Page 634 of 796

08-74850-03
Problem Possible Cause Action
Increased pedal
stroke
Air in brake line Bleed air
Oil leak Repair
Worn brake pad Replace
Excessive clearance between push rod and master
cylinderAdjust
Worn or damaged piston seal Replace
Brake dragging Parking brake is not fully released Replace
Incorrect adjustment of parking brake Adjust
Incorrectly adjusted clearance of parking brake shoe Adjust
Faulty brake pedal return spring Replace
Incorrectly adjusted free play of brake pedal Adjust
Faulty master cylinder Replace
Lack of lubrication in sliding parts Lubricate
Faulty brake booster (vacuum leak) Repair
Poor parking brake Wear, hardening or poor contact of brake pad Replace
Oil or water on lining Repair or replace
Fixed or broken parking brake cable Replace
Excessive stroke of brake lever Adjust notch
Faulty auto clearance adjuster Repair
Increased stroke of
parking brake leverLoosened parking brake cable Adjust or replace
Incorrectly adjusted parking brake cable Adjust
Defective automatic lining clearance adjuster Repair or replace
Worn brake lining Replace
Page 636 of 796
08-94850-03
Measure the disc thickness at over four
points.
If any of measured points is below the wear
limit, replace the brake disc with new one. 1.
2.
Clean the dissembled components and visually check the followings:
- Wear, rust and damage on the cylinder and piston
- Damage, crack and wear on cylinder body and guide pin
- Uneven wear and oil contamination on pad
- Damage and tear on boot
- Scratch and bending on disc plate
▶Pad Thickness
Remove the front tire.
Measure the pad thickness and replace it if it
is below the wear limit. 1.
2.
New pad Wear limit
28.0 mm 25.4 mm
▶Brake Disc Thickness
New pad Wear limit
10.5 mm 2 mm
5. INSPECTION
1) Front Brake System
Replace the brake pads at both sides as a
set.
Page 638 of 796
08-114850-03
Clean the dissembled components and visually check the followings:
- Wear, rust and damage on the cylinder and piston
- Damage, crack and wear on cylinder body and guide pin
- Uneven wear and oil contamination on pad
- Damage and tear on boot
- Scratch and bending on disc plate
Remove the rear tire.
Measure the pad thickness and replace it if it
is below the wear limit. 1.
2.
New pad Wear limit
20.0 mm 18.4 mm
Replace the brake pads at both sides as a
set.
Measure the disc thickness at over ten
points.
If any of measured points is below the wear
limit, replace the brake disc with new one. 1.
2.
New pad Wear limit
10 mm 2 mm
2) Rear Brake System
Pad Thickness ▶
Brake Disc Thickness ▶
Page 671 of 796
09-254891-01
▶DUMP (ESP is working) Mode
The pressure decreases just before the wheel speed drops and the wheels are locked.
The inlet valve closes and the outlet valve opens as in the ESP HECU and the oil is gathered at the
low pressure chamber while no additional oil is being supplied. Then the pump operates to allow fast oil
drainage. The shuttle valve and the separation valve do not operate while decompression.
