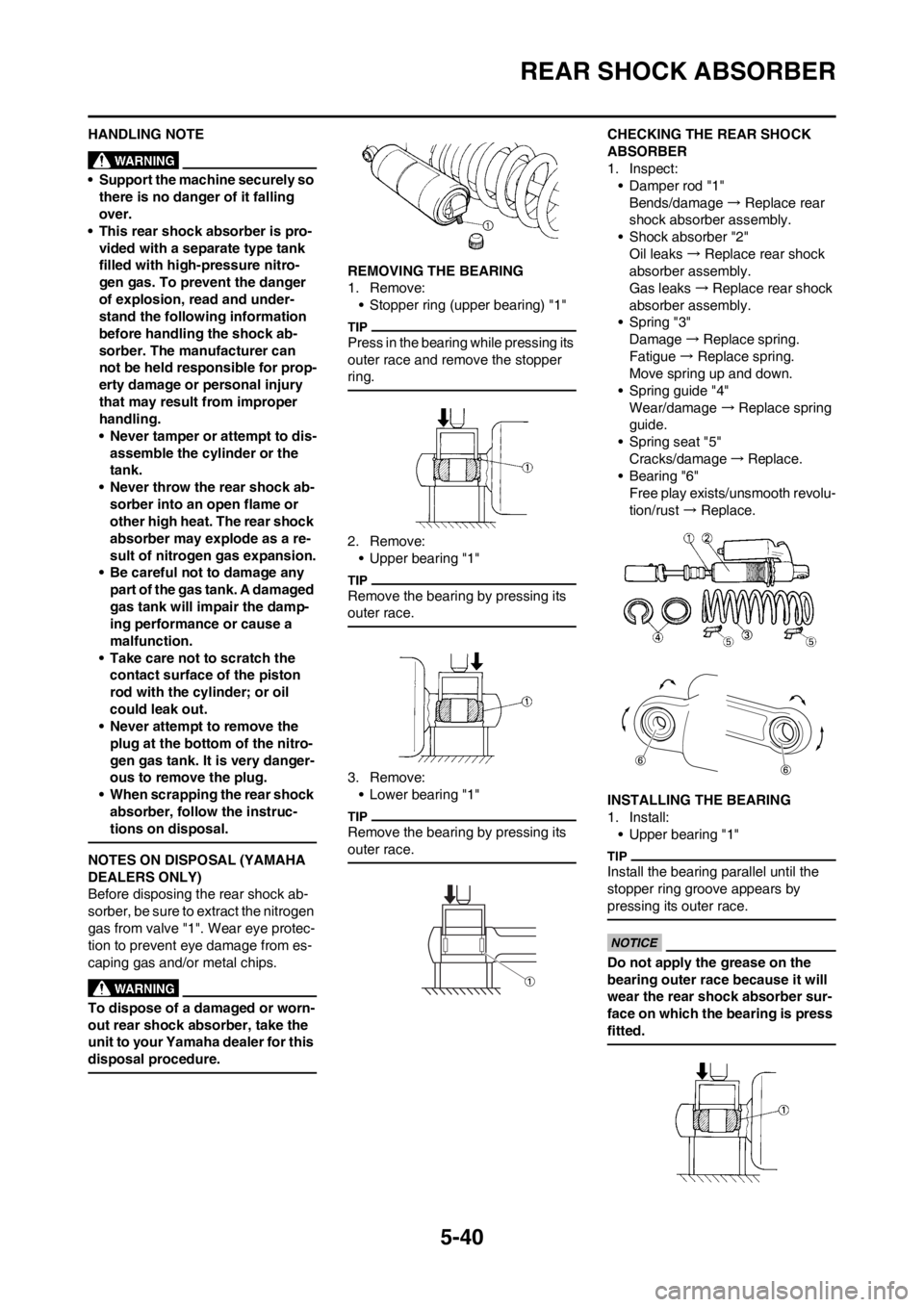
CHECKING THE REAR SHOCK
ABSORBER
1. Inspect:
• Damper rod "1"
Bends/damage → Replace rear
shock absorber assembly.
• Shock absorber "2"
Oil leaks → Replace rear shock
absorber assembly.
Gas leaks → Replace rear shock
absorber assembly.
• Spring "3"
Damage → Replace spring.
Fatigue → Replace spring.
