Page 395 of 1336
T-MAP sensor
D20DTF ECUOxygen sensor
Electronic
throttle bodyHFM sensor
(intake air temp.)
Coolant
temp.sensor
E-EGR valve
Crankshaft posi.
sensor
Accelerator
pedal
E-EGR cooler
(5) EGR control
a. Overview
The EGR (Electric-Exhaust Gas Recirculation) valve reduces the NOx emission level by recirculating
some of the exhaust gas to the intake system.
The major difference with the previous EURO 4 type, is that the DC motor with improved response rate
according to the EURO 5 regulation. The solenoid type actuator is used in the conventional model, but in
this new model, the DC motor type actuator with improved response rate is adopted. Also the hall senso
r
which provides a more stabilized signal than the potentiometer, and the EGR bypass flap which
improves engine warming up efficiency are also used. The HFM sensor and the position sensor are
used to feedback the amount of EGR for both EURO 4 and EURO 5.
b. Components
Page 397 of 1336

d. Bypass control for EGR cooler
1. Cooler temperature
2. Exhaust gas temperature
Otherwise, PM could be increased due to too low exhaust gas temperature.
e. Control elements for EGR system
Accelerator pedal (engine load) - Indicates the driver's intention and engine load. If the load goes up,
the EGR ratio is decreased.
T-MAP (boost pressure map stored in ECU) - Compensates the difference in boost pressure by
adjusting EGR ratio.
Engine rpm - Used as the signal for determining EGR operating range.
Coolant temperature - When the coolant temperature is low, NOx is decreased but PM could be
increased. So, to reduce PM, decrease EGR ratio when the coolant temperature is low.
Intake air mass and temperature - HFM sensor measures the intake air mass to calculate the actual
EGR volume. If the air mass is larger than programmed value in map, EGR ratio will be higher.
EGR position sensor - Detects the actual opening angle of EGR valve and performs feedback
function according to PWM control by ECU.
Wide band oxygen sensor - Detects the oxygen volume in exhaust gas to check if the EGR ratio is
proper.
Electronic throttle body - Keeps EGR ratio to optimized level by controlling the throttle body in EGR
operating range (decreasing pressure in intake manifold). -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Page 399 of 1336
Accelerator
pedalE-VGT
actuator
Coolant
temperature
Front EGT
sensorT-MAP sensorCrankshaft pos,
sensor
HFM sensor
(intake air temp)
ECU
(D20DTF)
(6) E-VGT control
a. Overview
E-VGT (Electric-Variable Geometry Turbine) turbocharger system in D20DTF engine uses the venturi
effect that controls the flow rate of exhaust gas by adjusting the passage in turbine housing. The newly
adopted DC motor actuator (E-actuator) controls the E-VGT system more precisely and faster. To get
the high operating power from turbine, the ECU reduces the exhaust gas passage In low speed range
and increases it in high speed range.
b. Components
Page 401 of 1336
d. E-VGT system control
Turbocharger system operates the E-VGT actuator according to the signals for engine epm, accelerator
pedal position, atmospheric pressure, T-MAP, coolant temperature and intake air temperature.
Turbocharger actuator is performed PWM control by ECU.
In general, the boost pressure feedbacks the turbocharger operation and the boost temperature is used
for calculating the precise density.
E-VGT provides higher engine power with faster reaction speed compared to conventional VGT.
Operating wave Vane Control
Low
speed
rangeIn low speed range:
retract the vane to
increase boost
pressure. The vane
has low (-) duty, and
the unison ring
moves to retract the
vane in weak PWM
signal.
High
speed
rangeThe unison ring
moves to extend the
vane in strong PWM
signal. Maximum
pressure is 3 bar
and the system
controls it according
to the input signals.
Page 405 of 1336

Coolant temp.
sensor
Refrigerant pres.
sensor
A/C compressor
ECU
D20DTFDSI 6 A/T
(ATF temp.)