Page 683 of 796
10-10
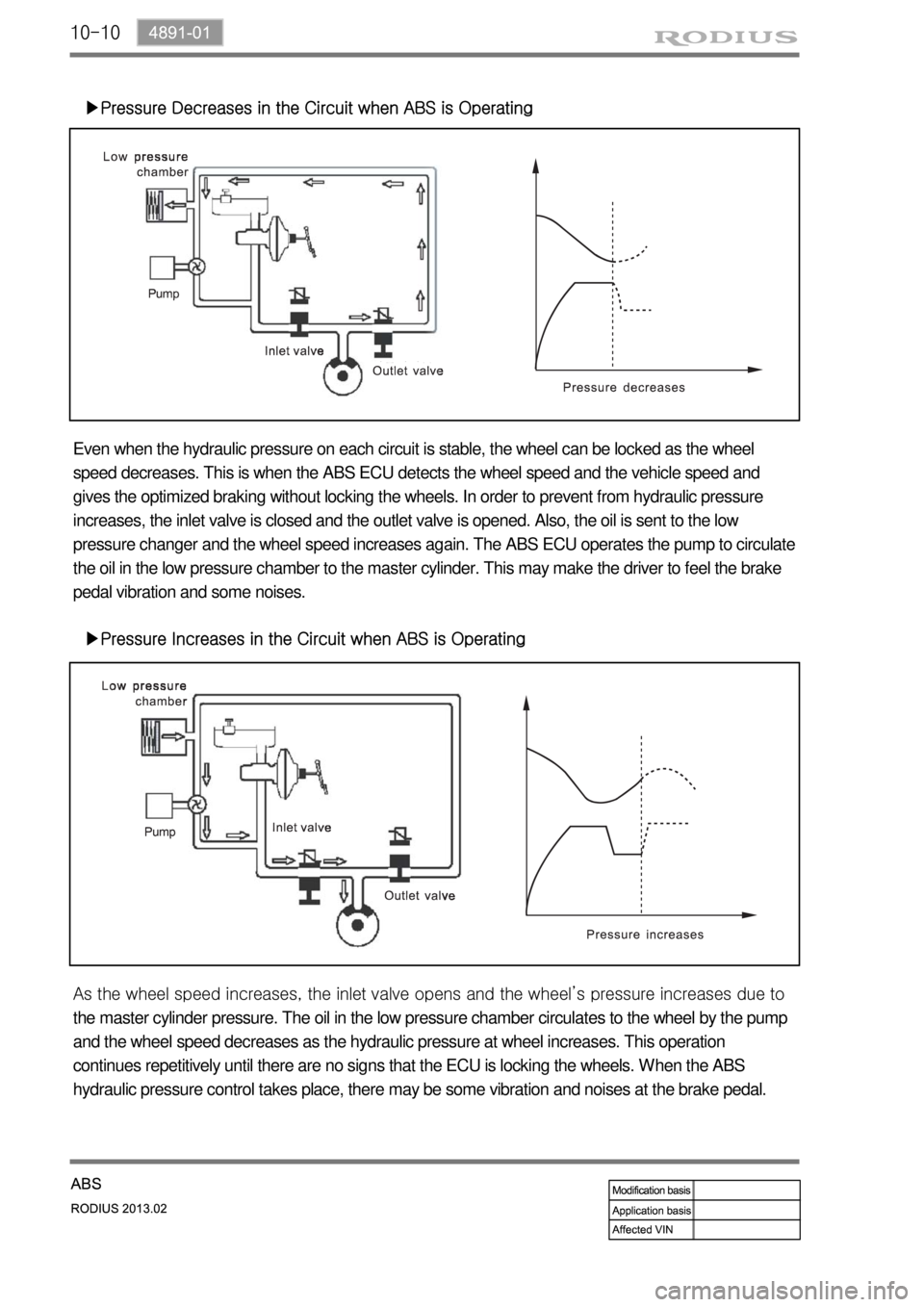
▶Pressure Decreases in the Circuit when ABS is Operating
Even when the hydraulic pressure on each circuit is stable, the wheel can be locked as the wheel
speed decreases. This is when the ABS ECU detects the wheel speed and the vehicle speed and
gives the optimized braking without locking the wheels. In order to prevent from hydraulic pressure
increases, the inlet valve is closed and the outlet valve is opened. Also, the oil is sent to the low
pressure changer and the wheel speed increases again. The ABS ECU operates the pump to circulate
the oil in the low pressure chamber to the master cylinder. This may make the driver to feel the brake
pedal vibration and some noises.
▶Pressure Increases in the Circuit when ABS is Operating
As the wheel speed increases, the inlet valve opens and the wheel’s pressure increases due to
the master cylinder pressure. The oil in the low pressure chamber circulates to the wheel by the pump
and the wheel speed decreases as the hydraulic pressure at wheel increases. This operation
continues repetitively until there are no signs that the ECU is locking the wheels. When the ABS
hydraulic pressure control takes place, there may be some vibration and noises at the brake pedal.