Move spring up and down.
• Spring guide "4"
Wear/damage → Replace spring
guide.
• Spring seat "5"
Cracks/damage → Replace.
• Bearing "6"
Free play exists/unsmooth revolu-
tion/rust → Replace.
INSTALLING THE BEARING
1. Install:
• Upper bearing "1"
Install the bearing parallel until the
stopper ring groove appears by
pressing its outer race.
Do not apply the grease on the
bearing outer race because it will
wear the rear shock absorber sur-
face on which the bearing is press
fitted.
Page 153 of 168

6-3
IGNITION SYSTEM
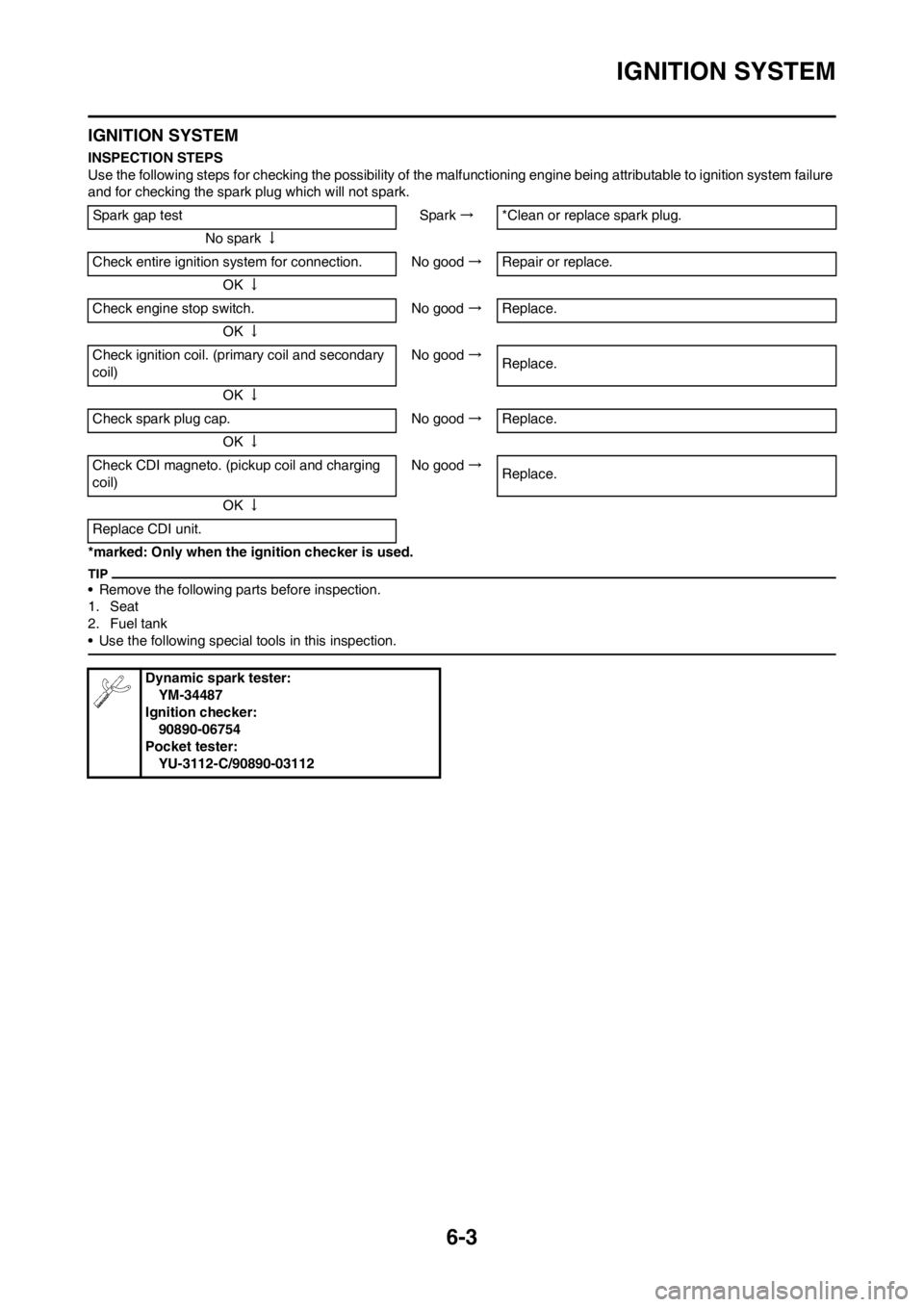
IGNITION SYSTEM
INSPECTION STEPS
Use the following steps for checking the possibility of the malfunctioning engine being attributable to ignition system failure
and for checking the spark plug which will not spark.