Cooling fan module
HFM sensor
(Intake air
temperature)
Engine room
relay box
(8) Cooling fan control
a. Overview of cooling fan and A/C compressor
The cooling system maintains the engine temperature at an efficient level during all engine operating
conditions. The water pump draws the coolant from the radiator. The coolant then circulates through
water jackets in the engine block, the intake manifold, and the cylinder head. When the coolant reaches
the operating temperature of the thermostat, the thermostat opens. The coolant then goes back to the
radiator where it cools. The heat from automatic transaxle is also cooled down through the radiator by
circulating the oil through the oil pump.
There are two cooling fans (200W+150W) in D20DTF engine. ECU controls the electric cooling fans
with three cooling fan relays to improve the engine torque and air conditioning performance.
For details about A/C compressor and refrigerant pressure sensor, refer to Chapter "Air Conditioning
System" in "Body" section.
b. Components
Page 408 of 1336
0000-00
PTC heater
Coolant
temp. sensor
D20DTF
ECU
Engine room relay box
HFM
(Intake air
temp.)
(9) PTC heater control
a. Overview
The supplementary electrical heater is installed in DI engine equipped vehicle as a basic equipment. The
PTC system is operated according to two temperature values measured at the coolant temperature
sensor and HFM sensor. This device is mounted in the heater air outlet and increase the temperature of
air to the passenger compartment. Because PTC system is heated by electrical power, high capacity
alternator is required. PTC does not operate during engine cranking, while the battery voltage is lower
than 11 V or during preheating process of glow plugs.
b. Components
A: PTC 1 (changeable)
B: PTC 2,3 (not changeable)
Page 417 of 1336
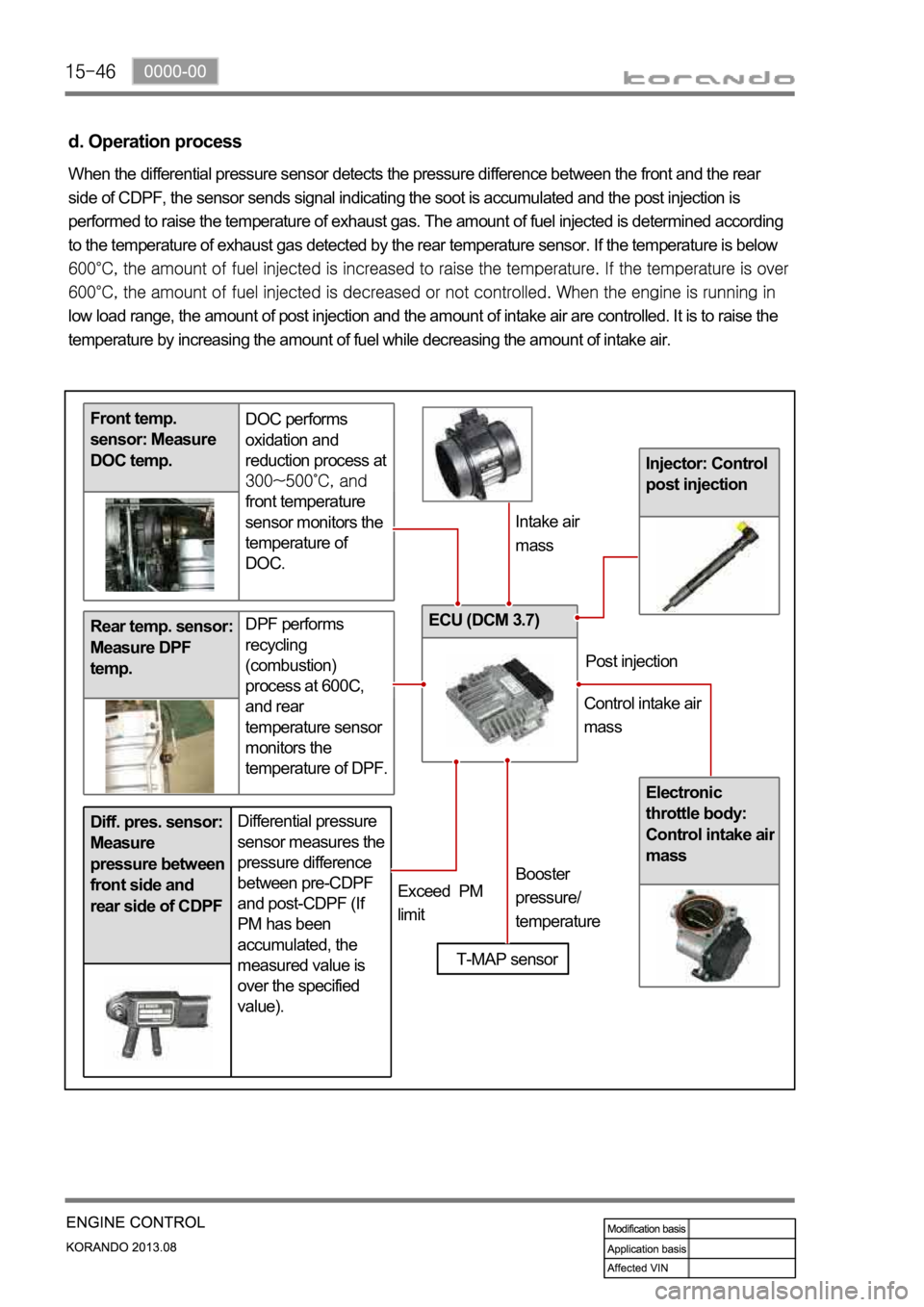
Rear temp. sensor:
Measure DPF
temp.DPF performs
recycling
(combustion)
process at 600C,