Page 685 of 796
11-34610-00
1. SPECIFICATIONS
Description Specification
Steering wheelType 4-spoke type
Outer diameter (mm) 390
Steering gear boxType Rack and pinion type
Steering angleInner36.4°
Outer31.5°
Steering oil pumpType Vane type
Maximum pressure (kgf/cm2) 93.3 ~ 100.4
Pulley size (mm)Ø115
Operating temperature-40℃ ~ 150℃
Steering oilType S-PSF3
Capacity (L) approx. 1.1
Lower shaftType Universal joint
Angle(°) 38°
ConfigurationUniversal joint(top/bottom)
rubber coupling
Minimum turning radius (m) 6.09
Steering column shaft Tilting angle±2°
Steering wheel heating
indicatorPower consumption Below 95 W
Rated voltage13.5 ± 0.1 V
Usable voltage 9~16 V
Low voltage7.5 ± 0.5 V
High voltage18.0 ± 0.5 V
Rated voltage Max. 12.4 A
MemoryLast switch ON/OFF mode
memorized
Page 687 of 796
11-54610-00
3. TIGHTENING TORQUE
Description Kgf?m N?m
Steering column shaftSteering column mounting bolt 2.0 ~ 2.5 19.6 ~ 24.5
Steering wheel and steering column shaft
lock nut4.0 ~ 6.0 39.2 ~ 58.8
Steering wheel and air bag module
mounting bolt0.7 ~ 1.1 6.8 ~ 10.8
Steering column and lower shaft
connection bolt.1.8 ~ 2.5 17.6 ~ 24.5
Power steering gear
boxSteering gear box and gear box cross
member mounting bolt7.0 ~ 9.0 68.6 ~ 88.2
Steering gear box and lower shaft
connection bolt2.5 ~ 3.0 24.5 ~ 29.4
Tie rod end and knuckle connection nut 3.5 ~ 4.5 34.3 ~ 44.1
Tie rod end lock nut 6.5 ~ 8.0 63.7 ~ 78.4
Steering gear box and pressure hose
connection nut3.2 ~ 3.8 31.4 ~ 37.2
Steering gear box and return line
connection nut3.2 ~ 3.8 31.4 ~ 37.2
Power steering pumpEye bolt for oil supply pipe to power
steering pump5.5 ~ 6.5 53.9 ~ 63.7
Power steering pump mounting bolt 2.0 ~ 2.5 19.6 ~ 24.5
Power steering line Return line and clip connection bolt 1.2 ~ 1.8 11.7 ~ 17.6
Page 688 of 796

11-6
4. TROUBLESHOOTING
Problem Possible Cause Action
Movements of steering
feels heavyIrregular wear or binding of steering ball joint
due to lack of lubrication or foreign material
insertionLubricate or replace
Damaged or defective steering gear Replace the steering gear
assembly
Incorrect steering pinion preload Adjust
Defective steering shaft join Replace
leakage of steering fluid Repair or replace
Insufficient steering fluid or air insertionFill up fluid or bleed air
Defective steering oil pump Replace
Damaged or loosened pump drive belt
Adjust or replace
Clogging of fluid line Repair or replace
Damaged wheel or tire Repair or replace
Defective suspension Repair or replace
Steering wheel pulls to
one sideDamaged steering linkage Replace
Damaged wheel or tire Repair or replace
Defective brake system Repair or replace
Defective suspension Repair or replace
Excessive free play of
steering wheelWorn steering gear Replace the steering gear
assembly
Worn or damaged steering ball joint Replace
Looseness of steering gear box Retighten
Poor returning of steering
wheelBroken or binding of steering ball joint Replace
Improper correct steering pinion preload Replace the steering gear
assembly
Damaged wheel or tire Repair or replace
Defective suspension Repair or replace