*marked: Only when the ignition checker is used.
• Remove the following parts before inspection.
1. Seat
2. Fuel tank
• Use the following special tools in this inspection.
Spark gap test Spark →*Clean or replace spark plug.
No spark ↓
Check entire ignition system for connection. No good →Repair or replace.
OK ↓
Check engine stop switch. No good →Replace.
OK ↓
Check ignition coil. (primary coil and secondary
coil)No good →
Replace.
OK ↓
Check spark plug cap. No good →Replace.
OK ↓
Check CDI magneto. (pickup coil and charging
coil)No good →
Replace.
OK ↓
Replace CDI unit.
Dynamic spark tester:
YM-34487
Ignition checker:
90890-06754
Pocket tester:
YU-3112-C/90890-03112
Page 154 of 168

6-4
IGNITION SYSTEM
SPARK GAP TEST
1. Disconnect the spark plug cap
from spark plug.
2. Connect the dynamic spark tester
"1" (ignition checker "2") as
shown.
• Ignition coil "3"
• Spark plug "4"
A. For USA and CDN
B. Except for USA and CDN
3. Kick the kickstarter crank.
4. Check the ignition spark gap.
5. Start engine, and increase spark
gap until misfire occurs. (for USA
and CDN only)
CHECKING THE COUPLERS,
LEADS AND IGNITION COIL
CONNECTION
1. Check:
• Couplers and leads connection
Rust/dust/looseness/short-cir-
cuit → Repair or replace. CHECKING THE ENGINE STOP
SWITCH
1. Inspect:
• Engine stop switch conduction
Not conductive while it is pushed →
Replace.
Conductive while it is freed → Re-
place.
Set the tester selection position to "
Ω × 1".
CHECKING THE IGNITION COIL
1. Inspect:
• Primary coil resistance