and rear
temperature sensor
monitors the
temperature of DPF.
Differential pressure
sensor measures the
pressure difference
between pre-CDPF
and post-CDPF (If
PM has been
accumulated, the
measured value is
over the specified
value).Diff. pres. sensor:
Measure
pressure between
front side and
rear side of CDPF
Injector: Control
post injection
Front temp.
sensor: Measure
DOC temp.DOC performs
oxidation and
reduction process at
front temperature
sensor monitors the
temperature of
DOC.
Electronic
throttle body:
Control intake ai
r
mass
ECU (DCM 3.7)
d. Operation process
When the differential pressure sensor detects the pressure difference between the front and the rear
side of CDPF, the sensor sends signal indicating the soot is accumulated and the post injection is
performed to raise the temperature of exhaust gas. The amount of fuel injected is determined according
to the temperature of exhaust gas detected by the rear temperature sensor. If the temperature is below
low load range, the amount of post injection and the amount of intake air are controlled. It is to raise the
temperature by increasing the amount of fuel while decreasing the amount of intake air.
T-MAP sensor
Intake air
mass
Exceed PM
limitBooster
pressure/
temperaturePost injection
Control intake air
mass
Page 436 of 1336
1116-01
1. SPECIFICATION
Unit Description Specification
Cylinder headHeight 142.5 mm
Weight 15.6 kg
Flatness Below 0.05 mm
Spark plug offset 2.5 mm
Thickness of cylinder head gasket (when compressed)
0.7 mm
CamshaftAxial end playIntake 0.1~0.35 mm
Exhaust 0.1~0.35mm
Valve timingIntake valve open BTDC 35/-10
Intake valve close ABDC 14/62
Exhaust valve open BBDC 40/40
Exhaust valve close ATDC 12/12
Journal bearingDiameter 24mm
Width 17 mm
Oil clearance 0.037~0.074 mm
Intake/exhaust
valveLift of intake valve Max. 9.0 mm
Lift of exhaust valve Max. 8.0 mm
Length of intake valve 115.0mm
Length of exhaust valve 114.0mm
Connecting rod End play 0.5~1.5mm