Out of specification → R e p l a c e .
2. Inspect:
• Secondary coil resistance
Out of specification → R e p l a c e .
• Remove the spark plug cap by turn-
ing it counterclockwise and inspect.
• Install the spark plug cap by turning
it clockwise until it is tight.
CHECKING THE SPARK PLUG
CAP
1. Inspect:
• Spark plug cap
Loose connection → T i g h t e n .
Deteriorated/damaged → Re-
place.
• Spark plug cap resistance
Out of specification → R e p l a c e . Minimum spark gap:
6.0 mm (0.24 in)
Tester (+) lead→Black/White lead
"1"
Tester (-) lead→Black lead "2"
Result
Conductive (while the
engine stop switch is
pushed)
Tester (+) lead→Yellow lead "1"
Tester (-) lead→Black lead "2"
Primary
coil resis-
tanceTester se-
lector posi-
tion
0.24–0.36
Ω at 20 °C
(68 °F) Ω × 1
Tester (+) lead→Spark plug lead
"1"
Tester (-) lead→Yellow lead "2"
Secondary
coil resis-
tanceTester se-
lector posi-
tion
5.7–8.5
kΩat 20 °C
(68 °F) kΩ × 1
Tester (+) lead→Spark plug lead
terminal "1"
Tester (-) lead→Spark plug termi-
nal "2"
Spark plug
cap resis-
tanceTester se-
lector posi-
tion
4–6 kΩ at
20 °C (68
°F) kΩ × 1
Page 155 of 168
6-5
IGNITION SYSTEM
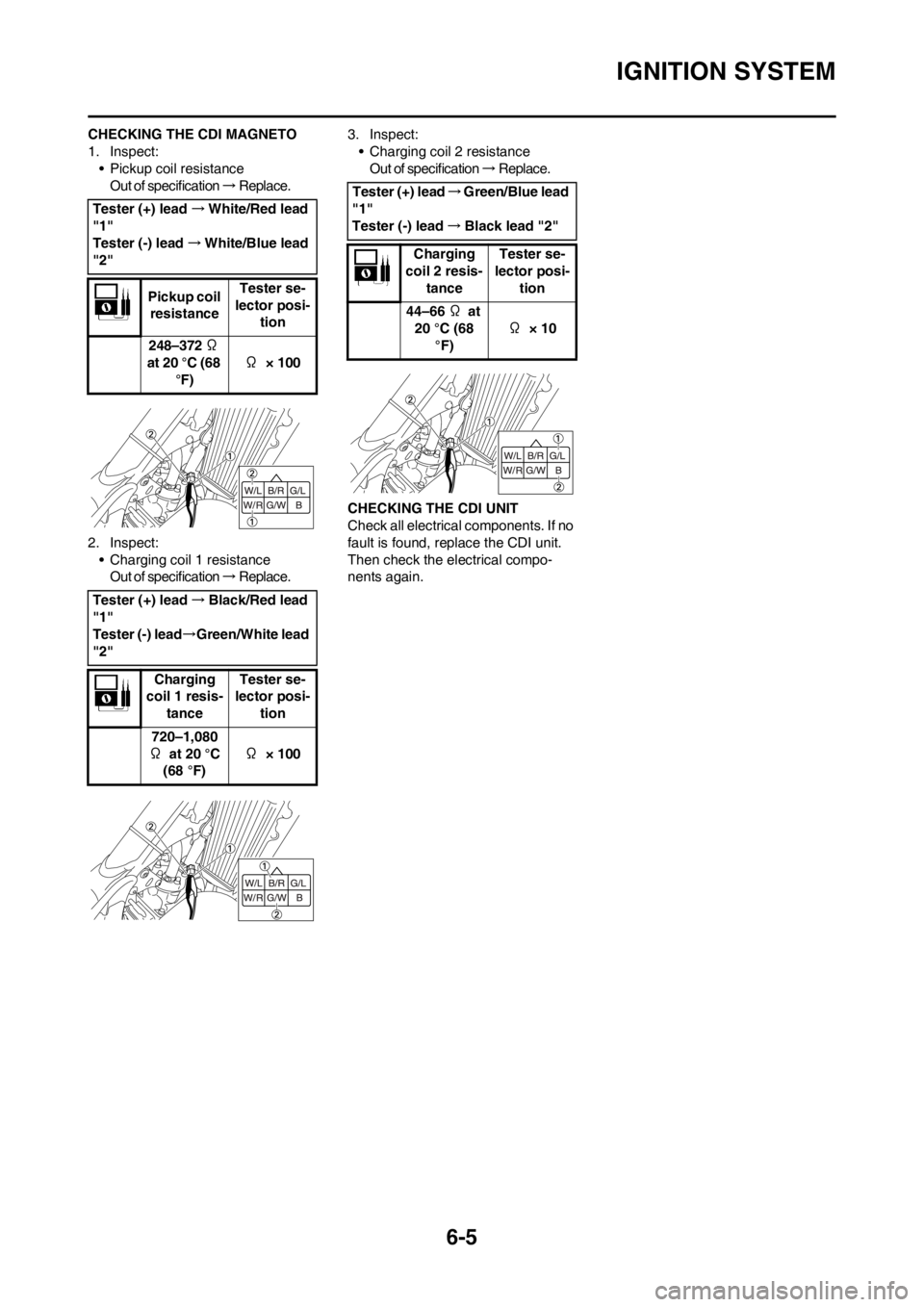
CHECKING THE CDI MAGNETO
1. Inspect:
• Pickup coil resistance
Out of specification → R e p l a c e .
2. Inspect:
• Charging coil 1 resistance
Out of specification → R e p l a c e . 3. Inspect:
• Charging coil 2 resistance
Out of specification → R e p l a c e .
CHECKING THE CDI UNIT
Check all electrical components. If no
fault is found, replace the CDI unit.
Then check the electrical compo-
nents again. Tester (+) lead→White/Red lead
"1"
Tester (-) lead→White/Blue lead
"2"
Pickup coil
resistanceTester se-
lector posi-
tion
248–372 Ω
at 20 °C (68
°F)Ω × 100
Tester (+) lead→Black/Red lead
"1"
Tester (-) lead→Green/White lead
"2"
Charging
coil 1 resis-
tanceTester se-
lector posi-
tion
720–1,080
Ω at 20 °C
(68 °F)Ω × 100
Tester (+) lead→Green/Blue lead
"1"
Tester (-) lead→Black lead "2"
Charging
coil 2 resis-
tanceTester se-
lector posi-
tion
44–66 Ω at
20 °C (68
°F)Ω × 10
Page 161 of 168

7-6
CHASSIS
CHANGE OF THE HEAT RANGE
OF SPARK PLUGS
Judging from the discoloration of
spark plugs, if they are found improp-
er, it can be corrected by the following
two methods; changing carburetor
settings and changing the heat range
of spark plug.
• In principle, it is advisable to first
use spark plugs of standard heat
range, and judging from the discol-
oration of spark plugs, adjust carbu-
retor settings.
• If the calibration No. of the main jet
must be changed by ±30, it is advis-
able to change the heat range of
spark plugs and newly select the
proper main jet.
• When checking the discoloration of
spark plugs, be sure to stop the en-
gine immediately after a run and
check.
• Avoid racing.
• When changing the heat range of
spark plugs, never attempt to
change it more than ±1 rank.
• When using a spark plug other than
standard, check its heat range
against the standard and check that
it is a resistance type.
• Note that even if the discoloration
seems proper, it may slightly vary
with the spark plug maker and oil in
use.
CHASSIS
SELECTION OF THE SECONDARY
REDUCTION RATIO (SPROCKET)
• It is generally said that the second-
ary gear ratio should be reduced for
a longer straight portion of a speed
course and should be increased for
a course with many corners. Actual-
ly, however, as the speed depends
on the ground condition of the day
of the race, be sure to run through
the circuit to set the machine suit-
able for the entire course.
• In actuality, it is very difficult to
achieve settings suitable for the en-
tire course and some settings may
be sacrificed. Thus, the settings
should be matched to the portion of
the course that has the greatest ef-
fect on the race result. In such a
case, run through the entire course
while making notes of lap times to
find the best balance; then, deter-
mine the secondary reduction ratio.
• If a course has a long straight por-
tion where a machine can run at
maximum speed, the machine is
generally set such that it can devel-
op its maximum revolutions toward
the end of the straight line, with care
taken to avoid the engine over-rev-
ving.
Riding technique varies from rider to
rider and the performance of a ma-
chine also vary from machine to ma-
chine. Therefore, do not imitate other
rider's settings from the beginning but
choose your own setting according to
the level of your riding technique.
DRIVE AND REAR WHEEL
SPROCKETS SETTING PARTSTIRE PRESSURE
Tire pressure should be adjust to suit
the road surface condition of the cir-
cuit.
• Under a rainy, muddy, sandy, or
slippery condition, the tire pressure
should be lower for a larger area of
contact with the road surface.
• Under a stony or hard road condi-
tion, the tire pressure should be
higher to prevent a flat tire.
FRONT FORK SETTING
The front fork setting should be made
depending on the rider's feeling of an
actual run and the circuit conditions.
The front fork setting includes the fol-
lowing three factors:
1. Setting of air spring characteris-
tics
• Change the fork oil amount.
2. Setting of spring preload
• Change the spring.
3. Setting of damping force
• Change the compression damp-
ing.
• Change the rebound damping.
The spring acts on the load and
the damping force acts on the
cushion travel speed.
CHANGE IN AMOUNT AND
CHARACTERISTICS OF FORK OIL
Damping characteristic near the final
stroke can be changed by changing
the fork oil amount. Standard spark
plugBR9EVX/NGK
(resistance
type)
Secondary reduction ratio =
Number of rear wheel sprocket
teeth/Number of drive sprocket
teeth
Standard second-
ary reduction ratio3.692 (48/13)
Part name Size Part number
Drive
sprocket
"1"
(STD) 13T 9383B-13218
Rear wheel
sprocket
"2"
47T 1C3-25447-00
(STD) 48T 1C3-25448-00
49T 1C3-25449-00
50T 1C3-25450-00
51T 1C3-25451-00
52T 1C3-25452-00
Standard tire pressure:
100 kPa (1.0 kgf/cm2,
15 psi)
Extent of adjustment:
60–80 kPa (0.6–0.8
kgf/cm
2, 9.0–12 psi)
Extent of adjustment:
100–120 kPa (1.0–1.2
kgf/cm
2, 15–18 psi)